What to take with you to the hospital: list of personal items
- Slippers (preferably rubberized so that you can go to the bathroom in them), or additional flip-flops for the bath (so as not to become infected with fungus)
- Suit for men
- Bathrobe for women (it is more convenient to wear a robe when the postoperative suture hurts)
- Nightgown (for women)
- Replacement panties (several sets)
- Socks
- Towels (1 medium and 2 small)
- Liquid soap (it’s more convenient because it won’t slip out of your hands, won’t fall, won’t get dirty, and you don’t need to take a soap dish; in addition, it will replace shower gel, and if you forget shampoo, it will also replace shampoo)
- Toothpaste and toothbrush
- Toilet paper
- Paper toilet seat covers (highly recommended!)
- Wet wipes
- A garbage bag, a bathroom bag (you will put a towel and other supplies in it, since the bathroom can be damp) and a shoe bag (which you will put in the cloakroom when hospitalized)
- Bag for clothes (when you go to the operating room you will need to change into a sterile shirt or your nightgown, and put your robe, socks and jewelry in a bag and give it to the nurse)
- For hair: comb, shampoo (small bottle)
- Deodorant
- You can buy a sippy cup (convenient after surgery if there is a long postoperative period and it is impossible to eat while sitting).
- Additionally, take to the hospital for women: cosmetic discs, toner and face cream, hygienic lipstick, hair tie (if you have long hair), pads and a disposable diaper (especially for gynecological operations)
- What to take a man to the hospital (optional): razor and shaving foam
- In the off-season, when the heating has not yet been turned on, but it is cold outside at night, take a warm jacket and socks with you. By the way, it is not advisable to take woolen items to the surgical department; it is better to prefer fleece items.
- Phone charger and top up phone account
- Mug, spoon, napkins
- Book, crossword, notepad and pen
- If you are used to sleeping in absolute silence, then as an adaptation for the first day you can take earplugs (what if your neighbor snores?)
If an operation is to be performed, then the underwear that comes into contact with the skin next to the surgical suture should be ironed.
How to ease the postoperative period?
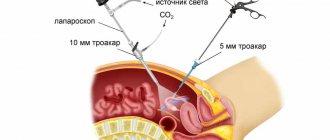
The recovery period after laparoscopic interventions rarely presents surprises in the form of complications. This is due to its minimal invasiveness, which allows the body to quickly adapt. Bed rest is prescribed to all patients, and its duration depends on the nature of the intervention. After a simple diagnosis, you do not need to stay in bed for more than a day; for more complex interventions involving the removal of tumors or the gallbladder, this regime is extended at the discretion of the doctor. If necessary, the patient is placed in an intensive care ward, where he is under constant supervision of special equipment.
You should not start taking painkillers, blood thinners, or other medications on your own without consulting your doctor. If you have constipation or diarrhea, self-medication is also not allowed - you should inform your doctor about such symptoms immediately.
In most cases, you are allowed to walk independently the next day. A special diet is not required; it is indicated only after gall bladder surgery. You should start eating every other day, with light food - fermented milk products, soups. To quickly restore normal digestion and stool, prune compotes are recommended. It is recommended to drink at least 2 liters of water per day - it should be non-carbonated. Physical activity is resumed smoothly, but serious exercise is allowed no earlier than 2 weeks after surgery.
The most common complaint of patients after laparoscopy is pain. It can be localized in the abdominal cavity or radiate to the shoulders. All such symptoms are associated with the need to inflate the abdominal cavity with carbon dioxide during surgery. The need to use analgesics is rare - mainly after removal of tumors, cysts or cholecystectomy. After diagnostic laparoscopy, pain, bloating and other unpleasant symptoms disappear within 2-3 days.
Source https://diagnostinfo.ru/skopiya/laparoscopy/chto-br...v-bolnicu-na-laparoskopiu.html
All rights to materials posted on the site are protected by copyright and related rights legislation and cannot be reproduced or used in any way without the written permission of the copyright holder and placing an active link to the main page of the Eva.Ru portal (www.eva.ru) next to with the materials used.
The editors are not responsible for the content of advertising materials. Certificate of registration of mass media El No. FS77-36354 dated May 22, 2009 v.3.4.206
Password recovery
New User Registration
What you need to take for surgery and for the postoperative period
Compression stockings are very important!!! Compression stockings should be worn not only by older women and men, but also by young people, because... During anesthesia, everyone's blood becomes thick and viscous, which means there is a risk of blood clots (at any age!). There are special stockings for surgery - called hospital stockings or anti-embolic stockings (they will protect the legs from the formation of blood clots during anesthesia). Read about the requirements for hospital stockings in the section “stockings for surgery.”
