Diagnostics of internal organs with image output on digital or paper media with determination of cellular structure was considered science fiction until the 50s of the twentieth century. But scientists have developed a new method based on the work of computed tomography, positron emission tomography. The described type of examination is carried out in two stages and allows you to determine the condition of organs at the molecular level. The procedure is characterized by the absence of pain and reveals the cause of the disease. Prescribed by the attending physician in accordance with medical indications.
Description of technology
The PET (two-photon emission tomography) technique is based on the registration of gamma quanta of equal energy that arise during the decay of a radionuclide from an administered radiopharmaceutical.
A positron formed by the positron emission of an isotope interacts with an electron, followed by annihilation.
The radiation source is captured by detectors and transmitted to the recording system of the tomograph, which determines the exact coordinates of the signal.
With the help of a complex of converters, the glow from the interaction of gamma quanta with detectors is transformed into an electromagnetic pulse.
Next, the received pulses are recorded in the form of a graph, or sinogram. Computer processing of the sinogram is completed by performing a three-dimensional reconstruction of the isotope distribution in the study area.
Computed tomography allows you to obtain an image of the organs being examined and identify the localization of the pathological focus.
Combined PET/CT machines perform sequential scans, then the software creates an anatomical picture of the organs with an image of metabolic processes superimposed on them.
The abbreviation PET/CT represents the combination of two X-ray tomography techniques to obtain diagnostic information.
Where to do
The ability to carry out research using the PET-CT method is available to a relatively small number of clinics in Russia, which is associated not only with the lack of equipment for performing positron emission and computed tomography, but also with the lack of necessary equipment for the production of radiopharmaceuticals.
If in foreign countries the PET-CT technique is considered the “gold standard”, then domestic oncology centers are only at the beginning of the journey, confidently mastering the revolutionary approach to diagnosis. Today, such a service can be provided by foreign clinics in European countries, Israel, the USA and large oncology centers located in the CIS.
Table: List of medical institutions providing PET-CT diagnostic services in the CIS
| Clinic name | Location of medical centers |
| European Multidisciplinary Clinic (EMC) | Moscow |
| National Medical Research Center of Oncology named after N.N. Blokhin (RONC) | Saint Petersburg |
| Center for Nuclear Medicine "PET-Technology". | Moscow, St. Petersburg, Tyumen, Yekaterinburg, Minsk, Kyiv, Kharkov, Astana, etc. |
| Clinical Hospital "Feofania" at the All-Ukrainian Center for Radiosurgery | Kyiv |
| Oncology clinic "LISOD" | Israel, Kyiv |
| Medical Institute named after Sergey Berezin (MDC MIBS) | Saint Petersburg |
One of the leading Russian medical institutions developing and implementing the latest methods for diagnosing and treating cancer is the National Medical Research Center for Oncology named after N.N. Blokhin (RONC). PET-CT at the Russian Cancer Research Center is performed using various pharmaceuticals, the preparation of which is carried out directly in the clinic’s laboratory.
Oncological Scientific Center named after N.N. Blokhina
All clinics operating in the CIS are equipped with the latest generation tomographs, and the quality of diagnostics and medical reports is confirmed by leading specialists from Germany, Israel and France. In 2020, in St. Petersburg, as a public-private partnership, the Medical Institute named after Sergey Berezin (MIBS) completed the construction of a center for the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, unique for Russia, the Proton Therapy Center.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
PET has many advantages over other methods of ionizing radiation. For clinicians, the most valuable of these are:
- 100% reliability of results;
- ease of use due to clear protocols and an automated system;
- high throughput due to simultaneous data collection and processing, image reconstruction, and results analysis;
- visual diagnostic results;
- absence of pain and discomfort during diagnostics;
- no need to use additional diagnostic methods, including invasive ones;
- short terms for assessing the effectiveness of the therapy (1-2 weeks).
Disadvantages include high cost, the need to locate the Cyclotron near the diagnostic center, and the length of preparation and procedure.
Failure to comply with diagnostic deadlines after administration of a radionuclide increases the risk of false results.
Selection of radiopharmaceuticals
The importance of imaging methods in identifying cancer and their metastases cannot be underestimated, since it is an accurate assessment of the prevalence of pathology that allows us to develop an individual approach to treatment. As a result of the studies, it was revealed that the sensitivity of radiopharmaceuticals used for various types of cancer can range from 30 to 100%. Despite the high sensitivity of PET-CT, selecting the optimal radiopharmaceutical can significantly improve diagnostic results.
