Etiology of the disease
The insoluble type of mucus in question is called mucin. This secretion is synthesized by the auxiliary cells of the organ. Its presence is normal for humans; on the walls of the stomach there is a layer of mucin of about one and a half millimeters. It protects the layers of the digestive organ, otherwise, due to the action of hydrochloric acid and pepsins, they could digest themselves. Especially if there are gastrointestinal disorders, for example, gastritis or reflux gastritis (reflux of intestinal contents into the stomach). Under their influence, the layers of the mucous membrane can be destroyed.
So mucin is necessary. But its quantity may vary. The dynamics directly depend on the influence of the external and internal environment. If their exposure increases, then the amount of fluid in the stomach will increase. This in itself is not dangerous, but this factor reduces acidity and starts fermentation processes. As a result, the digested food rots, and this is a real, serious danger to the body. The patient suffers from bloating and belches with a rotten smell.
Thus, excess fluid requires treatment. This is only the initial stage, which can lead to serious defects and disturbances in the functioning of the stomach.
Interpretation of ultrasound results
Even if the baby’s parents are familiar with medical terms and know how to read a doctor’s report, the pediatrician or gastroenterologist should still decipher it directly.
So, the options that are included in the conclusion:
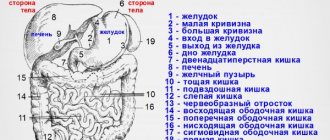
- when examining the liver, pay attention to its overall size and the size of the lobes, the edges and structure, as well as the size of the veins and bile ducts;
- the same is true for the spleen, the doctor evaluates its size, structure and other data;
- in the pancreas they try to look for the possible presence of neoplasms (not forgetting to examine its general condition);
- gallbladder - here, in addition to its shape, they look at the contents and the thickness of its walls;
- kidneys - here they look at their structure and the presence of stones.
Normally, all organs have standard outlines and structure; there are no neoplasms, fluid, cysts, or tissue proliferation in them. Here they also look at the vessels, or rather, at their sizes.
Parents of the baby should not immediately panic if an ultrasound revealed that some organs have sizes and shapes that are slightly inconsistent with the norm. The fact is that such inconsistencies do not always indicate a disease, because each living organism is individual. In the same way, one cannot talk about the absolute health of a baby if the condition of all his organs is within normal limits, since this can change over time.
What are the dangers of excess mucus?
Excessive mucin formation provokes processes that in the future can lead to ulceration of the walls or cancer. They penetrate the walls of the organ very deeply, which causes discomfort and even pain. Patients often complain of pain and vomiting may occur.
As a result, mucosal hypertrophy occurs. It leads to gastritis with varying degrees of acidity or ulcerative formations. The longer this process, the higher the likelihood of stomach cancer. To prevent this, it is recommended to consult a specialist at the first symptoms of this disorder. If this factor was identified during the examination, the doctor may insist on further treatment.
Advantages of ultrasound in diagnosing gastric diseases
The examination method is absolutely safe, has virtually no contraindications and, accordingly, is accessible to anyone, including children.
ease
The important thing is that the ultrasound examination does not take much time, after which the patient can freely go eat or go about his business.
observation in dynamics
Of course, ultrasound will not replace fibroesophagogastroscopy, since if neoplasms are detected, it is not possible to take material for a biopsy. An important advantage of ultrasound diagnostics is the ability to observe the state of the stomach in dynamics, which allows one to identify functional pathologies, for which establishing a diagnosis is often a very difficult task.
At the same time, with the help of ultrasound it is also possible to detect organic pathologies: gastritis, gastric ulcer, adenomas and stomach cancer, narrowing of the lumen of the pyloric canal and others.
comfort
Patient comfort during the procedure is important. Unlike fibroesophagogastroscopy, the subject does not have to go through the very unpleasant procedure of “swallowing the probe” (unless it is an ultrasound examination with the installation of a piezoelectric element in the stomach), which may then be accompanied by unpleasant sensations, including pain, up to a temporary refusal to eat . However, we should not forget that fibroesophagogastroscopy is very often vital for the patient.
documentary
An important point is that ultrasound equipment allows you to save video materials during the examination, which is a document.
