A complete blood count means counting the number of cells in a venous blood sample. Capillary blood is not a recommended testing medium for cell counting, but hemogram testing is often performed from a capillary blood sample in intensive care units.
Determination of the leukocyte formula, study of the average size of erythrocytes, platelets, determination of the number of erythrocyte precursors (reticulocytes) and the degree of their maturity, assessment of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, etc., all this is included in the concept of “clinical blood test”.
A clinical blood test is performed as the first screening test when the patient complains of malaise. An abbreviated clinical blood test, the so-called “troika”, can be performed - counting the number of red blood cells, white blood cells and determining the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). An abbreviated clinical blood test is not very informative, because can characterize only pronounced pathological processes.
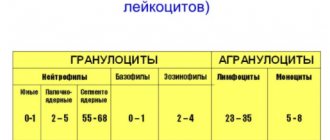
It is more advisable to perform a detailed hemogram from the same volume of blood sample: counting the number of red blood cells with an assessment of their average size (MCV), counting the total number of leukocytes and assessing the leukocyte formula (counting neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, monocytes, lymphocytes), counting the number of platelets and assessing average platelet size (MPV), reticulocytes and their average size (MRV), reticulocyte maturity (IRF).
Numerous cell characteristics can now be obtained automatically within 3-5 minutes after blood collection. Based on a detailed study of the hemogram, not only a conclusion can be made about the presence of an inflammatory reaction, anemia, but also the nature of other pathological processes, possible previous or ongoing blood loss, deficiency of not only iron, but also vitamin B12 and folic acid.
What is this analysis used for?
For such purposes:
- As part of determining abnormalities in shape and size, as well as changes in the number of red blood cells, platelets, white blood cells and various types of blood cells (including any immature forms) along with their percentage.
- For the diagnosis of various diseases associated with disorders of education, function or excessive destruction of a formed element.
- In order to monitor the formation of cells with their degree of maturity in leukemia, after radiation treatment, as well as in the framework of a violation of hemoglobin formation.
Indications for the purpose of the study
A general clinical blood test is the most prescribed laboratory test for the quantitative and qualitative assessment of the main classes of blood cells.
The study includes determination of the concentration of the main blood elements (erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets), hemoglobin level, hematocrit value, as well as calculation of erythrocyte indices (MCV, RDW, MCH, MCHC).
Erythrocytes (red blood cells) usually make up about 40% of blood volume. Their main function is to transport oxygen from the lungs throughout the body. The lifespan of an erythrocyte is on average 120 days. Thus, the bone marrow must continually produce new red blood cells to replace those that age and disintegrate or are lost through bleeding. Changes in the number of red blood cells are usually accompanied by changes in other indicators: hematocrit and hemoglobin level.
Hematocrit is the ratio of the volume of red blood cells to the volume of all components called whole blood; in practice, it is the proportion that all formed elements (quantitatively, mainly red blood cells) make up of the total blood volume.
Hemoglobin is an iron-containing protein found in all red blood cells that gives the cells their characteristic red color. Hemoglobin allows red blood cells to bind to oxygen in the lungs and carry it to tissues and organs throughout the body.
Most often, a low hemoglobin level is combined with a low red blood cell count and low hematocrit and indicates anemia.
When is this study prescribed?
If, according to the results of a general analysis and leukocyte formula (which is prescribed for the widest range of indications), a significant increase in the number of leukocytes, atypical or immature cells is detected, then it is necessary to make a blood smear. Among other things, such research is important to carry out in a number of situations:
- Against the background of suspicion of a disease that affects cells.
- When using medications that can affect their production.
As part of a blood smear analysis, doctors usually use venous or capillary biological fluid.
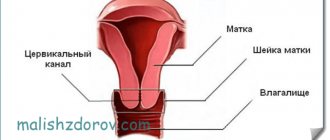
Microscopy of a gynecological smear
For women, smears are taken at every visit to the gynecologist, whether it is a planned visit.
A visit with complaints, planning a pregnancy or registration due to an interesting situation that has already occurred.
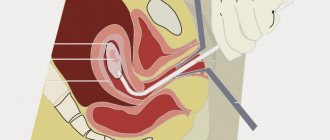
The smear is taken with swabs from the urethra, vagina and cervical canal during an examination on a chair.
