A cholesterol test is called a lipid profile. It has important diagnostic value for identifying atherosclerosis or predisposition to it. Blood is taken from the patient for testing. Using this analysis, you can assess the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases in individuals without clinical signs of pathology.
Decoding the cholesterol test is the responsibility of the attending physician. Since the lipid profile has several important indicators and a person who does not have special knowledge will not be able to objectively evaluate them. In addition, all designations in the form are given in Latin symbols.
Indications
A biochemical blood test is prescribed when visiting a doctor with complaints of pain and ailments, to monitor treatment and evaluate results, as part of routine checks (medical examination, clinical examination, intravenous blood test, perinatal screening, etc.). Blood is checked for biochemistry upon admission to hospital treatment.
Lipidogram is carried out according to personal indications:
- hypercholesterolemia (high cholesterol levels), previously identified;
- hypertonic disease;
- post-infarction post-stroke period.
Patients with chronic diseases of the cardiovascular, endocrine, and hepatobiliary systems regularly donate blood for an expanded lipid profile. Cholesterol control is recommended:
- women in the premenopausal period and during menopause;
- men aged 40+;
- people with a sedentary lifestyle and nicotine addiction.
Biochemistry is a mandatory study for children with hereditary pathologies.
What do deviations from the norm indicate?
If you have high cholesterol, you must have a lipid profile.
What are the causes of increased cholesterol?
- diabetes;
- cardiac ischemia;
- liver diseases;
- obesity;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- problems with the pancreas;
- kidney diseases;
- eating fatty and unhealthy foods.
Factors influencing the decline in the indicator include:
- anemia of various etiologies;
- stressful situations;
- lipid metabolism disorder;
- fasting, malabsorption of food.
With an increase in bad cholesterol or a decrease in good cholesterol, the content of triglycerides increases.
Also, an upward change in the indicator is observed in the following situations:
- heart attack;
- renal failure;
- diabetes;
- hepatitis;
- thrombosis of cerebral vessels;
- pancreatitis;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- cardiac ischemia.
An increase in triglycerides may occur when taking contraceptives. A decrease in indicators indicates various injuries, malnutrition, burns, and excessive intake of Omega-3.
Elevated atherogenic coefficient values indicate that elevated LDL predominates in the body. Increased AI also indicates the presence of atherosclerosis in the patient. A reduced rate does not pose any particular danger.
Important! The diagnosis of “atherosclerosis” is not made based on IA alone. Only in combination with other indicators can a diagnosis be made.
Cholesterol in the blood
The fat-containing alcohol cholesterol (the chemical name for cholesterol) is localized in the elastic cell membrane, acting as a protector of cells from the external environment. It participates in the most important biochemical processes that maintain the vitality of the body:
- production of bile acids and hormones (sex and steroid);
- communication between neurons of the brain and spinal cord;
- absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E.
Endogenous cholesterol is synthesized by liver cells. It accounts for up to 80% of the total. The body gets the rest from animal products.
Cholesterol metabolism
Metabolic processes are provided by high, low and very low density lipoproteins (HDL, LDL and VLDL). Their structure includes triglycerides, higher fatty acids, proteins, cholesterol, and phospholipids. Density is determined by the quantitative correlation of proteins and lipids (fats). The smaller the protein part of lipoproteins and the larger the fat part, the lower the density.
In a biochemical study, total cholesterol values are composed of lipoprotein and triglyceride values. LDL is conventionally called “bad” cholesterol, since it is low-density lipoproteins that settle on the inside of the arterial walls, forming plaques - the causes of vascular atherosclerosis. HDL (“good” cholesterol) clears blood vessels of excess free and “bad” cholesterol.
What to do in case of deviations
If there are minor deviations in the tests, it is recommended to adjust your lifestyle. First of all, the patient must give up smoking and alcohol. They slow down and disrupt fat metabolism. Low activity contributes to the formation of stagnant processes. Selected physical activity normalizes indicators and improves lipid metabolism.
