MRI for traumatic brain injury Concussion is the most common type of traumatic brain injury (TBI). The organ does not undergo anatomical changes, and the neurological symptoms go away on their own. The diagnostic process includes questioning, examination and the use of instrumental methods. Performing magnetic resonance imaging if a concussion is suspected is unreasonable in the acute period. This is due to the fact that the considered variant of TBI is not accompanied by structural changes. An MRI after a suspected concussion will most reliably show the condition of the nervous tissue and promptly identify the presence of serious problems several weeks and even months after the injury. In the acute period, diagnosis does not make sense.
A concussion is considered a minor injury, accompanied only by disruption of brain function. A person may experience certain symptoms after an injury, including:
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- short-term amnesia (memory loss);
- sleep disturbance;
- headache, etc.
Loss of consciousness lasts from seconds to 5 minutes. The patient may not remember events that preceded the traumatic exposure (retro-) or occurred immediately after it (anterograde amnesia). However, all symptoms will go away in no more than 7 days. The main task of doctors in such a situation is not to miss dangerous injuries.
A brain contusion is a more severe injury. In this variant of TBI, morphological changes occur, cells are damaged and the connections of their processes (axons) may be disrupted, intracranial vessels rupture with the formation of hemorrhages and hematomas. When physical force is applied to the head, the nervous tissue receives two blows: the first - directly at the site of impact, the second - on the opposite side. The described phenomenon occurs due to the fact that the brain is injured from the inside by its own skull. The recovery period for a bruise may take more than one month, but a computed tomography scan will show the presence of this type of injury and will allow treatment to begin, and an MRI will reveal the consequences of a severe head injury after a while, helping to choose the right method of rehabilitation.
Subdural hematoma due to traumatic brain injury
Common signs of a concussion
When answering the question of how to understand that you have a concussion, traumatologists emphasize a mild form of dysfunction disorder. In this case, a closed-type traumatic brain injury is assumed without compromising the integrity of the bone surface of the skull and destruction of brain tissue. Damage to brain structures is caused by mechanical stress and is reversible. Causes:
- A blow to the head area.
- Fall from any height.
- Bruise when colliding with a hard surface.
- Sudden movement of the head.
The listed influences lead to changes in the cells of brain structures at the molecular level. Synapses, the points of interaction of neurons with each other and with other formations that transmit information through nerve impulses, may be disrupted. Clinical manifestations of disorders depend on the type of brain structures (cerebral fluid, medulla, arteries and blood vessels) that have been damaged.
If, as a result of injury, destruction of the brain substance occurs, the pathology is classified as contusion or brain contusion. As a result of exposure, blood often accumulates under the membrane or in the substance of the brain, which leads to the formation of hematomas and hemorrhages. The pupils are constricted or dilated during a concussion. The period during which a deviation from the norm is observed lasts up to several hours after the moment of injury.
A weak reaction of the pupils to the light flux is a sign of a mild concussion that has occurred in the brain. If severe lesions have occurred, the pupil does not respond to changes in lighting. The state of disorder or loss of consciousness lasts variably - seconds, minutes and even hours. The period of disturbance of consciousness indirectly indicates the severity of the damage. Head concussions, which are accompanied by a coma, are extremely dangerous.
First aid
For the victim, you need to call an ambulance, and until they arrive, you need to monitor him all the time. This is necessary to provide assistance in case of vomiting or seizures.
The procedure is as follows:
- The person must be carefully placed in a horizontal position so that the head remains slightly elevated.
- If he is unconscious, you should lay the victim on his right side or turn his head. This way he can breathe normally, and vomit and saliva will not enter the respiratory tract.
- If there are open wounds, you need to treat them with an antiseptic and apply a sterile bandage. Apply something cold to the site of the injury.
- It is necessary to provide the patient with access to fresh air by opening the window, eliminating all loud sounds and dimming the lights. In the first hours after a concussion, the victim may develop special sensitivity to irritating external factors.
Important! It is not recommended to give the patient any medications before the doctors arrive, except for analgesics for severe pain. First aid involves providing optimal conditions for waiting for the ambulance to arrive.
Symptoms indicating a concussion
To understand the topic of how to determine at home that a concussion has occurred, you should pay attention to the main signs:
- headaches and dizziness;
- nausea, vomiting;
- visual impairment;
- partial or complete loss of sensitivity of the skin of the extremities;
- clouding of consciousness, fainting.
The level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure affects the nature of the headache. Unpleasant symptoms indicating a concussion in the brain are usually observed no longer than a week after the head injury.
Vegetative
If there is any doubt that a concussion has occurred, characteristic signs will help identify how it affected the body and recognize the presence or absence of internal injuries:
- increase in body temperature;
- tachycardia (rapid heartbeat) or bradycardia – a drop in sinus rhythm to 40 beats per minute;
- increased sweating;
- pallor or hyperemia of the skin;
- weakness, deterioration in general health.
