January 29, 2020 Admin Home page » MRI and CT scan of the abdominal organs Views: 5387
MRI of the retroperitoneal space is a study based on the principle of interaction of magnetic waves with the nuclei of a hydrogen atom occurring in the human body. This method is currently the most accurate when examining soft tissues of the body, for example, in contrast to methods such as ultrasound, computed tomography and x-rays.
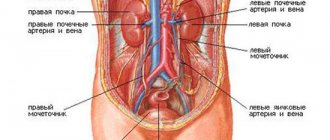
MRI of the retroperitoneal space is an examination of organs such as the kidneys, adrenal glands, perinephric tissue, ureters and other organs located in this area. Quite often, this procedure is prescribed in conjunction with other studies, for example, MR urography, which examines possible inflammation of the pyelocaliceal system of the kidneys, bladder and ureters. Such a study is absolutely not inferior to standard diagnostics - excretory urography, and also in some cases has an advantage in visualization and depth of visibility.
What does MRI of the retroperitoneum show? The examination makes it possible to visualize:
- various damage to the structure of organ tissue;
- infections, inflammatory processes;
- malignant and benign tumors, even in the initial stages of formation.
When using contrast agents on MRI, it is possible to visualize:
- blood flow power and speed;
- stages of inflammatory and tumor processes.
The images show nerve endings, soft tissues and blood vessels as clearly as possible.
Diseases of the retroperitoneum
Magnetic resonance scan: right kidney cyst (arrow)
In this anatomical region, magnetic scanning can identify many pathologies. What does MRI of the retroperitoneum show:
- Tumors and cysts. Neoplasms are divided into those originating from organs (kidneys, ureters, duodenum, etc.) and free tissues (fatty tissue, muscles, fascia, nerve and lymph nodes, blood vessels). Tumors can be benign or malignant, single or multiple. For a long time, the neoplastic process is asymptomatic, complaints appear when compression is applied to a nearby organ. A large volumetric formation compresses the vascular and lymphatic collectors, which leads to stagnation of blood in the lower extremities, ascites (accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity), and dilation of the subcutaneous veins of the abdomen. A benign tumor does not cause cancer intoxication, but can be complicated by dysfunction of neighboring organs. MRI of the retroperitoneal space shows the localization of the formation, suggests the origin (including metastatic), and differentiates it from an abscess, hematoma, or aneurysm of the abdominal aorta. Definitive diagnosis is impossible without a biopsy followed by morphological examination. Among organ tumors, the first place is occupied by neoplasms of the kidneys, the second - by the adrenal glands.
Giant hematoma while taking heparin-like drugs on an MR scan (secondary hemorrhages are indicated by black arrows)
- Injuries. A retroperitoneal hematoma is formed by a direct blow to the lumbar or abdominal area, a traffic accident, or a fall from a height. Often combined with bone fractures and other injuries. In emergency situations with severe clinical manifestations, computed tomography remains the priority test due to the speed of obtaining results. CT scans are better at assessing bleeding and fractures. MRI can show hidden damage to bones, ligaments, etc.
- Vascular changes. If contrast is applied, magnetic resonance imaging shows an aneurysm, stenosis, atherosclerotic lesions, thrombus formation, developmental anomalies, etc.
- Inflammatory processes. For uncomplicated cases, ultrasound is sufficient. Abscesses and phlegmon are considered as a complication of inflammation of organs with retroperitoneal localization. Using magnetic resonance scanning, paracolitis, paranephritis, peritonitis, and the formation of a fistula are diagnosed. The study is informative for differentiating chronic and acute pancreatitis, pyelonephritis, hydronephrotic transformation, kidney carbuncle, etc.
MRI of the retroperitoneal space helps to establish the cause of pathological changes, for example, external compression of the ureters by a tumor and, as a consequence, expansion of the collecting system. When performing contrast, the doctor is able to judge the excretory function of the kidneys. Nephrolithiasis and areas of calcification are best assessed with CT. Chronic inflammation of the retroperitoneal organs can lead to the development of Ormond's disease, characterized by excessive production of scar tissue, as shown by magnetic resonance imaging. Sometimes the fibrotic process is idiopathic (without identifying the cause).
Can everyone have an MRI?
Magnetic tomography has contraindications. Diagnostics is not prescribed for:
- artificial heart valves;
- vascular endoprostheses;
- metal plates;
- pregnancy in the 1st trimester;
- inability to remain still due to the presence of mental disorders;
- claustrophobia at an advanced stage.
