General information
Lymphocytosis is a condition when the number of lymphocytes —white cells that produce bone marrow tissue—increases in the peripheral bloodstream. If the number of these cells exceeds the norm, then this indicates the development of pathological processes in the body. Lymphocytosis is not an independent disease, but a phenomenon that develops in various pathologies and is considered a marker of whether recovery is occurring or the disease is progressing. Therefore, if tests show a deviation from the norm, it is necessary to determine the cause of this phenomenon in order to effectively eliminate it.
What are lymphocytes?
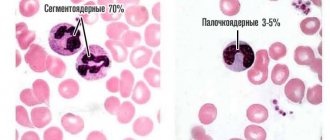
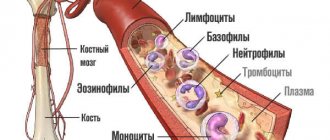
These are blood cells that are necessary for the normal functioning of the human immune system. White blood cells that perform immune function are called leukocytes . They are divided into several types:
- eosinophils;
- neutrophils;
- monocytes;
- basophils;
- lymphocytes.
It is the last of these groups of cells that provides long-term immunity , while the rest provide short-term immunity. There are three types of lymphocytes:
- B lymphocytes - produce antibodies important for fighting pathogenic bacteria, fungi and viruses, providing humoral immunity . They make up approximately 15% of all cells of this type. Their formation occurs in the spleen, then they migrate to the lymph nodes and concentrate there. Some cells of this type have a “memory” in relation to foreign objects, which they retain for several years. Therefore, they effectively fight against foreign agents in the event of their repeated attacks.
- T-lymphocytes - perform a number of important functions, in particular, coordinate immunity, activate other types of immune cells, destroy cells affected by viruses and bacteria, as well as some tumor cells. They also promote B lymphocytes in producing antibodies. Their number is about 75% of all lymphocytes. They originate in the bone marrow, then enter the thymus gland and transform into lymphocytes. The largest number of this type of cells is found in children.
- NK lymphocytes - their functions are to destroy those cells that are degenerating. We are talking about tumors, virus-infected cells. They can destroy even those cells that are not accessible to attacks by T lymphocytes. The proportion of cells of this type is about 10%.
Lymphocytes and monocytes belong to the category of agranulocytes. This is a type of cell whose internal structure does not contain granular inclusions. Such cells are more durable than other blood cells.
The number of lymphocytes increases during the period of illness associated with an attack of infection. But if a person recovers, then the number of lymphocytes, increased to fight foreign agents, gradually returns to normal. However, the constant presence of lymphocytosis without obvious reasons is an alarming sign and may indicate serious illness.
Childhood
After birth, the child experiences an increased concentration of neutrophils in the blood. On day 10, the level of lymphocytes begins to increase, reaching 60% of all cells in the circulatory system. A similar clinical picture is observed up to seven years, and in some cases up to five.
Subsequently, the concentration of this indicator returns to normal, approaching similar values in adults. Lymphocytosis in young children is considered a normal variant and is not a pathological condition. During an infectious and inflammatory process, the body begins an active fight against the pathogen, which leads to a jump in the level of lymphocytes. This phenomenon is called reactive lymphocytosis, since the remaining blood cells are normal.
Pathogenesis
A change in the number of lymphocytes in the blood in one direction or another from the norm indicates certain disturbances in the normal functioning of the body. This may be due to the appearance of disorders, to combat which an increased number of these cells are produced, as well as a violation of the mechanism of their production in the body.
Lymphocytosis
Treatment of lymphocytosis
Obviously, the treatment of lymphocytosis comes down to accurate diagnosis and treatment of the disease that caused the increase in lymphocytes in the blood.
What examinations are performed on a patient with lymphocytosis?
1.
Identification/exclusion of an infectious agent using modern immunodiagnostic methods.
2.
Determination of the patient's immune status.
Detection of autoimmune pathology, allergies. 3.
Cytological examination of bone marrow punctate - myelogram.
4.
Immunophenotyping of lymphocytes.
5.
For timely diagnosis of hematoblastoses, the molecular genetic method of studying gene rearrangement has recently been used.
6.
If lymphocytosis is combined with enlargement of the lymph nodes, spleen, liver, the patient is prescribed radiography, ultrasound, MRI, biopsy of lymph nodes (other neoplasms), followed by microscopic and histoimmunochemical examination of tissues.
