Many expectant mothers, having once heard a doctor’s verdict based on the results of a urine test, wonder how to reduce protein in the urine during pregnancy and how dangerous is this? It is no secret that women carrying children experience hormonal changes and the functioning of internal organs and systems may be disrupted. This is not surprising, because pregnancy is a great stress for the body, and not everyone prepares it in advance for such an event, thereby risking encountering unpleasant events while carrying a child. In particular, this applies to an increase in protein in the urine, which practically should not be there.
Normal indicators
Anyone who has not been pregnant does not know that a urine test is the best indicator of the general condition of the body, in particular the functioning of a woman’s urinary organs. It is they who bear a very heavy burden during gestation, especially from the middle of the second trimester, and only timely detection of the disorder will help preserve the health of the mother and the unborn baby.
Healthy people normally do not have protein in their urine, but in pregnant women it may be present in small quantities. Thus, the norm for women bearing a child is considered to be no more than 0.003 g/l of protein in one portion of urine. By the end of the last trimester, the amount of protein can normally increase to 0.032 g/l (this indicates mild proteinuria). If the permissible norm is exceeded several times, the presence of serious pathologies can be suspected.
Re-testing
If the levels of protein in the urine significantly exceed the norm, it is recommended that you retake the test before thinking about how to eliminate it. The thing is that urine levels can be affected by various factors:
- eating protein-rich food the day before;
- stressful situation;
- intense physical activity.
It may be that the woman did not collect urine according to all the rules, and this is what influenced the results of the study (false proteinuria). To get an accurate picture of the analysis, the expectant mother should carefully prepare for taking it. To do this, you need to thoroughly rinse your genitals in the morning under running warm water (bathing in herbal decoctions or infusions is prohibited). Afterwards, you should collect the average urine (the first portion and the last one is drained) into a sterile container. It is better to use a special container to collect urine, not a jar.
It often happens that a repeat test may not show an excess of protein or confirm a truly high amount of protein in the urine. If a repeat study shows that there is a lot of protein, additional diagnostics and treatment may be prescribed.
How to properly collect urine for analysis
In order for the interpretation of the analysis to be as correct as possible, it is necessary to correctly collect urine. How it's done:
- It is necessary to prepare a clean container in advance. It is better if it is a special sterile jar for testing, purchased at a pharmacy.
- You need to collect urine for analysis in the morning on the day of delivery, immediately after sleep.
- Before urinating, it is necessary to thoroughly wash the external genitalia.
- Very often, pregnant women experience an increase in the amount of vaginal discharge. This is a kind of protective function of the body. The mucus released prevents infections from entering the mother's genital tract and provides the child with reliable protection. But the release of secretions into the urine will blur the clinical picture and the analysis will be interpreted incorrectly. To prevent this, immediately before urinating, close the entrance to the vagina with a cotton swab. Please note that if, through negligence, a tampon falls into a container with urine, the analysis will have to be redone the next morning.
- Collect only the average portion of urine in a jar, flushing the first few milliliters into the toilet.
If an increased protein content is detected in the analysis, a repeat analysis is prescribed to check.
Traditional remedies
To reduce protein in the urine of pregnant women, medications are prescribed that will primarily help eliminate inflammation in the kidneys. For this purpose, treatment is prescribed with anti-inflammatory drugs and diuretics, the active ingredients of which are medicinal herbs. If an acute or chronic form of pyelonephritis is detected, antibacterial agents may be prescribed. To prevent congestion in the kidneys, a pregnant woman should not lie on her back for a long time. You can stand on your hands and feet during the day and move around in this position. If all recommendations are followed, protein should decrease to normal levels.
With gestosis, unfortunately, it is almost impossible to improve the general condition and reduce protein. Sometimes, in a favorable situation, it is possible to stabilize the indicators and keep them there until the birth itself. Often, women in this case successfully bear the child and give birth on time. However, when diagnosing gestosis, the risk of giving birth prematurely is always high.
The most terrible situation of such a violation in the body can be the death of the pregnant woman and her fetus. If doctors see a serious threat to the mother's health, they will most likely suggest terminating the pregnancy. Further pregnancy will be possible only with the consent of the pregnant woman herself and signing the necessary papers that she knows about the danger, but still wants to continue the pregnancy. In this case, strict bed rest in a hospital and delivery only by caesarean section are indicated. Treatment of gestosis during pregnancy is impossible, but with the help of medications and diet, the development of a life-threatening situation can be prevented.
Therapeutic diet
To reduce the amount of protein in the urine, pregnant women need to slightly adjust their diet. To do this you need to complete the menu:
- boiled meat;
- low-fat fish;
- cottage cheese;
- kefir;
- vegetables and fruits.