FDG can be considered a universal radiopharmaceutical used for the diagnosis of 60% of cancer types, for example, lung, esophageal, rectal, breast cancer, as well as melanomas and lymphomas. However, in some cases, its sensitivity reaches only 40%, which is not enough to detect bone metastases. Thus, to identify primary tumor processes, as well as when selecting the most active tumor zone for taking a biopsy, the amino acid tyrosine labeled with fluorine-18 is used.
The resulting fluoroethyltyrosine (FET) is a functional analogue of methionine, which is involved in the protein metabolism of tissues, including malignant ones. The use of FET allows one to accurately assess the size of the tumor lesion and its boundaries. The radiopharmaceutical fluoromethylcholine (FCH) is used to assess the extent of damage in prostate cancer, as well as to detect its relapse after treatment. Its use is also effective in diagnosing tumors of the brain and liver.
Due to the intensive consumption of glucose by brain tissue, a small tumor, when using FDG, may practically not stand out from the general background. The use of FCH allows you to get a clearer image. When diagnosing hormone-dependent malignant neoplasms of the female reproductive organs, a radionuclide-labeled hormone, estradiol, is used.
Fluoroestradiol (FES) accumulates with high intensity in tissues that have hormone-sensitive receptors. FES is most widely used for diagnosing hormone-dependent breast tumors. Due to the intense excretion of radiopharmaceuticals in the urine, bladder cancer can be detected using PET-CT only if metastases have spread beyond the organ.
What changes does PET scan show?
PET images are graded on a 4-level isotope accumulation intensity scale. When interpreting data, physiological foci of radionuclide accumulation are taken into account.
Level scale:
- levels 1-2 indicate foci of an inflammatory nature;
- level 3 - the probable nature of pathological changes includes tumors or metastatic lesions;
- level 4 - serves as a sign of a primary tumor, metastases.
The method shows the presence of atypical foci in organs and tissues, detects degenerative, dystrophic and post-traumatic changes.
PET with contrast reveals pathological activity of lesions based on accelerated metabolism. In the brain, PET scans trace the distribution of blood flow, which affects all aspects of brain activity.
Is PET CT contraindicated in pregnant women?
Positron emission diagnostics are not carried out both for women carrying a child and for mothers breastfeeding their children. This is due to the fact that the tomograph, when scanning tissue, emits an extremely small dose of radiation for a person, which, one way or another, will negatively affect the fetus, especially if the gestation period has not reached 12–13 weeks. Moreover, PET radiation elements have the ability to be “absorbed” into mothers’ milk, which does not allow them to put the newborn to the breast for 1-2 days.
PET in the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms
The first use of PET in oncology dates back to 1991. Today, 70% of all PET procedures performed in the world are aimed at identifying malignant tumors.
Central cancer of the right lung
The method allows you to determine the exact location of the tumor, identify relapse, stage of the process, differentiate malignant from benign tumors, and find regional and distant metastases.
Standard PET diagnostics determine the metabolic activity of the lesion based on the absorption of the injected isotope.
The method is capable of identifying pathological foci of a tumor nature with a size of at least 7 mm. In cases where the tumor intensively absorbs the radiopharmaceutical, formations ranging in size from 3 mm are detected.
Based on PET, the course of the disease is predicted, a radiation therapy plan is drawn up, the effectiveness of the treatment, and the radicality of tumor removal during surgical interventions are assessed.
Reviews
Ilya Petrovich Anishchenko, St. Petersburg: We did the PET-CT study at the N.N. Blokhin, when his son was diagnosed with a brain tumor. In such a difficult situation, the attentive attitude of the staff and the attending physician was very helpful and morally supportive. It is difficult not to note the professionalism of the entire medical staff, which certainly influenced the restoration of my son’s health after the operation.
Serebryakova Antonina Pavlovna, Kazan: In 2020, my husband was diagnosed with prostate cancer. The diagnosis was made after a biopsy, although a previous fluorodeoxyglucose PET-CT examination could not provide a definitive answer. It turned out that my husband has localized cancer (inactive form), which is difficult to detect using fluorodeoxyglucose. After treatment, the examination was carried out 2 more times. The first with fluorodeoxyglucose to detect metastases, and the second with fluoromethylcholine to diagnose relapse. Fortunately, in both cases, the result was negative.
Elena Stadnyuk, Volgograd: Thanks to the diagnostic capabilities of PET-CT and the professionalism of the doctors at the Sergey Berezin Medical Institute (MIBS), I was diagnosed with an early stage of breast cancer, although I was treated for mastopathy at the district clinic. It is fortunate that it is possible to detect the disease at the very beginning, when there is every chance of getting rid of it forever.