Lymphocytosis “for no reason” in a blood test is a good reason to consult a doctor: hematologist, immunologist, therapist.
Classification
In medicine, the following types of this manifestation are distinguished:
- Absolute lymphocytosis - in this case there is a significant increase in white blood cells relative to the norm. The absolute type can accompany a number of serious diseases - infectious mononucleosis , hepatitis , endocrine system disorders, lymphosarcoma , etc. That is, this indicator indicates the development of serious problems in the body, which requires urgent attention from a specialist.
- Relative lymphocytosis - in this case, the number of lymphocytes in the blood does not change, but their ratio with other types of white blood cells changes. The relative type appears more often. This phenomenon is recorded in those who are recovering from an illness or have recently had an infectious disease. It is also observed in adults and children at the very beginning of viral diseases. That is, this condition is actually evidence of a normal immune response to infection attacks.
Infectious lymphocytosis is also distinguished . This is a condition that develops during attacks by a lymphotropic virus, during acute viral damage.
A decrease in the number of lymphocytes in the blood is called lymphopenia .
Temporary and permanent lymphocytosis is also determined.
- Temporary – a consequence of infections, injuries, medication, poisoning, etc.
- Permanent is a consequence of the development of serious problems in the body.
Differential diagnosis
As doctors emphasize, it is not tests that need to be treated, but a specific disease. Before starting therapy, the exact cause of lymphocytosis should be established. For this purpose, one general blood test is not enough. To diagnose a respiratory infection, a thorough examination of the patient is necessary, listening to wheezing in the bronchi or lungs to exclude pneumonia.
Measles, rubella, and chickenpox are accompanied by the appearance of a characteristic rash. Mononucleosis occurs in the form of a sore throat, accompanied by severe enlargement of the lymph nodes. Although, to clarify the type of virus, additional tests for lymphocytosis, such as PCR, should be done. This is a way to detect the DNA of the pathogen.
In terms of diagnostics, autoimmune diseases are difficult, especially if there are no other symptoms other than lymphocytosis. A specific marker for such pathologies is an increase in antibody titer in the ANA analysis. Then, if the result is positive, the presence of a number of interleukins, peptides and other protein compounds is checked. They are specific and are produced for any one type of autoimmune disease.
Oncology is diagnosed in a similar way. Additionally, it is necessary to do an ultrasound of the internal organs. Long-term chronic lymphocytosis is characterized by hepato- and splenomegaly (an increase in the size of the liver and spleen, respectively). Hearts and joints are also checked. It is necessary to emphasize that lymphocytosis is a condition that persists for several weeks after recovery (this form is called post-infectious).
Causes of lymphocytosis in the blood
The reasons for the development of this condition may be different. First of all, the causes of lymphocytosis in adults and children may be associated with the development of infectious diseases. If the body of an adult or a child is exposed to an infectious agent, in particular a virus, the immune system produces a large number of T lymphocytes and NK cells to effectively fight the pathogens. In this case we are talking about reactive lymphocytosis .
The reasons for changes in the number of lymphocytes may be as follows:
- influenza and ARVI;
- Infectious mononucleosis ;
- AIDS - the human immunodeficiency virus infects the cells of the immune system, and in the early stages of AIDS there is an increase in the number of lymphocytes;
- herpes;
- chickenpox;
- viral hepatitis;
- rubella;
- measles;
- mumps;
- whooping cough;
- adenovirus infection.
The causes of relative lymphocytosis in adults may also be due to the fact that the person has recently suffered from the disease, and his body is currently recovering.
Bacterial and protozoal infections can also provoke lymphocytosis:
- brucellosis;
- tuberculosis;
- toxoplasmosis;
- syphilis.
But it should be noted that lymphocytosis is not observed in all bacterial infections.
This phenomenon is also detected in diseases of the hematopoietic system and lymphatic tissue. Often such diseases are malignant. They are characterized by lymphocytosis, but the immune cells are not able to perform their functions, since they are not full-fledged. This is observed in the following diseases:
- lymphoma;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- lymphoblastic leukemia in acute and chronic forms;
- lymphosarcoma;
- myeloma.
In autoimmune diseases, when healthy cells are attacked by their own immunity, lymphocytosis is also a hallmark. This is observed in the following diseases:
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- Crohn's disease;
- rheumatoid arthritis.
