Hello, dear moms and dads! In this article we will look at how MRIs of the brain are done for children. You are probably worried before carrying out this procedure, have doubts, and are looking for the best place to do it. Yes, it’s not surprising, here you will worry about an adult and think about how he feels there in this “spacesuit”. But imagine if the child is 2 or 3 years old, because he is still very small and he has to go through some testing. Let's take a closer look at what this procedure is and what pitfalls can await you there.
What is the essence of tomography?
For more than one year in a row, medicine has been improving its diagnostic capabilities; new techniques are emerging, including in pediatrics. You can diagnose a child’s body in different ways, the most universal and informative of which is considered to be magnetic resonance imaging. Is it possible to do MRI on children? How dangerous is it, and from what age is it allowed?
MRI is a universal procedure that is currently recognized as safe. In view of this, it can be done from an early age, even for newborn children. Sometimes diagnostics are carried out in order to identify a disease, and sometimes to prevent the development of pathology.
During an MRI you need to lie motionless for quite a long time, prepare your child psychologically for this
The body is examined using a tomograph. This is a device that is a tunnel where the patient is placed. The scan is carried out under the influence of electromagnetic waves, which cause hydrogen ions in the body to move and align at a certain angle. This allows you to read information about the organ layer by layer, which gives a complete picture of the child’s condition. Exposure to magnetic rays is not dangerous, so no one prohibits children from having MRI scans.
Magnetic tomography for children: features of its implementation
Diagnostics is carried out in a closed or open magnetic resonance imaging scanner. In the case of diagnosing children suffering from claustrophobia, especially when scanning without anesthesia, it is preferable to use an open tomograph.
MRI (open machine type)
The device is a magnetic tunnel with holes on both sides. The fixed part of the device “holds” the moving table. The patient is placed on this table and secured with special fasteners. The procedure takes from half an hour to an hour. When using a contrast agent, specialists need more time.
Sensors are installed near the child’s head that send magnetic impulses to the patient’s brain; they are transmitted to the computer software. The program converts the received data into an image, which will then be used to make a diagnosis. The specialist monitors the progress of the diagnosis in the next room behind a glass partition.
At the end of the tomography of the child’s head, the patient is moved out of the magnetic tunnel. When using anesthesia, the patient is placed under medical supervision until he wakes up.
How is the procedure performed in children?
Any patient who undergoes an MRI is placed on a tomograph, which means that a psychological and moral attitude is necessary. It is difficult to do this with children, the baby understands everything, but purely physiologically he is not always able to withstand this procedure from beginning to end.
Magnetic resonance imaging in children causes certain difficulties. During the examination, the baby is placed horizontally on the table, where he must remain motionless for 30-60 minutes. Most devices are closed; the baby remains alone in the tunnel. For children under 12-14 years of age, it is not possible to carry out such a procedure without the help of medications.
The doctor may suggest doing an MRI for children under anesthesia, or using sedatives and sedatives. This is not dangerous, but provides a guarantee for a successful scan.
The most difficult is an MRI of the brain, since in this case it is the head that must be motionless, which cannot be fixed in any way. If tomography of other organs can be carried out using open-type devices, fixing the limb, and using the help of one of the parents, then control over the scanning of the head will not be possible. In view of this, MRIs of the brain are performed on children using anesthesia. For babies, a special gas is used, which dulls sensitivity for a while; the child does not show interest and curiosity, being half asleep.
Features of the procedure
4.1. Closed (capsule) tomograph
An MRI tomograph is a closed installation with a movable table surrounded by magnets and emitters. The child is placed on the table with his back down and his limbs are secured with clamps. This is necessary to avoid accidental movements during diagnosis. Headphones are placed on the little patient's head to minimize the unpleasant sounds generated by the device. The specialist takes a series of layer-by-layer images, which are then printed onto tape or stored on information media.
The duration of the procedure, depending on the area being examined, ranges from 15-40 minutes. Modern capsule devices are equipped with monitors on which cartoons are broadcast during the study. This will make it easier for the child to maintain a still position.