Why is this happening?
The concentration of mucus may vary depending on external or internal factors. The main reasons for the appearance of fluid in the stomach on an empty stomach include :
- violation of diet, abuse of fatty, fried, smoked foods;
- dry meals, snacks on the go;
- frequent overeating;
- alcohol abuse;
- smoking.
Frequent eating disorders can cause an extensive list of negative symptoms. Therefore, the main method of preventing this disease and many others is healthy nutrition at the same time. It is also recommended to eat small, fractional portions to avoid stress on the stomach.
How much fluid can accumulate in the abdomen?
In severe cases, up to 35 liters of fluid can accumulate in the abdominal cavity. Depending on its volume and clinical manifestations, three degrees of ascites are distinguished:
- Mild degree : there are no external manifestations, the liquid can only be detected during an ultrasound examination.
- Moderate : Ascites results in moderate abdominal enlargement. This usually occurs when more than 400–1000 ml of fluid accumulates in the abdomen.
- Severe: Severe symptoms occur.
Drug treatment
Based on the results of the examination, the gastroenterologist will draw up an individual treatment regimen. It includes, first of all, taking a drug that normalizes stomach function and fluid secretion. In addition, this disorder itself rarely appears. Usually the amount of mucin increases against the background of another disease, most often gastritis. Endoscopic examination may be required to determine this.
Usually prescribed:
- Bellasthesin, an analgesic based on novocaine. Recommended for superficial gastritis, when it is not so much the walls of the stomach that are affected, but the protective layer of mucus. This causes the patient to feel heartburn and experience nausea after eating, which is relieved by this drug;
- Maalox, an antacid drug recommended for atrophic gastritis. The mucous membrane becomes very thin, the protective functions of the mucus are disrupted, and hydrochloric acid acts directly on the walls. Pain and nausea are complemented by the urge to vomit and attacks that go away when taking antacids;
- Festal or Gastal, analogues of Maalox, approved for people with low stomach acidity;
- antibiotics that kill the causative agent of gastritis, the microorganism Helicobacter pylori. But they are accepted only on the recommendations of a specialist.
Traditional recipes against excess mucin
Along with prescribed medications, you can use folk remedies prepared according to classic recipes.
Complete fasting shows good effectiveness. It is recommended to carry it out once a week, no more. It is better to start with a day, gradually increasing the fasting session to a day and a half. After a hunger strike, it is important to return to proper nutrition gradually. The first meal should include fruits and juices, which dissolve mucous secretions. The fiber they contain helps remove secretions.
To compensate for hunger, you can take water with lemon juice. Allowed up to three liters per day.
Actively remove mucus and products such as:
- black peppercorns: take a teaspoon before dinner with water. You can't chew pepper. Dosage regimen: every 3 days for 3 weeks. After which you need to take a break for a quarter. Before taking pepper, it is recommended to consult a doctor: for gastrointestinal pathologies, it can do more harm than good;
- ginger: the root of the plant is used in crushed form. for this you will need a teaspoon of this product and half a liter of boiling water. The solution must cool down; it is forbidden to take it hot. Add honey and lemon to the warm drink.
How to prevent excess mucin?
It is easier to prevent a disease than to cure it. Therefore, it is recommended to adhere to proper nutrition, especially at the first symptoms of a gastrointestinal disorder.
The most effective preventive measure is a balanced diet. Food is primarily a way to obtain energy, so it should be healthy, not just tasty. Not only sick, but also healthy people are not recommended to abuse fried, fatty or smoked foods.
It is recommended to minimize alcohol intake, or better yet, abstain from it altogether. Alcohol destroys the gastric mucosa and reduces natural defenses. If you have a stomach ulcer, alcohol can cause a perforation.
The most healthy foods are low-fat soups and cereals. These are the ones you should stick to if you feel discomfort in your stomach. Pureed soups are best digested.
It is recommended to include boiled vegetables and fermented milk products in your diet. But it is recommended to abstain from whole milk: the adult body contains very few enzymes that break it down.
