Ultrasound diagnostics has gained great popularity due to its safety and relative ease of implementation. This is explained by the fact that high-frequency sound waves are not capable of causing harm to tissues or causing negative reactions in the human body.
Ultrasound has found application in the following areas of medicine:
- gynecology and obstetrics (transvaginal or transabdominal examination);
- gastroenterology (study of the abdominal organs);
- urology (examination of the pelvic organs in men, the urinary system);
- endocrinology (ultrasound of the thyroid, parathyroid, thymus glands);
- pediatrics (brain, hip joints);
- angiology, phlebology, neurology (ultrasound of vessels of the neck and extremities);
- rheumatology, arthrology (ultrasound of joints and adjacent tissues);
- oncology (detection of primary tumors).
No matter which doctor sends them for such a diagnosis, patients are always interested in deciphering the ultrasound.
Diagnostic features
Some patients are interested in: what does abdominal ultrasound give to an adult? This examination is carried out when certain symptoms of improper functioning of the digestive system occur. The patient may experience pain in the peritoneum or lower back, and may also feel weakness and nausea. If certain diseases are suspected, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound scan.
This is a painless, harmless procedure. It has virtually no contraindications. The equipment includes a scanner that directs ultrasound into the body. Next, the equipment receives the signal reflected from the tissue and displays the image on the screen. The doctor sees a black and white picture. It can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional. In this case, the image is displayed in real time.
It is worth noting that there are certain standards for abdominal ultrasound in adults. Only a physician with appropriate qualifications can interpret the result. An ordinary person, looking at the image of an organ on the screen, will not be able to determine whether there is a pathology. Therefore, such a task can only be done by a professional. After the examination, the patient is given a form indicating the parameters of the organs, as well as the data obtained during the examination. To draw a conclusion about the state of the internal organs, you can familiarize yourself with the basic norms, as well as deviations.
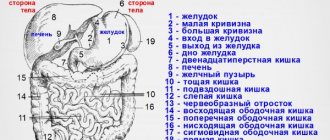
During the examination, one or more organs may be examined. The cost of the procedure depends on this. A complete examination includes the study of the following organs:
- Pancreas.
- Liver.
- Gallbladder.
- Spleen.
- Genitourinary system, kidneys.
- Vessels, lymph nodes.
Ultrasound will be uninformative when examining the stomach and intestines. There are gases here, which makes it difficult to study the condition of the organ. The walls of the stomach are too thick for ultrasound to penetrate. In this case, a different examination is required.
Normal indicators of organs of OBP and deviations
The study protocol prescribes the norms for abdominal ultrasound, indicating age and gender distinctions, so even the patient himself can see any inconsistencies in his form.
Liver and gallbladder
Due to close contact and interaction, these two organs are examined almost simultaneously and always together. Most of the diseases of these two organs are interrelated, and they affect a significant part of the population not only in our country. Therefore, the liver and gall bladder are subjected to the most scrupulous study.
The normal dimensions of the natural filter - the liver - for an adult are:
- right lobe: length up to 5 cm, thickness 12–13 cm;
- left lobe: height up to 10 cm, thickness up to 7 cm;
- oblique vertical size – up to 15 cm.
If diagnostic materials indicate increased echogenicity of liver tissue, it is understood that this organ is characterized by an increase in the ability to reflect ultrasonic waves. This phenomenon is characteristic of hepatosis - changes in the quality and quantity of liver fat cells. In extreme stages of this disease, ultrasound cannot detect hepatic vessels.
Exceeding the normal size of the liver and the presence of fluid in it in most cases indicate the development of cirrhosis. In this case, the expansion of venous vessels (especially the portal vein) is visualized, the shape and contours of the liver change. If an increase in liver parameters is detected on an ultrasound scan of the liver, its contours become rounded and the large vena cava expands, the patient is asked to inhale, and if the diameter of the vessel does not decrease, then the presence of pulmonary and cardiac diseases is likely.
