Timing of detection and fetal heart rate
The baby's heartbeat can be detected early. Using a conventional abdominal ultrasound sensor, the doctor will detect heart beats at 5 weeks of pregnancy, and a vaginal sensor will allow you to do this already at 3-4 weeks, that is, almost immediately after the first beat of a small heart (see calculating the gestational age - calculator).
The fetal heart rate varies not only depending on its activity, but also changes with the duration of pregnancy.
- At 6-8 weeks, the beat frequency is 110-130 per minute
- from 8 to 11 weeks it can increase to 190 beats
- starting from 11 weeks it stays in the range of 140-160 beats, with slight deviations in one direction or another.
| gestational age | number of strokes/min. | |
| 4-6 weeks | 80-85 | |
| 6 weeks | 100-130 | |
| 7 weeks | 130-150 | |
| 8 weeks | 150-170 | |
| 9 weeks | 170-190 | |
| 10 weeks | 170-190 | |
| 11 weeks | 140-160 | |
| 12-40 week | 140-160 |
The doctor evaluates not only what the fetal heartbeat is like by week, but also takes into account additional factors (illnesses of the mother and child, listening time and the baby’s activity phase).
Duplex scanning
Duplex scanning of the heart and blood vessels (USDG) consists of the following - ultrasound generates high-frequency waves that are reflected from a moving object. These waves are then captured by a sensor and transmitted to the monitor. The procedure is used to assess the state of blood flow in the vessels.
Ultrasound scanning is mandatory for all pregnant women in the third trimester, but can be used in the early stages if the mother has:
- arterial hypertension;
- threats of miscarriage;
- anemia;
Ultrasound is performed if there is a history of anemia
- uterine fibroids;
- heart failure;
- changes in the structure of the placenta.
Indications for this may include a congenital defect in the fetus, infections, a large fetus, or a loop of the umbilical cord around the neck.
Pathologies in an unborn child are rare, so the mother should not panic ahead of time. It is best to visit an antenatal clinic if you suspect abnormalities and follow the recommendations of a specialist. The fetal heart is connected to the emotional state of the mother, so you need to carefully monitor your health and mood.
Causes of heart rhythm disturbances
| First weeks of pregnancy | From 12 weeks of pregnancy until birth | Childbirth | |
| Heart rate below 120 beats per minute |
|
|
|
| Heart rate above 170 beats per minute |
|
|
|
| Dull, hard to hear tones |
|
|
|
| Absence of fetal heartbeat |
|
|
|
Why is the fetal heartbeat determined?
Establishing the fact of developing pregnancy
After the first delay of menstruation and the appearance of two cherished stripes, the expectant mother is usually sent for an ultrasound. With the help of modern devices, already in the third week of pregnancy you can hear the rapid beating of the heart of a small embryo. If during the first ultrasound the fetal heartbeat is not heard when there is a fertilized egg in the uterus, then this is not a reason to panic. Usually, when re-examined a week later, the grown embryo allows you to hear its heartbeat. But in some cases, a heartbeat does not appear, and the fertilized egg is deformed. This condition is called frozen pregnancy. In this case, a medical abortion (complications) is performed with the help of hormonal drugs, and a new attempt to become pregnant is recommended after 3-6 months.
Fetal assessment
The baby's heart reacts to the slightest changes in the world around him. Stress, illness or physical activity of the mother, the state of sleep or activity of the fetus, the concentration of oxygen in the surrounding air are instantly reflected in the heart rate. But these changes are temporary. If the heart beats too fast for a long time, this indicates a violation of the blood supply to the fetus, the so-called fetoplacental insufficiency. Most often it is chronic. In rare cases, the baby’s compensatory capabilities are depleted, the heart begins to beat slower than normal, which indicates a deterioration in his condition. In such cases, emergency delivery is often required. The choice of treatment largely depends on the week at which the fetal heartbeat became pathological.
Monitoring the condition of the fetus during labor
At the time of birth, the child experiences enormous stress, compression and oxygen deficiency. In most cases, his cardiovascular system successfully copes with these difficulties. But sometimes umbilical cord compression, placental abruption, or other emergencies occur that require immediate medical attention. Therefore, during childbirth, the baby’s heart rate is checked after each contraction so as not to miss signs of an acute lack of oxygen.