If fluid accumulates in the stomach in excessive quantities, this may indicate the development of pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract. A normal amount of mucus is always present in the gastric cavity, but its volume is strictly limited. Symptoms of the pathology appear gradually, but to successfully get rid of them it is necessary to eliminate the cause.
Preparation
The study is carried out only on an empty stomach. You should not drink before the ultrasound. A few days before the procedure, you should follow a diet that excludes milk, yeast products, fresh vegetables and fruits. You need to stop eating 8 hours before the test. Foods that should be consumed 24 hours before the procedure:
- cereals;
- yeast-free bread;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir;
- pasta.
It is important to tell your child about the nuances of the procedure. You need to listen to the doctor and not change your body position on your own. It is important to bring the baby to the procedure on an empty stomach; feeding should not be done, otherwise you may receive inaccurate information.
Indications and contraindications
An ultrasound of the stomach in a child helps to identify the condition of the walls of the organ, as well as its functional activity. The indication for the study is frequent abdominal pain. In infants, an ultrasound is performed if there is frequent regurgitation, refusal to eat, and digestive disorders. The condition of the gastrointestinal tract and the first deviations from the norm will be shown by ultrasound diagnostics with proper preparation.
Additional indications:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- increased gas formation;
- loss of appetite.
The procedure helps control the course of chronic gastritis, ulcers and other diseases. On the computer screen during the examination, one may suspect the presence of gastric obstruction, as well as narrowing of its lumen. This method helps to diagnose the presence of malignant tumors.
The procedure has minimal contraindications. The study cannot be carried out if the child’s condition is unsatisfactory. You cannot resort to ultrasound if all preparation conditions have not been met. Otherwise, there is a high probability of obtaining a false result. If the child has a severe abdominal injury or the skin in the area where the examination will be performed is damaged, the procedure is postponed to another time.
Causes of fluid accumulation
An excessive amount of fluid in the gastric cavity indicates that not only the secretory function of the organ is impaired, but also the functioning of other systems. Excess water in the stomach can vary. Pathologies are classified according to a number of characteristics:
- By amount of liquid:
- slight excess of the norm;
- moderate accumulation;
- significant.
- Based on the presence of microorganisms in the liquid:
- sterile;
- infected.
- By reaction to medications:
- treatable;
- stable.
- stomach and ovarian cancer;
- liver cirrhosis in the final stage;
- general stagnation of blood in the body, provoked by cardiac pathologies;
- pathologies of internal organs in a child obtained during intrauterine development;
- tuberculosis;
- alcoholic hepatitis;
- renal failure;
- acute dilatation of the stomach;
- poor nutrition.
If the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen occurs repeatedly, it becomes stable and does not respond to conservative therapy.
The causes of the pathology are:
Pathology occurs against the background of stomach cancer.
Return to contents
How to prepare your baby for an ultrasound?
When it comes to ultrasound examination of a newborn, preparation depends on the organs that will be examined. As you know, a child up to six months old will not be able to go without food for more than 2–2.5 hours. An older baby, about a year old, can withstand a “hungry” period of 3.5–4 hours and the same amount without water. Porridge, meat products and vegetables take much longer to digest than breast milk and formula. Therefore, milk is something you should feed your child before going to the doctor.
If there is a need to look at the gallbladder or pancreas, then you should not feed the child before the procedure, at least 2-4 hours. This is important because a swollen intestine and stomach will hide these organs from the doctor's view. In addition, the gallbladder shrinks in size during the digestion of food, and it can be difficult to see its shape and lumen.
The pancreas can become significantly enlarged due to blood flow during digestion, and its size may be misinterpreted. If an examination of the organs of the excretory system is planned, then about half an hour before the ultrasound it is necessary to give the baby something to drink so that his bladder has time to fill a little by the time of the procedure. Otherwise, ultrasound diagnostics will be uninformative, and you will be invited to come another time. If your baby is crying from hunger, give him water. Pure drinking water in small quantities, without sugar or additives, will not distort the picture on the monitor of the diagnostic device.
A medical examination is not a whim of modern medicine, but a necessary preventive stage in the life of every child. Abdominal ultrasound is part of the newborn screening program: preventing the disease is much easier than treating it later. In addition, timely measures will protect you and your baby from possible adverse consequences.
