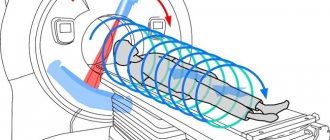
Computed tomography is a first-class diagnostic equipment that allows you to see a highly accurate three-dimensional image and identify initial pathological changes in small organs that cannot be detected using other studies.
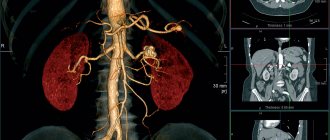
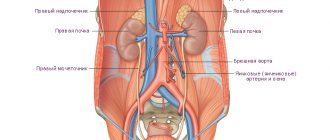
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is one of the main diagnostic methods, during which a specialist is able to visualize the condition, structure and localization of the internal organs of the abdominal cavity, as well as the retroperitoneal space. In addition, along with abdominal organs, CT allows you to see blood vessels and lymph nodes.
At the Yusupov Hospital, CT scans of the abdominal cavity are performed using innovative equipment - a multislice tomograph. Qualified hospital specialists have been studying the features of this technique for many years and use only the best contrast agent in their work, which does not cause unpleasant side effects.
What it is?
Computed tomography with contrast has been actively used in domestic medicine for more than 15 years. This diagnostic method remains one of the most informative , since it allows you to detect even minor structural changes in tissue.
Its essence is quite simple - before the start of the study, the patient is intravenously injected with a special drug that contains iodine salts.
Their molecules are capable of almost completely absorbing X-ray radiation, while they accumulate well in certain types of tissues and are also quickly eliminated from the body without causing harm.
Initially, contrast was used to study the lumen of the digestive tract, thyroid gland and blood vessels. But over time, experts noticed that there are patterns in the accumulation of the drug that make it possible to detect a malignant process, the proliferation of connective tissue and other changes.
The procedure for administering contrast is simple. The patient lies down on the tomograph table in the required position. Then a catheter is placed on the ulnar vein, through which a contrast agent is injected manually by a nurse or using an infusion pump (an automatic device). At this time, the doctor monitors the general condition of the patient (to avoid allergic reactions).
Help An important advantage of computed tomography with contrast is the ability, during one session, to diagnose not only the abdominal cavity, but also the chest, pelvic organs, limbs, and head. In this case, the diagnostic time is extended by only a few minutes. This is especially important in emergency situations when it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis as quickly as possible.
Preparing for CT
The abdominal space and parts of the peritoneal space are interconnected with each other, located close to each other, and therefore deformation and changes in one affect the other. The attending physician who prescribes a CT scan talks about the preparatory stage in advance. The characteristics of the patient's body are taken into account.
For computed tomography:
- They do a preliminary examination - ultrasound, FGS, colonoscopy, x-ray diagnostics.
- The patient is consulted by an anesthesiologist about the side effects of the drugs. Signs documents on the administration of a contrast agent.
- It is necessary to test blood biochemistry for the predominance of creatinine and liver enzymes. Deciphering the tests allows us to identify organ pathology.
You need to prepare for a CT scan of the abdominal cavity in advance. A clogged intestine reduces the information content when the procedure is performed. The administration of contrast may cause vomiting and volvulus. For three days before the procedure, you must follow a strict diet and not eat certain foods.
Assess the condition:
- pancreas;
- liver;
- stomach;
- gallbladder;
- lymph nodes;
- pelvis;
- intestines;
- spleen;
- lungs;
- vessels;
- kidneys;
- bladder.
A diet is followed to prepare for a CT scan with contrast. It helps reduce gas formation and normalizes intestinal function in terms of stool movement. The pictures will be better quality and the results will be more accurate.
The diet lasts from two to three days. The patient can eat:
- cottage cheese;
- steamed vegetables;
- lean poultry, fish, meat;
- steamed dishes;
- hard cookies and dry white bread;
- oatmeal cooked in water;
- steamed chicken;
- empty broths;
- lean steamed fish;
- omelette without oil.
Prohibited: baked goods, peas, dairy products, vegetables and fruits, flour, kefir, prunes, chocolate. If you follow and adhere to the recommendations, complications from the stomach and intestines can be avoided. The procedure can be done on an empty stomach.
You need to prepare your intestines for the examination:
- Enemas are given in the evening and in the morning.