Methods for listening to the fetal heartbeat
Ultrasound
This is the very first method used during pregnancy. When conducting a study, along with determining the heart rate, the doctor evaluates the size of the fetus, the condition of the placenta and gives a comprehensive conclusion. Listen especially carefully to heart sounds and study the structure of the heart in case of developmental defects in a pregnant woman and the birth of children with defects of the cardiovascular system in the past. It is very important to identify abnormalities in the structure and functioning of the heart in cases of infections suffered by the mother during pregnancy.
Auscultation
This is listening to heart sounds using a special obstetric stethoscope. You can determine your heartbeat in this way starting from 18-20 weeks of pregnancy. An experienced doctor can use a tube to determine the approximate heart rate, clarity of tones, and the best place to hear them. But even a person without medical education is able to detect heart sounds and count their number per minute using a stopwatch.
In some cases, auscultation with a stethoscope is difficult or impossible:
- for overweight pregnant women
- when the placenta is located on the anterior wall of the uterus (then vascular noise interferes with auscultation)
- with too little or too much amniotic fluid
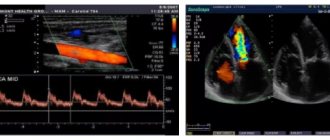
Cardiotocography (CTG)
A very informative method that allows you to assess the baby’s heartbeat. Using this procedure, it is possible to identify oxygen starvation of the fetus in the early stages and take appropriate measures (see interpretation of fetal CTG during pregnancy).
The CTG machine is an ultrasound sensor that sends and receives reflected signals from the fetal heart. All changes in heart rate are recorded on film. Together with the main sensor, a uterine contraction sensor is also installed. It shows the activity of the uterus, which is especially important during childbirth.
IN
In recent years, devices have special sensors for fetal movements; sometimes, using a separate button, a pregnant woman can record them independently. All information coming from the sensors is displayed on the tape. The duration of the CTG procedure is 50-60 minutes. This time is usually enough to catch the baby’s moments of activity and sleep. In special cases, sensors are attached to the pregnant woman’s belly and left for a day.
For fetal heartbeat analysis, gestational age plays a very important role. The first CTG study is carried out after 32 weeks, since before this period the data will be uninformative. It is after 31-32 weeks that the connection between motor activity and cardiac activity of the fetus is formed. Typically, a woman undergoes CTG twice during pregnancy (at 32 weeks and immediately before birth). According to indications, CTG can be performed an unlimited number of times, since the procedure is harmless.
The CTG tape is deciphered by a doctor who compares the results of this study with the data of ultrasound and tests. Cardiotocography itself is not a source of definitive diagnosis.
“Good” CTG includes the following parameters
The normal fetal heart rate is on average 120 to 160 beats per minute.
- in response to movements, the heart rate increases
- There are no decreases in heart rate or they are present in minimal quantities
The device independently analyzes all these parameters and produces the result in the form of a special bandwidth index. Normally it does not exceed one. But the functioning of the baby’s heart is influenced by many other factors, which only a doctor can evaluate.
Causes of “bad” CTG
- Hypoxia (oxygen starvation) of the fetus is the most common cause of changes on CTG.
If the baby experiences a lack of air, then his heart begins to work harder and the frequency of contractions increases. In response to a contraction or his own movement, the baby may react by slowing down the heartbeat, which is also not the norm.
- Pressing the umbilical cord against the fetal head or bones causes short-term changes in the band. They look the same as during oxygen starvation, but the child feels good and does not lack oxygen.
- Incorrectly attached sensors
If, when listening to the fetal heartbeat, hypoxia is detected, confirmed by other methods, then the doctor prescribes treatment or performs an emergency delivery (depending on the period and condition of the fetus).
Echocardiography
Echocardiography is used at 18-28 weeks of pregnancy only if the development of heart defects in the child is suspected. This is an ultrasound method that studies the characteristics of blood flow and the structure of the heart. It is indicated if:
- the woman already has children with heart defects
- the mother herself has congenital heart defects
- past infectious diseases during this pregnancy, especially in the 1st trimester
- woman over 38 years old
- pregnant woman has diabetes mellitus
- intrauterine growth restriction
- detected malformations in the fetus in other organs and there is a suspicion of congenital heart defects
The echocardiography method is also used as two-dimensional ultrasound, and other modes of the ultrasound scanner are used: one-dimensional ultrasound and Doppler mode. This combination of techniques helps to thoroughly study both the structure of the heart and the nature of blood flow in large vessels.
How the vascular system and heart are formed in the embryo
- From about 4 weeks of pregnancy, embryonic development begins. It is within 4-10 weeks that the main organ systems are formed - nervous, circulatory, muscle and bone. This period is very important in the development of the fetus, since some actions of the expectant mother or consumption of certain foods can lead to complications.