The condition is often accompanied by tinnitus and loss of orientation in time and space. The patient is characterized by inhibited, incoherent speech, loss of the ability to concentrate.
Neurological
Checking the Mann-Gurevich symptom will help determine whether or not there is a concussion. The patient is asked to follow the trajectory of a moving object with his eyes without turning his head. In this case, the doctor makes up to 5 pendulum movements of different amplitudes with the object within the frontal plane. If during the process of observing the subject the patient’s well-being worsened, pain, tachycardia and characteristic symptoms of a vegetative disorder appeared, the reaction is considered positive. Other tests and signs:
- impaired memory function - retrograde (loss of memories of events preceding the injury) or anterograde (impaired function of remembering events after the injury) amnesia;
- hemiparesis – partial paralysis of muscles on one side of the body;
- Babinski reflex - unconscious extension of the 1st toe with slight irritation of the sole along the lateral edge.
Difficulties in the question of how to check for a concussion are eliminated after a visual examination of the patient. The presence of disorders is illustrated by signs - facial asymmetry, deviation (deviation of position) of the tongue, nystagmus (involuntary vibrations of the eyes at high frequency). If the symptoms persist longer than 2-3 days, there is a high probability of a more serious pathology - brain contusion.
Late manifestations of pathology
The consequences of a concussion can manifest as sleep disturbances, lack of appetite, general weakness, and malaise. Pathological abnormalities can be caused by ruptures of small vessels and increased permeability of the blood-brain barrier resulting from injury. In most clinical cases, complications are caused by damage to axons - processes of nerve tissue cells.
In the normal state, axons participate in the formation of groups of neurons united by functional characteristics. The severity of the consequences depends on the severity of the bruise and the age of the patient. The older the patient, the higher the risk of complications. With repeated injuries, the likelihood of complications increases. The current neurological status can be found out in the hospital at a follow-up appointment with a neurologist.
Features of radiographs
The human brain is reliably protected by the bones of the skull, but due to injuries and diseases, the skull can weaken its protective functions. In such cases, radiography of the brain is indicated.
X-ray of the head is considered a low-cost research method and has virtually no alternative. It is possible to evaluate both the overall picture and a more detailed one using a variety of projections.
Three types of radiographs are widely used in medical practice:
- Overview projection is not aimed at any specific organ and is usually performed for head injuries and suspected brain injuries. Using a survey projection, anomalies in the entire cranium are diagnosed: congenital defects, fractures, and neoplasms.
- A targeted projection facilitates the diagnosis of anomalies in a specific area of the skull, if the doctor suspects. Such an x-ray reveals pathologies of blood vessels, nasal bones, eye sockets and other bones; malformations of the pituitary gland can also be examined.
- Digital X-ray helps diagnose problems with almost one hundred percent probability, since the image is displayed on a computer monitor. With this method, cerebrovascular diseases and concussions of varying severity are determined.
The latter method is more modern and high-tech, the advantage of which is a reduction in the radiation dose compared to film X-rays.
Diagnosis of a concussion occurring in the brain
During an examination, a neurologist can diagnose a concussion or differentiate the disorder as one of the more severe forms of pathology - bruise or compression of brain tissue, axonal damage to diffuse type brain structures. To diagnose a concussion that has occurred in the brain, the Glasgow scale is used - a set of tests that help identify the degree of change and state of consciousness. The Glasgow scale examines key reactions:
- Opening the eyes. It can be voluntary or as a response to tactile stimulation, painful stimulation.
- Speech reaction. There are correct and confused speech, inarticulate sounds and their absence.
- Motor reaction. Performing a physical action at the request or as a result of painful irritation, complete lack of motor activity.
The eye opening reaction, motor and speech functions are assessed on a 15-point scale. A patient with a score of 3 is diagnosed with brain death, with a score of 15 - clear consciousness. Other visual diagnostic methods include the upper lip reflex described by Bekhterev.
The doctor lightly hits the area of the upper lip above the gums with a hammer. In response to irritation, the lips stretch into a tube and protrude forward. Often there is a simultaneous protrusion of the lower jaw. A positive reaction to irritation indicates organic damage to the brain matter. According to statistics, the oral ankylosing spondylitis reflex is observed in 75% of people with a concussion, the Marinescu-Radovici palmar-chin reflex is observed in more than 56% of patients, and the Wartenberg carpal reflex is observed in more than 72%.
The palmar-chin reflex, described by Marinescu and Radovici, is caused by weak line irritation of the inner side of the palm in the area of the base of the thumb. The pathological reaction consists of contraction of the chin muscles, which causes displacement of the skin, leading to the formation of a skin fold in this part of the face. A positive reaction indicates damage to the corticonuclear pathways.
