What are hormones?
Hormones are biologically active substances that are produced by endocrine glands. They are transported throughout the body in the bloodstream to ensure its proper functioning. The concentration of these substances in a woman depends on the following factors:
- Times of Day.
- Age.
- Day of menstruation.
The result of the study depends most on the last indicator. Therefore, a woman should understand which day of the cycle is best to undergo the test. This is especially important during pregnancy planning.
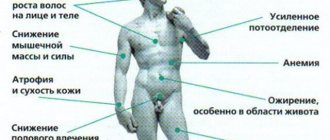
Symptoms of deviation from the norm
There are many symptoms that appear when hormonal levels are disrupted, so the following list includes only the main ones:
- hair growth of the skin according to the male type;
- hoarseness of voice;
- lack of sexual desire;
- fertility disorders;
- memory impairment;
- fatigue;
- drowsiness;
- headache;
- depression;
- memory loss;
- obesity or weight loss;
- swelling;
- pallor;
- dizziness.
More precisely, the symptoms can be traced depending on the woman’s age. In girls, before the onset of hormonal levels and its stabilization, the failure manifests itself as follows:
- There is no menstruation in a girl over 16 years of age;
- narrow pelvis, breasts do not grow;
- excess weight;
- stretch marks on the stomach and thighs;
- acne on the face.
The appearance of these signs is not a reason to panic. The girl and her mother need to see a gynecologist. The doctor will conduct an examination and, if necessary, prescribe laboratory tests. Simple tests will determine the cause of the failure, after which the doctor will select corrective compounds.
Disorders in women of reproductive age manifest themselves as follows:
- appearance of facial hair;
- hump;
- swelling;
- increase in heart size, pain in the chest;
- subcutaneous fat accumulates in the upper body, diets and exercises show poor results;
- vomit;
- depression;
- soreness of the mammary glands.
The main symptom of a lack of female sex hormones is amenorrhea - the absence of menstrual bleeding in a woman. There is often a deterioration in blood clotting, and wounds on the skin do not heal well. The most dangerous are hormonal imbalances after a miscarriage or termination of pregnancy. These processes are not typical for the female body, so restoring hormonal levels can be difficult. Often the violation becomes the cause of oncological processes.
A woman's hormonal levels during menopause should change systematically; normally, this process lasts for several years and does not manifest itself intensively. Among the possible symptoms of this process:
- loss of breast firmness;
- frequent urination;
- increased blood pressure;
- problems with blood vessels;
- increased sweating;
- headache.
Gynecological diseases associated with hormonal imbalance have many causes and symptoms. To eliminate the provocateur factor and treat the disease, you need to see a doctor, undergo an examination and determine treatment tactics. Only this scheme will ensure good results and recovery.
General indications for checking hormonal levels
Specialists refer the patient to this event for the following reasons:
- Irregular menstrual bleeding.
- Sudden, causeless weight loss or weight gain.
- Repeated miscarriages.
- Inability to conceive a child.
- Diseases of the mammary glands.
- Acne and acne.
- Excess body hair.
- Improper functioning of the kidneys.
Preparatory recommendations
For the analysis to give the most accurate results, the patient must:
- Avoid eating 12 hours before the procedure.
- Do not consume alcohol or nicotine three days before the event.
- Visit the laboratory in the morning and be calm.
- Do not drink water, brush your teeth or chew gum.
- Avoid physical and mental stress.
- Submit the material on the correct day of menstruation.
- Do not carry out the procedure if there are inflammatory processes in the body.
- Do not take pills ten days before the procedure.
Note! The timing of taking medications must be discussed with your doctor.
Statistical reporting
Statistical reports must be submitted under any taxation regime, but only if your company is included in the sample of the regulatory authority, of which you will be notified in writing. Having received a written request from the statistical authorities for information, forms and instructions for filling them out, you need to prepare report No. 1-IP for the year before March 1 of the current period. The presence of your enterprise in the statistical sample can be monitored on the official website of the statistical office.
On what days of the cycle should I take tests for the FSH hormone?
According to the generally accepted standard, the amount of follicle-stimulating hormone should be checked from 3 to 8 or from 18 to 22 days of the menstrual cycle. A man can undergo such an analysis at any time. The material is collected only on an empty stomach, otherwise the result will be unreliable.
In the female body FSH:
- Provokes the growth and development of follicles in the ovaries.
- Promotes estrogen production.
- Ensures the growth of the uterine endometrium.
The maximum concentration of follicle-stimulating substance is recorded during the ovulation period.