The number of immune cells in the blood may increase due to other reasons, of which there are quite a few:
- alcohol abuse and heavy smoking;
- taking narcotic drugs;
- treatment with certain drugs ( Phenytoin , Levodopa , a number of antibiotics and analgesics);
- prolonged fasting and very strict diets;
- abuse of carbohydrate foods;
- hyperthyroidism;
- premenstrual period;
- allergic manifestations;
- dysfunction of the endocrine system;
- poisoning by toxins ;
- some cancers in the early stages;
- stress, neurasthenia;
- consequences of removing the spleen - since immune cells disintegrate in this organ, its removal often provokes a temporary increase in lymphocytes;
- wounds, injuries;
- irradiation;
- consequences of the introduction of a number of vaccines;
- very strong physical overload;
- vitamin B12 deficiency .
The causes of lymphocytosis in a child can also be very different. In children, a relative increase in lymphocytes is a very common phenomenon. This is noted in the first years of life, when the formation of normal immune system function occurs. Children are often attacked by various infections. In addition, disturbances in the blood formula can be provoked even by severe stress and physical activity.
However, the possibility of more complex problems should not be discounted. Thus, an increase in lymphocytes is characteristic of serious blood diseases. One of these is acute lymphoblastic leukemia , which is characterized by the formation of immature immune cells in the bone marrow. Therefore, if your blood count is abnormal, it is important to undergo an examination and consult with a specialist.
Symptoms of lymphocytosis
It is not an independent disease, except for the infectious form. In most cases, this is an additional symptom to the disease. Therefore, signs of lymphocytosis are the symptoms of the underlying disease, which caused a shift in the leukocyte formula.
Only a qualified specialist can prescribe treatment after a complete examination and diagnosis.
Symptoms of probable lymphocytosis include:
- Enlarged liver – hepatomegaly, spleen – splenomegaly.
- Enlarged lymph nodes – lymphadenopathy.
- Increased activity of the sweat glands.
- Weakness and fatigue.
- A sharp change in body temperature, which is accompanied by exhaustion and chills.
- Disturbances in the digestive system - vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, alternation of stools.
- Hyperthermia of the pharynx mucosa, cough, runny nose, and other symptoms of respiratory tract disease.
- Nervous disorder, lack of appetite, sleep disturbances.
- Almost white skin.
- Enlargement of the tonsils of the throat against the background of high body temperature up to 40 degrees.
- The level of lymphocytes in the bone marrow is increased.
In children, the general symptoms include bloating, unstable stools, paroxysmal vomiting, skin rashes (rarely), lethargy and tearfulness.
Symptoms
The main manifestation of lymphocytosis is a change in the blood picture. However, if this condition was provoked by an infection, then the patient will be bothered by the signs that are characteristic of an infectious disease - fever, cough, rash, runny nose, etc. However, these symptoms are not directly signs of an increase in the number of lymphocytes.
In some cases, with lymphocytosis, which was caused by non-infectious causes, the spleen and lymph nodes become enlarged.
All other manifestations of the relative type of this condition will depend on the reason that provoked the shift in the person’s blood formula.
If we are talking about a change in the number of lymphocytes in a person who has already had an infectious disease, then his general condition will be relatively normal, without pathological manifestations.
With absolute lymphocytosis, which develops due to a tumor of the hematopoietic tissue, signs will appear indicating the growth of neoplasia . The patient's internal organs - the liver and spleen - become enlarged, bone pain appears, and signs are observed that indicate a blood clotting disorder. Infections become more frequent and more severe due to a general decrease in immunity.
Lymphocytosis in adults is often combined with other abnormalities in the blood count. With viral infections, as well as during the recovery period after them, neutropenia and lymphocytosis . The reasons for this combination may also be associated with the development of certain immunodeficiency syndromes.
In childhood infections - measles , chickenpox , mumps - lymphocytosis and monocytosis .
What is lymphocytosis?
Lymphocytosis is a pathological condition characterized by high levels of lymphocytes in the peripheral bloodstream of an adult. In most cases, classic lymphocytosis is considered as a complex of pathologies.
Blood cells protect the human body from various diseases. When pathogenic agents are detected, the level of lymphocytes increases. The thymus and bone marrow are responsible for their production. Therefore, if the level of lymphocytes is high, it means that a pathological process is developing in the human body.
