Today, modern technologies make it possible to conduct high-quality monitoring throughout pregnancy. Screening of the fetus and woman is carried out at least three times during the entire period. This allows complete control over the general condition and health of the pregnant woman, as well as her unborn child. Ultrasound examination is one such way of monitoring women's health. It allows not only to carry out a general description regarding parameters and timing, but also allows you to identify existing pathologies, congenital diseases of the child, as well as other anomalies. In the same way, children with diabetes are identified by ultrasound.
Identifying Down syndrome before the baby is born is very important
What is Down syndrome
Down syndrome is a developmental pathology caused by an extra chromosome. A healthy person has 46 of them, while a carrier of the disease has 47. A child with this diagnosis is limited in mental and cognitive activity, and the disease is often accompanied by other ailments:
- congenital heart defects;
- developmental abnormalities of the limbs;
- formations in the brain;
- vision problems.
The disease is not linked to gender: both girls and boys are born with this pathology.
Children require serious supervision and complete dedication from their parents. They work successfully with children; the quality of life, taking into account technologies and methods, is high.
However, not all parents are ready for such tests, so the expectant mother is monitored by specialists throughout her pregnancy. Tests, ultrasound and examinations by doctors are the key to timely diagnosis of diseases.
Prognosis for a confirmed diagnosis
According to long-term observations, children with this diagnosis develop differently. The severity of their intellectual and speech developmental delay does not depend on the existing congenital pathology, but on the individual contribution to a particular child. That is, children with Down syndrome can learn, it’s just that this process is harder for them than for their healthy peers, hence the lag.
Experts believe that with appropriate care and treatment, the prognosis will be as follows:
- with a certain delay, but the child will learn to speak, walk, master the basics of literacy, that is, he will be able to do what many can;
- there will definitely be speech problems;
- training can take place both in a specialized and in a general education school;
- marriage unions are possible;
- half of women with Down syndrome can achieve the happiness of motherhood, but half of these children will be born unhealthy;
- Currently, the average life expectancy of such people is 50 years;
- their likelihood of cancer is reduced to a minimum.
It is difficult to predict what a child born with Down syndrome will be like. Everything is very individual. Future parents who decide to leave the pregnancy can be guided by the above-listed forecasts for this gene deviation.
Is it possible to prevent the occurrence of this pathology in an unborn child? Unfortunately, there are no preventive measures to prevent this deviation.
But doctors advise not to ignore the following recommendations::
- undergo consultation with a geneticist before and after conception;
- give birth to children before 40 years of age;
- take multivitamins, including folic acid, when planning pregnancy and in the first trimester.
It is important to understand that no one is to blame for the conception and birth of a special child. This is just an accident of nature, a chromosomal error. Because of her, extraordinary children come into our lives - bright, kind, trusting. Whether or not to accept such a baby into their family is up to each family to decide individually.
Author: Olga Rogozhkina, doctor, especially for Mama66.ru
Why are children born with Down syndrome?
The doctor will not always tell you with certainty why the child was born with such a disease. But there are a number of objective reasons why children appear with this diagnosis:
- mother's age is more than 35 years or less than 18 years;
- father's age is more than 42 years;
- burdened heredity;
- drinking alcohol, smoking during pregnancy;
- viral diseases of the mother in the early stages (herpes, rubella, cytomegalovirus);
- unfavorable living conditions (air, soil, water pollution).
If a pregnant woman is at risk for these parameters, then she must undergo a routine ultrasound.
In addition to the topic, watch the medical video review:
Invasive diagnostic methods
When the initial tests show a positive or questionable result, the doctor prescribes additional procedures. They help make an accurate diagnosis. Specific diagnostic methods are invasive. These include:
- amniocentesis;
- cordocentesis;
- chorionic villus test.
At the tenth to twelfth week, if indicated, a chorionic villus biopsy can be performed. This procedure involves the collection of the outer membrane of the fetus and subsequent examination of the material. The chorionic villi can be used to identify the genetic characteristics of the fetus. The collection of material involves penetration into the uterus. The analysis results will be ready in a couple of days.