In the male body, the main task of FSH is to stimulate the development of the vas deferens. Thanks to this substance, the level of testosterone in the blood increases, which, in turn, ensures the maturation of sperm.
How long does it take to prepare results?
Each laboratory may have its own deadline for issuing blood test results, but most often they are one day for the entire range of female hormones.
This time interval is needed for determination using the immunochemiluminescence method. Blood taken from a vein is separated into plasma and cells in the laboratory. Fibrinogen is removed from the plasma and serum is obtained. Then antibodies that are specific to the hormone being tested are added to the test tube. They are pre-treated with an enzyme that causes a glow reaction.
Blood sampling scheme
After the formation of immune complexes, the resulting light quanta are recorded by the apparatus. Based on the data obtained, the concentration of the substance in the blood is determined. This entire procedure takes about 3 hours. Therefore, if necessary, the analysis can be performed urgently (for example, when diagnosing an ectopic pregnancy).
Female luteinizing hormone: what day to take the test
LH is given in the period from 3 to 8 or from 19 to 21 days. A prerequisite is blood sampling on an empty stomach, abstaining from food before the event - 13 hours.
Luteinizing hormone is required for:
- Follicle maturation.
- Proper estrogen production.
- Ensuring ovulation.
- Formations of the corpus luteum.
In the male body it provides:
- Globulin synthesis.
- The relationship between sex hormones.
- Openness of the seminal ducts to testosterone.
The last function is especially important, since a man’s ability to impregnate a girl depends on it.
In women, the normative LH level is closely related to the phase of menstruation. The maximum level is allowed for the ovulation period, after which the levels decrease and remain so until the next ovulation. These changes provide the corpus luteum with the conditions to function in the ovaries.
The highest concentration of luteinizing substance is permissible one day before the onset of ovulation. Such indicators are recorded for another day, after which they gradually drop.
Important! During ovulation, the LH level is ten times higher than the level characteristic of the non-ovulatory period. In case of pregnancy, the concentration of the substance is minimal.
If a woman suspects infertility, the doctor must compare follicle-stimulating hormone with LH. According to generally accepted standards, before the onset of bleeding it is equal to one, 14 months after the first menstruation - 1 - 1.5, after two years of menstruation and before menopause - 1.4 - 2.01.
Features of analysis and preparation for laboratory research
The doctor will refer you to determine the concentration of a specific sex hormone, taking into account the day of the cycle and the date of ovulation.
| Hormone | On what day of the cycle should I take it? |
| Progesterone | On the 22nd (with a 28-day cycle) or on the 28th (with a 35-day cycle) |
| Prolactin | Any day of the cycle |
| Estradiol | On the 7th |
| Estrogens (general) | On the 4th, repeated on the 21st |
| LH | On 3-8th or 18-22nd |
| FSH | On 3-8th or 18-22nd |
| Testosterone | On the 6th or 7th |
| hCG | Delay of menstruation up to 1 day to determine pregnancy |
They take a hormone test in a specialized laboratory. Preparation for gynecological tests for hormones involves following the following rules:
- Venous blood sampling for gynecological hormone tests is done on an empty stomach.
- You need to donate blood for analysis in the morning. The level of active substances fluctuates throughout the day, the “morning” value of active substances is considered the most accurate.
- Be sure to take into account the doctor’s recommendation on which day of the cycle to take the test.
- Before the study, exclude active loads.
- The day before blood sampling, smoking and drinking alcohol are prohibited.
- Check with your doctor for how many days you need to abstain from intimacy.
- A week before the test, stop using hormonal medications.
Common reasons for diagnosing hormone levels in women include infertility and menstrual irregularities. For men, it is most often necessary to know the level of estradiol in case of female-type fat deposition and sexual weakness. Enlarged mammary glands and fluid discharge from the nipples necessitate prolactin testing. There are also specific indications for each hormone.
Estradiol
A blood test is needed for the following conditions:
- early puberty in girls;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- irregular menstruation;
- alternating delays and heavy bleeding (dysfunctional);
- decrease or increase in menstrual flow;
- determining the time of menopause, the causes of hot flashes, cessation of menstruation, night sweats, insomnia;
- monitoring the course of pregnancy in the early stages;
- during the artificial insemination program (observation of follicle maturation).
It is very rarely prescribed as an independent test; most often it is necessary to study the content of all female sex hormones.
Progesterone
The study is recommended if:
- threats of abortion;
- pain and bleeding, including dysfunctional;
- ectopic attachment of the fertilized egg;
- suffered a miscarriage in the past;
- diseases of the endocrine organs (pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands), autoimmune pathologies (antibodies to one’s own tissues), infections during pregnancy;
- suspicion of cycles without ovulation;
- cessation of menstruation;
- post-term pregnancy;
- breast cancer tumor.