Structural changes in the liver in several areas of different nature may be evidence of the occurrence of various pathological processes. This is observed in cancer, cystic formations and abscesses. In parallel with the liver, the gallbladder is also being studied. The normal level of this organ and its ducts in an adult healthy person has the following characteristics:
- shape: round, oval or pear-shaped;
- dimensions: width – 3–5 cm, length – 6–10 cm;
- walls: smooth, without changes or growths;
- The thickness of the walls of the organ itself is 4 mm.
If there are areas of growth in the gallbladder, ultrasound diagnostics will show them in the form of shadows. Such changes often indicate the presence of stones in the organ cavity. Oncological neoplasms can also be visualized as growths attached to the walls of the bladder. Based on the results obtained, an experienced specialist can determine the nature (benign or malignant) and size of the formed pathology.
An ultrasound examination can detect symptoms of inflammatory processes in the organ. This is indicated by a decrease or increase in its size, as well as thickening of the walls. Such changes indicate the development of acute cholecystitis. In the chronic course of the disease, during the procedure, compaction of the walls and contours is visualized, while the latter have clearly defined boundaries.
In case of combined inflammation with the formation of stones, called calculous cholecystitis, the uneven boundaries of the edges of the bladder and the shadows from them are visualized using ultrasound. Among other things, the procedure allows you to diagnose a condition dangerous to human health, characterized by the presence of fluid - ascites. This indicates the development of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum) and requires urgent surgical assistance. Another case that requires emergency surgery is when the bile duct is blocked by a stone.
Pancreas
Examination of this organ helps to detect the presence of inflammatory and oncological processes in it. Normal parameters of the pancreas in an adult are:
- head – up to 3.5 cm,
- body – up to 2.5 cm,
- tail – up to 3 cm,
- contours are smooth,
- structure – homogeneous,
- sufficient echogenicity,
- no growths,
- The diameter of the gland duct is 1.5–2 mm.
Low echogenicity (insufficient throughput of the gland) indicates acute pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas. In the chronic form of the disease, the organ enlarges and an expansion of its duct is visualized on ultrasound. The volume of the gland is the main criterion that determines its condition. With neoplasms, as a rule, there is an uneven increase in the size of the gland. If there are areas in the image that differ in structure from the tissue that makes up the gland, we can conclude that there are abscesses, cystic formations or tumors.
Spleen
Ultrasound diagnostics rarely reveal pathologies of this organ, and the spleen itself is rarely affected by diseases. The following are considered normal parameters for it:
- length – 10–12 cm;
- width – 5cm;
- thickness – 5 cm;
- structure – homogeneous;
- the vein does not leave the portal of the organ.
An enlarged spleen, detected by ultrasound, indicates diseases of the liver or hematopoietic organs, as well as infections, including parasitic ones. If compacted areas are detected, a conclusion is drawn about the presence of a splenic infarction, which can occur due to bruises or blockage of venous vessels by a blood clot. During ultrasound examinations, it is possible to diagnose rupture of the spleen due to traumatic injuries, its pronounced displacement, which has the second name “wandering spleen”. It also becomes possible for a specialist to track congenital anomalies, underdevelopment of an organ, or the presence of additional lobes.
Urinary system
For certain indications, during an examination of the abdominal cavity, an ultrasound examination of the urinary organs can also be performed. They are located in the retroperitoneal space, and their study does not require any additional measures for the doctor, but the patient needs to have a full bladder at the time of the study. The norm for the kidneys is:
- width – 5–6 cm;
- length – 11 cm;
- thickness – 4–5 cm;
- parenchyma (shell) – about 2.3 cm.
Moreover, in the normal state, during the procedure, no inclusions or altered areas in the ureters and renal pelvis are visualized. To determine the presence of stones, the bladder must be examined - ultrasound diagnostics makes it possible to determine the number and size of stones without much effort. Elderly males are characterized by the formation of stones in the bladder cavity itself - this occurs due to problems with the outflow of urine, most often due to prostate diseases.