- Within 18 hours, the intestines are cleansed with drugs, for example, laxatives, sorbents.
The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach. Don't eat for 6 hours. A patient with a contrast examination undergoes blood tests for biochemistry before a CT scan simultaneously with a study of creatinine and urea. The contrast is administered by solution, enema, and intravenously (done on an empty stomach). Substances containing iodine are used. For example, it is part of Urografin and Omnipaque. These solutions can detect tumors in organs and metastases.
If the contrast agent is administered orally, take Urografin long before the procedure. One ampoule dissolves in 1 liter of water. Patients are often recommended a certain regimen with the reagent: Take 250 ml at 18-00, 23-00, 3 hours before the procedure, before the start of the CT scan.
The medications are prescribed by the doctor. Before the procedure, the patient takes a laxative, enterosorbent and antispasmodic orally before CT. This will cleanse the intestines. Independent use and use of medications will lead to ineffective tomography and a distorted diagnosis. Before a CT scan with contrast, your doctor may stop taking your medication. The procedure is comfortable if you follow the doctor's recommendations. Having started the procedure, the patient needs to relax and comply with the doctor’s requirements. The patient does not feel any discomfort or discomfort.
The contrast agent, penetrating into the diseased area, significantly enhances the contrast and clear contours of the images. This allows you to see violations. The diagnostician shows the shape, structure of organs and blood vessels.
Types of contrast
To examine the abdominal organs with contrast, initially Barium preparations were used, which the patient had to drink. However, this made it possible to better visualize only the cavity of the esophagus, stomach and intestines. Therefore, after the introduction of iodine preparations into clinical practice, which must be administered intravenously, they are used for CT scanning in the vast majority of cases.
Barium preparations are increasingly being abandoned , since they pass exclusively into the cavity of the stomach and intestines and do not accumulate in the walls and tissues of the abdominal organs. In fact, they are only suitable in situations where there is a pathological process on the surface of the mucous membrane.
Contrast agents with Iodine differ from each other due to different physical and chemical properties (osmolarity, viscosity, solubility in water).
Usually the CT specialist works with only one of them.
At the same time, there are different types of diagnostics, which affects the method of contrast administration:
- Classic . The patient is slowly injected with the drug intravenously, after which diagnostics of the abdominal cavity begins. Allows you to study its accumulation in organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, intestinal wall, stomach). The technique is used if there is no need to visualize the flow of contrast into the vessels.
- Bolus contrast enhancement.
- Permanent . A drip with a contrast agent is connected to the venous catheter. This allows you to maintain its concentration in the body at a constant level during the entire diagnosis. Used to visualize the abdominal aorta and its branches.
- Double . The patient is given a double dosage of contrast once before starting the CT scan. This technique is used in specialized cancer centers to search for metastases in lymph nodes and soft tissues.
- Rectal . The patient is given contrast using an enema, after which the study begins. Used in proctological practice.
Bolus organ boost
This is a technique that is considered the standard in CT. Its peculiarity is that the contrast agent is administered intravenously to the patient using a special device , which makes it possible to control the dose and speed of injection. Before starting the procedure, the doctor calculates the individual amount of contrast for a particular patient. The examination of the patient begins a few seconds after the start of administration.
Thanks to this, the specialist is able to clearly observe two phases of contrast distribution:
- vascular - when the drug sequentially fills large arteries, small arterioles, and then veins;
- parenchymal – accumulation of contrast in the patient’s organs (the speed of this process depends on the type of tissue).
As a result, it is possible to examine all the anatomical structures of the abdominal cavity with maximum information.
The role of diet
Computed tomography of the abdomen should be performed in patients on a diet. The fact is that all organs are located quite compactly, so overfilling and overstretching one can distort the image of another and disrupt its functioning. As a rule, this feature concerns hollow organs, in particular the intestines, the walls of which contract and perform peristaltic movements.
IMPORTANT! Compliance with the doctor’s diet instructions in a short time will help cleanse the body and make the results of an abdominal CT scan more informative.
The fact is that during the study, not only the person, but also his internal organs must remain completely calm. Therefore, reducing the frequency and intensity of peristaltic movements will allow you to obtain a clearer image without possible distortion. Therefore, it is necessary to adjust your diet.