A test for this hormone is needed to identify the cause of the lack of ovulation and impaired sperm production. It is recommended when planning pregnancy and for diagnosing the time of puberty and menopause.
The analysis is indicated in case of suspicion of the following diseases:
- developmental disorders of the testicles and ovaries;
- early and late appearance of secondary sexual characteristics;
- tumor process, cysts of the ovaries, pituitary gland, testicles, hypothalamus;
- irradiation, chemotherapy of tumors;
- genetic abnormalities associated with the functioning of the gonads.
Due to the fact that there is a rhythmic release of the hormone by the pituitary gland, you need to undergo 2-3 tests.
Its level needs to be known to determine:
- hormonal activity of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, testes, ovaries;
- causes of puberty disorders;
- time of menopause;
- disease that caused uterine bleeding;
- hormonal imbalance in polycystic ovary syndrome;
- day of optimal conception (date of ovulation).
Luteinizing hormone: normal in women
In men, reasons for research include abnormalities in sperm analysis, low libido and erectile dysfunction.
Prolactin
The analysis is needed for signs of a pituitary tumor - blurred vision, headache, discharge from the nipples in men and non-pregnant women. It is prescribed to patients with the following disorders:
- infertility;
- dysfunctional bleeding;
- reduction in blood loss during menstruation, delay;
- a feeling of fullness in the mammary glands, compaction, increase in their size;
- post-term pregnancy;
- breastfeeding problems after childbirth.
On what days of the cycle should I take tests for the hormone prolactin?
Calculating the quantitative indicator of this substance will be rational when donating blood during the first or second phase of the cycle. The study requires standard preparation: do not eat 12-13 hours before the procedure, donate blood in the morning on an empty stomach. A prerequisite is to sit quietly for forty minutes before visiting the laboratory assistant. Prolactin reacts sensitively to emotional arousal, so with the slightest surge it can show the wrong level in the analysis.
Prolactin is very important for a woman’s body: it ensures ovulation and stimulates the development of lactation after the birth of a child. In addition, it greatly affects the concentration of FSH. When a woman is pregnant, prolactin prevents the formation of follicles, which is normal.
If a non-pregnant woman experiences unusual spikes in prolactin concentrations, she will not ovulate.
In the female body, prolactin has different concentrations depending on the time of day. During night sleep, its levels are increased. In the period after waking up in the morning and before lunch, it drops sharply. After 12-14 hours of the day, the indicators “creep” up again. The concentration of prolactin in the luteal phase is higher than in the follicular phase.
Normal sex hormones in women
Hormonal levels in women change during different periods of life and every month. Problems arise if there is a dysfunctional disorder in the functioning of, for example, the thyroid gland, or the main center that regulates the activity of the endocrine system - the pituitary gland and hypothalamus. Changes that have begun are sometimes irreversible.
Changes in hormonal levels in women during the cycle.
- The first significant change occurs during the maturation period.
- With the onset of intimate relationships, the ratio of hormones also changes.
- With the onset of pregnancy, the body hormonally prepares for bearing and giving birth to a child. In the 1st trimester there is a significant increase in progesterone.
- After childbirth, the hormone ratio changes again, ensuring the onset of the lactation period.
- With age, reproductive function declines, and this again causes changes. The production of the hormone estradiol stops, the concentration of calcitocin and progesterone decreases.
- There are also seasonal and monthly fluctuations associated with menstruation, when the quantitative content of estrogen and progesterone changes.
Gynecological tests for hormones should be interpreted by the doctor who referred you for laboratory testing. A deviation in the concentration of a substance indicates certain pathologies:
- LH ensures the normal functioning of the female reproductive system. Its high content is associated with hypofunction or polycystic ovaries, early menopause. Injuries, tumors, unbalanced nutrition, and physical overload cause a decrease in the amount of the substance.
- FSH is responsible for the secretion of estrogen and ovarian health. Delayed puberty, inflammatory processes in the genital organs, frigidity, infertility indicate a lack of this hormone.
- Estradiol is the main sex hormone in women. During menopause and menopause, its amount decreases sharply. The lack of this substance in women of childbearing age causes disturbances in the uterine cycle, dysfunction of the uterus, fallopian tubes, and deviations in the development of the genital organs.
- Prolactin is responsible for the functioning of the mammary glands, ensures their formation and growth in girls, and stimulates lactation in women in labor. A high content of this substance indicates ovarian dysfunction, autoimmune pathologies, and thyroid pathologies.