Types of radioactive drugs for PET
Radiopharmaceuticals make it possible to study biological processes occurring in the human body.
Based on the data obtained, the metabolism of glucose, oxygen, secondary active transport of amino acids, and protein biosynthesis are assessed. Tissue hypoxia is detected and the rate of growth of tumor cells is determined.
Types of isotopes for tomography:
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose - used to diagnose malignant neoplasms, determine the stage and extent of the process. In cardiological practice, a drug with glucose is prescribed to patients to assess the viability of the myocardium before surgery. In patients with epilepsy, it reveals foci of hypometabolism in the brain;
- 11C-methionine - prescribed to detect brain cancer, multiple myeloma, tumors of the lymphatic system. Diagnoses pathology of the parathyroid glands: adenoma, carcinoma;
- 11C-choline – used for the diagnosis of prostate diseases: adenoma, cancer and its metastases. Detects hepatocellular cancer, differentiates from benign formations;
- 18F-sodium fluoride - used to detect pathology of the skeletal system in oncology. Prescribed for the diagnosis of benign and malignant bone formations, post-traumatic changes, inflammatory and degenerative processes.
Possibilities
In order to evaluate the diagnostic capabilities of PET-CT, it is necessary to become familiar with the fundamental principles underlying the method. So what is PET-KT? The method is a combination of two types of diagnostic studies - positron emission tomography (PET) and computed tomography (CT).
Despite its prevalence, computed tomography, like most other radiation research methods, is based on anatomical criteria for assessing the condition of an organ, for example, shape, homogeneity of structure, clarity of contours. However, at a certain point, data on the size and location of the ischemic area of the myocardium or tumor becomes insufficient. There is a need to assess the functional state of the anatomical zone under study, since often, with externally unchanged indicators, the activity of metabolic processes can change significantly.
For example, after chemotherapy, a malignant lesion may retain its shape and size, however, when examined using PET, a significant or complete decrease in metabolism in the tumor can be seen, which indicates positive results of treatment. A similar example can be given with the study of an ischemic area of the heart, where, with externally unchanged contours of the affected area, after intensive therapy, an improvement in metabolic processes can be observed.
On a PET image of the heart after a heart attack, there is practically no regional accumulation of radiopharmaceuticals, which indicates a violation of the functional activity of the myocardium
Thus, the combination of diverse diagnostic information (structural and functional) in one study makes it possible to determine the following clinical conditions with high accuracy. When diagnosing cancer:
- degree of activity of the malignant neoplasm;
- differentiate between benign and malignant tumors;
- determine the location of metastases;
- evaluate the results of chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
For cardiac diseases:
- identify areas with impaired blood supply;
- determine the rate of myocardial metabolism;
- evaluate the effectiveness of treatment after a heart attack.
For neurological diseases and brain diseases:
- determine the localization of intracranial neoplasms;
- identify the causes of epileptic seizures;
- differentiate neurological diseases (Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease).
Important! The ability to detect the exact location of metastases in malignant tumors makes it possible to reduce the irradiation area during radiation therapy, which has a positive effect on the patient’s recovery rate and reduces the risk of complications.
When is a PET scan indicated?
The PET method combined with CT is used to search for foci of pathological accumulation of the isotope, indicating the development of the disease.
The procedure is carried out in the absence of clinical symptoms, to monitor the process over time and evaluate therapeutic measures.
PET CT indications for diagnostics:
- formations of the head and neck: diagnosis of the nature of the tumor;
- neoplasms of the thyroid gland: identification of differentiated and medullary carcinoma with the stage of the process;
- malignant tumors of the lung: large cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma;
- cancer of the upper gastrointestinal tract - damage to the esophagus and stomach;
- cancer of the lower gastrointestinal tract - damage to the colon;
- pancreas cancer;
- tumor diseases of lymphatic tissue: lymphogranulomatosis, non-Hodgkin lymphoma;
- malignant neoplasm of the breast;
- malignant skin tumors – melanoma;
- formation of bones and soft tissues;
- neoplasms of the genitourinary tract;
- brain tumors;
- neurological diseases caused by the occurrence of pathological foci in the substance of the brain (temporal and extratemporal epilepsy);
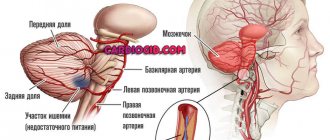
- brain diseases associated with vascular damage and thrombosis: ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, carotid artery stenosis;
- traumatic brain injuries: assessment of the volume and degree of brain damage in the early and late post-traumatic period;
- degenerative and dystrophic diseases of the brain: Alzheimer's, Huntington's, Parkinson's diseases.