In this case, the description of the results will indicate that primary stones are present. This is not a sign of urolithiasis. If the description talks about secondary stones, then this is a direct confirmation of urolithiasis. That is, the stones were formed in the kidneys and entered the bladder cavity through the urinary tract. When inflammatory processes develop in the bladder during ultrasound, its walls are visualized as thickened
Blood vessels and lymph nodes
Reference. The standard ultrasound technique is not aimed at a thorough examination of the bloodstream of the ABP. Other methods are used for this, such as Dopplerography and angiography. Ultrasound examination allows you to assess the condition of large vessels of the abdominal aorta, portal and inferior vena cava. It is possible for a diagnostician to identify aneurysms - thinned areas of blood vessels that can cause wall rupture and lead to internal bleeding.
During the procedure, the specialist determines the size of the peritoneal vessels, which normally are:
- aorta – 2–2.5 cm;
- inferior vena cava – 2.5 cm;
- splenic artery – 1–4 mm;
- splenic vein – 5 mm.
If the above indicators do not deviate from the norm, then further diagnostic measures are not recommended, otherwise Dopplerography or angiography is additionally performed. The following can be said about the lymph nodes: in a healthy person they are not enlarged and are not detected during diagnosis.
If ultrasound materials indicate their enlarged state, then this is a sign of the presence of an infection or a malignant tumor process. When examining a child’s ABP, special tables are used to evaluate the indicators of the norm and possible deviations corresponding to age, weight and gender.
Information content of the technique
What will an abdominal ultrasound show in adults? This technique is very informative. It allows you to consider both the external structure of the organ and its internal space. In this case, pathology can be detected even at an early stage of development. Even small details are visible in the image. However, functional deviations cannot be determined during the presented procedure.
Using ultrasound, the size of internal organs is assessed. This allows you to determine the presence of certain pathologies. The doctor also evaluates the internal structure of the peritoneal organs, their contents and location. The presented technique allows us to identify foci of chronic or acute inflammatory process and the condition of blood vessels.
On ultrasound, neoplasms are clearly visible. The doctor can evaluate their structure, the presence of fluid inside or metastases. Stones can be seen in the kidneys, bladder and gall bladder.
What do they look for in an abdominal ultrasound in adults? Each medical center offers a specific list of internal organs that are assessed during the procedure. Usually, if the cost of a service exceeds 2 thousand rubles, the doctor examines all the organs that are located in the abdominal cavity step by step. If the price of an ultrasound is 1-1.5 thousand rubles, during the procedure only the hepatobiliary system is examined.
In addition, in some cases, diagnostics of only one organ is required. In this case, the cost varies from 500 rubles. and higher, depending on the pricing policy of the clinic.
Ultrasound of neck vessels
In a typical ultrasound protocol of extracranial vessels of the neck, they describe: whether the examined vessels are passable or not (if the lumen is disturbed, the size of the stenosis and its effect on blood flow is described in detail), the thickness of the intima-media complex (IMC), the condition of the vascular wall, the course and deformation of the vessels, the diameter of the spinal arteries , type of blood flow in the artery, speed indicators and resistance indices.
When you inhale, the blood flow in the veins of the neck decreases, and when you exhale, it increases
Healthy vessels must be completely passable and have a straight direction. The inner and middle layers of the vascular wall should be clearly visible. The paired venous vessels of the neck are normally oval in cross section, and with slight pressure they are easily compressed.
Conducting a survey
When considering the question of how an abdominal ultrasound is performed in adults, it should be noted that this is a rather lengthy process. This is due to the examination of several internal organs at once. The minimum duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. If a full range of examinations is required, diagnostics can be carried out within an hour.
The examination is carried out using special equipment called an echotomoscope. Modern clinics use new equipment that is capable of displaying high-quality images on the screen. Old devices may cause interference. Because of this, interpretation of the result may be difficult. Therefore, you should only contact large medical centers that have high-quality equipment.
Upon entering the office, the patient undresses to the waist. He lies down on the couch on his back. The doctor may ask you to turn over on your side or stomach during the examination. This makes it possible to better examine some organs.