Causes of lymphocytosis
There are numerous disorders and pathological conditions against which the level of lymphocytes changes. A comprehensive diagnosis, which is prescribed by a doctor, taking into account the patient’s complaints and a preliminary examination, will help to establish an accurate diagnosis.
| Name | Description |
| Physiological conditions |
|
| Viral infections |
|
| Bacterial infections |
|
| Malignant blood diseases |
|
| Endocrine disorders |
|
| Other reasons |
|
Provoking sources of lymphocytosis in adults are also parasitic infection of the body, rheumatic pathologies (gout, arthritis), damage to the lymphatic system.
Tests and diagnostics
To determine the number of lymphocytes in the blood, it is enough to conduct a general analysis. It is important to take a blood test on an empty stomach. On the day before taking tests, you should refrain from intense physical activity and from consuming fatty foods and alcohol. You should not smoke in the morning before the test. Blood is taken from a finger.
In the results obtained, the specialist evaluates the leukocyte formula, that is, the ratio of different types of white blood cells. If the doctor notices changes in the number of cells, he, if necessary, prescribes a repeat study in order to calculate the absolute numbers of lymphocytes.
Depending on the age of the patient, the normal number of these cells is from 20 to 40% of the total number of white blood cells. In absolute numbers, this is 0.8-3.6 g per 1 liter of blood. As a rule, the relative number of these cells is higher in children compared to adults. The older a person gets, the lower the number of these cells in the blood is detected. There is also an individuality factor - the number of them differs from person to person. Lymphocytosis is determined if the number of lymphocytes from the total number of leukocytes is more than 41%.
If, in the process of studying test results, a specialist notes the presence of deviations, he compares the obtained indicators with the patient’s complaints and symptoms.
During the diagnostic process, the specialist takes into account the following points:
- An increased number of lymphocytes, which is combined with an increased total level of leukocytes.
- Simultaneous increase in the level of red blood cells and lymphocytes.
- A significant increase in the lymphocytic formula and platelets - hypersplenism and autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura .
- Imbalance with reduced white blood cell count and low lymphocyte count.
- Symptoms of bacterial and viral infections.
- Leukopenia as a complication of viral diseases.
The doctor may prescribe additional studies - determination of antigens , antibodies, immunophenotyping. The purpose of specific studies depends on what exact cause of this condition the doctor suspects. Additional studies may also be needed - ultrasound, MRI, CT, x-ray. Sometimes a bone marrow or lymph node puncture is prescribed.
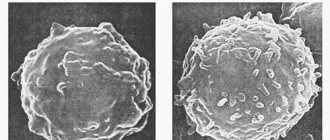
To determine the cause of lymphocytosis, it is also important to determine the number of typical and atypical lymphocytes . Atypical cells have different properties and sizes when compared with normal ones.
Atypical cells are most often detected in the following diseases:
- toxoplasmosis;
- pneumonia;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- chickenpox;
- herpes;
- hepatitis;
- Infectious mononucleosis .
However, in many equally serious diseases, no atypical cells are found in the blood.
Relative lymphocytosis with an unchanged total number of leukocytes is observed in severe bacterial infections. This phenomenon is also recorded in rheumatic diseases, splenomegaly , Addison's disease , hyperthyroidism .
Diagnostics
The level of lymphocytes is measured during a clinical blood test. Due to the fact that lymphocytosis has a fairly wide etiological spectrum, if it is detected, you should contact a generalist (general practitioner or pediatrician) so that, based on the patient’s complaints, anamnestic data, and physical examination, he will prescribe an additional examination, which may include:
- Blood tests
. The leukocyte formula is calculated to determine the percentage of all forms of leukocytes. A blood smear is studied using microscopy to identify atypical mononuclear cells, Botkin-Gumprecht shadows (remnants of destroyed lymphocytes). Inflammatory markers are determined - increased ESR, CRP. To detect tumor antigens, immunophenotyping and immunohistochemical studies are performed. - Pathogen identification
. In order to identify an infectious agent, tests are performed for the presence of antibodies to pathogens and their DNA (by ELISA, PCR). Bacteriological studies are carried out - culture, sputum microscopy (tuberculosis, whooping cough), serological diagnostics - Wright, Heddelson reaction (brucellosis), microprecipitation reaction (syphilis). - Instrumental Research
. With tuberculosis, an X-ray of the lungs shows an increase in the hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes, infiltration of the upper lobes of the lungs, and sometimes effusion into the pleural cavity. In case of mononucleosis and hemoblastoses, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity reveals pronounced splenomegaly, less often hepatomegaly. - Histological studies
. In chronic lymphocytic leukemia, a large number of lymphoblasts are found in the bone marrow punctate. In lymphomas, a lymph node biopsy obtained by fine-needle aspiration reveals diffuse proliferation of lymphoid cells with blast morphology. A specific sign of lymphogranulomatosis is Berezovsky-Sternberg giant cells.