Symptoms and stages
Ascites in gastric cancer develops in stages. There are three stages of progression of the pathology, each of which is characterized by separate symptoms and methods of therapy. Also, depending on the phase of development, therapeutic methods are selected. Only a doctor can correctly determine the stage of progression after diagnosis.
Symptoms and stages of development of ascites
| Stage of development | Pathological process | Symptom complex |
| Transient ascites | Liquid volume does not exceed 400 ml | Painful sensations in the abdominal cavity |
| Moderate ascites | The appearance of soft belly syndrome | The peritoneum increases |
| Heaviness in the stomach | ||
| Problems with bowel movements | ||
| Resistant ascites | Liquid volume – more than 20 liters | The abdominal area is greatly enlarged |
| Abdominal skin is firm and shiny | ||
| Respiratory failure | ||
| Peritonitis |
Ascites in children: photos, symptoms, causes and treatment of abdominal dropsy
Ascites in children is a serious pathological condition.
The presence of ascites (dropsy) is indicated by the accumulation of fluid outside individual organs. Dropsy impedes blood circulation, compresses organs and can cause many diseases. Complications of the disease can lead to serious consequences and even death. Do you think that abdominal enlargement is always associated with ascites?
Causes of the disease
Most often, dropsy in children occurs during the baby’s intrauterine development in the mother’s body. The cause is improper or pathological development of the bile ducts or the body’s natural filter – the liver.
The occurrence of abdominal ascites in a child is influenced by:
- cicatricial changes in the biliary tract;
- bile stagnation;
- infectious lesions of the mother’s body - herpes, viral hepatitis, rubella, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, listeriosis;
- malnutrition;
- cardiovascular diseases;
- chromosomal abnormalities - Gaucher disease, Down and Turner syndromes;
- hemolytic disease of the fetus;
- diffuse peritonitis;
- heart diseases;
- congenital nephrotic syndrome.
Ascitic fluid is formed due to polyserositis, peritoneal lesions, maternal cancer and diseases accompanied by portal hypertension. Portal hypertension syndrome is characterized by increased pressure in the portal vein of the liver.
An equally significant role in the formation of dropsy is played by a decrease in protein levels in the blood, gastrointestinal diseases, characteristic symptoms of heart failure, lymphostasis, and myxedema. Often, ascites occurs with kidney disease.
Such conditions are accompanied by metabolic disorders, inflammatory processes, and water and electrolyte disturbances.
Symptoms of ascites in children
Depending on what became the root cause of ascites, the symptoms of the disease can manifest themselves clearly or unnoticed.
Symptoms of dropsy in children:
- feeling of fullness in the stomach;
- nausea;
- increase in abdominal volume;
- abdominal pain;
- belching;
- pronounced flatulence;
- heartburn;
- heaviness in the stomach.
As ascitic fluid accumulates, the abdomen enlarges and the baby's navel protrudes greatly. Severe shortness of breath, characteristic swelling, and severe difficulty in movement appear.
When the process is neglected, dropsy causes hernia, hemorrhoids, varicocele, and rectal prolapse.
Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of ascites
Diagnosis of this serious illness begins with palpation and percussion of the abdominal cavity, ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound are performed.
Mandatory diagnostic items are:
- MSCT of the abdominal cavity;
- laparoscopy;
- studies of ascitic fluid;
- liver scintigraphy;
- abdominal radiography;
- study of biochemical liver samples;
- Analysis of urine;
- coagulogram;
- fluid collection for analysis during laparocentesis.
After diagnosis and evaluation of tests, the doctor can accurately determine the presence of the disease and begin treatment of abdominal dropsy.
On ultrasound you can see ascites with a volume of 100 ml or more
Treatment of dropsy includes complete elimination of the cause of the disease. Treatment includes a salt-free diet, diuretics, and reducing the amount of fluid you drink. During therapy, water and electrolyte metabolism is corrected and portal hypertension is reduced.
To drain ascitic fluid, a special peritoneovenous shunt is installed. Operations are being carried out to reduce pressure in the portal system. If ascites is resistant, liver transplantation is indicated.