At the initial stage of correcting cholesterol levels, attention is paid to proper nutrition. It is recommended to temporarily stop consuming sausages and other semi-finished products, products containing trans fats (mayonnaise, margarine), fried and smoked foods, omelets, fatty foods (cream, sour cream), potatoes
Reduce the amount of sweets and starchy foods in your diet. Preference should be given to products containing vegetable fats. The diet should include fish of different varieties, nuts, and cereals. Vegetables and fruits help regulate cholesterol levels.
Video material about ways to reduce cholesterol:
Three weeks after correcting activity and changing diet, a repeat test is taken. In case of deviations from the standards, the doctor conducts a further examination and, depending on the clinical picture, prescribes treatment.
A cholesterol test is an important point in monitoring your health. It helps to identify the disease in time, identify existing risks and take preventive measures. Full information is contained in the biochemical analysis.
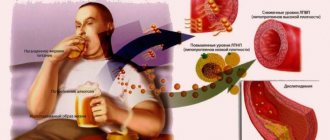
Many people are surprised when they first hear about the levels of bad and good cholesterol. We are accustomed to seeing this fat-like substance as only a hidden threat to health. In reality, everything is a little more complicated. It turns out that there are several fractions of lipophilic compounds in the body that can both cause harm to blood vessels and be beneficial. In our review, we’ll talk about the difference and age-specific norms of good and bad cholesterol, as well as the reasons for the analysis to deviate upward or downward.
Lipidogram and detailed biochemistry
To fully determine the lipid status (profile), lipids of various fractions are also studied in the laboratory. The purpose of the analysis is to assess fat metabolism in the body. In clinical and laboratory practice, all research parameters are designated in Latin letters.
Advanced Analysis Options
| Index | Definition, functions | Russian abbreviation | Designation in Latin |
| Total cholesterol | Set of lipid fractions | OH | Cho (Cholesterol) |
| Low and very low density lipoproteins | Transfer cholesterol molecules from the intestines and liver to cells (to ensure their functions) | LDL and VLDL | LDL and VLDL |
| High-density lipoproteins | Transport excess low-density lipoproteins and free cholesterol in the opposite direction (for catabolism in the liver and excretion from the body) | HDL | HDL |
| Trigrycerides | The body's fat reserves, consumed in the intervals between the intake and production of lipids (to replenish energy) | TG | TRIG or TG |
| Atherogenic coefficient (otherwise, index) | Shows the risk of developing vascular atherosclerosis, stroke and ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease) | CA | I.A. |
In the forms you can find the abbreviation TC - this is how cholesterol is indicated in a blood test in some laboratories. The designations OX, TC, Cho are equivalent. The unit of measurement for total cholesterol, LDL, VLDL, HDL is mmol/l or the number of millimoles of lipid dissolved in 1 liter of blood. The atherogenicity coefficient is measured in units. It is calculated using a special formula.
Additional parameters of the lipid profile study are:
- apoproteins - proteins that are part of lipoproteins and determine which cells LDL and HDL are intended for;
- chylomicrons (CM) are a special type of lipoproteins formed in the intestines and endowed with the function of transporting exogenous fats (triglycerides and cholesterol) into the cells and tissues of the body.
Content of apoproteins, triglycerides, cholesterol and other fats in lipoproteins and chylomicrons in percent (%)
An imbalance of different density lipoproteins is called dyslipidemia. Most often, this disorder is caused by an increase in LDL concentration against the background of a decrease in HDL levels. Dyslipidemia is reflected in blood composition by hypercholesterolemia. The lipid profile indicates all parameters with specific numbers. Conventional biochemistry gives only OC results.
What kind of cholesterol test is this?
It is impossible to detect cholesterol molecules in a general blood test. Biochemistry is used to identify them. It identifies “bad” cholesterol, which is designated by capital letters of its biochemical characteristics.