Starting from the seventeenth to twenty-second week, the doctor may recommend that the expectant mother at risk undergo a procedure for collecting amniotic fluid. This method is called amniocentesis. Amniotic fluid can tell you about the baby's chromosome makeup. A special needle is used for the procedure. With its help, a hole is created in the fetal membrane. After collection, the liquid is examined in laboratory conditions. The results will be ready only in two to three weeks. Cordocentesis can be performed in parallel. This method involves studying cord blood.
Risks of additional diagnostic methods
Using invasive methods, Down syndrome is diagnosed with virtually no errors. However, the procedures are characterized not only by high accuracy, but also by the risks of pregnancy complications. Such risks include:
- miscarriage (the highest incidence is observed with chorionic villus biopsy - 3%);
- effusion of amniotic fluid;
- embryo infection;
- detachment of membranes.
Due to possible complications, invasive methods are not widely used. Tests are carried out for pregnant women for special indications. If the initial screening does not reveal factors indicating Down syndrome, then special tests are not prescribed. The expectant mother should be aware of the risks of specific prenatal tests. Parents independently decide whether to conduct an additional examination. Tests are optional.
A consultation with a highly qualified specialist will help you take a balanced approach to the issue of the need for invasive procedures aimed at identifying Down syndrome in utero.
Requirements for conducting the study
In a normal pregnancy, it is recommended to do 3 ultrasound examinations of the fetus:
- at 11–14 weeks,
- at 15–20 weeks,
- at 30–36 weeks.
At any time, starting from the eleventh week, Down syndrome can be detected by ultrasound in the fetus. In the first trimester, this is indicated by indirect signs, in the second – indirect and objective. In the third trimester, the diagnosis is almost 100% reliable, but medical termination of pregnancy is not performed after the 22nd week. A woman has a choice: artificial childbirth or physiological.
The exact timing of the screening will be determined by your obstetrician-gynecologist. Since the method is absolutely harmless, ultrasound can be done as prescribed by a doctor an unlimited number of times.
To obtain reliable results and correct data, contact experienced specialists who use modern equipment.
To make the image of the fetus three-dimensional, 2D, 3D, 4D ultrasound is used. The better your research, the lower the risk of bias.
Objective results
A diagnosis carried out in accordance with all the rules reliably establishes the presence of a chromosomal mutation in a child. The results of the examination are assessed only as a whole. The following should have a positive meaning regarding gene pathology: direct and indirect signs of ultrasound examination, hormone tests, biopsy results. According to statistics, for every 700–800 newborns there is only one baby with a Down chromosomal anomaly. In 85% of cases, parents decide to have an abortion or abandon the child in the maternity hospital.
Diagnosis of the first trimester
From the 11th to the 14th week, the first ultrasound of the fetus is performed. It includes ultrasound diagnostics and blood tests:
- free beta human chorionic gonadotropin;
- pregnancy-associated protein A.
For example, a woman with a 12-week pregnancy comes for a routine ultrasound. The doctor conducts a test and sends the patient to the treatment room to donate blood. Next, the resulting tests are sent to the laboratory along with a copy of the ultrasound results. Only in this case can we talk about high-quality, complete screening.
In order to identify pathologies, including Down syndrome, the following indicators are assessed:
- coccyx-parietal size;
- collar space thickness;
- heart rate;
- chorion structure.
If the screening result differs from the norm, a repeat screening may be performed. Recommendations and prescriptions for more in-depth studies of the pregnant woman will be given by the attending physician.
Please watch a useful video on how an ultrasound can determine whether a fetus has Down syndrome:
What are the signs of the disease?
Objective markers detected by ultrasound diagnostics and indicating a high risk of having a child with Down syndrome are:
- Neck space thickness (TNT). The collar area is a fold of skin on the back of the baby’s neck. It contains a certain amount of fluid, but in the case of trisomy 21, the volume of fluid is exceeded. When examined during the period from 10 to 14 weeks of pregnancy, the width of the fold is normally 0.8–2.8 mm. For accurate ultrasound diagnosis, gestational age is extremely important, because TVP increases with the age of the child. On the ultrasound monitor, the fold is visible as a white line, and the liquid is black.
- Condition of the nasal bone. Children with Down syndrome have shortened nasal bones. A negative symptom is if the baby’s nasal bone is not visualized on ultrasound at 12 weeks. During this period, the normal size of the nasal bone lies in the range from 2–4.2 mm. If pathology of the nasal bone is detected, the diagnosis is confirmed in 70% of cases.