An increase in prolactin levels is associated with stress, injuries in the chest area, vitamin deficiency, and renal failure. An increase in prolactin levels occurs after abortion. An excess of the substance provokes disruptions in the uterine cycle, infertility, the formation of cysts, malignant tumors in the mammary glands, and frigidity.
A reduced level of prolactin is recorded during post-term pregnancy, as a result of taking certain pharmaceutical drugs.
- High levels of testosterone (the main sex hormone in men) cause skin problems. The norm for women of childbearing age is only 0.290-1.67 nmol/l. But to study hormonal status, testosterone concentration must be determined. Deviations from normal values can cause reproductive dysfunction in a woman.
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland and is responsible for the full functioning of the thyroid gland. The level of sex hormones depends on the amount of this substance. Metabolic processes in a woman’s body, which are controlled by the thyroid gland, provide the possibility of conceiving and bearing a child.
- Progesterone is the hormone of pregnancy; its normal course depends on it. In non-pregnant women, its high content provokes excess weight.
There are many gynecological hormone tests available. It is not always necessary to prescribe everything. After clarifying the clinical picture, the doctor makes a referral. To obtain reliable results, it is important to adhere to the rules of preparation for laboratory tests. To prescribe and interpret tests, contact only qualified specialists.
Women are characterized by changes in the amount of sex hormones produced. This is due to the specific phase of the menstrual cycle:
- Follicular. The beginning refers to the 1st day of menstruation, and the end refers to the formation of a dominant follicle, i.e. until about 14 days.
- Ovulatory. This includes a period of 3 days after the dominant follicle leaves the egg. This is 14-16 days.
- Luteal. Includes the time from ovulation to the next menstruation, i.e. from 16 to 28 days.
Before the onset of puberty, the balance of FSH and LH is 1:1. As you grow older, this proportion gradually becomes 1:1.5, i.e. the amount of luteinizing agent becomes greater. This ratio remains in the normal state of health of a woman until the onset of menopause - the FSH norm in women is approximately 1.5 times less than the amount of LH.
| Hormone | Amount, µU/ml | ||
| Follicular | Ovulatory | Luteal | |
| FSH | 3-10 | 10-46 | 1,4-7 |
| LH | 2-15 | 24-151 | 2-16 |
Hormone progesterone
| Amount, nmol/l | |||||
| Women from 18 to 90 years old | |||||
| Follicular | Ovulatory | Luteal | Climax | ||
| 0,3-2,2 | 0,5-9,4 | 7,0-56,6 | Less than 0.6 | ||
| Pregnant | |||||
| 1st trimester | 2nd trimester | 3rd trimester | |||
| 8,9-468,4 | 71,5-303,1 | 88,7-771,5 | |||
Estradiol
| Hormone | Amount, pg/ml | ||||
| Follicular | Ovulatory | Luteal | Menopause period | Pregnancy | |
| Estradiol | 57-227 | 127-476 | 77-227 | 19,7-82 | Variable from 210 to 26,960 |
When analyzing the hormone testosterone in women, 2 types are examined: total and free. The first indicates the level of this substance, associated and not associated with protein transport. The latter indicator is indicated by free testosterone. The total level is 0.26-1.3 ng/ml. The amount of free testosterone depends not on the phase of the cycle, but on the age of the woman.
| Hormone | Amount, pg/ml | |||
| Up to 20 years | 20-39 years old | 40-59 years old | Over 60 years old | |
| Testosterone | 0,13-3,09 | 0,13-3,09 | 0,13-2,6 | 0,13-1,8 |
Prolactin
The permissible level of the hormone prolactin is determined by clinics using individual methods, so even the units of measurement are different. In general, an amount from 4 to 33 ng/ml is considered normal. The number changes during each specific phase of the menstrual cycle. For pregnant women, it is normal for the hormone prolactin to have a high level: its value can range from 34 to 386 ng/ml, and it increases gradually with the development of the fetus.
Hormone DHEA
The abbreviation DHEA is the name for the steroid hormone dehydroepiandrosterone. In women, it is produced by the ovaries, but only in an amount of 5%. The remainder is synthesized by the adrenal glands. For people under 35 years of age, the level of this substance varies from 2660 to 11200 nmol/l. In each trimester, a hormone test in women should show the following DHEA values:
- in 1 – 3.12-12.48 nmol/l;
- in 2 – 1.7-7.0 nmol/l;
- in 3 – 0.86-3.6 nmol/l.
On what day of the cycle are tests for the hormone estradiol taken?
Blood sampling to test this substance is performed on any convenient day. Participates in the production of estradiol:
- Follicle.
- Corpus luteum of the ovary.