Before taking a smear, it is recommended not to urinate for a couple of hours (so that urine does not wash away the microflora of the urethra), not to douche, and not to use antiseptics for intimate hygiene.
Often, simultaneously with the material for microscopy, a PCR analysis or a sample for culture is taken.
A sterile tampon is inserted into the urethra 2 centimeters and removed, pressing it against the wall of the canal.
From the vagina, they try to take a sample from the surface of areas suspected of inflammation or from the posterior fornix.
When the results of the “smear microscopy” analysis arrive, the transcript contains several parameters for each of the departments (urethra, vagina, cervical canal).
- The number of leukocytes (immune cells that indicate the presence of inflammation, if they are more than normal) is indicated. In a vaginal smear there should be no more than 10, in a sample from the urethra there should be about 5, in the cervical canal they should not exceed 30. Smear microscopy during pregnancy can show up to 30 leukocyte cells in a vaginal sample. Typically, leukocytosis of a vaginal smear means the presence of colpitis, a urethral smear means urethritis, and the growth of leukocytes in the cervical canal is characteristic of endocervicitis.
- Epithelial cells of more than 5-10 in the field of view also indirectly indicate an inflammatory process. If such cells are not identified, then most likely the mucosa is atrophic or there is a hormonal imbalance.
- If a smear microscopy is performed, the norm suggests the presence of a small amount of mucus.
- The normal analysis option also involves the detection of lactic acid bacteria (lactobacillus). By providing an acidic environment, they suppress the growth of pathogenic or opportunistic microflora.
- Epithelial cells on the surface of which bacterial agents accumulate are called key cells. They are fixed in bacterial vaginosis, when enterococci, gardnerella or leptotrichia become the culprits of dysbiosis with a reduced number of lactobacilli.
- Cocci (strepto- and staphylococci) are the causes of nonspecific inflammation in the genital tract in women.
What to do if there are deviations in the smear, based on the normal indicators, should be decided by the gynecologist.
If there is a suspicion that specific flora (causative agents of sexually transmitted infections) have been detected, then PCR tests (endothelial scrapings) are advisable.
For example, femoflor for 12 or 16 STD pathogens.
Based on descriptions of smears, it is customary to use the concept of four degrees of purity of the vaginal environment.
- The first is called normocenosis. In this case, epithelial cells and a large number of Doderlein rods (lactobacteria) are detected. The reaction of the medium is acidic (pH from 2.8 to 4.2). Leukocytes are not detected.
- In the second degree, carriage of certain microorganisms related to conditional pathogens is possible. The proportion of lactic acid bacteria drops significantly. Leukocytes are found within 10 cells. The environment is still acidic, although the pH rises to 4-4.5. Rods and Gram-positive coccal flora are visualized.
- Bacterial dysbiosis or bacterial vaginosis is considered the third degree. Here, there may be more leukocytes than normal or they may fall within its limits. Not only coccal flora is detected, but also pathogens of sexually transmitted infections: Trichomonas. The most commonly found bacteria are Clostridia, Gardnerella, Leptotrichia, Megaspheres, and Mobiluncus. They cluster on the surface of epithelial cells, forming key cells.
- The fourth degree confirms the inflammatory process: with an alkaline reaction there are a lot of leukocytes and pathogenic microflora. Trichomonas, gonococcus, and spores of the fungus of the genus Candida may occur.
The third and fourth degrees require an active diagnostic search and the prescription of specific therapy.
A control (after treatment) smear is always performed.
A cytological smear of the cervix allows one to identify five types of changes in the cervical epithelium.
They may be normal or regarded as a precancerous condition or cervical carcinoma.
The analysis takes about a day to complete.
This study is required once a year for all women.
It is also carried out before pregnancy, during pregnancy, before choosing contraception, in case of ectopia or inflammation of the cervix.
The density of cellular material, the size and shape of cells, and the presence of their pathological changes are assessed.
Preparation
When collecting biomaterial with an average diameter of the vein expansion, blood should flow quickly into a test tube that contains an anticoagulant. Ethylenediaminetetraacetate is often used because it makes it possible to better preserve the formed element being studied. True, in order to prevent various kinds of morphological degradation of cells, the time interval between taking fresh and well-homogenized biomaterial and manufacturing the preparation should be as short as possible.