Study indirect signs. If deviations from the norm in the TVP space are detected in the 1st trimester, the rest of the fetal organs and skeleton are examined by ultrasound. Accompanying signs of the disease appear:
- In shortened sizes of the shin bones;
- Enlarged interocular space;
- In changing the structure of the brain;
- There is only one umbilical artery (normally there are two);
- In an increased size of the bladder;
- Rapid heartbeat (tachycardia);
- In multiple heart defects.
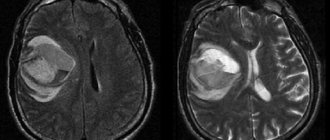
The length of the iliac bones and the angle between them are measured on the scanner monitor. The fetal brain is examined for cerebellar hypoplasia (underdevelopment of the organ and its functional areas). At the same time, in the ultrasound photo, the cerebellum looks reduced in size compared to the frontal lobe of the brain. Also, with the disease, a decrease in the size of the frontal lobe is observed compared to the norm.
When the fetal brain is examined with ultrasound, the disease test is confirmed by the combination of a reduced frontothalamic distance and a cross-section of the cerebellum. It takes less time than scanning the entire brain.
The size of the TVP alone cannot serve as a sufficient basis for the final diagnosis of the disease during pregnancy. The geneticist is obliged to take into account the results of a biochemical blood test and the ultrasound conclusion together.
Ultrasound is usually performed in a two-dimensional black and white image, with many organs appearing enlarged and not fully visualized. Therefore, the three-dimensional ultrasound method, carried out for additional diagnosis of genetic pathologies, will show surface defects, such as, for example, the width of the distance between the fetal eyes.
To obtain reliable information, ultrasound in the first trimester must be carried out within the allotted period, namely, no earlier than the 11th obstetric week and no later than 13 weeks 6 days!
Second trimester scan
From the 14th week the second trimester begins. Before the 20th week of pregnancy, the expectant mother must attend a second ultrasound to exclude signs of Down syndrome in the fetus. The doctor evaluates:
- compliance of the development of the skeleton and organs with the period;
- size and structure of internal organs.
At this time, you can see heart defects, bladder enlargement, brain abnormalities and other pathologies.
Doctors analyze 3 blood parameters:
- human chorionic gonadotropin;
- alpha-fetoprotein;
- free estriol.
If there are deviations, the pregnant woman may be referred to a specialized center to clarify the diagnosis.
An ultrasound monitor shows a fetus with Down syndrome at 24 weeks:
Ultrasound during the perinatal period
The use of ultrasound during pregnancy is completely safe for both mother and fetus. Moreover, such an examination provides a large amount of information about the development of the unborn child. You can perform an ultrasound an unlimited number of times.
Marks at 12 and 20 weeks of pregnancy are the dates for the first and second screenings. It is possible to diagnose Down syndrome using ultrasound at each of these stages. In the first trimester, by the appointed date, the rudiments of the main organs have already formed in the embryo, and by the 20th week the heart and skull with facial bones and ears are clearly visible.
Various methods are used for diagnosis. The form of visualization of the studied area also depends on them:
- 2D – two-dimensional monochrome image;
- 3D – volumetric projection;
- 4D – three-dimensional dynamic picture.
If there is insufficient data, the doctor prescribes a repeat ultrasound scan. All types of examinations are carried out externally only. It is not recommended to do the procedure transvaginally, that is, through the vagina, due to the increased risk of uterine tone.
Diagnosis of the first trimester
Is it possible to see Down syndrome on an ultrasound in the early stages? Yes, a sonologist will confirm or refute such an anomaly based on how the main organs of the fetus are formed, which are visible already in the first trimester. The examination is carried out between the 10th and 14th weeks. Using ultrasound, the doctor assesses the size of the embryo, its location in the womb and, based on these signs, judges the nature of the pregnancy. With the help of established markers, already at the first screening, the presence or absence of genomic pathology in the embryo is determined with a high degree of accuracy. Regulatory standards are taken as a basis.
One of the main signs of the described genetic disease is the absence of a nasal bone in the fetus. This anomaly is detected even during the simplest gray scale scanning using the 2D ultrasound technique, which makes it possible to determine the characteristics of the development of the embryo as early as the 11th...14th weeks. In addition, Down syndrome is identified by a number of signs:
- the size of the collar space is thick;
- the shape of the maxillary bone is shortened;
- anatomy of the ears – underdeveloped;
- number of heart beats per minute – tachycardia (indirect sign).