Lymphoma
When is it prescribed and what does this study show?
The main area of application of PET CT is the diagnosis of malignant neoplasms. The study may be prescribed if the oncologist needs:
- identify a tumor node at stage zero, that is, when it cannot be detected in any other way;
- clarify the nature of the pathology detected during CT scanning, ultrasound, x-ray, etc.;
- determine the presence and localization of metastases, including distant ones;
- evaluate the results of chemotherapy at the very beginning of the course of treatment;
- differentiate tumor relapse or progression from necrosis that developed as a result of radiation;
- solve other specific problems.
The most important advantage of this method in oncological diagnostics is the ability to determine absolutely all tumor foci, including the smallest metastases up to 1 mm in size, during one examination.
The second direction is the diagnosis of neurological diseases. Based on the examination results, neurologists can:
- assess the condition of the arteries supplying the brain and their role in cerebrovascular accidents;
- differentiate between malignant and benign brain tumors;
- establish the cause of dementia, including diagnosing Alzheimer's disease in the early stages;
- accurately identify foci of epilepsy, which is especially important when planning surgical intervention;
- obtain valuable diagnostic information for Parkinson's disease, Huttington's disease, degenerative diseases of the central nervous system (multiple sclerosis, etc.)
Cardiologists rarely resort to PET CT. In this case, the procedure allows:
- diagnose a temporary adaptive decrease in the volume of work of the heart muscle and differentiate it from heart failure;
- accurately determine areas of myocardial ischemia before surgery to restore impaired blood circulation (angioplasty, shunt installation);
- identify areas of post-infarction cardiosclerosis.
Types and modes of research
Depending on the diagnostic purposes, the following may be prescribed:
- full body scan;
- local brain scan;
- examination of the chest area.
Based on the type of radiopharmaceuticals (RP) used, PET is divided into:
- With 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose. Allows you to identify areas with different intensity of glucose accumulation. The cells of most cancers and other malignant tumors take up glucose most quickly. The more the drug accumulates in the tumor tissues, the brighter they glow in the images and the higher the degree of malignancy of the cancer cells.
- With choline, gallium-PSMA, PSMA-7. It is used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer, the tumors of which actively accumulate this substance. Choline is also sometimes used in liver and brain examinations.
- With methionine or tyrosine. Provides high quality images when visualizing gliomas (a type of brain tumor);
- With 13N-ammonium. Used to diagnose changes in the heart muscle.
- With FP-CIT and F-DOPA. Used for Parkinson's disease.
- With F18-FBB. Prescribed for Alzheimer's disease.
If it is necessary to obtain clearer CT images, the patient may need the injection of a contrast agent, and therefore PET/CT is also distinguished without contrast and with contrast.
Limitations, contraindications, complications
In addition to the contraindications common to any diagnostic methods associated with radiation exposure, positron emission tomography is not performed:
- in the first month after completion of chemotherapy;
- in the postoperative period;
- in the presence of severe inflammatory processes or during the height of an infectious disease.
In all of the above cases, the reliability of the results will be insufficient.
In addition, examination by this method is not indicated for patients during radiotherapy treatment and immediately after its completion. The recommended pause after a course of RT is 3 months.
If the prescription rules are followed, the examination does not cause any side effects, and the radiation dose is so small that, if indicated, it can be prescribed to children and nursing mothers. The only possible complication is individual intolerance to radiopharmaceuticals (extremely rare) or contrast agent (higher probability).
Preparation for PET diagnostics
Preparation for the study varies depending on the type of study and the patient’s health characteristics.
General recommendations boil down to limiting physical activity, stopping drinking alcohol and smoking 24 hours before, and stopping carbonated water and food 6 hours before the test.
These recommendations must be followed because intense physical activity, excess glucose, the presence of nicotine and alcohol in the blood lead to changes in the intensity of radiopharmaceutical accumulation, and gases and food make scanning of the abdominal organs difficult.
To increase the accuracy of diagnosis and reduce the risk of side effects from the administration of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose, patients with diabetes mellitus take drugs that normalize the metabolism of sugars (trimetazidine, etc.) for 8–12 days before the examination. The day before the tomography, coffee is excluded from their diet and taking caffeine-containing medications is prohibited.