A special water-based gel is applied to the skin. It does not allow an air gap to form between the scanner and the surface of the abdomen. Ultrasound will be able to penetrate inside the body.
During the procedure, you may need to hold your breath for a few seconds. The doctor will inform you about this at a certain point during the examination. The result is given to the patient immediately after the ultrasound.
Liver, gall bladder
Only a doctor with appropriate qualifications can interpret ultrasound of the abdominal organs in adults. The liver and gall bladder are nearby. Therefore, their diagnosis is carried out simultaneously. There are certain standards for determining the dimensions of these organs. Deviations indicate the development of pathology. The following standards have been established for the liver:
- The height of the left lobe is up to 10 cm.
- The thickness of the left lobe is about 7 cm.
- The length of the right lobe is up to 5 cm.
- The thickness of the right lobe is 12-13 cm.
- Oblique vertical size - 15 cm.
The tissue structure is also checked. If echogenicity is increased, liver tissue strongly reflects ultrasound. This indicates hepatosis (fatty changes in the structure of the organ). At an advanced stage of this pathology, liver vessels are not detected at all during the examination. If the size of the liver is enlarged and there is fluid in it, this indicates the presence of cirrhosis.
If the structure of the organ tissue is changed in one or more places, this may indicate the development of a neoplasm or abscess.
Considering the features of deciphering ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in adults, the norms of physical indicators of the gallbladder should be studied separately. A healthy organ has the following parameters:
- Width - 3-5 cm.
- Length - 6-10 cm.
- Volume - 30-79 cm³.
- Wall thickness - 4 mm.
- Shape: oval, round, pear-shaped.
- The cavity is smooth.
Growths inside the organ are visible in the image as shadows. This often indicates the presence of stones. The growths can also be neoplasms. A doctor can determine whether they are benign or malignant.
Any deviations in the size of the organ indicate the development of various pathologies. Their character is determined by the doctor.
In what cases is it prescribed?
Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs is prescribed by doctors of various specialties (therapists, gastroenterologists, general and vascular surgeons). It is indicated if the patient has the following symptoms:
- pain syndrome of varying intensity localized in any part of the abdomen, aching, cutting or stabbing in nature, which may intensify after eating or changing position;
- feeling of heaviness in the right hypochondrium ;
- nausea and vomiting after eating;
- chronic constipation or tendency to diarrhea;
- the appearance of blood , pus or undigested food particles in the stool;
- yellowness of the skin or mucous membranes;
- sensations of rapid filling of the stomach while eating;
- intolerance to fatty, meat or carbohydrate products;
- increased gas formation;
- weight loss in the absence of changes in diet and physical activity;
- burning sensation behind the breastbone or in the mouth;
- enlargement of the abdomen or individual organs, which is revealed by palpation.
Pancreas
Examination of the pancreas deserves special attention. Specialists compare with the norm, decipher ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in adults and, if possible, make a final diagnosis based on these data.
The study allows us to identify inflammation, neoplasms and other structural changes. The pancreas should have the following dimensions:
- Tail - up to 3 cm.
- Head - up to 3.5 cm.
- Body - up to 2.5 cm.
- The size of the pancreatic duct is 1.5-2 mm.
- The contours are smooth.
- The structure is homogeneous.
- Echogenicity is high.
There should be no growths in the organ. If the echogenicity is low, this indicates the development of acute pancreatitis. In the chronic course of the disease, the duct is dilated. At the same time, the size of the pancreas is increased. In patients over 50 years of age, low echogenicity is not always a sign of pathology. This may be caused by fat accumulation in the gland. This is the norm for this age.
If the volume is increased unevenly, this indicates the development of a tumor. Uneven lesions on organ tissues can be an abscess or tumors.
Decoding the research results
The ultrasound of the abdominal cavity is interpreted by a sonologist or a specialist who referred for examination - a hepatologist, oncologist, nephrologist. How to determine pathology by ultrasound? The doctor looks at the deviation from normal values and compares them with the obtained values.
