The child has predominantly increased direct bilirubin (from 7.9 µmol/l) in diseases of the biliary tract with difficulty in the flow of bile into the intestines. This happens when there is a blockage with a stone, tumor or a ball of worms. Both types of bilirubin, but more direct, increase with active inflammation (infectious hepatitis) and severe consequences of chronic liver diseases (cirrhosis), poisoning. The indirect part increases with the destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis).
To normalize the indicators, it is necessary to accurately establish the cause. To improve liver function, it is recommended to eat a diet limiting fatty, fried foods, and processed foods. Droppers, enterosorbents (Atoxil, Polysorb), and hepatoprotectors (Essentiale) help cleanse the blood.
Direct bilirubin is elevated in a child: where to look for the cause
If a child has predominantly elevated direct bilirubin, the most common cause is the following diseases:
- hepatitis of viral origin;
- cytomegalovirus, herpetic infection;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- parasitic and helminthic infestations;
- poisoning by toxic substances, medications;
- inflammation of the bile ducts with impaired bile outflow;
- liver tumors;
- congenital enzymopathies (changes in the activity of enzymes involved in pigment metabolism);
- stone blockage or cicatricial narrowing of the bile duct, developmental abnormalities;
- hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) in newborns.
Normally, direct (bound) bilirubin is not detected in the blood or its concentration is low. The growth of this part of the pigment occurs in two ways:
- bile does not pass into the intestines due to obstacles in the path of its movement (blockage with a stone, accumulation of worms, tumor);
- due to active inflammation or its complications, liver cells are destroyed (infections, poisoning).
In the first case, predominantly direct bilirubin increases, and in the second, both parts – bound and unbound – increase.
We recommend reading about how bilirubin is exchanged in the body. From the article you will learn about the mechanism of bilirubin formation, neutralization in the liver, excretion, metabolism of bilirubin in diseases, causes of bilirubin metabolism disorders. And here is more information about normal indicators and deviations of bilirubin in men.
Why is total bilirubin increased in a child?
Total bilirubin can be increased in a child due to direct bilirubin in liver diseases and blockage of the bile ducts, as well as increased destruction of red blood cells when the indirect part grows.
Main reasons:
- acute and chronic hepatitis;
- diseases of the intrahepatic bile ducts and extrahepatic ducts;
- hemolytic anemia;
- severe infections with blood poisoning (sepsis).
If indirect is changed
Indirect bilirubin is formed from hemoglobin in red blood cells and changes when these cells are destroyed. Diseases with a predominant increase in the indicator:
- hemolytic anemia;
- extensive hemorrhage;
- malaria;
- sepsis;
- liver dysfunction when indirect does not bind to glucuronic acid (for example, toxic, drug-induced hepatitis);
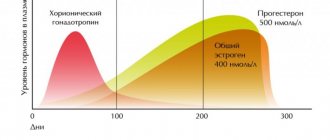
- physiological (natural) jaundice of a newborn on days 2-6, when the enzyme that converts indirect to direct does not yet work;
- hereditary enzyme deficiency – Gilbert, Crigler-Najjar syndrome.
Pathogenesis of hemolytic jaundice
How is elevated bilirubin diagnosed in a child at 2 months, a newborn and up to a year?
Bilirubin is considered elevated in a newborn baby, at 1 and 2 months, up to a year, when the indicators indicated in the table are detected. All values are in mmol/l.
| Child's age | Direct bilirubin | Indirect bilirubin | Total bilirubin |
| From birthday to 14 days | 5,7-12,1 | 20-180 | 1 day – 24-150, 2-5 days – 60-200, 5-14 days – 26-200 |
| From 14 days to 2 months | 0-5,2 | 3,4-15,3 | 3,4-20,5 |
| From 2 months to a year | 0-3,4 | 3,4-18,4 | 3,4-21 |
For analysis, blood is taken from a vessel on the heel or head of a newborn, then any clearly visible peripheral vein can be used. The material must be given 1.5-2 hours after feeding. Direct bilirubin is not determined in isolation, since to make a diagnosis it is necessary to know other blood parameters:
- total and indirect bilirubin;
- liver transaminases (AST, ALT);
- alkaline phosphatase;
- total protein and albumin;
- glucose;
- cholesterol;
- creatinine
To clarify the diagnosis, tests are performed for infections (viral hepatitis antigens, herpes, cytomegalovirus, mononucleosis). The condition of the liver is assessed using ultrasound.
Norms
The very first test for a newborn is a blood test taken from the umbilical cord, which determines the content of various substances in the baby’s body, including liver pigments. Due to the fact that blood cell renewal occurs continuously, bilirubin will always be present in the blood.
At birth, liver pigment levels will always be higher than in adults, as well as in children who are several months old. This occurs due to the increased breakdown of hemoglobin, which is part of the fetal red blood cells. After birth, normal hemoglobin is synthesized in the baby's body.