You can periodically do fasting days - this will help reduce swelling on the body and reduce the amount of protein. You will definitely need to remove salt from your diet or reduce its consumption to a minimum. The doctor may also recommend taking No-shpa and Dibazol.
Of the folk remedies that also often help cope with proteinuria, cranberry is most suitable. You can eat it, make delicious juice or fruit drink. Previously, pregnant women, when protein in the urine increased, reduced it with the help of parsley infusion. To do this, you need to pour 0.5 tsp of plant seeds into 150 ml of boiling water, leave and drink throughout the day.
If there are no contraindications, protein can be reduced using a decoction of birch buds. To do this, pour 1 tablespoon of kidneys into 200 ml of water, boil, cool in a thermos and drink.
Traditional therapy is used only as an addition to the main treatment. In addition to this, you will need to take medications recommended by your doctor, monitor your diet and lifestyle in general.
Protein in the urine during pregnancy indicates the development of pathological abnormalities in the body. These include late toxicosis (preeclampsia), inflammatory processes in the kidneys and infectious lesions of the urinary system. Protein determination is a mandatory test that is taken every 2 weeks in the laboratory. Monitoring the level of the component allows you to monitor the general condition of the woman, and if deviations develop, begin to comprehensively eliminate them. Inaction is dangerous due to the development of complications, including protracted and difficult labor.
Prevention
To prevent proteinuria, the expectant mother should not engage in heavy physical activity or experience emotional stress.
Your daily schedule should include a visit to the pool, light exercise or walks in the fresh air. While carrying a baby, it is recommended to follow a diet. It is necessary to remove very salty foods from the diet - canned food, smoked meats, sausage, chips, crackers. She is also advised to maintain a drinking regime of 1 to 1.5 liters of clean water per day.
The diet should consist of 30% protein, 20% fat and 50% carbohydrates. The expectant mother should give up chocolate, flour products, sweets, white bread, pasta and rice. Include a sufficient amount of lean meat, fresh vegetables and fruits, dairy products, and grains in your diet.
For early detection of pathology, a pregnant woman is not recommended to skip routine gynecological examinations. Before each of them, she is advised to submit her urine for a general analysis.
Generally accepted standards
Protein in urine during pregnancy should not exceed generally accepted standards of 0.08-0.2 grams per liter. If about 0.033 grams was found in the biological material, it is advisable to consult with your doctor. Deviation from the norm is dangerous both for the woman in labor and for her child.
High protein levels require careful monitoring by healthcare professionals. If the deviations are not critical, the woman is recommended to submit her urine for laboratory testing every week. Tracking indicators will allow you to track the trend of changes. In case of deviations to a greater extent, a comprehensive examination is indicated, followed by the prescription of effective therapy.
Attention: in some cases, laboratory technicians receive unreliable results. This is due to the woman’s improper preparation for the test and the abuse of junk food.
The following factors can affect the correctness of the data:
- abuse of dairy products, including cottage cheese and sour cream,
- taking medications,
- take a cold shower before collecting urine,
- increased body temperature,
- high intensity physical activity,
- nervous overstrain.
If traces of protein are found in the urine, the pregnant woman is sent for re-analysis. It is possible that a small amount of the substance is due to the influence of provoking factors. If a repeat test confirms the presence of a dangerous component, complex therapy is prescribed.
Important: the appearance of a substance in biological material is not always associated with abnormalities in the body. When asymptomatic, this process is physiological in nature. Its development is influenced only by the main provoking factors.
Causes of high protein
Protein levels vary in different trimesters, but within normal limits
It is important to monitor indicators to prevent pathologies. In the early stages, proteinuria indicates inflammation, exacerbation of chronic pathologies
External factors cannot be excluded:
- improper preparation for analysis, urine collection;
- the influence of food eaten the day before;
- physical fatigue;
- stress, excessive anxiety;
- taking medications.
At different trimesters, the protein level varies, and within normal limits.
The cause of proteinuria may be hidden in the growth of the uterus, which puts pressure on the ureters and kidneys, disrupting their blood supply. The condition does not require treatment, only control.
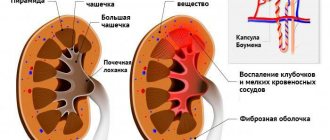
A number of pathologies can increase protein - diabetes, heart failure and hypertension. The most common provoking factors are:
- pyelonephritis. Accompanied by pain, chills, and fever. Analyzes show protein, leukocytes, and sometimes red blood cells;
- glomerulonephritis. Accompanied by redness of urine and pain in the kidneys. Analyzes show an increase in protein, red blood cells, leukocytes;
- cystitis. Characterized by frequent urination, accompanied by pain;
- polycystic disease Kidney disease caused by genetics.