4.2. Open tomograph
If a child is allowed to undergo examination on open-type tomographs, then parents need to familiarize themselves with the basic specifics of the procedure. Unlike capsule-type devices, in open-loop devices the magnetic field is generated only from 2 sides, which reduces the information content and clarity of the images.
The advantages of such a study for children include:
- the ability to be accompanied by a doctor or close relative during the scan;
- providing comfort to patients who suffer from spinal injuries;
- the ability to take medications during the procedure;
- low noise level.
4.3. Anesthesia and drug-induced sleep
Depending on the age of the child and his ability to remain in one position for a long time, the issue of the need for anesthesia is decided. Doctors can offer parents several options for putting a child into medicated sleep: superficial (using special masks) and deep (using the injection of medications into a vein). Some diseases require a combination of superficial and deep anesthesia.
The question of how to introduce a child into medicated sleep is decided by the parents together with the resuscitator who will be responsible for this procedure. Indications for the use of general anesthesia include:
- children's age up to 5-6 years;
- claustrophobia;
- hyperactivity;
- examination of brain structures (this condition is mandatory for both children and adults);
- psychological disorders;
- patient's fear of the procedure.
Diagnosis can be carried out without medicated sleep in children who are old enough and are able to maintain a motionless position for a long time. Anesthesia is not required for examination of internal organs and bone tissue.
4.4. MRI with contrast
To diagnose certain pathologies, the child is given a contrast agent intravenously. The procedure is painless for the little patient. The contrast allows doctors to better see blood vessels and small tumors. The drugs used during the scanning process rarely cause allergic reactions. Before administering it, the laboratory technician will ask the parents if the child has had negative reactions to food and medications.
A contrast-enhanced procedure requires more preparation than a regular MRI. The child's parents must adhere to the following rules:
- Exclude gas-forming foods (cabbage, carbonated drinks, fresh baked goods, confectionery) from the subject’s diet. The rule must be followed before examining the abdominal organs. Gases in the intestines distort the information content of images and prevent doctors from examining pathological processes.
- Do not feed the child for 6-8 hours before the scan and do not give water for 2 hours. This rule must be observed so that after an MRI with contrast, a small patient does not experience any adverse reactions from the gastrointestinal tract - nausea, vomiting, defecation disorders.
Indications for tomography
Children may be prescribed an MRI if they have certain symptoms:
- if children have constant complaints of headache and dizziness;
- there is a decrease in hearing and vision (you need to do a comprehensive diagnosis);
- when causeless convulsive processes occur;
- changes in the development of the spine;
- injuries, bruises, falls;
- children's retardation in physical and mental development;
- complaints of abdominal pain without changes in general condition;
- general deterioration of health against the background of normal temperature and pressure;
- Children experience sudden weight loss.
In order to go for a body examination, you need a doctor's referral. Which area requires careful diagnosis is determined solely by the doctor. An MRI of the child’s brain is prescribed for injuries, concussions, loss of analyzer sensitivity, headaches, and dizziness. By determining the condition of subcortical tissues, brain structures, and the vascular system, MRI of the brain will help identify the causes of pathology and determine the presence of tumors and neoplasms even at the earliest stages.
At what age can an MRI be done?
Despite the safety of MRI for children, the procedure still has certain contraindications. Although experts say that newborns can also be scanned if necessary. The following factors hinder diagnosis in children:
- recent surgery;
- the presence of metal staples, clamps, clips, implants in the body;
- installed life support devices that cannot be removed even for a short time (ventilator, hemodialysis, hearing aid, pacemaker, defibrillator);
- Magnetic resonance imaging cannot be done if there are shrapnel or bullets in the body;
- tattoos applied to the body (tomography is prohibited; there may be metal particles in the paint);
- If MRI is performed with contrast, then diagnosis is prohibited if you are allergic to the contrast agent or its components.