- Adrenal glands.
- Adipose tissue under the influence of prolactin, LH and FSH.
For women, estradiol plays a very important role - it regulates menstruation and egg maturation.
The ovulation phase occurs approximately within a day and a half after the maximum release of estradiol into the blood. After this, the level of this substance gradually drops, and after a while there is no longer such a strong surge. Then estradiol levels decrease again until the onset of new ovulation.
The individual entrepreneur is clean before the tax authorities
The chosen taxation regime dictates the number and timing of both the tax payments themselves and the submission of information about them.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION! The deadlines for paying taxes and the deadlines for tax reports are legally different dates; they may not always coincide.
The most voluminous “package” of reports during the year must be submitted to businessmen who adhere to the general tax regime. Using other modes, you can reduce your tax burden and simplify communication with regulatory authorities.
The laws of the Russian Federation offer entrepreneurs a choice of 5 tax payment options.
- The general system is OSN.
- “Simplified” – simplified tax system.
- “Imputation” – UTII.
- Agricultural system – Unified Agricultural Tax.
- Patent system – PSN.
IMPORTANT! If there is a combination of different systems, then each of them must be accompanied by its own separate accounting.
Declarations for different regimes
Each tax system provides for its own type of declaration, submitted to the Federal Tax Service at one time or another.
- On OSN 3 types of tax returns are submitted:
- 3-NDFL – sums up the results of the year; must be submitted before the beginning of May of the following reporting year;
- 4-NDFL – registers income; submitted no later than 5 days after the end of the month marked by the first income;
- VAT – quarterly report; rented until the 20th day of the month opening a new quarter.
- The simplified tax system provides for a corresponding declaration to be submitted annually before April 30 of the reporting year. If no activity was carried out, a “zero” report must be submitted.
- UTII requires a quarterly declaration, the deadline of which is the 20th day of the beginning of the next quarter.
- The Unified Agricultural Tax Service proposes to report on the results of the year, submitting reports a month earlier than the simplified tax system (by March 31).
- PSN does not imply a tax return.
Don't forget about KUDIR!
A book of income and expenses must be kept by all entrepreneurs, except those working under “imputation” (they must register significant physical indicators). Failure to obtain this book may result in a fine.
The KUDIR must be stitched and numbered, the individual entrepreneur keeps it at home. There is no need to certify it since 2013.
Entrepreneurs using the Unified Agricultural Tax can maintain KUDIR both in paper and electronic form:
- the hard copy must be certified by the signature and seal of the tax authorities before the start of maintenance;
- Electronic accounting must be similarly certified annually before the beginning of April of the following year.
What else should I submit to the Federal Tax Service?
What documents and when should be submitted to the Federal Tax Service, see Table 1.
Table 1
| № | Information | Periodicity | Deadlines |
| 1 | List number of employees | At the end of the year | Until 20.01 next year |
| 2 | Certificates 2-NDFL | At the end of the year | Until the beginning of April next year |
| 3 | Appendix to certificates 2-NDFL (register of income of individuals) | See point 2 | See point 2 |
| 4 | Report 6-NDFL (introduced in 2020) | Quarterly | Until the end of 1 month of the next quarter |
Progesterone hormone: on what days is the test taken?
The most accurate indicator of progesterone is obtained when blood is taken from days 18 to 22 of the cycle. The production of this substance involves the corpus luteum and placenta (in pregnant women). Progesterone is responsible for preparing the uterus to receive and store a fertilized egg.
Indications for progesterone testing
- Possibility of ectopic pregnancy.
- Threat of spontaneous miscarriage.
- The need to calculate ovulation when planning pregnancy.
- Assessment of the luteal phase in the treatment of infertility.
- Lack of menstruation in non-pregnant girls.
- Pathological activity of the corpus luteum.
- The need to control the placenta when carrying a child.
- Manifestation of cysts or tumor lesions of the ovaries on ultrasound diagnostics.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of the use of pharmaceutical progesterone products.
- Children with congenital adrenal disease.
- Children who are delayed in puberty.
What disorders require hormonal analysis?
Progesterone testing is important in situations where:
- uterine bleeding occurs;
- if menstruation occurs at different intervals;
- in the absence of the opportunity to give birth to a child.
This analysis is taken 22-23 days after the start of the menstrual cycle. It is used to monitor the condition of a pregnant woman in the third trimester of pregnancy.
Estrogen testing can help in the following cases:
- in the presence of infertility;
- if there are estrogen-dependent tumors in the body;
- if you have problems with excess weight.
Blood donation should occur on days 6-7 of the cycle. This study is also important if the patient is experiencing menopause.