Drugs
As already emphasized, almost all preparations used for computed tomography contain iodine salts. However, they differ from each other in the following important indicators:
- Concentration of the active substance. On the one hand, the more contrast molecules in the preparation, the better, since this should improve image quality. But an interesting paradox was discovered - with increasing concentration, the viscosity of the drug also increased, which negatively affects its distribution in the vascular bed. Therefore, in all modern contrasts this figure does not exceed 350 mg/ml.
- Hydrophilicity (ability to absorb water). Contrasts with high hydrophilicity do not penetrate cell walls well, but are less likely to cause adverse reactions, and therefore are ideal for CT angiography (Urografin, Telebrix). Drugs with low hydrophilicity (Omnipak, Ultravist, Vizipak, Imagopak) penetrate well into the middle of the cells, so they are used if it is necessary to examine individual organs of the abdominal cavity.
- Osmolarity (an indicator that shows the concentration of active molecules in the drug). The toxicity of contrast is directly related to it. The highest osmolarity is in Urografina, the lowest in Vizipak.
"Urografin"
The drug of choice for CT angiography is a study in which the vessels of the abdominal cavity are visualized. Contrast does not penetrate well from the vascular bed into tissues and organs. The recommended dose of Urografin for adult patients for oral administration before CT is 20-50 ml, but in certain situations it can be further increased. The dosage of Urografin for children is presented in the following table:
| Age | Contrast volume, ml |
| Up to a year | 7-10 |
| 1-2 years | 10-12 |
| 2-6 years | 12-15 |
| 6-12 years | 15-20 |
| Over 12 years old | 20 |
The drug is administered intravenously slowly so that the procedure lasts 5-10 minutes. The only exception to this rule is patients with uncompensated pathologies of the cardiovascular system (20-30 minutes).
The study begins a minute before the end of the administration of Urografin. The diagnostic window lasts 20 minutes in patients without kidney pathologies.
The drug "Urografin"
"Omnipak"
The drug is used both for angiography and for contrast enhancement in CT. Its particles penetrate well through the cell membrane and accumulate in peripheral tissues. Therefore, with its help it is easier to detect areas of inflammation or oncological processes . For adult patients, 100-200 ml of the drug is administered intravenously, and for children, an individual dosage is calculated based on the ratio of 2-3 ml per 1 kg of body weight.
The drug "Omnipak"
Scanning with contrast
When it comes to the need for MSCT of organs located in the abdominal cavity, in most cases the doctor decides to use contrast. This is largely determined by the diagnostic features and the fact that most organs in the examined area are hollow. Contrast allows you to “highlight” the organ for which the examination is being carried out, visualizing information more clearly and deeply. How can this be achieved? When examining an MSCT of the abdominal cavity, contrast is injected directly into the organ - for example, if it is necessary to examine the condition of the liver, an iodine-containing contrast agent is injected directly into the artery that leads directly to the liver. In other cases, contrast may be given orally.
The consequences of injecting a contrast agent into a vein may include dizziness and a metallic taste. Oral contrast may cause nausea. In any case, if you notice these symptoms, you must immediately report them to the doctor via audio communication during the study.
For what symptoms is it prescribed?
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography is prescribed if the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- abdominal pain of various localization and nature;
- the appearance of blood or pus in the stool;
- nausea, repeated vomiting;
- abdominal muscle tension;
- reducing body weight without changing the nature of nutrition or physical activity;
- decreased appetite, aversion to certain foods;
- chronic constipation;
- detection of enlarged lymph nodes;
- severe weakness;
- closed or penetrating abdominal injury;
- decreased blood pressure and increased heart rate (signs of hemorrhagic shock without external bleeding).
This imaging method allows you to diagnose a number of pathologies of the digestive tract and other body systems:
- acute and chronic pancreatitis;
- pancreatic cysts and adenomas
- abnormalities of the digestive tract
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis;
- acute appendicitis
- cholelithiasis;
- acute and chronic cholecystitis;
- cholangitis;
cirrhosis of the liver;
- acute and chronic hepatitis;
- increased pressure in the portal vein system
- detachment of the wall of the abdominal aorta;
- aortic rupture;
- thrombosis of arterial or venous vessels;
- splenomegaly (enlarged spleen);
- lymphadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes);
- oncological process in the abdominal organs and/or its metastases.