Use of anesthesia for MRI
In order for MRI to give the most accurate results, it is necessary to remain motionless throughout the examination, and when using contrast agents, this can increase to an hour. Since not all people can stay in one position for a long time, they are diagnosed under general anesthesia. This is especially necessary for examining children, since their psyche cannot always withstand fear or the strong sounds of a working apparatus.
Of course, no person is immune from the negative effects of medical sleep. However, hypersensitivity to its administration, which can manifest itself in the form of an allergic reaction, up to anaphylactic shock, is only an individual reaction of the body. Exceptional reactions to them are possible, in the form of depression of respiratory function.
To perform an MRI, the doctor uses drugs that have a short-term effect with such advantages as:
- rapid removal from the human body;
- minimal effect on the central nervous system;
- rapid achievement of the desired result.
Patients suffering from epilepsy are given intravenous anesthesia only.
As a result of their short action, anesthesia drugs can even be used for diagnosis in children of the first year of life, whose nervous system is not fully formed.
MRI scanning is done under anesthesia for children on an empty stomach. The anesthesiologist prepares and puts the little patient to sleep. It also remains until the end of the procedure for control purposes.
Parents should inform the specialist if their child is allergic to any product or drug, has a serious illness, or needs to take any medication on a regular basis. Usually, before an MRI, a consultation is carried out, where all the patient’s characteristics are considered - this is necessary for the correct choice of anesthesia.
An MRI under anesthesia usually means the use of Sevoflurane. This is an inhalation drug - it is delivered to the patient through a mask. A similar agent is used for sedation. After being put into medicinal sleep, the condition is constantly monitored. To do this, the small patient is connected to a heart monitor and heart rate monitor. During the diagnosis, the anesthesiologist monitors pulse, blood pressure and blood oxygen saturation levels.
There are certain contraindications to inhalation anesthesia. For example, it cannot be used on MRI for epilepsy in children. In this case, the drug is administered intravenously. Intravenous and inhalation anesthesia is superficial. There is also deep sedation - it involves the use of tranquilizers.
How to prepare your baby for magnetic resonance imaging?
How an MRI is done for children and how to prepare for it is of concern to all parents. If the procedure is prescribed, the attending physician will definitely give the necessary recommendations, indicate what needs to be done before the procedure and what nuances to follow.
The necessary tests will be taken. You must not eat food 5 hours before the diagnosis and do not drink liquids 2 hours before the diagnosis. The parent or his representative must be present with the baby during the procedure and monitor the process along with the doctors.
Before entering the MRI room, the child and parent leave all metal objects, electronic devices, gadgets, keys, etc. in a special container. Clothes should also be free of iron parts and electronics.
The device has a communication sensor, usually a rubber bulb, which when the patient feels worse or feels uncomfortable, the diagnostician receives a signal and pauses the procedure as necessary. Along with the sensor, the tomograph has a microphone so that the doctor can hear the patient. Just like the patient hears the doctor. For maximum comfort, the tomograph is provided with fresh air and ventilation.
Is MRI harmful for children: how often can the procedure be repeated?
Due to its absolute harmlessness, tomography can be repeated as many times as desired (in the absence of contraindications). Repeated diagnostics are also prescribed by the attending physician. This may be necessary if you need to monitor the course of the disease over time, if you want to monitor the treatment process before and after surgery, if previous results turned out to be ineffective or controversial for various reasons.
Children's MRI may be prohibited if there is:
- the presence of foreign metal objects in the child’s body (implants, prostheses, retainers, clamps);
- electronic devices and stimulants;
- severe allergic reactions to medications (with planned administration of contrast).
What will the procedure show?
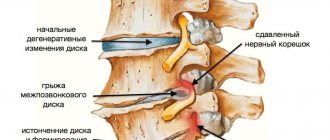
MRI is a unique diagnostic method with which you can see the real state of internal organs and all body systems. Resonance tomography can detect tumors in soft tissues, the presence of hemorrhages in blood vessels, pinched nerves, the development of anomalies and pathologies, and malfunctions in the functioning of any body system.