Leukocyte count
Treatment with folk remedies
It is important to consider that traditional methods are only an aid to strengthening the body's defenses. They cannot lower the level of lymphocytes, but they help increase the effect of treatment.
It is recommended to introduce immunity-boosting drinks into your diet - teas, infusions, decoctions, juices.
- Linden tea - take 1 tbsp for 1 glass of boiling water. l. crushed linden blossom and leave for 20 minutes. You can drink this tea three times a day, half a glass. It calms, activates defenses, and helps you sleep.
- Tea from a mixture of herbs - to prepare it, take equal parts of lemon balm, mint, chamomile, yarrow, mix everything and 1 tbsp. l. pour a glass of boiling water. You can drink a glass of this tea several times a day.
- Cranberries with honey – you should eat a small glass of cranberries a day, adding a little honey.
- To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to drink tinctures of eleutherococcus, propolis, and echinacea. You can choose one of the tinctures and drink as recommended in the instructions.
- Natural juices – drink a glass of freshly squeezed juice twice a day. Juice can be prepared from carrots, apples, and beets. Drink fresh.
- Take 30 g of strawberry leaves, wild strawberries, rose hips, and nettle leaves. Pour all 500 ml of boiling water and cook for about 15 minutes in a water bath. Drink 50 g twice a day, continue the course for at least a month.
- Chop the beets and put them in a two-liter jar. Pour warm water and put 1 tbsp in a jar. l. salt and 2 tbsp. l. honey Infuse for three days, then strain and drink the resulting infusion three times a day, 50 ml for two weeks.
- Dissolve 200 g of copper and 50 g of bee bread in 1 liter of water. Every other day, drink 2 tbsp. l. twice a day for a month.
What are lymphocytes and their role in the immune system.
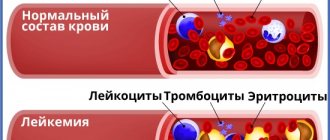
Blood is the only tissue of its kind in the human body. It consists of a liquid part, plasma, which contains several types of cells. These are red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Their number and ratio are different for men and women, and also depend on age.
Each of these groups performs its own specific functions. Red blood cells contain a special protein, hemoglobin. In the lungs it combines with oxygen, carries it to the tissues, “exchanges” it for carbon dioxide, which is returned to the lungs. Platelets are the main element of the blood coagulation system. They maintain the integrity of the vascular wall and help stop bleeding.
Leukocytes represent the body's defense system. By their number, you can not only identify the acute or chronic course of the disease, but also the state of the human immune system as a whole. This name combines a group of cells that differ in appearance and mechanism of response to stimuli. The fact is that viruses, bacteria, fungi, and allergens are different from each other, therefore the immune bodies must also be structured differently to fight them. This:
- neutrophils, thanks to the function of phagocytosis, absorb and digest viruses and bacteria;
- eosinophils are involved in the formation of allergic reactions;
- basophils, their functions are not fully understood;
- lymphocytes ensure the normal functioning of all parts of the immune system. Up to 80% of their number are T lymphocytes. Killer T cells react to foreign cells and destroy them. Helper T cells recognize pathogenic microorganisms and initiate a protective response. Suppressor T cells suppress the body's autoimmune reactions. B lymphocytes produce immunoglobulins that neutralize bacteria. NK lymphocytes react to their own cells when they degenerate during malignant processes or the introduction of a virus;
- monocytes accelerate wound regeneration and participate in the development and inhibition of inflammation.
The synthesis of “young” lymphocytes occurs in the bone marrow. They finally “mature” in the spleen, lymph nodes and thymus. The function of this organ in the immune system was discovered by scientist Jackie Miller. The lifespan of these cells is about three months. They are found in the general bloodstream and, if necessary, are delivered to the site of localization of the infectious process.
Prevention
The main preventive measures include a healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition and timely medical examinations.
- It is important to strengthen the immune system from childhood - to harden yourself, consume enough healthy food, and exercise.