Second trimester scan
Down syndrome is noticeable on ultrasound and in the second trimester. By this time, the fetal organs are enlarging. With the help of ultrasound, the doctor can:
- assess the degree of underdevelopment of the nasal bones;
- identify heart defects that often accompany such an anomaly;
- to record underdevelopment of the bones of the hips, shoulders and iliac segment of the fetal skeleton.
A sign of chromosomal abnormalities are also pathologies in the development of internal organs, which during this period of pregnancy can already be examined in detail using ultrasound. If the functionality of key organs is impaired, as evidenced, for example, by the size of the cerebellum (smaller than normal) or bladder (larger than normal), the doctor makes an appropriate diagnosis.
At this time, at the request of the parents, it is possible to terminate the pregnancy by inducing artificial labor. The decision is made by the mother and father when severe genetic abnormalities are confirmed in the fetus.
Decoding the results
Based on the ultrasound examination data, the doctor issues a medical report on the condition of the fetus at the time of the procedure. A number of symptoms may indicate that a child has Down syndrome:
- The thickness of the collar space is more than 2.8 mm. This suggests that the volume of fluid that accumulates in the skin fold on the neck is greater than normal. On ultrasound, this fold is white, and the liquid underneath is dark.
- If the nasal bone is missing or smaller than expected on an ultrasound, this is a characteristic sign of Down syndrome.
- A shortened upper jaw also indicates intrauterine pathology.
- Increased heart rate and heart defects may be signs of illness.
- Underdeveloped ears, anomalies in the development of the skeletal system and internal organs indirectly indicate defects in the development of the fetus.
If, according to ultrasound examinations before the 20th week, signs of Down syndrome are detected in the fetus, the pregnant woman has the opportunity to terminate the pregnancy. After the 22nd week, abortions are not performed, so before this period, future parents need to decide whether they are ready to raise a special child.
Down syndrome in children is a disease that can be diagnosed using ultrasound. Pregnancy management in specialized medical centers allows us to identify potential risks and pathologies. Therefore, routine monitoring by doctors is necessary for the health of mother and child.
We hope that our material was useful to you. Share information with your friends. Thank you.
Second screening and third
The second screening is carried out at 20-24 weeks of pregnancy. Much more information can be obtained during this examination. Many organs are formed. In the second trimester, you can already clearly see the irregular shape of the skull (brachycephaly), heart defects, cysts, underdevelopment of the facial bones (cleft lip), the presence of an additional fold in the neck, intestinal obstruction, short bones of the limbs, disorders of the kidneys, and the central nervous system. The location and thickness of the placenta and the volume of amniotic fluid are studied.
But even such a detailed study of the anatomical structure does not answer all questions. Minor deviations of individual systems cannot be recorded. If alarming signs are detected during this study, the pregnant woman is also referred for consultation with a geneticist.
At 30-32 weeks, signs that were hidden earlier may appear. For example, hydrocephalus, heart defects, developmental disorders of the urinary tract.
Unfortunately, ultrasound examinations do not always detect genetic abnormalities that are poorly manifested anatomically. Such deviations include Down syndrome. But a timely procedure will help not to miss fetal malformations in the vast majority of cases.
Invasive fetal chromosome analysis
High-tech methods make it possible to establish a diagnosis with almost one hundred percent probability.
Minimally invasive diagnostic methods include:
- Amniocentesis. is carried out for mothers who are at risk of having a child with genetic disorders, as well as with disappointing results of the first screening. Amniocentesis is a study of amniotic fluid to determine the level of ACE. The procedure is performed in a hospital setting. Under the control of an ultrasound sensor: a needle is inserted into the anterior wall of the abdomen and amniotic fluid is collected in a volume of no more than 15 ml. Laboratory testing establishes the concentration of AFP. Its decrease confirms the preliminary diagnosis.
- Cordocentesis is the removal of fetal blood from the umbilical cord. Cordocentesis is the 100th result of intrauterine examination. During the procedure, the obtained blood is subjected to a thorough analysis, which reveals not only a chromosomal mutation, but also a number of other diseases. The procedure is quite expensive and is accompanied by the risks of placental abruption and spontaneous miscarriage.