CT technique
It's time to find out how the tomography procedure works:
- After presenting all the necessary documents, previous test results, consultation, the patient is asked to take a horizontal position, lie down on the tomograph table and lie still.
- If a patient undergoes a CT scan with contrast, then he is first given an injection with a contrast agent (provided that he did not take the contrast agent orally).
- After the patient lies down on the couch of the device, he is automatically moved inside the ring of the device. This is where the CT scan procedure is performed.
- During a CT scan of the retroperitoneal space and abdominal cavity, the specialist can ask questions to the patient via two-way communication, give commands to hold his breath, ask how he feels, etc. When CT scanning the abdominal organs, and indeed any organ in general, it is forbidden to move .
The duration of a medical scan of the abdominal organs depends on the type of study and the quantitative indicators of checking the internal organs. Typically, a CT scan with contrast lasts no longer than 30 minutes, without it – 15 minutes.
Computed tomography does not cause pain or discomfort. All that is required of the patient is to lie still and listen to the doctor.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
The main advantages and disadvantages of the technique are summarized in the following table:
| CT scan with contrast of the abdomen | |
| Advantages | Flaws |
| 1. Highly informative research (especially vascular changes, bones and intestinal wall).2. Ability to detect small tumors and their metastases. 3. Speed of the procedure (compared to MRI), which is necessary in emergency situations. 4. Painless. 5. Possibility to simultaneously conduct an examination of the entire body. | 1. Radiation exposure to the patient’s body.2. Toxic effect of contrast. 3. The need to pre-assess renal function. |
results
Each patient receives examination results 30 minutes after the procedure. Some clinics offer the service of recording study results on a disk or flash drive. The quality of the image depends both on the tomograph itself and on the patient’s compliance with all the radiologist’s recommendations and his immobility during the examination. If all the rules were followed during a CT scan, the resulting image will clearly visualize, for example, the location and number of kidney stones or signs of thrombosis.
Yusupov Hospital offers services in various diagnostic methods. The diagnostic building has modern equipment. The device of a computed tomograph allows you to significantly reduce the radiation dose to the body and conduct the study as quickly as possible. At the end of the study, the patient receives a conclusion and ready-made images - in “paper” format, on a CD or in the form of an email.
The hospital has polite and attentive medical staff who create a comfortable atmosphere for the patient. Administrators are always ready to answer your questions. You can make an appointment by calling the hospital call center. Yusupov Hospital is a multidisciplinary center that provides qualified care to each patient on an individual basis.
Make an appointment
Author
Harm of computed tomography with an enhancing agent
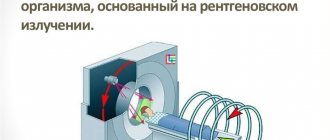
Computed tomography is an x-ray diagnostic method, therefore, the patient is susceptible to radiation. In this case, the radiation exposure is much higher than with radiography. Typically, with an abdominal CT scan, the patient receives 5-14 mSv (depending on the type of machine). Although this dose exceeds the recommended dose for an ordinary healthy person (1-2 mSv), it remains safe.
Without emergency indications, it is recommended to conduct the next study no earlier than 6 months after the previous one. If you do CT scans frequently, you can increase the risk of developing malignant neoplasms.
Important The contrast used for the procedure is not radioactive. But during its administration and 30 minutes after, medical monitoring of the patient’s condition is required. It is during this period that undesirable reactions most often develop.
Side effects
The vast majority of patients tolerate the procedure well. But in a small number of cases the following side effects may occur:
- Allergic reactions (rash, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, disturbances in heartbeat and breathing).
- Increased body temperature.
- Dyspeptic disorders (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting).
- Pain in the head or peripheral muscles.
- Systemic fibrosis (skin, muscles, liver, heart, lungs).
- Nephrotoxicity and acute renal failure.
- Thyroid dysfunction (hyperthyroidism).
What medications are taken during preparation for a CT scan?
Sometimes your doctor may recommend using the following medications before diagnosis:
- enterosorbents: activated (or white) carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb and others (they are prescribed a few days before the study). These drugs help reduce gas formation in the intestines. When taking them, you must consume a sufficient amount of fluid, otherwise constipation may occur;
- a laxative (“Fortrans”) is used before the study according to the scheme in the instructions to cleanse the intestines;
- Antispasmodics are taken before scanning if intestinal motility is increased.