If the doctor orders an MRI of the brain, then most likely there is a suspicion of the following pathologies:
- cystic neoplasms;
- cerebral ischemia;
- vascular changes;
- medulloblastoma;
- brainstem glioma;
- astrocytoma;
- ependymoma;
- choroid plexus carcinoma;
- pineoblastoma;
- neuroblastoma;
- nephroblastoma;
- hypoxia;
- multiple sclerosis;
- pituitary gland disorders;
- anomalies and infections of the inner ear, eyeball;
- epilepsy;
- cerebral hemorrhages.
An MRI will indicate changes in the skeletal system of the spine, inflammatory processes in the abdominal cavity, infections and diseases of the spinal cord, and vascular changes in the body.
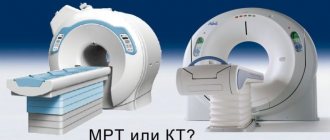
CT or MRI for a child: which is better?
MRI and CT (computed tomography) are two highly informative diagnostic methods, which are not always interchangeable. They visualize organs and tissues differently, so the choice of one or the other depends on the indication and area of study.
MRI is best used to study the structure of the brain and spinal cord, abdominal and pelvic organs. Compared to CT, MRI more clearly visualizes changes in soft tissues, spine, joints - ligaments, tendons, cartilage. This method can be performed as often as required, since there is no radiation exposure, which is very important when examining a child.
The optimal frequency of CT scanning for children is no more than once a year. The radiation dose is adjusted to the weight of the small patient. With new CT machines, the necessary information can be obtained within 1-2 minutes, so CT is indispensable for polytraumas. For example, if you fall out of a window or have a car accident, you need to urgently conduct a full examination. Spending 20 minutes on an MRI may not be practical and is not always possible. In addition, CT is more appropriate for any bone pathology, traumatic brain injury, as well as lung pathology (tuberculosis, bronchiectasis, cystic fibrosis); lungs are not examined with MRI.
Is MRI of the brain harmful?
It is the absence of harmful radiation that has made the tomography scanning procedure so popular. If your baby is scheduled for magnetic resonance imaging, there is no need to panic; it is important to follow the doctor’s recommendations without listening to the advice of amateurs.
Computer diagnostics of the body should not be underestimated, either in children or adults. It is worth understanding that while an adult is able to talk about his illness based on his feelings and associate it with certain events, a child cannot explain anything like that. And MRI is often the only way to understand what is happening to the child, what ailment is bothering him and how the body is developing. This will help the doctor determine the course of treatment, prescribe surgery if necessary, monitor the development of the disease and prevent the condition from worsening.
Anesthesia or sedation may be used for MRI scans in children.
Advantages of our center
- We help parents find and use the opportunity to have an MRI performed on their children without anesthesia.
- We spare no time and patience to find an approach to the little ones. Thus, the youngest of our patients, who was examined without anesthesia, was only 2 years 8 months old at the time of the MRI.
- We allow parents to be with the child during the examination process so that the child feels more confident and protected around someone close to him.
- We use an open-type tomograph, which reduces children's fears and eliminates attacks of fear of closed spaces.
- Despite the fact that examining children often requires more time than the same procedure on adults, the cost of MRI scanning of children and adults in our center is equally affordable.
Device diagnostic modes
To understand the MRI technique of the brain in children, it is important to know about aspects of the functioning of this organ. Brain pathologies often have different origins, so tomography is carried out in several modes:
1. MRI of the head - to clarify whether there are consequences of hypoxia, developmental anomalies and intrauterine infections in the structures of the brain, in its substance. It is possible to diagnose tumors, ischemic zones, hematomas and cysts and neoplasms. 2. CT scan of the pituitary gland – is usually prescribed in case of hormonal imbalance. 3. MRI of the brain and cranial nerves - finds the cause of tingling, numbness, pain and other sensitivity disorders of the facial muscles. 4. MRI angiography – allows you to scan the circulatory system and brain vessels in children. 5. MRI of the eyeball - examination of the structures of the eye and adjacent orbit.