If the disease is not associated with liver pathology, treatment is carried out with vitamins, diuretics and hormonal drugs.
Parents should ensure that everything fatty, sweet, salty and smoked disappears from the child’s diet; it is worth reducing the consumption of spices and salt.
To prevent the development of ascites in a child, the expectant mother should carefully monitor her health and undergo regular screening examinations.
To avoid the risks of acquired dropsy, the mother should adhere to a healthy lifestyle for the baby and a balanced diet. It is worth teaching your child to play sports, walk in the fresh air and play active games.
Complications of ascites
Dropsy in infants leads to the following diseases:
- bacterial peritonitis;
- hydrothorax;
- hepatorenal syndrome;
- intestinal obstruction;
- compression of the heart;
- umbilical hernia;
- compression of the diaphragm;
- respiratory failure;
- compression of blood vessels.
Ascites in children is a complex and dangerous condition. You need to carefully monitor the child’s condition, nutrition and proper lifestyle of the baby. It is extremely important to pay attention to the first symptoms of ascites. With correct treatment of dropsy, the child’s body recovers in the shortest possible time.
Source: https://progepatity.ru/ascit/astsit-u-detej
Treatment of pathology
If the ultrasound showed a critical accumulation of fluid in the body, it is necessary to begin immediate treatment of the deviation. Treatment measures should be aimed not only at relieving the symptoms of the disease, but also at eliminating the cause. Timely therapy minimizes the need for surgery. For treatment, an integrated approach is used, which includes taking medications, traditional medicine and surgery at the last stage of the disease.
Medicines
The treatment regimen for each patient is prescribed based on the results of ultrasound and laboratory tests. Conservative treatment involves the use of medications that normalize stomach function and mucus production. The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
Bellasthesin will help get rid of pathology caused by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the digestive organ.
- "Bellasthesin." Painkiller based on analgin. Used to treat excess fluid due to gastritis.
- "Maalox." An antacid medication that is used to restore the mucous membrane.
- "Festal". Accelerates metabolism and normalizes acidity levels in the body.
- Antibiotics. Eliminate bacteria that provoke inflammatory processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is prohibited to use medications if contraindications are found.
Traditional methods
In addition to taking medications, alternative medicine recipes are also used. The following methods have a good effect:
- Therapeutic fasting. Once a week you need to give up food and drink only water. To relieve hunger, you can add lemon juice to the liquid.
- Black peppercorns. In the evening you need to eat 1 tsp. before meals with water. You can't chew it.
- Ginger. Infuse the crushed rhizome in 2-2.5 liters of boiling water, mix with lemon and honey and drink on an empty stomach, immediately after sleep.
Return to contents
Diet food
The most important condition for successful treatment of ascites is proper nutrition. The diet is based on maintaining the balance of sodium in the body and enriching the body with proteins. The amount of salt consumed per day should be no more than 1 gram. In addition, you must avoid the following products:
- fresh baked goods;
- fat meat;
- sausage and smoked meats;
- milk;
- spicy broths and sauces;
- coffee and strong tea;
- alcohol.
It is better to cook food by steaming or in the oven, in its own juice. Instead of salt, you need to add fresh herbs. It is better not to eat raw vegetables. It is better to eat 5-6 times a day, in small portions. The amount of liquid consumed should not exceed 1 liter. In addition, it is necessary to ensure that the temperature of the food is not too low or high.
Possible operations
If the fluid is foamy, the walls are inflamed, and medications do not help, the patient undergoes surgery. Surgical treatment is used for 10% of patients. The operation involves peritoneovenous shunting - special tubes are installed in the veins, which create additional channels for removing fluid. However, this technique causes complications, so you should consult a doctor before performing it.
Fluid in the abdominal cavity on ultrasound
The accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity occurs as a result of an inflammatory reaction, impaired outflow of lymph and blood circulation due to various reasons. This condition is called ascites (dropsy), its occurrence can lead to the development of serious consequences for human health.
The fluid accumulated in the peritoneum is an ideal habitat for pathogenic microflora, which is the causative agent of peritonitis, hepatorenal syndrome, umbilical hernia, hepatic encephalopathy and other equally dangerous pathologies.