The analysis is indicated for people who suspect atherosclerotic disorders in the vascular walls. The latter may manifest themselves with the following clinical symptoms:
- Pressure surges. They are noted when measured with a tonometer and recorded in a special diary. If systolic and diastolic blood pressure regularly increases, we are talking about hypertension due to atherosclerosis.
- Dizziness, paresthesia and dysfunction of the sensory organs. Symptoms appear when the atherosclerotic process reaches large and small vessels of the central or peripheral nervous system.
- Dyspnea. Against the background of elevated blood pressure numbers, “pulmonary” heart occurs. It is characterized by enlargement of the left ventricle - its dilatation. The patient develops respiratory failure.
- Cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle. It is often accompanied by cyanosis of the distal phalanges of the fingers of the upper and lower extremities. This indicates poor oxygenation of these areas of the body.
- Contouring of capillaries, veins and arteries beneath the surface of the skin. Often, their pulsation is observed.
- Deterioration of the patient's mnestic functions. These include the ability to think, remember new events and remember old ones.
Reference values for children
You can also read: Flaxseed oil for high cholesterol
Cholesterol standards are graded depending on age. The accepted values for children are lower than for adult patients, since in a child’s body:
- the reproductive and reproductive systems are not fully formed;
- the rate of metabolism of fat and sugar differs;
- the process of processing and assimilation of food is different;
- hormonal levels are unstable.
The amount of endogenous and exogenous cholesterol increases in proportion to the growth and development of the child. Accordingly, the norms of its content in the blood change.
Normal children's indicators
| Age | Up to 30 days | Up to a year | Up to 12 years | Up to 16 years old |
| mmol/l | 1,6 – 3 | 1,8 – 3,7 | 3,7 – 4,5 | 3,8 – 5,0 |
How to get tested correctly
In order to avoid errors in laboratory tests, it is very important to follow a number of rules before taking a blood test for cholesterol. The slightest deviation in error may cause an incorrect diagnosis
The analysis does not require specific equipment, so you can take a total cholesterol test at any medical center. State medical institutions, regardless of their focus, provide blood sampling free of charge, as part of a general diagnosis of the body’s condition. Determination of cholesterol levels is included in the list of measures for preventive medical examination of the population.
When testing blood for cholesterol and deciphering it, it is important to take into account the general condition of the patient’s body. The results of the analysis can be an indicator of the disease only in combination with other pronounced signs inherent in this disease
Simple methods are used for the study, so a test for total cholesterol is ready in no more than a day. For laboratory determination of cholesterol, the following methods are used:
- Direct biochemical studies. This method is based on the Liebermann-Burkhard reaction. These methods give the most accurate results, despite the low cost of analysis. But the reagents involved in this analysis have a side effect, causing corrosion. They are very inconvenient to store. Therefore, this technique is not used in large research centers.
- Direct biochemical studies are mainly represented by the Abel method. They have a small percentage of error compared to the direct method.
- Enzymatic studies. Such methods are used by about 95% of all research laboratories. These are accurate tests with no side effects.
- Chromatographic studies. They are mainly used when it is not possible to obtain a high-quality blood sample. Extremely accurate and expensive technique.
Before the analysis, it is necessary to completely limit food intake for at least 7-8 hours. It is correct to donate blood from a vein only on an empty stomach. Food can completely change the test result, either up or down, and if you donate blood after eating, you may get completely wrong results. It would be advisable to exclude heavy and fatty foods from the diet a few days before the examination.
The fact that this substance is harmful to blood vessels and the heart is a known fact, but only partially true. It is found in the tissues of the body and is indispensable for its normal functioning. The cholesterol level in the blood is determined during testing and compared with acceptable standards. This must be done regularly.
Adult Cholesterol Standards
Reference TC values for men and women of fertile age are identical. The lower limit of normal is 3.2 mmol/l, the upper limit is 5.2 mmol/l. Hypercholesterolemia is considered to be results exceeding 6.7 mmol/l.