Preparation of smears begins with collecting a drop of blood (usually just one from the capillary tube) onto the edge of a microscope slide. It is then smeared using a second glass element sliding over the first. A well-prepared smear has a so-called “cat’s tongue” at the end, indicating that the sample was performed correctly and makes it possible to conduct a high-quality examination.
Blood is a whole world of cells that can be compared to space.
And each cell is a living being with its own life, with its own purpose, performing its own function. When using traditional analysis methods, many indicators remain normal for a long time, so early signs of the disease ( fatigue, sleepiness during the day, memory impairment - the most common and obvious signs of a blood disorder ) go unnoticed...
And, probably, it has happened to many that when they were feeling unwell, their blood tests for some reason turned out to be within the normal range. What is the reason for the discrepancy?
What can be revealed by microscopic examination of blood?
A routine blood test is done after a few hours, when all cell movement has stopped. The study of a “live” drop of blood is an examination of a sample immediately after collection for no more than 5 minutes and is carried out with a magnification of more than 1000 times.
- An important difference between this method and conventional tests is the examination of a blood sample without any preliminary treatment and in the presence of the patient.
- The patient has a unique opportunity to look into the cellular world of his body, see deviations in the functioning of cells, and take care of his health at the earliest stages of illness.
- We managed to connect the microscope with a video camera and a computer, which will give you the opportunity to see your blood on the screen.
The “live” blood drop method allows you to evaluate:
- Qualitative analysis of blood composition.
- With the state of metabolism and hormonal imbalance.
- And changes in blood cells, which are observed under stress, exposure to radiation, electromagnetic radiation, inflammatory processes in the body, deficiency of vitamins, microelements and protein.
- of red blood cells: shape, size, their interaction, location in the blood plasma, aggregation (sticking together), leading to oxygen starvation.
- The condition of leukocytes, their size, activity (it is important to remember that a decrease in the number of leukocytes signals inflammatory processes in the body).
- The state of lymphocytes in the blood and the body’s ability to self-heal;
- With the state of platelets and the tendency to form blood clots, a predisposition to increased coagulation, vascular thrombosis, ischemia, hypertension;
- The degree of purity of blood plasma and various inclusions: cholesterol, sugar, urine salts;
- With the stage of accumulation and distribution of toxins in the human body;
- The causes of damage to red blood cells are lack of folic acid and vitamin B12, iron deficiency;
- With the state of fat metabolism and predisposition to atherosclerotic processes.
Preparation for the procedure:
Do not eat food 2 hours before ;
On the day of diagnosis, try not to eat meat, sweets and fatty foods.
Blood is the main living medium on which all processes occurring in organs and cells depend!
Using a microscopic diagnostic method using a drop of live blood, the doctor can select a more accurate and individual treatment plan.
Don't put off visiting a doctor - it's dangerous!
Coloring
Painting is carried out using the standard method. Before this procedure, the prepared blood smear is air-dried by shaking the slide, which makes it possible to avoid the formation of an unstained light zone in the center of the red blood cells. This consequently eliminates the erroneous interpretation of hypochromia.
There may be other coloring artifacts. For example, Wright staining provides a precipitate. This happens when the paint was not renewed after some period, the slide was left in the staining solution for a long time, or was poorly washed. As a result, the accumulation of dye can be interpreted as the presence of parasites and bacteria in the blood. In addition, the staining of the smear with cell morphology can be changed when the slide comes into contact with formaldehyde vapor. Typically, samples are stained using the Romanovsky method based on methylene blue and eosin.
Classic staining of blood smears, as a rule, differs significantly from fast staining. Recently, such methods have their advantages, since they are resistant to variations in the acidity of solutions and the formation of a substance depot. But, nevertheless, they are less effective in identifying polychromatophils and do not change the color of basophil and mast cell granules well.
In order to obtain a visually specific picture of reticulocytes, staining with new methylene blue is required. In plastic tubes, a drop of blood is mixed with two NBM elements. The test tube is left at room temperature for ten minutes. After mixing, a small drop is placed on a glass slide and smeared in the same way as during a smear. The slide is then quickly air dried and examined under a microscope with extreme magnification.
Red blood cell norm
How many of these bodies should be present in the biomaterial? Normally, there should be no red blood cells in the flora smear. However, a small amount of them is not harmful to the body and health.