When should you check your testosterone?
Available any day for both men and women. This substance is important for both sexes, but is considered a male hormone. In the female body, the ovaries and adrenal glands are responsible for its production.
High testosterone levels have serious consequences:
- Pathological ovulation.
- Threat of fetal development failure.
- Possibility of miscarriage.
The maximum level of testosterone is observed during the luteal period and ovulation.
For men, violation of acceptable testosterone levels is also very harmful: sperm lose activity and the ability to fertilize an egg.
Indications for the procedure
- Inability to get pregnant.
- Tumor lesions of the adrenal glands and ovaries.
- Rapid weight gain.
- Acne on the face.
- Uncharacteristic bleeding from the uterus.
- Irregular periods.
- Freezing of fetal development.
- Miscarriages.
- Development of endometriosis.
Time to Test DEA Sulfate
Produced by the adrenal cortex. Tested in men and women at any time. Refers to the male sex hormone system, but is equally important for both partners.
Indications for the procedure
- Delayed puberty.
- Checking the functioning of the adrenal glands.
- Rapid hair loss in women.
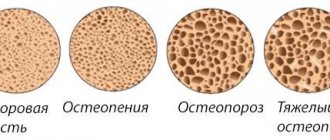
- Development of osteoporosis.
- Suspicion of an adrenal tumor.
- Formation of hormone-dependent tumors.
Useful videos about hormonal levels in women, normal indicators and recovery methods
The results of a study of hormones in the blood are an important stage of the examination, but to evaluate them it is important to understand the significance of the identified changes. Therefore, only a gynecologist can make a correct diagnosis, taking into account the clinical picture, ultrasound data, and other tests.
For healthy men and women during puberty, the indicators indicated in the table are typical.
| Hormones | Men | Women (depending on cycle phase) | ||
| first | ovulation | second | ||
| Estradiol, pg/ml | 7,6-43 | 12,5-165 | 86-500 | 44-210 |
| Progesterone, nmol/l | 1,5-6,3 | 0,3-2,2 | 0,5-9,5 | 7-57 |
| FSH, mIU/ml | 0,95-12 | 1,37-9,95 | 6,2-17,2 | 1,1-9,2 |
| LH, mIU/ml | 1,7-8,6 | 2,4-12,5 | 14-96 | 1-11,5 |
| Prolactin, µIU/ml | 86-325 | 102-495 | ||
It should be taken into account that depending on the reagents used, a particular laboratory may have slightly different standards. Therefore, the norm values are indicated on the results form. When re-diagnosis, it is advisable to undergo examination at the same institution.
Promotion
Estradiol levels increase in the following diseases:
- ovarian tumor, cyst;
- persistence (absence of rupture) of the follicle;
- high thyroid function;
- overdose of drugs containing estrogens;
- stimulation of ovarian function in case of infertility, artificial insemination.
In men, an increase in female sex hormones occurs with genetic disorders, tumors of the testicles and the adrenal cortex.
An increase in progesterone is associated with:
- cystic formations in the ovaries, tumor;
- proliferation of the adrenal cortex;
- impaired hormone excretion due to kidney disease;
- the use of medications similar to the hormone or blocking its receptors (the amount of free progesterone increases).
Follicle stimulating hormone increases as estrogen levels decrease. In men, the cause may be a violation of the formation of testosterone by the testicles due to anomalies in their development, neoplasms, or Klinefelter syndrome.
In women, high rates are typical for:
- the onset of menopause, including after surgery, radiation therapy, medication, premature;
- tumors of the ovary, pituitary gland;
- Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome;
- chronic alcoholism;
- autoimmune diseases, infections.
High LH values are found when:
- congenital genetic diseases;
- benign and malignant tumors of the gonads, hypothalamus, pituitary gland;
- encephalitis, meningitis;
- low hormonal activity of the thyroid gland;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- operations, injuries affecting the pelvic organs.
Excess prolactin occurs with a tumor of the pituitary gland, as well as inflammation in the hypothalamic-pituitary region, and vascular disorders.
LH hormonal norm
One of the reasons for high concentrations is an active rheumatic process, kidney and liver diseases.
The following may lead to an increase in the indicator:
- low levels of sex hormones, thyroid and adrenal glands;
- trauma, chest tumors;
- herpes in the mammary glands.
Level reduction
Low estrogen concentrations occur when:
- chromosomal diseases;
- impaired ovarian response to FSH;
- infectious, inflammatory, tumor process, radiation, trauma;
- poor functioning of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, liver;
- exhaustion.