Before the choline PET/CT scan, a special diet is also prescribed, excluding protein-rich foods, B vitamins and some vegetables.
How the research is carried out
The patient is administered a radiopharmaceutical, most often intravenously, as well as a diuretic to accelerate the distribution of isotopes throughout the body. The radiopharmaceutical dose depends on the scope of the study and the patient’s weight.
After a certain period of time, during which the maximum accumulation of isotopes occurs in the parts of the body being studied, a scan is performed. In this case, the couch with the subject moves slowly inside or along the module with scanners. The whole process takes from half an hour to an hour or a little more.
After the procedure, it is recommended to consume large amounts of fluid to remove isotope decay products from the body, the lifespan of which is very short - from 2 to 22 hours. Thanks to this, no later than 24 hours later you can communicate with others, including pregnant women and children, without any restrictions.
Decoding the results
Data interpretation is carried out by radiologists with appropriate specialization. As a rule, it takes no more than an hour to evaluate the results and draw up a conclusion.
Contraindications for the study
When referred for diagnostics, with the help of anamnesis and additional clinical studies, patient conditions are identified that serve as an absolute or relative contraindication to tomography.
The following persons are not allowed to take a PET scan:
- children under 18 years of age;
- pregnant women, regardless of gestational age;
- patients suffering from diabetes mellitus in subcompensated or decompensated form;
- with severe pain that makes it difficult to remain still during the procedure;
- obese patients whose body weight exceeds the permissible technical standards of the tomograph;
- with pulmonary emphysema.
The question of the benefit and advisability of diagnosing patients in a severe, unconscious state is considered on an individual basis.
Persons with mental and movement disorders, with a phobia of limited space, undergo tomography after the administration of sedatives.
Lactating women abstain from breastfeeding for 3 days after the procedure. The child is transferred to adapted milk formulas, and the milk is expressed.
Diagnosis restrictions:
- Tomography is performed no earlier than 30-90 days after surgery. The exception is cases when detection of distant metastases from the primary tumor site is required;
- for patients prescribed chemotherapy, the procedure is carried out before treatment, or 30 days after completion of the course;
- if there are results of PET-CT performed before the start of chemotherapy, re-diagnosis to assess the effect of drugs on the tumor process is carried out 7 days after the end of the administration of chemotherapeutic agents;
- For patients who have undergone radiation therapy, the procedure is scheduled after 90 days.
After PET examination
After the procedure, you can go about your business unless your doctor, of course, gives other instructions.
The radioactive drug will remain in your body for another 12 hours, so you are advised to limit contact with pregnant women and young children.
Drink more water after PET-CT scan, because... water promotes the rapid removal of radioactive substances from the body. Typically, radioactive tracers are completely eliminated from the human body after 48 hours.
At this time, a specialist radiologist will interpret the results of the study and transmit this information to your doctor. Such decryption usually takes no more than 2 business days. Look forward to your next appointment with your doctor to discuss your results and whether or not to prescribe any necessary treatment.
Preparing the patient for the procedure
The patient prepares for tomography with radiopharmaceuticals 6-12 hours before diagnosis. Avoid eating food, carbonated drinks, and sweet juices.
Medicines containing glucose are discontinued. The patient refuses physical activity, avoids overwork and stress factors.
Upon admission to the diagnostic center, the patient is allowed to rest for 15-20 minutes and drink 500 ml of clean water. After determining the level of glucose in the blood, which should not exceed 8-11 mmol/l, a catheter is installed in the vein of the elbow. The person being examined is helped to change into comfortable clothes that do not contain metal elements.
The patient is placed on the couch in a supine position. The radiopharmaceutical is administered using a syringe or an automatic dispenser.
Then 500 ml of 0.9% NaCl is infused by infusion; during brain tomography - 20 ml of 0.9% NaCl. After administration of the drug, the patient is left in a motionless position with his eyes closed in a darkened room for 30-60 minutes. During this time, the product is distributed and the concentration in organs and tissues is equalized.
It is prohibited to use a mobile phone, talk, chew gum, or strain muscles. Before the scan, the patient is asked to urinate or the bladder is catheterized.
Management of patients with diabetes mellitus
Patients registered with diabetes mellitus are prepared for the study after consulting an endocrinologist and deciding whether to take glucose-lowering medications.
Recommended:
- patients taking insulin by injection should receive a dose of the drug along with their last meal 5 hours before the introduction of diagnostic tools for scanning;
- For patients receiving treatment with substances from the sulfonylurea group, discontinue the medications on the day of the procedure;
- For persons taking medications from the biguanide group, keep the same dose and time of taking the drug.