We found out what number of red blood cells in a smear for flora in women is considered normal. It is also considered normal to have several bodies in the field of view of the laboratory doctor who is looking through the eyepiece of the microscope. An increased number of red blood cells in women in a smear for flora indicates an inflammatory process in the cervix. This sign is not direct, but indirect.
A woman's cervical smear should be taken with a special brush with silicone bristles. With a strong inflammatory process, the cervical tissue becomes so vulnerable that the elastic bristles of the brush scratch it until it bleeds, and a huge amount of red blood cells penetrate into the smear.
Systematic study
It is critical that the assessment follows a consistent research design. Microscopy of a blood smear, which is made in one thin layer with a roundness at the tip, thickens towards its base. Cells are evaluated on a thin drawing, since a thick one carries little information. At low magnification, the marginal part of the smear, mainly its rounded end, is usually examined to identify platelet aggregates or atypical broad cells (lymphoblasts or dendritic elements).
The layer may have a zigzag or pigtail shape, which allows for a fairly clear observation of various blood cells within the framework of a directed study using the APEL algorithm, where A suggests other atypical elements with parasites, P indicates platelets, E indicates erythrocytes, and L indicates leukocytes.
The examination of blood smears is a fairly common technique that allows you to quickly diagnose various common disorders. The main conditions for the effective use of this method are strict adherence to the smear examination technique with systematic analysis in compliance with the procedure algorithm.
Smear microscopy in urological practice
Smear microscopy in men usually involves examining material from the urethra.
The reason for performing the study is when you complain about urinary disorders or discharge from the urethra.
It is advisable to perform not only smears, but also scrapings, which are subjected to polymerase chain reaction in order to find the genetic material of pathogens.
Allows you to find smear microscopy: leukocytosis, some types of STI pathogens, that is, to establish signs of inflammation.
If a smear microscopy is planned, how is the analysis taken?
The manipulation is usually performed at an appointment by a urologist or venereologist.
If the doctor is experienced, the procedure is not particularly painful and is not accompanied by any complications.
The probe is inserted into the urethra 1.5-2 centimeters.
Since it is necessary not only to collect material for cellular analysis, but also to collect a sample for PCR diagnostics, the probe is equipped with a brush that lifts the cells of the urethral epithelium.
During standard sampling of material, this can lead to unpleasant sensations and minor contact bleeding.
The result is pain when urinating, lasting up to two days.
To reduce these side effects, you can use intraurethral numbing gels immediately after the procedure.
Or contact the experienced venereologists of our clinic, who have their own experience in painlessly collecting smears.
When a smear microscopy is prescribed, what preparation is required for the analysis?
It is recommended to refrain from sexual contact for two days before the study and to abstain from urination for two hours before collecting the material.
Feasibility of analysis
There is a fairly large range of diseases, and at the same time disorders, against the background of which the properties of cells that circulate in the bloodstream can change. Normally, only mature elements penetrate into this biomaterial from the bone marrow, but in a number of pathologies, for example, leukemia, immature analogues in the form of blasts can enter it. In some painful conditions, for example, with massive infections, characteristic impurities may appear in leukocytes, and the cells themselves become atypical, as, for example, with infectious mononucleosis.
With a deficiency of iron or vitamin B12, with a congenital disorder of hemoglobin synthesis, the properties and appearance of red blood cells may change. The detection of such pathological cells in an excessive amount in a smear makes it possible to suspect the pathology that caused them and prescribe additional examination to the patient. A blood smear can be regularly prescribed to people with cancer of the bone marrow or lymph nodes as part of monitoring the dynamics and monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
Microscopy of prostatic secretion
A microscopy of a prostate smear is taken at an appointment with a urologist.
After a digital massage of the gland, performed through the rectum, prostatic secretion is collected, released from the urethra.
It is usually examined using the PCR technique (looking for pathogens of sexually transmitted infections) and microscoped.
For this purpose, smears are prepared on a glass slide, which are examined with or without staining.
- Just like for the urethra, leukocytes are counted. Normally, there should be no more than 5-10 cells in the field of view.
- Lecithin grains are an indicator of prostate functioning. Normally there are about 100 of them. If there are fewer grains, this indirectly indicates a decrease in the performance of the gland and affects the quality of sperm.
- Mucus is released in large quantities when the prostate itself is inflamed or mixed in the urethra.