The need to take medications in preparation for tomography is discussed with your doctor. You cannot drink them on your own, this will affect the overall picture of the disease, and the diagnosis will be uninformative.
Indications and contraindications
There are a number of conditions when CT scanning using contrast allows not only to increase the diagnostic information, but has practically no alternatives. Among these indications it is necessary to highlight:
- oncological pathologies of the abdominal organs, as well as regional or distant metastases;
- liver disease, as well as the presence of ascites or jaundice of unknown origin;
- presence of contraindications to MRI;
- traumatic injury to the abdomen;
- hematological pathologies (leukemia, lymphoma);
- aneurysm or dissection of the abdominal aorta;
- developmental abnormalities of the digestive or urinary systems.
The diagnostic procedure cannot be carried out if patients have the following conditions:
- intolerance to iodine-containing contrast agents;
- diseases of the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by thyrotoxicosis;
- period of pregnancy or breastfeeding;
- end-stage renal failure (decrease in GFR<15 ml/min);
- acute heart failure.
Children can undergo contrasting from the first year of life.
Contraindications
For male patients, there are practically no absolute contraindications, except for mental disorders and other conditions that make examination with a tomograph impossible. For women, pregnancy and lactation period are contraindications.
Relative contraindications, in which the doctor individually decides on the possibility of MSCT with or without contrast, are:
- Age up to 14 years;
- Significant body weight;
- Kidney pathologies;
- Decompensated diabetes mellitus.
The presence of implants and devices with metal components in the patient's body may distort the results. It is imperative to inform the radiologist about them so that he can adjust the operation of the device taking these circumstances into account.
Preparation
If a more thorough examination of the vessels of the abdominal cavity, retroperitoneal space or intestinal wall is planned using computed tomography with contrast, then the patient must be prescribed a diet , the purpose of which is to reduce the production of gases in its lumen. This makes it possible to increase the information content of diagnostics.
You can only eat foods that do not cause increased gas formation. The preparation also includes a study on the tolerability of the contrast agent and kidney function. This allows you to avoid complications during the procedure. You can read more about preparing for a CT scan here.
Please note: If the examination is carried out in emergency conditions, then diet and preliminary water load can be neglected.
What diseases does an abdominal CT scan detect?
The method allows you to determine the focus of the disease, establish the volume and boundaries of the pathology, check the circulatory and lymphatic system of the area under study, and clarify the homogeneity of the structure. It helps you see:
- Polyps, adenomas, fibromas;
- Abscesses, foci of inflammation;
- Neoplasms of a malignant nature;
- Dropsy;
- Atherosclerosis, lymphadenopathy and other vascular problems;
- Lymphadenitis;
- Tissue necrosis;
- Cirrhosis;
- Cysts;
- Congenital anomalies;
- Hepatosis;
- Gallbladder diseases;
- Pancreatitis;
- Aneurysms;
- The presence of parasites in tissues;
- Chronic and acute hepatitis;
- Appendicitis.
This is not the entire list of diseases that can be detected using computed tomography.
Price
How much a contrast-enhanced procedure costs depends on the region in which the patient lives. In Moscow, you can undergo an abdominal CT scan with contrast in many private medical centers. The cost of the examination ranges from 4,500 (“Be Healthy”) to 11,500 (“Pokrovsky Gate”) rubles. In state clinics, the price of stomach diagnostics is slightly lower - 4500-8000 rubles (Research Institute of Rheumatology, Scientific Center for Children's Health of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Clinical Hospital No. 85).
In St. Petersburg, the cost of a CT scan with contrast in private clinics is 5,500-10,500 rubles. In the Pokrovskaya Hospital the price for diagnostics is 7,000, and in the City Clinical Hospital No. 31 - 7,500 rubles.
In Yekaterinburg, the procedure costs 5,500 (“Diagnostics Plus”), and in Kazan – 7,500 rubles (“Expert+”).
Often, an abdominal tomography with contrast is done simultaneously with an examination of other organs, such as the chest or pelvis, and the price for both procedures is more favorable.
Diagnostics can be done under the compulsory medical insurance policy in all public and some private clinics. In this case, the patient must undergo a preliminary full examination and receive a referral from the attending physician in the prescribed form (valid for 3 months after discharge).