The table shows a breakdown of the results and the presumed diagnosis:
| Organ | Decoding indicators | Presumable diagnosis |
| Gallbladder | Dense wall, hypoechogenicity, blurred contour. | Acute cholecystitis |
| Reduced echogenicity, clear outlines, deformation of the structure. | Chronic cholecystitis | |
| Increased echo, moving shadow. | Stones in the gallbladder | |
| Liver | Enhanced and rapid signals, hypertrophy, the portal vein with compacted parenchyma is visible. | Hepatosis |
| Uneven edges, changes in echostructure, enlarged spleen, dilated veins, fluid in the abdominal cavity. | Cirrhosis | |
| Changes in echogenicity and size, convex borders. | Focal neoplasms | |
| Pancreas | Diffuse enlargement, blurry contours, reduced echostructure. | Swelling due to inflammation |
| Decreased echostructure, unclear foci, shift of the inferior vena cava, increased diameter of the Wirsung duct. | Tumors or cysts | |
| Kidneys | Hyperechoic, moving formations. | Kidney stones |
| Narrowed or enlarged sinus, hypoechogenicity. | Pyelonephritis | |
| Spleen | Increased density, hyperechogenicity, uneven edges, organ hypertrophy. | Heart attack or rupture of the spleen |
| Lymph nodes | Visible on ultrasound. | Infection, cancer of the lymphatic system or metastases of other organs |
The conclusion after the study is drawn up by a sonologist who fills out a special form. Then the attending physician gets acquainted with this medical document and, based on its contents and the results of additional tests, makes a diagnosis.
9 minutes Author: Irina Bredikhina 17293
Interpretation of the results of many studies is quite difficult and requires high professionalism. And with diagnostic procedures aimed at studying several organs at once, it becomes even more difficult to correctly describe the materials obtained.
Deciphering an ultrasound scan of the abdominal cavity is considered to be exactly such an event. So that, based on the examination materials, the attending physician can develop the most appropriate therapeutic strategy, each organ must be carefully studied by a diagnostician. And his conclusion must contain all the necessary information about the condition of the examined organs.
Spleen, urinary system
When considering the norms for abdominal ultrasound in adults, indicators for the spleen should also be considered.
Pathologies in this organ are rarely diagnosed. Its parameters should be like this:
- Width - 5 cm.
- Length - 10-12 cm.
- Thickness - 5 cm.
- The structure is homogeneous.
- There is a vein at the organ's gate.
If the organ is enlarged, this may indicate problems with the liver or circulatory system. Also, the cause of such changes may be parasites or an inflammatory process. Seals in tissues indicate an organ infarction. This happens due to blockage of the vein by a blood clot or stroke.
The list of organs examined may include the kidneys and bladder. The normal sizes of these organs are as follows:
- The width of the buds is 5-6 cm.
- Length - 11 cm.
- Thickness - 2.3 cm.
- Shell (parenchyma) - 2.3 cm.
At the same time, there should be no inclusions or tissue changes in the renal pelvis and ureters. The bladder is examined for the presence of stones and sand. If they exist, the size and number of stones are determined.
If stones formed in the kidneys and then entered the bladder, these are secondary stones. This indicates the development of urolithiasis. Thickened bladder walls indicate the development of an inflammatory process.
Indicators that are measured during the study, their norms in adults and children
What indicators are normal in the absence of diseases of the internal organs? Norms of liver ultrasound indicators:
Norms for the gallbladder:
Norms for the spleen:
- length - 11 cm;
- thickness - 5 cm;
- longitudinal section - 40 sq.cm;
- splenic index - 20 sq.cm.
Kidney ultrasound results are normal:
- length - 11 cm;
- width - 5-6 cm;
- thickness - 4-5 cm;
- parenchyma - 2.3 cm.
Normally, the lymph nodes are not visible, the sonologist writes as much in the conclusion. In children, the size of organs depends on their age, so a pediatric specialist should be involved in decoding. However, the norms for structure, echogenicity and absence of additional formations in children are the same as in adults.