Postoperative bandage (will help reduce pain in the area of the postoperative suture and avoid adhesions). Be sure to buy a bandage before you go to the hospital, because as the saying goes, “a spoon is dear to dinner,” and the bandage should be purchased and selected in advance. In addition, you will save your relatives from the need to run around stores, take your measurements over the phone and take the first model that comes along. Call us, we will help you choose, and if necessary, we will even deliver you to the hospital. Look in our catalog “postoperative bandages” from the simplest models to the super-functional ones. Disposable diaper (it is convenient to place a bedpan or a “duck” on it so as not to stain the bed linen, and it is also necessary for women during gynecological surgery, and for all patients who have a catheter placed) In some cases, diapers (depending on the type of operation) If you do not want to use public hygiene products, then purchase your own plastic bedpan (for women) and a “duck” urinal for men. It's not expensive, but it's hygienic.
A convenient device is a rope ladder (attached to the bed to make it easier to get up)
In the postoperative period, if the rehabilitation is planned to be long, and there are no functional beds in the hospital, then an adjustable headrest for the bed will be useful (you can then take it home and use it at home and in the country).
For older people with an unsteady gait, take care of rehabilitation walkers (you can not only buy them from us, but also rent them).
Constipation after surgery: what to take with you to the hospital
In the postoperative period, there is often constipation and it is difficult to go to the toilet, so we recommend taking a laxative with you; “Amplifir” (produced by the Russian research and production enterprise “NPP Biotika-S”) has proven to work best. Amplifier forms stool, does not cause painful spasms and diarrhea, but acts carefully and gently, and what is important - does not interfere with the absorption of vitamins and microelements, and also has a beneficial effect on the intestinal flora, it can be taken for a long time, therefore, thanks to all the above characteristics, we recommend it this drug. Sold in the online store shop.biotika-s.ru
What should you take to the hospital for varicose vein surgery?
Varicose veins
are deformation and expansion of veins with an accompanying loss of their elasticity, and is also accompanied by a deterioration in blood flow
About 40% of women over the age of 30 experience varicose veins, in whom the disease affects the lower calf muscles and the back of the knee joints. .
The causes of varicose veins
include the following factors:
• being overweight;
• long periods of standing;
• disease of the venous walls;
• insufficiency of venous valves.
Sometimes varicose veins occur in women in the last months of pregnancy due to insufficient rest and excessive stress on the legs.
Signs of varicose veins on the legs:
• veins protruding through the skin;
• frequent cramps in the calf muscles;
• thinning of the skin and itching;
A phlebologist diagnoses and treats venous disease.
.
As a rule, varicose veins are treated for aesthetic reasons, however, if the problem is neglected, treatment may be recommended for medical reasons. Complications of varicose veins can lead to the development of diseases such as acute thrombophlebitis, trophic ulcers, thrombosis and bleeding.
Treatment of varicose veins in Moscow under the compulsory medical insurance policy:
• compression therapy (reducing the width of veins through external compression);
• phlebectomy (surgical operation to remove a vein);
• foam sclerotherapy (injection of a special drug into the lumen of a varicose vein).
Regardless of the region of residence in Moscow, you can begin treatment for varicose veins free of charge under the compulsory medical insurance policy in leading hospitals.
For the convenience of citizens from other regions, a hotline for free planned hospitalization of nonresident patients in Moscow hospitals “Capital of Health” operates around the clock. To receive scheduled treatment, you need to call the Health Capital hotline or leave a request on the website. The curator will tell you whether the necessary assistance is included in the list of diseases under the compulsory medical insurance policy, will help you decide on a specialized hospital and a convenient date for hospitalization, and also organize hospitalization.
All services are provided free of charge.
After hospitalization, the curator will continue to receive information about the patient’s stay in the hospital until his discharge and, if necessary, will be ready to provide information support.
You can learn more about the possibility of planned free hospitalization for nonresidents under compulsory medical insurance in a Moscow hospital and get informational assistance from a specialist by calling the hotline at
Source https://www.xn--80aefldrufatdm9c5ezb.xn--p1ai/varikoz-prichiny-i-lechenie.html
Medicines (for chronic patients)
When you are admitted to the hospital, take with you the medications that you take regularly (be sure to tell your doctor about them!).