Progesterone below normal is found in women with the following diseases:
- threat of miscarriage, post-term pregnancy, ectopic pregnancy;
- follicle persistence;
- dysfunctional bleeding;
- polycystic ovary syndrome.
A decrease in the content of pituitary hormones (FSH, LH and prolactin) is characteristic of insufficient release of GnRH by the hypothalamus, postpartum tumor damage to the pituitary gland. This also happens as a consequence of operations, infections, and vascular abnormalities. Their formation decreases with an excess of sex hormones in the blood, as well as an overdose of drugs for replacement therapy.
Study of thyroid-stimulating hormone levels
One of the most important hormones for humans, as it regulates the functioning of the thyroid gland. Under its action, the organ produces substances T3 and T4, which are closely related to the female and male reproductive system.
Indications for testing thyroid-stimulating hormone
- Diagnosis of thyroid function.
- Inability to conceive a child.
- Systematically low body temperature (maximum 35°C).
- Long-term depression.
- Impotence.
- Retardation of mental and physical development in children.
What is TSH, T3 and T4
The abbreviation TSH means "thyroid-stimulating hormone" . This substance is produced and synthesized by the pituitary gland, a gland in the brain. TSH is a regulatory hormone. Although TSH is not produced by the thyroid gland, it takes an active part in the activity of its hormones. When thyroid hormones are concentrated in the blood in smaller quantities, the TSH level increases, and when in larger quantities, it decreases (the feedback principle is activated). Thus, hormonal levels remain stable.
In addition to feedback from thyroid hormones, TSH levels are affected by the production of statins and liberins by the hypothalamus (another endocrine center of the brain). The hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid ligament provides mutual influence on each other and on the synthesis of active compounds. The main purpose of TSH is to control all working processes of the thyroid gland and regulate hormonal production.
T3 (triiodothyronine) and T4 (thyroxine) are thyroid hormones. These substances are produced by the thyroid gland. These hormones contain iodine in their composition. The thyroxine molecule contains four iodine atoms. When one of the atoms is separated, T3 is formed. The correct production of T3 and T4 depends on the concentration of iodine in the entire body.
Thyroid hormones are involved in many areas of the body's life. Most importantly, development and growth depend on them, and they also control energy metabolism.
The general functions performed by TSH, T3 and T4 in the body are colossal - these substances:
- carry out the production of proteins;
- regulate the synthesis of red blood cells;
- control the activity of the heart and blood vessels;
- regulate the metabolic process;
- with their participation, glucose is formed.
The hormones TSH and T4 together are responsible for:
- for general fat metabolism;
- normal and healthy growth of the body;
- production of vitamins A;
- for the state of the nervous system;
- for the condition of the auditory and visual organs;
- are responsible for adequate functioning of the gastrointestinal tract and menstrual cycle.
Let's look at each hormone in more detail.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
The TSH blood test is prescribed first if you need to donate blood for thyroid hormones. Thyrotropin is involved in all spheres of life of the human body.
Without the action of TSH it will become impossible:
- normal muscle activity;
- completeness of thought processes;
- supply of oxygen to tissue cells.
Thyrotropin is especially important for women. The pattern of its influence on reproductive functions is quite complex. To put it simply, we can say that it, together with thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), has an effect on the production of prolactin.
Prolactin is a hormone that is produced in the second half of the menstrual cycle: without its participation, the maturation of new eggs is impossible - and during pregnancy, the hormone supports the work of the corpus luteum - a temporary gland that helps the development and preservation of the unborn child during the first three months after conception. Prolactin also inhibits ovulation, preventing conception during pregnancy.
Thyrotropin is responsible for the proper absorption of iodine by the thyroid gland and the distribution of iodine throughout the body. It supports heat and glucose metabolism and takes part in the activation of metabolic processes. The hormone has an effect on the mental and nervous state of a person.
The TSH level is different at different ages and in people of different genders. Pregnancy also has its own normal indicators.
A thyrotropin test is prescribed when it is suspected that the functioning of the thyroid gland is impaired. In this case, the indications are usually considered in combination with thyroid hormones in order to understand at what level the pathological process occurs.
If the concentration of the substance exceeds the normal value, this means a decrease in thyroid function. Detection of a low level of thyrotropin concentration in the blood means the opposite - an increase in gland function.
Thyroxine (T4)
Thyroid hormone T4 (thyroxine) is the most active hormone of the thyroid gland - it is not surprising that T4 is produced by 90% of the total number of all hormones.
Thyroxine is formed from iodine and various amino acids in the thyroid gland. While in the blood serum, the hormone exists in two states: bound and free. The substance has a catabolic effect, stimulating the breakdown of fats and glycogen with the subsequent release of energy.