Passing diagnostics
The patient sits on a sliding table and is immersed inside the tomograph. Position – lying on your back with your hands behind your head.
At the first stage, a low-dose CT scan of the planned area or the whole body is performed. Then they begin PET diagnostics.
The pelvic area is scanned first to avoid artifacts from the bladder filling with urine.
The duration of the procedure ranges from 10 minutes for a brain diagnosis to 70 minutes for a full body examination.
When studying the brain, a repeated delayed diagnosis is carried out 180 minutes after the administration of the radiopharmaceutical.
At the end of the tomography, the patient is placed in a rest room for 40-60 minutes to reduce the radiation level.
After the procedure, the doctor gives recommendations on drinking fluid in the amount of 1500-2000 ml per day and observing radiation safety measures.
What you can eat:
- Meat: beef and pork.
- Any green vegetables (zucchini, broccoli, asparagus, green beans).
- Chicken.
- Fish and tuna.
- Eggs.
- Cauliflower and mushrooms.
- Eggs.
For drinks, give preference to pure still water, unsweetened tea, and black coffee. It is also better not to drink compotes and fruit drinks. If a tomography with choline is planned, then the patient will have to exclude all foods containing choline from the diet for 2-3 days: cabbage, nuts, eggs, legumes, organ meats and B vitamins.
Complications and side effects
Adverse events that may occur during PET scanning are associated with the administration of a contrast radiopharmaceutical.
Occurs in 10-20% of cases. Patients with a history of allergic reactions are given premedication before tomography.
If consequences develop in the form of severe systemic complications, emergency intensive therapy is carried out.
| Local reactions: | Systemic reactions with organ damage: |
| · redness, itching, burning, urticaria at the injection site of the radioactive drug; · damage to the skin, vascular wall, hematoma; · inflammation of the nerve; · abscess, necrosis of underlying tissues; Pain when moving the elbow joint. | · anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema; collapse, loss of consciousness, cardiogenic shock; · convulsions, paresis; acute renal failure; pulmonary edema, status asthmaticus; · thyrotoxic crisis. |
Considering the radioactive radiation emanating from the subject, patients are advised to avoid pregnant and lactating women, children, and crowded places after the procedure. For two hours, it is prohibited to approach the specified category of persons more than 1 meter.
Radiation exposure to the patient
The combination of radiation received from X-rays from a CT scan and from the administered radiopharmaceutical drug constitutes the amount of radiation exposure to the patient.
Without taking into account delayed scans, the radiation dose for a full body diagnosis does not exceed 10-13 mSv. This dosage is considered unsafe and harms the body.
| Effective radiation doses when administering 1 MBq of radiopharmaceutical (FDG) | |
| Children 0-12 months. | 0.13 mSv |
| Children 1-5 years old | 0.073 mSv |
| Children 5-10 years old | 0.047 mSv |
| Children 10-15 years old | 0.032 mSv |
| Adults | 0.027 mSv |
Note: For a complete diagnosis of the body, 370-400 MBq of radiopharmaceuticals are required.
Diagnostic price
The PET procedure combined with CT is an expensive diagnostic method. The patient pays the cost of the radioactive drug, CT scan, delayed PET scan, disc and imaging scans.
The average price for the procedure is 60-80 thousand rubles. Some clinics offer a 10-25% discount program for the second and subsequent diagnostic sessions.
The information content of PET, close to 100% and sensitivity of 97-98%, allows one to find out the nature of the disease in one procedure.
The correct approach to the technique determines the correct choice of patient management and treatment plan, on which the health and life of the patient depends.
The high cost of PET justifies the range and value of diagnostic information that cannot be obtained by any other known method.
What is this diagnostic method?
PET CT examination is a radionuclide tomographic scan. A radiopharmaceutical containing a radionuclide is first introduced into the body. It undergoes the process of positron beta decay. As a result, positrons appear, which, when in contact with electrons, trigger a reaction that transforms particles - annihilation.
Positron-emitting radioisotopes mark biologically active compounds distributed throughout the body. This distribution is monitored using a PET scanner.
Radiopharmaceuticals are used in different ways, and therefore different processes can be studied with their help. Thanks to radioactive drugs, positron emission tomography is a universal technique in modern medicine. Work continues on the synthesis of already proven radiopharmaceuticals and the development of new similar agents.
The information obtained during the examination is visualized on the screen. Specialists see a full three-dimensional picture, which allows them to give an accurate assessment of the state of the body.