- By the beginning of the second month of pregnancy, the embryo does not yet closely resemble the future human being. The baby is pear-shaped and consists of 3 layers, each of which is responsible for the development of a particular system. The outer layer, the ectoderm, is responsible for the development of the skin and neural tube. And the latter, in turn, is for the development of the brain and spinal cord.
- The inner layer, the endoderm, is responsible for the development of the intestines and lungs. And finally, from the middle layer - the mesoderm - the heart and circulatory system will develop. If you are wondering at what week of pregnancy the fetal heartbeat appears, then I can confidently answer that already at 5, since by this period it begins to pulsate in the embryo. By this time, the development of the main human organ had already passed several stages. This process is quite difficult, so let’s take a little look at what week of pregnancy the moment of conception occurred and what main stages the heart goes through until the moment it begins to beat.
At 2-3 weeks of development, the foundations are laid and large vessels of the heart begin to develop. At the very beginning, it looks like two tubes that gradually join together. This tube begins to grow so actively that after a short amount of time, it no longer has enough space in the chest, it has to bend and narrow.
- This process results in an organ that is very similar to the human heart. By about 4 weeks, a constriction is formed, which divides it into two sections - venous and arterial. And by 6 weeks the arterial duct is formed, and by 10-12 weeks the venous duct begins to work. From the 5th week, a septum begins to form, which divides the common atrium into right and left.
- After a little more time, another septum will appear in the three-chambered heart in the area of the ventricles. And as a result, by approximately 6-8 weeks of pregnancy the baby has a full-fledged, human, four-chambered heart. It has some other features that are characteristic of an intrauterine organ. But with birth, when the baby’s lungs are involved in all processes, everything will fall into place.
At what stage does the heart begin to beat and how can you listen to the heartbeat that appears in the fetus?
Most often, the expectant mother does not notice those symptoms that may hint to her that a belly has settled in her stomach. But there is another type of woman who feels when life is born in them, almost from the first minutes.
The heart is, if not the most important, then certainly one of the most important organs in human life. That is why every mother wants to make sure that her baby is healthy and nothing interferes with his life. In order to study the functioning of this organ, the following are used: ultrasound, echocardiography, CTG, auscultation (listening to the fetus).
It is worth noting that at such early stages the most effective method is ultrasound. It makes it possible not only to listen to the heart rate, but also to look and verify the correct location of the organ in the chest. The least effective method for this period is listening to the embryo.
Since when it just begins to beat, its blows do not yet have such force as to drown out the mother’s heartbeat. Echocardiography is possible only according to a doctor’s indications. It is aimed not only at studying the structure of this organ, but also at analyzing the work of large vessels.
To identify defects, an additional “four-chamber” section can be performed. This is one of the possible ultrasound examinations that helps to see all four chambers of the heart at the same time - two ventricles and two atria. Such a study helps to identify 75% of possible deviations.
Is it possible to determine the sex of a baby by heartbeat?
Most women are in an interesting position, and even some medical professionals believe that the baby’s heart rate in the womb can be used to determine its gender. For some reason, there is a belief that girls’ hearts “accelerate,” that is, beat 150-160 times per minute, while boys’ heart rate is 135-150 beats. This hypothesis has no scientific basis, so gender can be guessed with only 50 percent confidence in this way.
The fetal heart rate reflects the body's ability to cope with oxygen deficiency. Gender does not affect this ability in any way. If the expectant mother wants to know in advance what color diapers to buy, then you can contact a good ultrasound specialist who will be able to determine the sex of the baby with great accuracy.
How is such a diagnosis made?
Visual study of the structures of the cardiovascular system of the embryo using ultrasound - echocardiography. Ultrasound of the fetal heart can be done both through the anterior abdominal wall (transabdominal) and through the woman’s genital tract (transvaginally).
In the short term, preference is given to the transvaginal method , since the fetal heartbeat is discernible only after the fourth week . At the sixth week, the contraction of the fetal heart can also be distinguished using the transabdominal method. During the first screening, two methods may be used to better visualize the heart.
When using the transabdominal method, it is advisable not to urinate before the examination in order to better visualize the uterine cavity, which is raised by a full bladder. With the transvaginal method, the bladder must be emptied before the procedure.