Don't forget the bandage and compression stockings for surgery! The bandage will greatly facilitate the postoperative period! Look at our catalog “Postoperative Bandages”, and stockings will protect your veins from complications.
Is it possible to take a body cross to the hospital for surgery?
You can wear a pectoral cross to the hospital and even need to if you are Orthodox, but unfortunately, you will have to remove it directly for the operation. Why? Because during anesthesia nothing should restrict the chest and, especially, the neck. In an emergency, seconds matter, so the doctor may not have time to unfasten your chain, and if it is damaged, patients may file a claim. A pectoral cross on a string is also not a solution, because the cross cannot be removed over the head, you will only have to cut the string, but in the turmoil the cross can be lost, and this is a matter of financial responsibility.
What to take your child to the hospital:
1. For babies, diapers and a potty.
2. Disposable diapers (for babies).
3. A change of clothes for the child according to the season, several sets, including warm socks and a blouse, a change of shoes: slippers or sandals.
4. Hygiene products for children.
5. Babies may need bottles, formula, and a pacifier. For older children, take your favorite treats, fruits, and nuts.
6. Take your child a few toys and books.
Some hospitals allow the use of electric kettles and boilers. Many patients bring their own bed linen from home, which is also permitted.
Once in the hospital, just in case, write down the list of medications you are taking; this may be important for the attending physician, and you will not forget anything due to stress.
According to the laws of our country, parents of children under 15 years of age have the right to stay in a hospital with their child. Know your rights, you have every right to be in the hospital with your son or daughter. Often, parents whose children are undergoing treatment are not even provided with a separate place. Essentially, mothers or fathers share one bed with their child.
(420, today: 30)
Recommendations for preparing for laparoscopy
Not all of our patients have the opportunity to adhere to a diet and undergo certain tests. In case of emergency surgery, preparation is not carried out, since the patient and doctors are limited in time. In this case, specialists pursue one goal - to save the patient’s life.
To perform laparoscopic surgery, most patients are given a referral to donate blood and urine. The attending doctor collects all data about the patient’s health status. The patient must prepare for the intervention carefully and responsibly, adhering to a certain diet. A week before laparoscopy, foods that cause gas formation are excluded from the diet. This is about:
- milk;
- legumes;
- cabbage;
- plums, pears and other fruits.
The diet should consist of lean meats, boiled eggs, fermented milk products and dietary cereals. 5 days before laparoscopy, they begin taking activated carbon and enzymatic preparations. Thanks to diet and medications, patients in the gynecology department are able to normalize digestion.
Immediately the day before laparoscopy, you are allowed to eat:
- liquid lean porridges;
- vegetable low-fat soups, pre-blended in a blender.
Dinner is strictly not recommended. Since laparoscopy is performed in the morning, patients do not drink water or food. The bladder and intestines should be empty. Often the night before, an enema is given in the gynecology department.
If there is time to prepare, patients undergo the following tests:
- UAC;
- Ultrasound of the pelvis;
- fluorography;
- cardiogram;
- blood group and Rh factor, hepatitis, bilirubin, glucose and venereal diseases, coagulation.
It is advisable to provide the gynecologist with an outpatient card or report chronic diseases. After receiving the test results, the doctor evaluates the feasibility of laparoscopy. In the absence of contraindications, a specialist in the field of surgery and gynecology appoints the day of the operation, determining its volume. The anesthesiologist also begins work, selecting the appropriate type of anesthesia and drug.
Preoperative preparation includes:
- Premedication. An hour before laparoscopy, an anesthesiologist comes to the patient’s room. He administers medications that will prevent complications after surgery and improve the course of anesthesia.
- Catheter installation. Directly in the operating room, the patient is administered intravenously the previously prescribed drugs. The condition is constantly monitored using special equipment. Data on blood hemoglobin saturation and heart activity are displayed on the monitor screen.
- Administration of anesthesia and relaxants to relax muscles. The first drugs provoke sleep, and the second ones simplify the installation of an endotracheal tube in the trachea. After these manipulations, the view of the abdominal cavity improves. Thanks to relaxants and anesthesia, laparoscopy in gynecology becomes effective, painless and safe.
- Connection of the anesthesia machine and endotracheal tube. After these steps, the operation begins. Artificial ventilation and administration of drugs to maintain anesthesia are available.
Pre-preparation for laparoscopy in gynecology is exciting, but painless. The described manipulations take about 10 minutes. The attending doctor tells each individual patient how to prepare for laparoscopy.