- Behçet crystals are salt deposits that indirectly indicate a low sperm count.
- Amyloid bodies indicate prostatic stagnation.
- Red blood cells are a sign of bleeding due to injury to the prostate by stones or due to cancerous lesions.
- Macrophages also become signs of chronic prostatitis.
- Coccal flora, fungi, trichomonas, and gonococci can be visualized, but their detection must be confirmed by polymerase chain reactions.
Most often, along with microscopic examination of prostatic juice samples, PCR testing and bacteriological cultures are performed.
If necessary, with determination of the sensitivity of microflora to antibiotics.
Previously, provocation methods were widely used before microscopy, which revived the microflora and made it possible to stimulate a latent infection.
Today, these techniques may not be used due to more advanced methods for verifying pathogens of sexually transmitted infections, for example, polymerase chain reaction.
Provocative methods include: eating spicy and salty foods, alcohol, administering pyrogenal or gonovaccine.
The drugs are administered one to two days before the study.
About the flora smear
The normal microflora of the female vagina is quite diverse; it contains a large number of different bacteria. In representatives of the weaker half of humanity of reproductive age, the main microorganisms are lactobacilli, but in addition to them, ureaplasma (in 80% of patients), gardnerella (in 45% of patients), candida (in 30% of patients) and mycoplasma (in 15% of patients) are also found - this opportunistic microorganisms, with a decrease in the immune system, which can rapidly multiply and also lead to the occurrence of an inflammatory process. They require adequate treatment. In the absence of any clinical manifestation, for example, pathological discharge with an unpleasant odor or itching in the perineal area, the definition of these microorganisms as a pathology should not be interpreted.
Chlamydia, as well as viruses, can be present in patients who do not show any complaints, but these agents are not considered part of the natural microflora, and their presence indicates a hidden infection.
The microflora in the vagina is dynamic, it can change on different days of the cycle. There are periods when the lactobacillary flora dominates and those days when gardnerella predominates. A significant disturbance in the balance of microorganisms in the microflora, which is accompanied by clinical symptoms, is the basis of such conditions, for example, bacterial vaginosis and candidiasis. Such conditions can often recur, including even the slightest change in the patient's health status or while taking antibiotics. Women who have a family predisposition especially suffer from this.
A flora smear (also called a “general smear”) is the first and important step in assessing an infectious and inflammatory process localized in the urogenital area. This smear allows you to quickly identify one of the following conditions:
- Norm.
- Vaginal microflora disorders, which include bacterial vaginosis.
- An infection caused by Candida fungi, such as thrush.
- Infections that are sexually transmitted, in particular gonorrhea and trichomoniasis.
- Nonspecific, or bacterial, vulvovaginitis. In this case, leukocytes are present in large numbers in the smear. If a huge number of leukocytes are detected and there is a clinical picture of the inflammatory process, it is possible to prescribe broad-spectrum antibiotics that destroy up to 90% of bacteria. If there is no therapeutic effect, it is necessary to carry out bacteriological culture, since microscopically it is impossible to determine the specific type of microorganism that caused the inflammation. Bacterial culture is usually accompanied by identification of sensitivity to antibiotics, thanks to which you can choose the optimal drug, as well as achieve the desired effect of therapy.
A flora smear is not able to determine:
- Intracellular and hidden infections (chlamydia, mycoplasma, herpes, HPV, ureaplasma, HIV). To determine them, the DNA of the agent must be determined by PCR.
- A woman is pregnant.
- Pretumor and tumor pathology. A smear is made for cytology, the essence of which is to determine the qualitative change in the epithelium using special stains.
Red blood cells in biomaterial for cytology
In some cases, red blood cells in a smear in women can be detected in the biomaterial for cytology. This happens due to the fact that the specialist took the material for the smear roughly and accidentally destroyed the vessels that pass through the delicate tissue of the cervix.
In this case, after taking a smear, a woman may experience a slight discharge with a small admixture of blood for several hours. Of course, under these circumstances there will be a large number of red blood cells in the smear.
In this situation, the presence of blood cells will not be a pathology. The doctor who took the material for the study noted on the form accompanying the microslide the real reason for the presence of red elements - red blood cells in the smear, which normally should be absent. The reasons for the appearance of these bodies can be different, ranging from the area where biomaterials were taken and ending with circumstances independent of the patient’s health status.