- During influenza epidemics, you should avoid crowded places, avoid hypothermia, and wear personal protective equipment.
- It is better not to practice physical activity during a cold. During this time, you should drink a lot and avoid eating heavy food. It is very important to use the correct treatment regimen when taking the medications prescribed by your doctor. Self-medication in this case is unacceptable.
- It is important to regularly take preventative blood tests. This will help diagnose serious diseases in the early stages.
Treatment
The basic principle of treating lymphocytosis in children is the elimination of the underlying, main disease, which caused such changes in the blood.
Goal of treatment:
- detection and adequate treatment of the disease;
- reduction of symptoms of the underlying disease;
- reducing the severity of the child’s condition;
- use outpatient treatment whenever possible;
- avoiding hospitalization;
- prevention of the development of serious and life-threatening complications.
Indications for hospitalization:
- severe form of the disease;
- the need to isolate the patient;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- the presence of serious complications;
- the presence of chronic diseases that worsen the general condition of the child;
- if it is impossible to carry out treatment at home;
- if long-term outpatient treatment is ineffective.
The principles and methods of treatment are different and completely depend on the underlying disease:
- antibiotic therapy;
- antiviral therapy;
- anti-inflammatory therapy;
- antipyretics;
- chemotherapy;
- hormone therapy;
- vitamin therapy;
- immunomodulators.
Find the necessary supplies and medications that should be in every first aid kit for a newborn in the following article.
Strengthening the immune system with vitamins is an auxiliary therapy that accelerates recovery
Another important point in the treatment of lymphocytosis in children is compliance with general strengthening and preventive measures such as:
- Maintaining the child's daily routine.
- Complete balanced nutrition.
- Thermally process food.
- Compliance with basic hygiene rules.
- Moderate physical activity.
- Carrying out hardening.
- If possible, avoid contact with sick people.
- Ventilation of premises.
- Wet cleaning of premises.
- Wearing personal protective equipment (masks).
- Hand washing.
- Avoiding crowds of large numbers of people.
All of these methods are aimed at naturally increasing the child’s immune defense..
In modern medicine, additional measures to protect against certain diseases are also possible - vaccination. Even if the virus penetrates the vaccinated body, it will not manifest itself in an acute form of the disease and will not cause serious complications.
The prognosis depends on the timeliness of treatment, the severity of the condition and compliance with prescribed recommendations.
In children
Parents should be aware that after the baby is born, the level of lymphocytes is quite low. But later their active production begins, and already in the first weeks of life, lymphocytosis is noted in the child, which is a physiological norm. Relative lymphocytosis is the norm in the first two years of a child’s life. As it grows, the number of immune cells decreases and gradually approaches the same level as in adults.
But if the number of these cells at a certain age deviates from the norm, parents need to take the child to a specialist and find out the reasons for this phenomenon.
Treatment methods for lymphocytosis
Treatment of lymphocytosis consists of eliminating its cause. ARVI can be dealt with using folk remedies. This includes drinking plenty of water (it is better to use rosehip decoction, tea with raspberry or currant jam, fruit drinks for this purpose), mustard plasters, warm compresses on the chest (however, the area of the lymph nodes should be avoided). It is also necessary to rinse the nose with saline solutions and gargle with calendula tincture.
Drug treatment consists of the use of herbal or chemical-based antiviral drugs. Also shown are nasal drops, solutions for treating the oral cavity, palatine arches and tonsil areas. If lymphocytosis is caused by bacterial infections, a course of antibiotic therapy is necessary. When autoimmune or oncological diseases are detected, treatment should begin as early as possible, this increases the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
It will take more than one year to take the drugs. Cytostatics, steroids, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are prescribed. As for infectious lymphocytosis, it does not require any treatment and goes away on its own. Despite numerous reviews on forums dedicated to traditional or folk medicine, only a doctor should diagnose the cause of lymphocytosis and prescribe medications.
Any deviations from the norm in a clinical blood test require a mandatory consultation with a doctor. In most cases, an elevated lymphocyte count indicates a viral infection, which is easily treatable. However, this can also serve as a sign of the hidden course of serious diseases. Therefore, to prevent them, you need to undergo such examination regularly, once every 4–5 months.