It is undesirable to resort to MRI with contrast during pregnancy at any stage. When breastfeeding, after diagnosis, you should stop feeding and replace breast milk with artificial formula.
MRI of the retroperitoneum, which organs are checked?
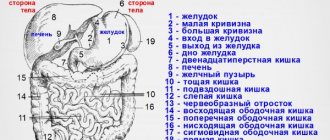
This anatomical region is the seat of vital systems. MRI of the retroperitoneum shows:
- adrenal glands, kidneys, ureters (before entering the bladder), perirenal fatty tissue;
- distal esophagus, lower part of the duodenum, ascending and descending colon;
- pancreas (except tail);
- abdominal aorta, inferior vena cava and their branches; vessels of the kidneys, mesentery, pancreas, bladder, etc.;
- solar plexus, sympathetic trunks;
- lymphoid structures, etc.
Which is better: ultrasound, MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity
If we compare MRI and ultrasound, the first research method is more modern and accurate. However, the first diagnostic method also has its drawbacks.
Comparison of MRI and ultrasound of the abdominal cavity:
- Some types of MRI require the use of special markers that provoke an allergic reaction. In addition, the study is not performed on patients with metal prostheses or pacemakers;
- Ultrasound, unlike MRI, cannot detect tumors in the early stages. Ultrasound tests depend on the skill of the doctor. MR imaging provides a more detailed clinical picture;
- Ultrasound costs 2–3 times less than MRI;
- The total duration of an ultrasound is from 10 to 15 minutes, and an MRI is from 30 to 90 minutes.
Despite the fact that ultrasound has more advantages, this research method is significantly inferior to MRI in terms of accuracy in diagnosing cancer at an early stage. That is, the second diagnostic method allows you to identify dangerous diseases at an early stage, and therefore the patient has a greater chance of recovery.
During a computed tomography (CT) scan, the body is exposed to ionizing radiation. In addition, for a more accurate diagnosis of pathological changes, CT scans are performed using an iodine-containing contrast agent. For this reason, CT is contraindicated for diseases of the thyroid gland, kidneys, contrast agent intolerance, and pregnancy.
MRI is a safer research method, during which radiation is not used. In addition, scanning is most often performed without the use of a contrast agent. However, during MRI you need to lie still in a confined space, and this is quite difficult for patients who suffer from claustrophobia and children. MRI is more effective in detecting pathologies of the liver and gallbladder. CT is advantageous in detecting urolithiasis and kidney stones.
MRI is considered the safest and most accurate diagnostic method.
Preparation for MRI of the retroperitoneum
Don’t forget to take your passport, results of previous diagnostics, an extract from your medical history, and a doctor’s referral with you to the MRI.
To get the maximum benefit from the diagnostic procedure, you should not ignore the advice of doctors. Cleansing the intestines and reducing flatulence is the main task aimed at improving visualization. Preparation for MRI of the retroperitoneal space involves switching to a gentle diet 2-3 days before the study. You should exclude foods that cause bloating and constipation from your diet:
- raw vegetables and fruits, especially cabbage, peas, beans, corn;
- fresh herbs;
- hot spices;
- milk, cream, curdled milk;
- fatty meats;
- black bread;
- potato;
- nuts, seeds;
- mushrooms;
- kvass, carbonated drinks, alcohol, etc.
A cleansing enema or laxative is necessary for patients suffering from chronic constipation. If bowel movements occur regularly, following a diet and natural bowel movements before an MRI are quite sufficient.
During the day, it is preferable to eat chicken or turkey breast, fish prepared by boiling, baking, or steaming. Unsaturated meat broths, minced meat products, unsweetened compotes, weak tea or coffee are allowed. MRI of the retroperitoneal space is performed on an empty stomach; dinner should be no later than 6 hours before the diagnostic procedure. If the study is planned for the middle of the day, you can have a light breakfast in the morning.
During enhanced MRI scanning, autonomic reactions are recorded in some patients: dizziness, nausea, and flickering of spots before the eyes. A light snack 20 minutes before leaving the house eliminates unpleasant phenomena. MRI of the retroperitoneal space does not require filling the bladder.
During the diagnosis, you will have to lie motionless on your back for about 45 minutes, so wear loose-fitting clothes without metal buttons or zippers.