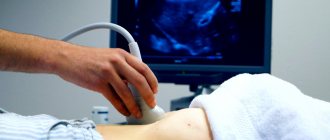
To diagnose ascites, one of the safest and non-invasive, but highly accurate methods is used - research using ultrasound waves. Detection of the presence of fluid in the abdominal cavity by ultrasound is carried out as prescribed by the attending physician based on existing clinical signs of the pathological process.
The abdominal cavity is a separate anatomical zone, which constantly releases moisture to improve the sliding of the visceral layers of the peritoneum.
Normally, this effusion is able to be dynamically absorbed and not accumulate in areas convenient for it.
In our article we want to provide information about the causes of abnormal fluid reserve, diagnosing the pathological condition on ultrasound and effective methods of treating it.
Why does free fluid accumulate in the abdominal cavity?
Ascites develops as a result of various kinds of pathological processes in the pelvic organs.
Initially, the accumulated transudate is not inflammatory in nature; its amount can range from 30 ml to 10–12 liters.
The most common reasons for its development are a violation of the secretion of proteins, which ensure the impermeability of tissues and pathways conducting lymph and circulating blood.
This condition can be caused by congenital anomalies or development in the body:
- liver cirrhosis;
- chronic heart or kidney failure;
- portal hypertension;
- protein starvation;
- lymphostasis;
- tuberculous or malignant lesions of the peritoneum;
- diabetes mellitus;
- systemic lupus erythematosus.
Dropsy often develops when tumor-like formations form in the mammary glands, ovaries, digestive organs, serous membranes of the pleura and peritoneum.
In addition, free fluid can accumulate due to complications of the postoperative period, pseudomyxoma peritonei (an accumulation of mucus that undergoes reorganization over time), amyloid dystrophy (disorders of protein metabolism), hypothyroid coma (myxedema).
The mechanism of dropsy formation is the leakage of fluid into the abdominal cavity from the main lymphatic ducts, blood vessels and organ tissues
Signs of ascites
In the early stages of the development of this condition, patients do not have any complaints; the accumulation of free fluid can only be detected using ultrasound. Visible symptoms appear when the amount of transudate exceeds one and a half liters, the person feels:
- increase in the abdominal region and body weight;
- deterioration in general health;
- feeling of fullness in the abdominal cavity;
- swelling of the lower extremities and scrotal tissue (in men);
- burping;
- heartburn;
- nausea;
- difficulty breathing;
- flatulence;
- tachycardia;
- protrusion of the umbilical node;
- discomfort and pain in the abdomen;
- stool and urinary disorders.
When a large amount of effusion accumulates in the peritoneum, a person can hear a characteristic splash of liquid and feel a wave.
If an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity shows existing excess moisture, the attending physician must accurately determine the root cause of the pathological condition. Pumping out accumulated transudate is not an effective method of treating ascites.
Preparation for ultrasound and its progress
This study does not have any contraindications or restrictions; in emergency cases it is carried out without prior preparation of the patient.
The planned procedure requires improved visualization of pathological changes in organs.
The patient is recommended to exclude from the diet 3 days before the study foods that contain large amounts of fiber and increase gas formation.
On the eve of the study, drink a laxative or do a cleansing enema. To reduce the accumulation of gases in the intestines on the day of the ultrasound, you need to take Mezim or activated charcoal. Modern methods of ultrasound diagnostics make it possible to determine the most likely areas of accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity.
What is an abdominal ultrasound?
That is why qualified specialists inspect the following anatomical areas:
- The upper “floor” of the peritoneum, which is located under the diaphragm. Of particular diagnostic importance are the spaces located under the liver and formed by the main part of the small intestine - the ascending and descending parts of the colon. Normally, the so-called lateral canals do not exist - the peritoneum is tightly adjacent to the intestine.
- Small pelvis, in which, with the development of pathological processes, effusion may accumulate, flowing from the lateral canals.
The physical characteristics of moisture accumulated in the peritoneum for any reason do not allow the ultrasound wave to be reflected; this phenomenon makes the diagnostic procedure as informative as possible. The presence of effusion in the studied anatomical spaces creates a dark moving focus on the device monitor. If there is no free fluid, the diagnosis lasts no more than 5 minutes.