Source: kakiebolezni.ru
During pregnancy
As a rule, during pregnancy a woman experiences moderate lymphopenia . But the number of immune cells, as a rule, does not decrease significantly below normal. If this happens, the immune system becomes weak and the risk of developing infectious diseases increases. If the number of such cells increases and exceeds the norm, this significantly increases the likelihood of miscarriage. To avoid missing warning signs, women should get tested regularly during pregnancy.
The role of lymphocytes and the norm in the blood
To protect the body, the immune system produces certain cells - lymphocytes. These white blood cells recognize alien cells that have entered the human body.
By synthesizing antibodies to fight them, they help destroy the danger. T-lymphocytes are assigned the role of implementing cellular immunity. B cells are engaged in the production of antibodies and are just waiting for a command to begin their activities.
Cells have different lifespans. Some die within a month, while others store information, providing long-term immune protection.
Normally, the blood contains from 18 to 40 percent lymphocytes, based on the total number of leukocytes. In women, their number changes as a result of pregnancy or menstruation. Therefore, for them, 50-55 percent is not considered a deviation from the norm.
The number of lymphocytes depends on the psycho-emotional state a person is in, how he eats, and what the ambient temperature is . The occurrence of lymphocytosis is determined if white blood cells rise by 15 percent.
In children, the rates are higher, since both the spleen and the thymus gland, which produce blood cells, work more actively. From the day of birth, the child’s body develops its immunity, and therefore the number of lymphocytes reaches from 30 to 70 percent.
Diet
Diet for influenza, ARVI, colds
- Efficacy: therapeutic effect after 4-7 days
- Terms: 5-12 days
- Cost of products: 1500-1600 rubles per week
Proper nutrition for such indicators helps speed up the body's recovery process. It is important to eat in such a way as to provide the body with energy, proteins, vitamins, minerals, but at the same time avoid an excess of calories. The following products should be included in the menu:
- Plant fiber – it helps cleanse the intestines and remove harmful substances from the body. The menu must include red and green vegetables, oatmeal, whole grain bread and crispbread.
- Nuts, legumes, seeds.
- Dairy products.
- Citrus fruits, pineapples, berries, dried fruits - they help strengthen the immune system.
- Fish and meat - it is better to avoid fatty varieties.
- Fresh natural juices from fruits and vegetables, fruit drinks from berries.
In general, nutrition should be balanced and include a maximum of natural products.
Types of lymphocytosis in adults, causes and symptoms
Any deviation in the composition of the blood is a sign that the pathology in the body is caused by acute and chronic infections of viral or bacterial etiology.
In addition to the response to the action of pathogenic microorganisms, the leukocyte formula changes due to:
- leukemia;
- lymphomas;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- Addison's disease;
- liver damage;
- chronic stress;
- intense physical activity in athletes.
Reactive lymphocytosis is determined when the body responds to the occurrence of pathology with an increase in blood cells. After treatment, lymphocytes return to normal .
The malignant form is diagnosed if the patient is diagnosed with chronic or acute leukemia. And only additional tests will be able to give an accurate picture of what is happening in the body of a patient with lymphocytosis. The sooner his cancer is detected, the more successful the treatment will be.
Decreased neutrophils and increased lymphocytes at the same time
The leukocyte formula is important when making a diagnosis. It is in the leukogram that changes most often occur. However, the total number of leukocytes remains normal.
- Viral infections are characterized by an increase in lymphocytes and a decrease in neutrophils. The absolute level of leukocytes in the blood does not exceed normal limits. Such leukogram data indicate the body’s active fight against viruses. They are often obtained at the incubation stage, when there are no symptoms of the disease, and the microbes have already entered the body and begun their life activity. Neutropenia and lymphocytosis are observed in persons who have recently had acute respiratory viral infections. Lymphocytes migrate to the site of inflammation, multiply and differentiate to provide reliable antimicrobial protection. It takes some time for blood counts to normalize. When recovery occurs, the concentration of leukocytes is restored.
- Cancers are characterized by an imbalance of immune cells that form and mature in the bone marrow. Tumors of an organ disrupt its functioning. At the same time, the level of lymphocytes increases and the number of neutrophils in the blood decreases. Aplastic anemia is manifested by pallor, impotence, dizziness, and bleeding. In the absence of timely diagnosis and adequate treatment, the disease develops into leukemia. The most common oncohematological diseases include chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. B lymphocytes accumulate in the bone marrow, lymph nodes, and liver. These oncopathologies are characterized by a slow course and specific symptoms.