Don't be surprised by the doctor's questions about a possible early pregnancy, the presence of metal in the body or implanted devices (pacemaker, drug pump, etc.). - Under these conditions, MRI is contraindicated. Contrast is limited by: gestation period, allergic reaction to gadolinium, renal failure with a decrease in glomerular filtration rate (less than 30 ml/min).
Women during lactation can undergo enhanced MRI, but experts recommend stocking up on breast milk for the day: during this time, gadolinium chelates are eliminated from the body naturally. For claustrophobia, the examination is performed under sedation in a hospital.
Contraindications
There are a number of minor contraindications for undergoing MRI:
- the presence of metal implants, prostheses, pacemakers and other items in the body;
- claustrophobia, schizophrenia;
- various types of injuries that prevent the patient from remaining motionless during the study.
MRI examinations using contrast will be contraindicated:
- pregnant women and nursing mothers, since the contrast agent is quite toxic to the fetus and milk;
- patients suffering from renal failure, as side effects are possible.
How is an MRI of the retroperitoneum done?
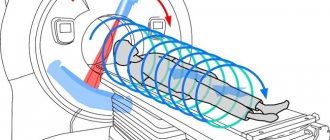
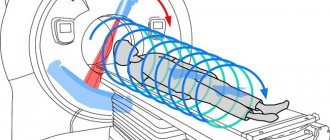
Intensifying magnetic coils provide better detail of internal organs and surrounding tissues.
The diagnostic procedure includes several stages:
- preparation of medical documentation and questionnaires to identify contraindications;
- depositing items with paramagnetic properties - cell phones, payment cards, coins, keys, metal jewelry, etc.;
- placing the patient on the tomograph table; to prevent blurring on the films (due to involuntary movements), the limbs are fixed with bolsters and belts;
- scanning the area of interest, if contrast is required, the enhancer drug is administered intravenously after a series of native images;
- description and presentation of results.
MRI of the retroperitoneum is an absolutely painless procedure; the only inconvenience is technical noise, which can be dealt with using headphones. The patient's condition is monitored by medical staff from an adjacent room through a window. Communication takes place via speakerphone.
What is the essence of the procedure
MRI is a non-invasive diagnostic method. The survey is considered innovative. Internal organs can be visualized qualitatively.
The procedure is based on the action of magnetic fields. In response to them, organs and other structures send signals that are processed by special software. Subsequently, a detailed cross-sectional image is formed from the obtained data.
The examination does not generate ionizing radiation.
The operating principle of MRI is based on the signal sent by the nucleus of a hydrogen atom in a magnetic field. In this way, the entire body is scanned. Diagnosis is made due to the saturation of organs and tissues with hydrogen.
Modern medical equipment has a power of 1.5–3 Tesla. This helps to significantly reduce the duration of the procedure.
The MRI procedure is quite simple.
MRI of the retroperitoneum with contrast
The introduction of an amplifier is necessary for clearer visualization of pathological processes localized in hard-to-reach places. For tumors, MRI of the retroperitoneal space with contrast makes it possible to determine the boundaries of the tumor, the degree of invasion into surrounding structures, demonstrate changes during therapy, and diagnose relapse. Vascular assessment is not performed using unenhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
The drug based on gadolinium chelates is safe and tolerated without serious adverse reactions. The dosage is calculated individually depending on body weight, which affects the total cost of the study. The contrast increases the intensity of the energy released by the hydrogen protons by reducing the relaxation time, so the pathologically altered tissue is better detailed.
Main indications for imaging studies
The list of abdominal organs that need to be examined for pathology includes:
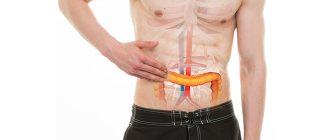
- pancreas;
- lymph nodes, vascular system;
- spleen;
- soft tissues of the abdominal cavity, abdominal walls;
- liver;
- bile ducts (common hepatic duct, intrahepatic bile ducts, gallbladder + its ducts);
- gastrointestinal tract, which includes the small intestine, large intestine, and stomach.
In the retroperitoneal space, visualization of the following organs is usually required:
- adrenal glands;
- kidneys;
- perinephric fiber.
The main indications for diagnostics in the retroperitoneal space are:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- congenital defects, abnormalities in organ development;
- fatty degeneration;
- tumor lesion (primary, secondary);
- inflammatory process, the presence of infiltrates inside the peritoneum;
- organ injury;
- presence of foreign bodies (non-metallic);
- obstructive jaundice;
- circulatory disorders within parenchymal organs. These pathologies can develop into a heart attack, ischemic disorder;
- pancreatitis (acute, chronic);
- volumetric processes that are characterized by a non-tumor nature (hematomas, abscesses, cysts);
- portal hypertension;
- hepatomegaly of unknown nature;
- metastatic lesions of the lymphatic system;
- cholelithiasis;
- cirrhotic processes;
- diffuse lesions of parenchymal organs.