The main danger of an increased concentration of cholesterol in the blood is the development of atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries of the heart, vessels of the lower extremities, brain, and kidneys. Atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels are irreversible. If control is lost, the disease leads to heart attack, ischemic stroke, renal failure, and dry gangrene of the legs.
Cho values less than 3.0 mmol/l indicate hypocholesterolemia. With such a disorder of lipid metabolism, there is a risk of:
- destruction of cell membranes;
- vitamin D hypovitaminosis;
- dysfunctions of the reproductive and reproductive systems;
- malfunction of the autonomic nervous system.
Cholesterol deficiency provokes hemorrhagic stroke. For pregnant women, the consequences of hypocholesterolemia are miscarriage and premature birth. A slight age-related change in HDL concentration (on average, 2 mmol/l) is not a pathology. This is due to the decline of sexual activity, slowdown of metabolic processes, and general aging of the body.
Differences by gender
Lipoprotein standards are classified by gender. This is explained:
- differences in the composition, production and consumption of sex hormones;
- It is the natural nature of a woman’s body to store fat to maintain a potential pregnancy.
Female and male triglyceride and lipoprotein levels
| Options | TRIG | LDL | HDL | VLDL | ||||
| Floor | husband. | wives | husband. | wives | husband. | wives | husband. | wives |
| Norm in mmol/l | 0,41-1,8 | 2,25-4,82 | 1,92-4,51 | 0,7-1,73 | 0,86-2,28 | 0,26-1,04 | ||
Separate indicators have been adopted for the perinatal period. Cholesterol becomes the basic lipid for the formation and development of the placenta. In addition, when hormonal status changes, progesterone is synthesized in an enhanced mode - a sex hormone that protects the unborn child. Endogenous cholesterol is required for its production. The values of TC and its fractions increase from the second trimester of pregnancy.
Normal values for expectant mothers
The wave of hormonal changes during menopause also affects cholesterol concentrations. The premenopausal and menopausal periods are characterized by a gradual inhibition (followed by a stop) of the production of the sex hormone estradiol. It is replaced by estrone, synthesized from lipids, so the level of OX increases.
Indicators for women in menopause
Atherogenicity index (coefficient)
The IA symbol can only be found on the lipid profile form. The atherogenic index is not calculated as part of standard blood biochemistry. For the lipid profile the following formulas are used:
- IA= (LDL + VLDL) / HDL;
- IA= (Cho – HDL) / HDL.
The atherogenicity index reflects the degree of development (risk of development) of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. The obtained CA values can be deciphered as follows:
| Meaning | Analysis result | Preliminary diagnosis |
| 2-2,5 | Norm | Proper lipid metabolism |
| 3-4 | Elevated | Threat of atherosclerosis |
| >4 | High | Atherosclerosis, risk of stroke, heart attack |
An underestimated KA has no diagnostic value.
Explanation of meanings
Normal cholesterol levels are in the range of 3-5.4 mmol/l.
At levels of 5.5-6.5 mmol/l, moderate hypercholesterolemia is determined; more than 7.9 mmol, high hypercholesterolemia is diagnosed. Acceptable values for HDL are from 1.2 mmol/l, for LDL – from 2.5 to 4.3 mmol/l.
In Latin it is designated: cholesterol - CHOL, bad cholesterol - LDL, good cholesterol - HDL.
The norm for the atherogenic index is from 2 to 2.9. The maximum permissible value for women is 3.2 units, for men – 3.5 units. In people with severe atherosclerosis, AI is 4-7 units.
The atherogenicity index is written in the analysis in Latin letters - CATR.
The acceptable level of triglycerides is 0.55 – 2.25 mmol/l. At levels of about 2.27 mmol/l, there is no danger of developing cardiovascular pathologies if the cholesterol complex is normal.
The Latin designation for triglycerides is TRIG.
Note! Indicators may vary slightly depending on the patient's gender. During menopause and pregnancy, results vary slightly. Sometimes heredity contributes to high cholesterol. Some hormones, statins and fibrates affect the concentration of the substance in the blood.