Preparation for the procedure
Sometimes the image during the examination may have noise. Due to bloating and flatulence, internal organs cannot be clearly seen on an abdominal ultrasound. How can an adult prepare for the procedure? First of all, you should review your diet. Three days before the examination, a whole list of products is excluded from it.
You should not eat raw vegetables and fruits during preparation. You should avoid cabbage altogether. It cannot be eaten during the preparation period, even in stewed or pickled form. All legumes are also excluded from the diet. You should also give up sweets and starchy foods. Even eating bread is undesirable.
You should also avoid eating dairy products and drinking carbonated drinks. Chewing gum is prohibited. In the process of chewing them, uncontrolled swallowing of air occurs.
You should definitely give up alcohol and smoking. They may affect the results of the examination. If it is difficult to quit smoking completely, reduce the amount of nicotine consumption. On the day of the examination before the procedure, you should not smoke at all.
What should an adult eat before an abdominal ultrasound? You can eat lean meat or steamed fish. You can eat baked apples. Porridge with water is allowed. Meals should be fractional. You can't overeat. You need to drink 1.5 liters of pure water without gas per day. It is permissible to drink weak tea, but unsweetened. The last meal before the examination should take place no later than 6 hours.
Gentle diet
When considering how to prepare for an abdominal ultrasound in an adult, it should be noted that in some cases a gentle diet is acceptable. It is prescribed before the examination for people with diabetes, as well as pregnant women. Everyone else should follow the usual recommendations.
Diabetics can eat on the day of the procedure. In the morning you can drink a cup of unsweetened tea and also eat a couple of crackers. The diet is developed by the attending physician.
Preparation for abdominal ultrasound in adults can be gentle for pregnant women. Their body needs a constant supply of nutrients and vitamins. Diets are unacceptable for them. The list of products for this category of patients has been expanded. Dairy products must be added to it in small quantities. You can eat vegetables and fruits, but only thermally processed ones.
For pregnant women, the procedure is scheduled early in the morning. You are allowed to have a snack 3 hours before the examination. However, it is not necessary to take a 6-hour break. It can be difficult for an expectant mother to stick to a strict diet. Her health may worsen because of this.
Medications
Preparation for an abdominal ultrasound in adults may involve taking special medications. They will be prescribed by a doctor if necessary. Not every patient needs this. Such medications improve digestion. They are prescribed to people who suffer from indigestion and increased flatulence. In this case, the doctor may prescribe Smecta, Festal, Mezim or Enterosgel.
Medicines may have side effects. Therefore, they are prescribed only in cases of extreme necessity. At the same time, the characteristics of the patient’s body, the presence of pathologies and concomitant diseases are taken into account.
The doctor should also be told if the person is taking certain medications on an ongoing basis. You cannot refuse them even before the examination. In this case, the medical specialist will take into account the peculiarities of taking the medicine and prescribe the procedure at the most appropriate time.
It is worth noting that some medications should not be taken before the examination. These include No-Shpa, acetylsalicylic acid and aspirin.
In some cases, a laxative may be required. It is drunk 12 hours before the ultrasound. If the drug does not have time to act, you need to give an enema a couple of hours before the procedure. If the bowel is full, this may negatively affect the examination.
Other preparation details
Doctors must give recommendations before ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in adults. If the urinary system is being examined, the patient should drink 1.5 liters of water before the examination. This is necessary in order to clearly examine the contents of the kidneys, bladder, and ducts.
You can drink clean water without gas or impurities. It is also allowed to replace it with regular tea without sugar. Just it shouldn't be too strong. However, under no circumstances should you replace water with juice or compote. This can lead to bloating. As a result, it can be difficult to interpret the result.
If the patient underwent FDGS, colonoscopy, irrigoscopy or gastrography a few days ago, the doctor should be informed about this. Such procedures lead to the inability to obtain an accurate result. Therefore, the procedure will need to be postponed.
Having considered the features and norms of abdominal ultrasound in adults, we can draw conclusions about the features of this procedure. Proper preparation allows you to get an accurate result.