- A no less accurate result is obtained with chorionic villus biopsy. The material for the study is chorionic villi, obtained by introducing special mirrors into the vaginal cavity.
A cytogeneticist is examining the material. In most cases, the methods are microscopic in nature.
Is it possible to cure Down's disease?
There is currently no etiological treatment that eliminates the cause.
First of all, treatment for Down syndrome is based on classes with a speech therapist, neuropsychologist and other specialists who help develop the neuropsychic functions necessary for a more or less full life in society.
For physical development, exercise therapy, massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed.
For the symptomatic correction of some signs of the disease, the following groups of drugs are usually prescribed to help improve the patient’s quality of life:
- Vascular, metabolic, neuroprotective, vitamin preparations to improve brain function.
- Antiepileptic drugs.
- Drugs that correct cardiovascular activity.
- Drugs that improve intestinal motility, antispasmodics.
- Hormonal drugs.
If necessary, surgical treatment is carried out: surgical treatment of cataracts, heart defects, gastrointestinal tract, etc.
Treatment prices
Prices for various medical services vary depending on the region. If we take Moscow as an example, then a consultation with each specialist there costs between 2000-3000 rubles. Ultrasound of the abdominal organs or heart - about 2000 rubles. One massage procedure with elements of physical therapy – about 1500 rubles.
What is ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a diagnostic method that uses ultrasonic waves. Full explanation of this abbreviation: ultrasound examination. Sometimes a synonym for ultrasound can be used - sonography. This type of diagnosis is absolutely safe for humans and does not cause any harm to the body of the child or mother.
This is due to the waves themselves, which are used in ultrasound. In simple words, it is an extremely loud sound that the human ear is unable to perceive. Similar “technologies” are also used by animals, such as bats and dolphins.
Evidence that this type of diagnosis is safe is provided by clinical trials and many years of experience in the use of ultrasound, during which there was not a single case in which the pathology caused was caused by ultrasound.
In some sources that are negative about ultrasound, you can find data that ultrasound can cause malformations of the nervous system. However, this is not true, since scientists conducted an experiment in which some pregnant mice were irradiated with doses of ultrasound similar to those in humans, while others were left under ultrasound waves, the frequency of which was much higher, and the exposure itself was longer. And only the latter developed deviations, but minor ones.
High risk of Down syndrome, analysis and screening
High risk of Down syndrome?
Down syndrome is not a disease, it is a pathology that cannot be prevented or cured. A fetus with Down syndrome has a third extra chromosome on the 21st pair of chromosomes, resulting in a total of 47 instead of 46. Down syndrome occurs in one in 600-1000 newborns born to women over the age of 35. The reason why this happens , has not been fully clarified. English physician John Langdon Down first described this syndrome in 1866, and in 1959 French professor Lejeune proved that it is associated with genetic changes.
It is known that children receive half of their chromosomes from their mother, and half from their father. Since there is not a single effective method of treating Down syndrome, the disease is considered incurable, you can take action and, if you want to give birth to a healthy child, go to a medical genetic consultation, where, based on the chromosomal analysis of the parents, it will be determined whether the child will be born healthy or with Down syndrome.
Recently, such children are born more often; this is associated with late marriage, with planning a pregnancy at the age of 40. It is also believed that if a grandmother gave birth to her daughter after 35, then her grandchildren may be born with Down syndrome. Although prenatal diagnosis is a complex examination process, its implementation is very necessary in order to be able to terminate the pregnancy.
What is Down syndrome? It may usually be accompanied by delayed motor development. Such children have congenital heart defects and pathological development of the gastrointestinal tract. 8% of patients with Down syndrome have leukemia. Drug treatment can stimulate mental activity and normalize hormonal imbalance. With the help of physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and therapeutic exercises, you can help your child acquire the skills necessary for self-care. Down syndrome is associated with a genetic disorder, but this does not always lead to impaired physical and mental development of the child. Such children, and in the future adults, can participate in all walks of life, some of them become actors, athletes and can be involved in public affairs. How a person with this diagnosis will develop depends largely on the environment in which he grows up. Good conditions, love and care contribute to full development.
Down syndrome risk table by age
The likelihood of Down syndrome depends on the age of the mother, but it can be detected by a genetic test in the early stages of pregnancy and, in some cases, ultrasound. The baby is less likely to have Down syndrome at birth than in earlier stages of pregnancy because some fetuses with Down syndrome do not survive.