In women, the normal level of T4 in the body is much lower than in men - but during pregnancy, the production of the hormone increases.
Free T4 is usually taken for analysis, since its level does not depend on external influences on the body. It remains normal in any state of health - with the exception of diseases associated with the thyroid gland. Thanks to this property, free T4 analysis provides the most accurate information about the condition of the thyroid gland.
When you need to take thyroid hormones, a referral is usually given for TSH and free T4.
What does the thyroid hormone T4 affect?
Thyroxine takes an active part in the life of the body. Its main functions:
- activation of the thermoregulation center; stimulation of the heart and blood vessels;
- increasing the speed of the protein synthesis process; affects vitamin metabolic processes;
- acceleration of the metabolic process;
- ensuring the growth and functioning of every structure of the human body;
- lowering cholesterol levels.
An excess of T4 leads to the following consequences:
- weight deficiency (provided that the person does not intentionally lose weight);
- tachycardia;
- sleep disturbance – insomnia or frequent awakenings at night, restless and superficial sleep;
- absent-mindedness, inability to concentrate on anything;
- premature aging of the skin, the appearance of wrinkles even in young women;
- decreased brain activity, inhibition of thinking and reactions.
If the production of thyroxine does not occur in the required amount, the body’s activity decreases sharply, a loss of strength, general weakness, and apathy are observed. Even pregnancy does not occur due to a lack of T4.
Triiodothyronine (T3)
Triiodothyronine is a thyroid hormone, a growth hormone. Only 10% of the substance is formed directly in the thyroid gland. When it enters the bloodstream, T3 occurs with proteins and is transported to peripheral tissues. The hormone is still in a state of inactivity. It comes into action when this compound breaks down and the hormone enters a free state.
T3 regulates the rate of oxygen absorption by tissues and activates the production of sex hormones. Induces protein synthesis, increases the rate of bone growth.
The T3 norm ranges from 0.89-6.3 nmol/liter depending on gender and age.
Blood for T3 is donated if the TSH test shows a low level of thyroid-stimulating hormone with free T4 levels within normal limits, as well as with signs of hyperthyroidism.
The hormone level decreases when:
- hypothyroidism;
- anorexia nervosa;
- with severe iodine deficiency;
- low globulin levels;
- liver failure;
- acute thyroiditis;
- in the postoperative period.
In addition, the decrease and increase in T3 is influenced by taking various medications. During pregnancy, the level can be very elevated, which is normal, so when blood is taken for hormones, T3 may not be prescribed.
On what day of the cycle should I take tests for female hormones?
For greater convenience, we present to your attention a table with hormone testing on cyclic days.
| Hormone | Suitable time period |
| Follicle-stimulating | From 3 to 8 or from 18 to 22 days |
| Luteinizing | From 3 to 8 or from 18 to 22 days |
| Prolactin | First or second phase of the monthly cycle |
| Estradiol | No |
| Progesterone | From 18 to 22 days |
| Testosterone | No |
| DEA sulfate | No |
| Free T3 | No |
| General T4 | No |
| Thyroid-stimulating | No |
| AMG | 3 – 5 days of the cycle |
Useful videos about hormonal levels in women, normal indicators and recovery methods
- Tests for hormones for obesity: which ones are taken for...
It is mandatory to take tests for hormones for obesity, especially if a woman or man gains excess weight for no reason. The endocrinologist will prescribe which ones to take to identify the cause. - Before taking hormone tests: can you eat...
Before taking hormone tests, it is very important to find out exactly the days when to do it correctly, especially for women. Recommendations also include questions about whether you can eat and drink alcohol, and how general preparation is going. What else is not possible? How does sex affect blood tests?
- How long does it take to test for hormones if you take...
Several factors influence how much hormone testing is done: the type of hormone (thyroid, adrenal), the workload of the laboratory in the clinic or private. The fastest results in gynecology (for prolactin, estradiol, TSH) - on average 1 day after donating blood. Anti-Mullerians sometimes have to wait up to 6 days, and vasopressin – up to 14.
- General thyroxine: analysis, norm in women and men...
The thyroid gland produces total thyroxine, as well as free T4. Its norm in tests can fluctuate in women during pregnancy and decrease in everyone at night. Why increased or decreased? What is the difference between common and free?
- Parathyroid gland: tests to determine...
If there are suspicions of parathyroid dysfunction, tests will help confirm or refute the diagnosis. You should definitely donate blood for hormones, and in some cases, perform an ultrasound, scintigraphy, and biopsy. For example, if you suspect an adenoma or cancer.