Neurological tests can be performed at home to independently assess the condition of a person who has suffered a head injury. To distinguish a concussion that occurred in the brain in adults from other types of traumatic brain injuries, a diagnostic examination using instrumental methods is prescribed.
At home
According to statistics, 23% of people lost consciousness due to a fall or head injury, which indirectly indicates a concussion. There are several ways to test for brain disorders at home. What to pay attention to:
- Brain fog.
- Loss of balance.
- Abnormal gait.
- Blurred outlines of objects when viewed.
- Feeling of anxiety, groundless irritability.
With a slight blow to the popliteal area of the legs, anisoreflexia is observed - different intensity of tendon reflexes. Signs such as constant drowsiness or sleep disturbance should alert you. Statistics show that 90% of people who suffer a concussion suffer from insomnia.
In a medical facility
In a hospital, the pathology is diagnosed during an initial examination, when the doctor checks neurological reflexes, including the wrist and facial reflexes. Brain dysfunctions are diagnosed using instrumental methods:
- Radiography. The image will show the condition of the skull bones and its contents. X-rays are prescribed to children and adult patients.
- Neurosonography (performed for children under 2 years of age).
- Echoencephalography, electroencephalography. Using the method, the presence of disorders is determined, the volume and nature of pathological changes in brain structures are assessed.
- Lumbar puncture. Determination of cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
- CT, MRI.
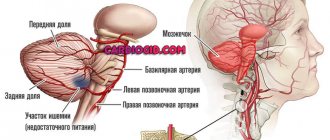
- Angiography, Dopplerography. During the study, the doctor identifies the condition of the vessels located in the head.
After 10-14 days, the neurologist conducts neuropsychological testing to identify abnormalities resulting from the injury. Often, after a concussion, doctors determine such disorders as cognitive failure, meningeal syndrome - skin hyperesthesia, stiffness of muscle fibers in the neck, increased sensitivity to light and sound stimuli.
Consequences and what awaits a person
It is very important to wait for this recovery period, since the main danger of a concussion is the consequences that can develop without proper treatment:
- Frequent attacks of dizziness.
- Severe headaches, migraines.
- Increased sensitivity to weather conditions.
- Memory impairment.
- Sleep disorders.
- Increased fatigue.
- Increased excitability, attacks of aggression, neuroses.
Therefore, you should not treat a concussion as something frivolous, because even a slight injury to this organ can have delayed and very serious consequences.
How to determine if a child has a concussion
Many parents are interested in how to know if their child has a concussion. Restless, active children are often hit in the head area. Damage is associated with falls from trees, stairs, slides, children's and sports equipment. The following factors contribute to increased traumatism in childhood:
- high physical activity;
- imperfect motor skills;
- insufficient degree of development of motor coordination;
- poorly developed sense of danger;
- no fear of heights;
- underdeveloped manual belay skills.
Externally, a disorder of brain function is manifested by a violation of gross and fine motor skills. The child looks distracted and confused, moves unsteadily, is unable to focus his eyes and remember the rules of the game. Depending on the age of the baby, symptoms manifest themselves differently:
- Up to 1 year. It goes unnoticed. Vomiting, nausea, and regurgitation may occur during feeding. In some cases, there is paleness of the skin, causeless anxiety, and anxious crying.
- From 2 to 7 years. There is a loss of consciousness. There is an increase or slowdown in heart rate, sweating, and sleep disturbances.
- Over 8 years old. Instability of blood pressure, psycho-emotional disorder. Visual impairment, expressed by nystagmus or post-traumatic blindness, is common.
In addition to the main symptoms of a concussion, poor balance and lethargy are added. The child does not remember how he fell or was hurt. The fact of a head injury, indicating the likelihood of developing disorders, is a reason to consult a doctor. If you notice signs of a concussion, you must urgently take the child to the hospital.
Why is a concussion dangerous?
After a minor injury, most symptoms disappear within 3-7 days. Even short-term disorders of brain function are fraught with complications. During the examination, 50% of patients were found to have disturbances in blood microcirculation, cellular metabolism, and ischemia in the damaged parts of the brain 10 days after the injury with complete disappearance of symptoms. Possible consequences of a head injury:
- Convulsions, epileptic disorders.
- Failures in the functioning of the autonomic system - changes in blood pressure, emotional instability, fatigue.
- Increased susceptibility to the effects of alcohol.
- Susceptibility to panic attacks, formation of phobias.
- Deterioration of physical and mental activity.
Patients often suffer from depression, regular headaches, and inability to concentrate several months after a head injury. Statistics show that 25% of people who have suffered a mild traumatic brain injury subsequently become disabled.