The concentration of bilirubin in the blood depends on several factors:
- The date at which the baby was born. Premature babies are at higher risk of developing jaundice.
- Features of pregnancy. Fetal hypoxia leads to an increase in liver pigment.
- Late excretion of original feces - meconium.
- Hunger in an infant or exposure to low temperatures leading to hypothermia.
At full-term birth, bilirubin levels are 50-60 mmol/l, but already on the second or third day this value increases sharply. In this case, values that exceed 256 mmol/l are considered critical.
In babies who were born on time, normal indicators have the following values::
- On the first day – up to 137 mmol/l.
- 48 hours after birth – up to 205 mmol/l.
- On days 3-5 – no more than 256 mmol/l.
- A week later – no higher than 256 mmol/l.
In premature infants, bilirubin testing is different. Exceeding the concentration of 171 mmol/l poses a serious threat to the health of the infant. On days 14-21 after birth, bilirubin in the blood drops, and under normal circumstances its value does not exceed 20.5 mmol/l.
When bilirubin levels exceed the maximum permissible value, this indicates the development of jaundice, pathological or physiological, which requires monitoring the baby’s condition, and in case of pathology, timely treatment.
How is it determined that bilirubin is elevated in a child from 2 to 10-15 years old?
Elevated bilirubin in a child from 2 to 10-15 years old is considered to be indicators (µmol/l) in the intervals indicated in the table.
| Age range | Total bilirubin | Direct bilirubin | Indirect bilirubin |
| 2-3 years | 3,4-17,1 | 1-7,5 | 2,4-19 |
| 4 years - 5 years | 3,4-17,5 | 0-5,9 | 3,4-11,6 |
| 6-7 years | 3,5-17,3 | 1-6,5 | 2,5-11,9 |
| 8-10 years | 3,4-17,1 | 0-7,9 | 3,4-13,1 |
| 12-15 years | 3,4-14,1 | 0-7,5 | 3,4-12,1 |
When using methods for determining bilirubin in the laboratory, different reagents may be used, so the normal values may differ slightly from those given.
How to suspect abnormalities yourself
The most specific sign of increased bilirubin is a yellowish coloration of the skin and sclera of the eyes. When the bile ducts are blocked, the pigment does not enter the intestines, so the stool is lighter, and the main part of the direct bilirubin is excreted by the kidneys and the urine becomes the color of beer. The child may also have signs of intoxication (poisoning of the body):
- elevated temperature;
- body aches, bone pain;
- nausea, vomiting;
- general weakness, lethargy;
- lack of appetite;
- itching and scratching of the skin;
- belching;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
In infants, high rates may be manifested by sluggish breastfeeding, frequent regurgitation, crying, sleep disturbances, bloating, and irregular bowel movements. A severe form of bilirubin intoxication is manifested by a monotonous cry, impaired concentration of gaze, followed by signs of brain damage:
- attacks of excitement;
- neck muscle tension;
- muscle spasm of the limbs;
- convulsions.
At this time, irreversible destruction of brain neurons occurs. After 2-3 months, the child may experience a deceptive improvement in his condition, and by six months, cerebral palsy, deafness, and impaired physical and mental development are discovered.
Watch this video about the causes, symptoms and treatment of jaundice in children:
Is increased direct bilirubin dangerous in children and general
Of all types of bilirubin, elevated direct bilirubin in children is less dangerous, since it does not have the ability to accumulate in the body. Total bilirubin is the total amount of bound and unbound pigment.
The second part (free, indirect) is very toxic specifically for newborns, as it passes through the cell membrane. As a result, metabolic processes and energy production are disrupted, and brain cells are destroyed (bilirubin encephalopathy).
Direct and total bilirubin at high levels indicate the presence of a disease in the child, so it is imperative to find the cause and undergo treatment.
Newborn blood level
Bilirubin in a recently born child is always higher than in an adult. Next, we will tell you why a child has increased bilirubin in the blood and what this means. In the first month of life, bilirubin is usually elevated and this phenomenon is called physiological jaundice. Why does this happen, you ask? The answer is simple, in the fetus the transfer of oxygen is carried out by fetal hemoglobin, which after birth stops functioning and is replaced by regular hemoglobin. Thus, in the first month of life, the breakdown products of fetal hemoglobin are removed from the child’s body.
As you may have noticed, newborns have their own standards for this indicator. If a deviation of the indicator from the generally accepted value is detected, then doctors closely monitor this condition and, if necessary, prescribe treatment. If the bilirubin level is slightly increased, then we speak of physiological jaundice, which goes away on its own. Serious deviations from the norm of this indicator indicate the presence of a pathological process.
Extremely high levels of bile pigment occur when:
- conflict regarding blood type and rhesus between mother and child;
- hepatitis and gallbladder diseases;
- intestinal obstruction;
- genetic diseases;
- lack of albumin;
- taking medications by the mother during pregnancy.