To detect excess moisture, the ultrasound device sensor is moved along the anterior and middle axillary lines on both sides of the patient’s body down the abdomen.
If it is not possible to detect a transudate, its presence may be indicated by indirect signs:
- displacement of colon loops;
- change in sound during percussion (tapping) - tympanic in the upper parts of the peritoneum, dull in the lower parts.
Types of abdominal hydrops by ultrasound
The international classification of diseases does not identify ascites as a separate disease - this condition is a complication of the last stages of other pathological processes. Based on the severity of clinical symptoms, the following forms of ascites are distinguished:
- initial – the amount of water accumulated inside the abdomen reaches 1.5 liters;
- with a moderate amount of liquid - manifested by swelling of the legs, a noticeable increase in the size of the chest, shortness of breath, heartburn, constipation, a feeling of heaviness in the abdomen;
- massive (exudate volume more than five liters) - a dangerous condition characterized by tension in the walls of the abdominal cavity, the development of insufficiency of the cardiac and respiratory systems, and infection of the transudate.
When bacteriologically assessing the quality of free fluid, which is carried out under special laboratory conditions, a distinction is made between sterile (absence of pathogenic microorganisms) and infected (presence of pathogenic microbes) dropsy.
According to diagnostic forecasts, there is ascites, which is amenable to drug therapy, and a stable pathological condition (its reoccurrence or not amenable to treatment).
The course of treatment depends on what disease caused the accumulation of excess moisture in the peritoneum. To accurately diagnose the pathological process, practitioners conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, including:
- biochemical and general clinical blood and urine tests;
- study of cancer markers and indicators of electrolyte metabolism;
- plain radiography of the chest and abdominal cavities;
- coagulogram - assessment of the parameters of the coagulation system;
- angiography of vessels, allowing to assess their condition;
- MRI or CT scan of the abdominal cavity;
- hepatoscintigraphy is a modern technique for studying the liver using a gamma camera, which allows visualization of the organ;
- diagnostic laparoscopy with therapeutic puncture of ascitic fluid.
To pump out transudate from the abdominal cavity, the method of therapeutic laparocentesis is used - a puncture is made in the anterior wall of the abdomen, through which excess fluid is removed
In patients with liver cirrhosis, intrahepatic portosystemic shunting is recommended, the technique of which involves placing a metal mesh stent to create an artificial connection between the collar and hepatic veins. In severe cases of the disease, organ transplantation is necessary.
In conclusion of the above information, I would like to emphasize once again that the accumulation of free fluid in the abdominal cavity is considered an unfavorable manifestation of the complicated course of the underlying disease. The development of ascites can provoke disruption of the functional activity of the heart and spleen, internal bleeding, peritonitis, and cerebral edema.
The mortality rate of patients with massive abdominal hydrops reaches 50%.
Measures to prevent the occurrence of this pathological condition include timely treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes, proper nutrition, avoidance of alcohol, moderate exercise, preventive examinations of medical specialists and strict implementation of their recommendations.
Source: https://apkhleb.ru/uzi/zhidkost-bryushnoy-polosti
Prevention and prognosis
The outcome of ascites directly depends on the disease that provoked it. Therefore, with proper and timely treatment, the pathology can be eliminated without consequences. Without urgent medical intervention, the disease is fatal. However, it is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. In the case of ascites, you need to monitor your diet and adhere to the rules for using medications. In addition, it is important to consult a doctor promptly.
Gastroenterological diseases are widespread among the population. Close attention to this problem is explained by the fact that these diseases tend to have a chronic, relapsing course and develop in people of working age.
Improvements in the ultrasonography method have significantly increased the diagnostic capabilities of gastric pathologies. So, if fluid appears in the stomach on an ultrasound - what does this mean, is it dangerous for the patient - specialists will decide in combination with other examination methods.
With water-siphon sample
The human stomach is designed in such a way that if there is no content in it, its walls collapse. In this condition, it cannot be examined normally on an ultrasound; it is impossible to evaluate the mucous membrane and determine the boundaries.