Experts carry out this diagnostic procedure only on high-field tomographs. Such devices have a power of 1 Tesla. On older machines, the patient had to hold his breath. Today, when conducting this research method, this discomfort is absent. The main thing is to remain still during the MRI.
This procedure usually takes 20 – 30 minutes.
The price of the procedure is calculated depending on the scale of the study, the rating of the medical institution where you are going to conduct the diagnosis, and the features of the device used. The cost for examination of the abdominal organs and retroperitoneal space ranges from 6,500 to 10,000 rubles. If it is necessary to additionally perform cholangiography, the cost of the procedure will be in the range of 25–30 thousand rubles.
How is the procedure performed?
MRI machines of the retroperitoneum and abdomen are of closed and open type. The open type is not so common; it is used for MRI of the retroperitoneal space or peritoneum in overweight people who, due to their size, do not fit into the tomograph tunnel, or for those who are afraid of confined spaces. As a rule, these are new generation devices. Basically, tunnel-type machines are used - i.e. closed. The installation consists of a camera and an automated couch table.
How is an abdominal MRI performed and what is included in the scan? The patient goes into the office and changes into the disposable clothing given to him. He receives instructions regarding the upcoming examination. If necessary, a venous catheter is installed in the patient's arm to administer a contrast agent. After the patient is laid on the table, he may be asked to cover his ears with special soundproof headphones, because the installation is quite noisy during operation (comparable to a worker working with a hammer on a metal surface). Arms and legs may be secured with straps to prevent the patient from making accidental movements during the scan. The table slides inside the magnetic tube. The doctor goes into the office, where behind the glass there is a tomograph control panel. When an MRI is performed, the patient has the constant opportunity to talk with the doctor through the internal communication built into the machine. During the examination, it may be necessary to exclude even minimal mobility of the patient, then the doctor asks him to hold his breath.
Important! If the patient feels any discomfort, he can always call a doctor by pressing the panic button, which is given to his hand before the test.
The entire MRI procedure of the retroperitoneal space and abdomen can last from half an hour to an hour and a half. After finishing, the couch moves out of the scanner, the patient is helped to stand up and given time to clean up while the doctors study the images. It often takes at least 2 hours to decipher. And in some cases, other specialists may be invited to decrypt. The patient does not have to wait for the results in the clinic. He can go home and get an MRI report the next day.
Why MRI and not another type of examination?
This examination is the safest and, moreover, completely painless and the most informative. The tomograph produces an incredibly detailed and high-quality image. No other diagnostic method can compete with these indicators.
During the examination, it is possible to visually trace the picture of deviations, the consequences of injuries, assess the damage, and identify pathology in the functioning of the internal organs of the required area. This diagnosis gives a real picture even when other types of examination turned out to be uninformative or controversial.
A huge advantage is provided by a contrast agent administered if necessary during diagnosis. There are practically no allergies or other body reactions to them. CT cannot boast of this. MRI allows you to identify the smallest formations in organs and establish morphological abnormalities of tissues even in the early stages.
Gallbladder
Normally, the gallbladder is pear-shaped with clear contours and homogeneous contents. Horizontal size - less than 5cm. Wall thickness 1-3 mm. The width of the common bile duct is less than 8 mm.
The most complete picture of the condition of the gallbladder is provided by non-contrast magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. MR cholangiography allows you to identify stones in the gallbladder and bile ducts, diagnose strictures (narrowing) of the bile ducts, and anomalies of their development.
On MR images, free bile has a hyperintense appearance and stones appear as dark spots (filling defect).
Types of MRI studies of the area in question
In diagnostic centers today, several types of MRI of the abdominal cavity are performed:
- general examination;
- tomography of the abdominal cavity with or without the use of a contrast agent;
- magnetic resonance angiography of the vascular system;
- MRI of arteries and venous sinuses.
During a general examination, the spleen, stomach, liver, intestines, pancreatic ducts, biliary tract, blood vessels, tissues of the waist region, lymph nodes, pancreas, kidneys, genitourinary system, and adrenal glands are subject to testing. MRI of the abdominal cavity can assess the nature of the interaction of internal organs