Results
Indicators of cholesterol, lipoproteins and triglycerides in the blood are a marker of fat metabolism processes and the threat of developing serious diseases. In the analysis forms, the study parameters are indicated in Latin:
- Cho (Cholesterol) – concentration of total cholesterol;
- LDL and VLDL – low-density and very low-density lipoproteins (LDL and LDLNP);
- HDL – high-density lipoproteins (HDL);
- TRIG or TG – triglycerides.
The IA sign means the atherogenicity index, reflecting the danger of atherosclerotic vascular pathology.
Lipidogram: analysis features
This test is prescribed if there is any suspicion of an incorrect level of cholesterol in the blood. Diagnosis is complex, identifies various metabolic disorders associated with lipid activity, and also helps to predict ischemia of the heart muscle. For research, blood samples are obtained from a vein.
In order for the results to be correct, it is important to follow the established rules
The very first condition is to donate biological fluid strictly on an empty stomach, in the morning. Before the procedure, you should not eat for at least eight hours, but it is better to abstain from food for half a day. This applies not only to nutritious dishes, but also to coffee and tea. It is allowed to drink water, but in reasonable quantities. You should also not drink alcoholic beverages - the ban on them applies for several days before the study. Similar restrictions are imposed on fatty and fried foods.
What does cholesterol consist of?
Although Chol, like all other medical terms, is denoted by Latin letters, its origin is from the Greek language, where the name was formed from two words that together give the phrase translated into Russian as solid bile. It was so named because it was first discovered in gallstones.
Its generator is our liver, which produces the main part of it; the body receives the rest through food.
Cholesterol is made up of a mixture of high-density lipoproteins (HDL) and low-density lipoproteins (LDL). If there is an imbalance between this connection, many serious diseases can develop.
Cholesterol circulates through the cardiovascular system along with the blood. It is responsible for the creation of new cells; without it, the cellular structure will not have the proper density
In addition to this important function, cholesterol has another mission - it is involved in the production of the main sex hormones - testosterone, estrogen and cortisone.
It transports antioxidants to the brain, which ensures normal nutrition of brain cells and oxygen saturation. Circulating in the blood, it helps the absorption of fats. But for all the above positive functions in the body, Chol should be within the specified limits.
How does cholesterol affect your health?
This component is indispensable in the body system. When its level is normal, new cells are formed, since it is an important component in their formation, necessary and important sex hormones are produced, which are responsible not only for the human reproductive system, but are also an important factor influencing his mood and general well-being .
If the level of Chol in the blood is too high, then this leads the body to a whole series of provocations of diseases, the most dangerous and having the greatest risk of death are: atherosclerosis, heart attack and stroke.
If the Chol level is reduced, this is also not good, as it can lead to the development of anemia and various disorders in lipid metabolism.
Therefore, it is important to take the necessary tests in a timely manner
How dangerous is this component for humans?
Previously, it was believed that any level of lipids in the blood was a negative aspect that needed to be eliminated. Blood studies had frightening statistics, from which it followed that every second heart attack or stroke occurs due to high cholesterol.
Now, for the normal functioning of the brain, medical scientists have determined the norm of this component, at which there is no harm to the functioning of all other organs.
It was previously noted that total cholesterol is divided into HDL and LDL, and an imbalance in the ratio of these two components can lead to a number of serious disorders:
- Atherosclerosis;
- Stroke;
- Hypertension;
- Heart attack.
These diseases are very dangerous and have a huge mortality rate.
Therefore, obtaining a detailed analysis that will reflect the content and ratio of lipids is very important
Many patients, having high cholesterol, are in an age group when it is already difficult to get to the clinic, or they are people with limited mobility. For such patients, the doctor especially recommends purchasing portable analyzers so that they can monitor their cholesterol in a timely manner, adjust their diet plan and monitor their general health.