The reasons for a slight deviation of the indicator from the norm can be very different:
- difficult pregnancy;
- the presence of extragenital diseases in the mother;
- complicated childbirth, the use of obstetric aids, which led to trauma to the baby;
- hypoxia in the antenatal and intranatal period;
- premature birth.
It should be understood that even a slight deviation from the norm requires specialist supervision. A huge amount of bilirubin is poisonous for a newborn. Untimely treatment can result in encephalopathy, which is accompanied by decreased hearing acuity and retardation in neuropsychic development.
If bilirubin is higher than normal in a child, how to stabilize it
To normalize bilirubin levels in a child’s blood, if they are higher than normal, it is necessary to influence the underlying disease. Children, regardless of the reason for the increase in indicators, are prescribed nutrition to improve the flow of bile and restore digestion. Drugs are used to cleanse the blood of excess pigment.
Diet
For newborns, the best type of nutrition is breast milk. It is necessary to feed the child as often as possible - 8-12 times a day without stopping at night. You need to increase your water intake by 10-20%. For young children and schoolchildren, the diet should include:
- vegetable soups;
- side dishes of boiled vegetables and cereals (buckwheat and oatmeal, red and black rice are healthy);
- steamed meatballs, steamed cutlets from lean meats and fish;
- non-sour cottage cheese;
- fresh fermented milk drinks;
- juice from currant berries;
- rosehip decoction;
- dried fruits compote;
- baked apples;
- protein steam omelette with added herbs;
- dried or yesterday's bread;
- biscuits, a little marmalade, honey.
Fatty meat and lard, cakes with butter cream, canned food, smoked foods, sausage, semi-finished products, and sharp cheese are completely excluded from the diet. Do not fry foods or stew with butter.
Schoolchildren and adolescents should be warned against consuming carbonated drinks, chips, and hot crackers even after bilirubin has normalized for at least 1 month. When preparing food, do not use vinegar, mustard, hot pepper, garlic and fresh onions. Limit tomatoes, eggplants and sour fruits.
Drugs
If jaundice appears, the child is hospitalized in a hospital. First (regardless of the underlying disease), the blood is cleansed from excess bilirubin using droppers with solutions (Glucose, Reopoliglyukin) and sorbents (Atoxil, Enterosgel, activated carbon).
If the outflow of bile is difficult, choleretic agents (Holosas, Chofitol), herbs that enhance the movement of the contents of the bile ducts can be used. In case of infection, antiviral or antibacterial therapy is prescribed. To improve liver function, Essentiale and Ursofalk are used. Enzymes (Mezim, Festal) help normalize digestion.
We recommend reading about what diet to follow if you have high bilirubin. From the article you will learn about the principles of a diet for high bilirubin, foods that increase and decrease bilirubin in the blood. And here is more information about how to donate blood for bilirubin - on an empty stomach or not.
An increase in direct bilirubin in children is associated with damage to liver cells or impaired bile outflow. A deviation can be suspected by yellowing of the skin, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting or regurgitation in the newborn.
Treatment
It is impossible to try to figure out on your own what kind of therapy should be carried out, even if direct bilirubin is slightly elevated. After all, it is impossible to get rid of a problem until its cause is determined.
It is also important to carry out detoxification measures. They include a special diet aimed at reducing the load on hepatocytes and enzymes responsible for removing toxins. In a hospital setting, infusion-transfusion therapy is often performed. It is designed to change the composition and volume of blood, intracellular and intercellular fluid. Only a doctor can choose the solution that will be administered intravenously. In some cases, a glucose solution, a mixture of amino acids, saline and other drugs may be prescribed.
Sometimes it is recommended to carry out phototherapy, which helps destroy toxic bilirubin. To reduce intoxication, doctors often prescribe activated carbon and gels designed to remove toxins, for example, Enterosgel.
So, if, as a result of intensive destruction of blood cells, it turns out that direct bilirubin is increased, the reasons for such hemolysis must be established without fail. First of all, you need to figure out what exactly led to this. After all, it will be necessary to treat not the consequences, but the cause of hemolysis. For this purpose, glucocorticoid hormones are used, for example, the drug Prednisolone. Once the cause is eliminated, the bilirubin level will decrease on its own.
If problems are caused by disruption of the process of bile outflow, then drug intervention cannot be avoided. In such cases, doctors prescribe a treatment regimen, which may include drugs such as “Ursosan”, “Febihol”, “Ceruglan”, “Ermital”, “Papazol”, “Gepabene”, “Analgin”. Therapy is aimed at stimulating the flow of bile and pain relief. But you should not use medications without the consent of your doctor. Indeed, in some cases antibacterial or antiparasitic therapy is necessary.
Hepatitis is often the cause of jaundice. In such a situation, it is necessary to treat the liver. For this, the following drugs can be prescribed: “Essentiale”, “Methionine”, “Heptral”.