Indications for use
Computed tomography of the abdominal cavity is usually prescribed by a specialist in the following situations:
- to examine organs before surgery;
- to diagnose diseases when it is not possible to determine them using other methods;
- to identify the causes of icterus and sudden weight loss;
- for the possibility of a complete examination of violations of the integrity of internal organs after an injury to the abdominal region;
- if you suspect the development of oncological pathology in the peritoneum or retroperitoneal space;
- to determine the degree of development of a tumor neoplasm;
- to track the dynamics of the disease or the effectiveness of treatment.
How does a computed tomography scan of the abdominal organs work?
CT scans can usually be performed either in a hospital setting or in a clinic.
If an abdominal CT scan with contrast is planned, a venous catheter is inserted into the cubital vein before the scan begins. This mechanism, using an automatic injector, gradually delivers the contrast drug into the body. In this case, we are talking about CT with bolus contrast. It is also possible to use a syringe to administer contrast. To examine the upper gastrointestinal tract, contrast is administered orally; if it is necessary to examine the pancreas, kidneys or liver in detail, contrast is administered parenterally - into a vein.
The patient is placed on the tomograph table and asked to take the most comfortable position. It is especially important that the person does not move during the process, so sometimes it is necessary to secure him with belts. The doctor may ask you to hold your breath for a short time.
The duration of the tomography is no more than 30 minutes. All this time the patient will be under the supervision of medical personnel. The radiologist and x-ray technician are in the next room, but can see and hear the subject and communicate with him. After the procedure, the patient may be prescribed plenty of fluids to speed up the process of removing the contrast.
For those people who suffer from claustrophobia, it is recommended to undergo an examination with an open-type tomograph.
What does a CT scan of the abdominal cavity without contrast show?
This type of tomography is used more often than CT with contrast, since it is more harmless, costs slightly less and is easier to perform, without double scanning and manipulations with the introduction of a contrast agent with special syringes or catheters.
CT without contrast makes it possible to assess the condition of the abdominal cavity and each organ separately, check for the presence of developmental anomalies, and also identify the presence of stones in the kidneys, gall bladder, bile ducts and ureter, an increase or decrease in the size of organs, and changes in their tissues.
This type of study helps to determine the presence and amount of calcifications in the arteries or pancreas, determine aneurysm, cirrhosis, the development of malignant tumors, and the spread of metastases.
What can you see on a CT scan?
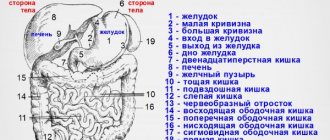
This relatively new method of human condition testing, which dates back to the early 1970s, continues to be highly effective in a variety of situations. With the help of clinical equipment, doctors receive highly accurate and informative information about the patient’s current health. Radiation screening helps to diagnose a dangerous disease in the initial stages, which ensures timely administration of therapy and a speedy recovery. The concept of the abdominal cavity includes many sections. Using diagnostics, you can study the condition of the following areas of the body:
- gastrointestinal tract structures;
- stomach;
- intestines;
- liver and biliary tract;
- pancreas;
- spleen.
Additionally, CT is used to examine the retroperitoneal region, which includes:
- kidneys;
- ureter;
- adrenal glands;
- lymph nodes;
- urinary canals.
Using diagnostic technology, doctors can find out the condition of the bone structures, as well as the lower thoracic region of the spinal column.
Results of the analysis
A CT scan of the abdominal cavity is interpreted immediately after the diagnosis is completed. The specialist receives the finished images and begins to decipher them. This process usually takes 1 hour. After deciphering the results, the patient is given the photographs, as well as a doctor’s report with his signature and seal.
What does an abdominal CT scan show? Based on the results of the procedure, specialists are able to obtain the following data:
- The exact location, size and shape of the organs being examined.
- The presence of benign or malignant tumors, metastases, infections, bleeding, excess fluid.
- Detection of stones in the kidneys and gall bladder.
- Presence of inflammation in internal organs, etc.
Abdominal CT is a modern, accurate method for diagnosing diseases of internal organs. This research method is performed only according to doctor's indications. A CT scan is prescribed if the specialist is unable to obtain accurate information about the condition of the organs during an ultrasound scan.