Therefore, to improve the quality of diagnostics, scanning with a water-siphon sample is carried out:
- the child drinks water in slow sips - at this stage the degree of patency of the esophagus can be assessed;
- when the stomach is filled with water, its walls straighten - this allows you to examine the mucous membrane in detail and determine the boundaries of the organ.
You can read about this and other types of stress ultrasound in this article.
Why is mucus in the stomach dangerous?
In the gastric wall on the mucosa there are additional cells of the glandular epithelium, which produce insoluble mucus - mucin. Covering the mucous membrane, this mucus plays a protective role - it protects it from the aggressive action of gastric juice, consisting of hydrochloric acid and proteolytic enzymes. Normally, mucus lies on the walls in a layer of up to 1.5 mm.
The volume of mucus produced is regulated depending on the increase or decrease in the acidity of gastric juice. If there is excess mucus, acidity decreases, which is an activator of enzyme activity, protein digestion is disrupted, food stagnates, and fermentation processes begin to predominate. The food bolus, insufficiently processed with acid and proteolytic enzymes, enters the duodenum. In the small intestine, parietal digestion is disrupted, many substances, microelements, vitamins are not absorbed - the body experiences a deficiency in the nutrients necessary for its normal functioning.
Symptoms that accompany increased production of gastric mucus:
- bloating;
- belching rotten;
- nausea, occasional vomiting;
- cramping abdominal pain;
- constant constipation;
- poor tolerance to meat foods;
- decreased appetite;
- disorders in the psycho-emotional sphere: irritability, tendency to apathy;
- weakness, fatigue, decreased performance.
Overproduction of mucin and a persistent decrease in the acidity of gastric juice can lead to the development of atrophic gastritis, which is considered a precancerous condition.
How is an ultrasound of the stomach done for children?
To carry out diagnostics, the child must be in a supine position. A small child needs to expose his stomach; older children undress on their own. After applying the gel, the doctor places the sensor in the epigastric region, after which the diagnosis begins. Sometimes the doctor asks the child to take a “half-sitting” position or turn on his side. During diagnosis, the doctor evaluates the thickness of the gastric walls (normal thickness is about 4 - 8 mm), examines the layers and looks at the shape of the side section.
Causes of fluid accumulation in the stomach
Diseases affecting the activity of accessory cells:
- congenital malformations of the esophagus, stomach;
- gallbladder inflammation;
- biliary dyskinesia;
- gastroesophageal reflux;
- duodenitis;
- pancreatitis;
- all inflammatory and destructive diseases of the stomach: ulcers, erosions, gastritis, tumors ;
- food poisoning;
- gastric wall injury;
- radiation exposure of an organ during malignant neoplasms.
Substances that irritate and damage the gastric mucosa provoke hypersecretion of mucin.
- The predominance of spicy, fatty, rough foods in the diet.
- Negative effects of combustion products of tobacco and ethyl alcohol on the mucous membrane.
- Passion for strict non-physiological diets, fasting.
- Long-term use of medications that damage the organ mucosa: steroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, cardiac glycosides.
- Occupational hazards: working with toxic chemicals and gases.
This pathology is especially often observed in men due to a greater tendency to bad habits, a disdainful attitude towards diet and the quality of products. All symptoms develop gradually over a long time.
What symptoms indicate improper stomach function in children?
- Bad breath;
- Hypotrophy – insufficient weight for a certain childhood age;
- Constant regurgitation in children under one year of age without identifying neurological diseases;
- Heartburn and sour belching;
- Pain under the ribs;
- Prolonged diarrhea, which is not related to infectious diseases.
Features of ultrasound in a child: Ultrasound of the esophagus and stomach in a child is performed when the doctor suspects a narrowing of the esophagus. In addition, such a study is also included in the list of planned studies for a newborn. In an older child, indications for ultrasound diagnostics of the stomach and esophagus will be suspicion of gastritis, GERD, esophagitis and diaphragmatic hernia with simultaneous prolapse of several organs. Another situation in which such a study is performed is when a child swallows a foreign body. Ultrasound helps in determining its location after the incident.