What risk is considered low and what is considered high?
In Israel, the risk of Down syndrome is considered high if it is higher than 1:380 (0.26%). Anyone who is in this risk group needs to have their amniotic fluid tested. This risk is equivalent to that of women who become pregnant at age 35 or older.
A risk lower than 1:380 is considered low.
But we must take into account that these boundaries can be floating! For example, in England, a high risk level is considered to be a risk above 1:200 (0.5%). This happens because some women consider a risk of 1 in 1000 to be high, while others consider a risk of 1 in 100 to be low, since with such a risk they have a 99% chance of having a healthy child.
Risk factors for Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, Patau syndrome
The main risk factors are age (especially significant for Down syndrome), as well as exposure to radiation and certain heavy metals. It should be borne in mind that even without risk factors, the fetus can have pathology.
As can be seen from the graph, the dependence of the risk on age is most significant for Down syndrome, and less significant for the other two trisomies:
Down syndrome risk screening
Today, all pregnant women, in addition to the required tests, are recommended to undergo a screening test to determine the degree of risk of Down syndrome due to the birth of a child and congenital defects of the fetus. The most productive examination occurs at week 11 + 1 day or at week 13 + 6 days when the coccygeal-parietal size of the embryo is from 45 mm to 84 mm. A pregnant woman can undergo an examination and use a specific ultrasound for this.
A more accurate diagnosis is made using chorionic villus biopsy and examination of amniotic fluid, which is taken directly from the amniotic sac using a special needle. But every woman should know that such methods are associated with the risk of pregnancy complications such as miscarriage, infection of the fetus, development of hearing loss in the child, and much more.
Complete combined screening of the first and second trimesters of pregnancy allows us to identify congenital defects in the fetus. What does this test include? First, an ultrasound examination is required at 10-13 weeks of pregnancy. The risk is calculated by determining the presence of the nasal bone and the width of the fetal neck fold, where subcutaneous fluid accumulates in the first trimester of pregnancy.
In the second, a blood test is taken for human chorionic gonadotropin at 10-13 weeks and for alpha-fetoprotein at 16-18 weeks. Combined screening data is processed using a special computer program. Scientists have proposed a new screening technique - combining the assessment of results obtained during studies in the first and second trimesters. This allows for a unified assessment of the risk of Down syndrome during pregnancy.
For the first trimester, the results of determining PAPP-A and measuring the thickness of the nuchal translucency are used, and for the second trimester, combinations of AFP, unconjugated estriol, hCG and inhibin-A are used. The use of an integral assessment for screening examination allows, after invasive interventions, to reduce the rate of abortion for fetuses with a normal karyotype according to the results of cytogenetic diagnostics.
Integral and biochemical testing for Down syndrome screening can further identify more cases of chromosomal abnormalities. This helps prevent unwanted pregnancy losses resulting from amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling.
Author of the article:
Mochalov Pavel Alexandrovich |
Doctor of Medical Sciences therapist Education: Moscow Medical Institute named after. I. M. Sechenov, specialty - “General Medicine” in 1991, in 1993 “Occupational diseases”, in 1996 “Therapy”. Our authors
How to prepare for screening studies?
It all depends on the diagnostic method. During the first screening ultrasound, ultrasound can be performed transvaginally and transabdominally. The first method is more accurate, but is not recommended for all pregnant women. For all subsequent ultrasounds, only transabdominal ultrasound is performed.
During the first ultrasound, if it is performed transabdominally, you should simply drink about 0.5-1 liters of water half an hour before diagnosis to fill the bladder, which will become a “window” for ultrasound. It is important that the liquid is not carbonated. With transvaginal diagnostics, everything is somewhat more complicated - three days before the ultrasound, you should follow a diet that excludes gas-forming products such as:
- fresh bakery,
- some fresh vegetables and fruits (cabbage, beets, bananas, etc.),
- legumes,
- dairy products.
You can get a more detailed list of foods to avoid from your doctor. If it is not possible to sufficiently free the intestines from gases, then before diagnosis you should take carminatives, for example espumizan.
No preparation will be required for the second and third screening. Amniotic fluid will act as a “window” for transabdominal ultrasound.