Ultrasound is usually done in the supine position. The gel is applied to the abdomen and the sensor is moved over the surface of the abdomen, and the embryo and the structures of interest to the doctor will be visible on the monitor. In the second method, an appropriate sensor is inserted into the vagina, on which a special condom is placed. The sensor is immersed to the required depth and the necessary calculations and measurements are made. Remains of the gel must be removed with a napkin.
Is it possible to hear the fetal heartbeat on your own?
If the expectant mother has a desire to listen to the heart of her baby, then it is not necessary to make an extraordinary visit to the antenatal clinic. There are several ways to listen to the sound of life developing.
Stethoscope
Auscultation with an obstetric stethoscope is accessible to absolutely everyone. This requires an obstetric tube (which costs very little) and an attentive and patient assistant. If he is not a doctor, then it is unlikely that he will be able to hear the heart before the 25th week of pregnancy.
The main thing is daily training. Then one fine day a husband, mother or other owner of a stethoscope will be able to hear the long-awaited sounds of a heartbeat. It is important to learn to distinguish them from the sounds of fetal movement, pulse or peristalsis of the mother.
Fetal Doppler - heartbeat detector
If you don’t have time to train in auscultation, you can purchase a portable ultrasound detector - a fetal doppler. This device works on the principle of a conventional CTG machine, but does not write a graphic image on film. Often, headphones are included with the device for comfortable listening. You can hear the heartbeat with this device as early as 8-12 weeks, but doctors recommend using it much later, when necessary, the study should last no more than 10 minutes.
| Pros of a portable doppler: | Disadvantages of a portable doppler: | |
|
Despite the safety of Doppler, you need to observe moderation in everything and not use the device often and for a long time |
Putting your ear to your stomach
When can you hear the fetal heartbeat in your ear? In late pregnancy (after 30 weeks), you can make sure that the fetal heartbeat is normal by simply placing your ear to the pregnant woman’s stomach, but it depends on the woman’s fat layer. You need to listen to the baby's heart in a certain place in the abdomen, depending on the location of the fetus in the uterus. If the baby lies head down, then his heart is better heard below the woman’s navel, from the side of the baby’s back. With a breech presentation, it is better to listen to tones above the navel. If the pregnancy is multiple, then the heart of each child can be heard in different parts of the abdomen.
Cases of serious pathologies causing heartbeat disturbances are quite rare. Nature has decreed that the vast majority of pregnancies end in the birth of an absolutely healthy and full-fledged child. Therefore, in parallel with observation by a doctor, you need to listen to the life emerging inside and rejoice in future motherhood.
Author:
Evtushenko Anna Aleksandrovna obstetrician-gynecologist
Common pathologies
The most commonly diagnosed abnormalities and pathologies shown by ultrasound of the unborn baby’s heart include:
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia). There are two main types of this deviation: reciprocal tachycardia of the supraventricular type and ectopic tachycardia. In the first case, excess contractions appear in the atria, in the second, they can occur in various parts of the organ.
- Decreased heart rate (bradycardia). Two types are also defined: basal and decelerant. The first type does not pose a danger; failure of the second type indicates oxygen starvation of the baby.
- Benign tumor of striated muscle tissue (rhabdomyoma). It is detected in the left or right ventricle or on the interventricular septum. It is a dangerous pathology because the tumor can block the blood flow and cause the death of the child.
- Functional noise, that is, between beats and during myocardial contraction, an extraneous sound is heard. This phenomenon is not always a pathology and requires special treatment. On the other hand, the presence of acoustic phenomena may be a sign of heart disease. Therefore, in case of a heart murmur, CTG is most often prescribed additionally.
- Not abnormal, but a special structure of the heart (hyperechoic focus or HEF). As a monosymptom it is not dangerous, but in combination with other abnormalities it requires regular monitoring.
- Congenital defect of the EVC (single ventricle of the heart);
- A narrowing of the opening of the aorta in the valve area, which makes it difficult for blood to flow out of the left ventricle (aortic stenosis).
- Congenital pathology of the formation of walls separating the chambers of the heart from each other or their absence (atrioventricular canal, otherwise endocardial cushion defect).
A stable heartbeat with a frequency of 140–160 beats/min is observed from the 14th week
The treatment tactics for diagnosed diseases are determined by the doctor. The woman may be referred for consultation to other medical specialists. Ultrasound of the fetal heart is one of the most important examinations during the perinatal period. Timely and competently performed diagnosis helps to avoid complications in the baby in the future, and possibly save his life. A woman can decide for herself where to have the procedure done in a antenatal clinic at her place of residence or a paid diagnostic center. The examination cannot be ignored.