- Neutropenia with lymphocytosis is also observed in allergic reactions . Such research results allow doctors to determine the presence of a tendency to allergies. At the same time, along with lymphocytes, eosinophils are also increased.
- Many lymphocytes in the blood are found not only during respiratory infections , but also during tuberculosis, brucellosis, typhoid fever, systemic lupus erythematosus, lymphogranulomatosis, and renal pathology.
- Purulent-destructive and vascular diseases also require a hemotest, which can be used to detect lymphocytosis and neutropenia. These include: abscesses, phlegmons, boils, gangrene, heart attack, stroke.
Decreased neutrophils and increased lymphocytes in the blood are a common sign of a bacterial or viral infection. Extensive infection is accompanied by the release of an infectious agent into the bloodstream. Neutrophils quickly die after interacting with the pathogen, and the bone marrow does not have time to produce them in sufficient quantities. Patients experience the main symptoms of the pathology: fever, chills, lethargy, rapid heartbeat, hyperhidrosis, tachypnea, hypotension. If signs of intoxication syndrome appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. To make a correct diagnosis and avoid mistakes, it is necessary to evaluate the quantitative indicators of blood cells not in isolation, but in the totality.
In children, low neutrophils and high lymphocytes are normal. This crossover is due to an incompletely formed immune system. A common reason for deviation is vaccination. In response to foreign invasion, the body reacts by producing antibodies - lymphocytes. In this case, granulocytes are not produced in full.
Prevention of lymphocytosis
To prevent an increase in the content of lymphocytes in the blood, it is advised to maintain immunity by playing sports and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Nutrition plays an important role in maintaining normal blood composition . Foods rich in vitamins, selenium, magnesium, potassium, zinc help improve the functioning of the entire body. This is especially true for children and the elderly.
Emotional peace and healthy sleep only benefit the immune system, which will protect against pathogenic bacteria and viruses.
Source: prososud.ru
Basic treatment methods
Lymphocytosis is a symptom of many diseases, so it is necessary to eliminate the causes of this pathology using traditional and folk medicine.
For identified therapy:
- for malignant tumors, radiation and chemical therapy, cytostatics are used;
- for a viral infection, medications based on interferon and M2 channel blockers are prescribed;
- bacterial disease - antibiotics;
- for inflammatory pathology, non-steroidal and corticosteroid drugs are taken.
In the treatment of children, sulfonamide drugs are used, the action of which is aimed at destroying pathogenic microbes. ACTH is used as a hormonal agent.
Lymphocytosis of non-malignant etiology is treated with traditional medicine:
- Taking echinacea tincture will improve immunity. Take it 20-30 drops three times a day. The product will not only cope with the infection, but will also have a detrimental effect on the cells of pathogenic microorganisms such as a virus or bacteria.
- An infusion of dandelion root will help cope with liver disorders and improve defenses. Prepare the medicine from two tablespoons of raw materials per 250 ml of boiling water. Drink three glasses a day, divided into doses before meals.
- Rosemary will strengthen the child's immune system. A tablespoon of leaves is poured into two glasses of boiling water and left for two hours. After straining, give half a glass to drink before meals. You can add a little honey to your tea.
- Stinging nettle is known as a plant that has a beneficial effect on metabolism and normalizes blood composition. To prepare the medicine, take two large spoons of leaves and pour 250 ml of boiling water. You should drink half a glass up to three to five times a day before meals.
- Among those that boost immunity are berries such as viburnum, cranberries, and raspberries. And grapes help normalize the process of hematopoiesis.
Diagnostic methods
Even if a blood test shows lymphocytosis, additional examination methods are necessary:
- Analysis of biological fluids will show the presence of antibodies, the appearance of which is associated with an allergic reaction of the body. A bacterial infection is determined in the same way.
- The bone marrow is examined using the myelogram method. Hematopoietic data are compared with the clinical picture of blood from peripheral vessels.
- To identify the structure of blood cells and distinguish deviations from the norm, immunophenotyping of lymphocytes is necessary. Identification of lymphoblasts will indicate pathologies in the body.
- Cytological examination of lymph node tissue will help diagnose malignant tumors.
Since the symptoms of lymphocytosis are similar to many diseases, treatment should be aimed at eliminating the disease that caused an increase in lymphocytes in the blood.
Accurate diagnosis of abnormalities in the blood will allow us to develop a set of therapeutic measures.