Protein in urine can increase in a number of pathologies
In the later stages, proteinuria signals similar pathologies, but preeclampsia is added to them. The condition develops after 34 weeks, another name is late toxicosis. Accompanied by deterioration in the functioning of the brain, blood vessels, and kidneys. Hands and feet swell.
Preeclampsia occurs in approximately 15% of women; women with multiple and first pregnancies are at risk. The condition always occurs with an increase in protein. The more it is, the more severe the disease. At a level of 0.8 g/l, the risk of gestosis increases, and if the pressure rises, a diagnosis can be made.
This combination is called preeclampsia. In this case, the woman develops brain damage, and in severe situations this can lead to a stroke. You need to worry when the pressure is above 160/110 mmHg.
Clinical manifestations of proteinuria
The development of proteinuria during pregnancy is indicated by clinical symptoms. Due to their non-specificity, it is not always possible to independently determine the presence of a problem. The main clinical manifestations include:
- high body temperature,
- frequent headaches,
- disorders of the digestive system (loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting),
- nervousness and irritability,
- discomfort in the lumbar region,
- pain localized in the lower abdomen,
- frequent urge to urinate, accompanied by pain.
The presence of the presented clinical picture is characteristic of many diseases, in particular, systemic lupus erythematosus, pyelonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), gestosis, chronic infections of the urinary system and cystitis. It is almost impossible to identify deviations on your own. The visual presence of protein in the urine is detected when its level increases excessively. This issue cannot be solved without additional research. According to theoretical information, heating urine can indicate the presence of abnormalities. This is a home method for determining protein in biological material. The technique has been used since ancient times. To determine protein, it is enough to heat the urine over a fire. If it begins to curl on the sides (like milk when heated), it means there is a foreign substance in it.
Attention: the home method is not reliable. Folding occurs both in the presence of protein within normal limits and in the development of abnormalities.
Symptoms
Symptoms of proteinuria depend on its degree and the underlying disease.
A small loss of protein up to 0.5-1 grams per day is not accompanied by any symptoms. Significant proteinuria is characterized by mild edema. They occur in the morning and are localized on the face. The earliest sign of pathology is swelling of the eyelids. Also, an average degree of protein loss may be accompanied by dizziness, fatigue and drowsiness.
The content of more than 5 grams of protein in the urine is characterized by a change in its appearance. Urine acquires sediment in the form of flakes, and a light foam appears on its surface.
Severe proteinuria is accompanied by severe edema. They do not go away during the day and are located on the face, upper and lower extremities. An expectant mother may notice a weekly weight gain of more than 500 grams. In severe cases, fluid accumulates in the abdominal and chest cavity.
Severe protein loss is accompanied by general symptoms. A pregnant woman complains of feeling unwell, drowsiness, headaches, nausea and vomiting.
Diagnostic measures
The presence of protein in biological material is identified in various ways. The simplest method is urine testing using special reagents. Upon contact with the material, a chemical reaction occurs, based on which the laboratory technician determines the protein level.
Primary diagnosis consists of conducting a qualitative test. The results of the study allow us to obtain reliable information about daily proteinuria. Diagnostic measures are based on the use of a few drops of sulfosalicylic acid. In the presence of protein, urine becomes cloudy and shimmering. The color intensity depends on the quantitative protein content.
Another method involves the use of nitric acid. It is added to the flask with urine (the volume of liquids must be equal). When protein levels increase, a white ring forms between the two substances.
Additionally, it is recommended that a pregnant woman undergo a urine test in the first and last trimester to identify bacteria in it. In medical practice, this study is called tank culture. The presented technique allows you to determine the acidity, shade, transparency and presence of sediment in urine (leukocytes, erythrocytes and key cells).
To determine the level of protein, it is necessary to correctly collect biological material for research. Experts recommend adhering to the following algorithm:
- flush the first few drops into the toilet, then collect,
- It is advisable to wash yourself before the procedure,
- urine must be collected in a specially designated container,
- deliver the material no later than 2 hours after collection.
Attention: urine testing begins in the first trimester of pregnancy before each scheduled visit to the doctor. In the later stages, the analysis is taken every week. During this period, the risk of developing late toxicosis increases.
The main reasons for deviations from the norm
Increased protein in urine - what causes this process? While carrying a child, the pregnant woman's body experiences enormous stress. All organs and systems work under wear and tear, which can lead to disruptions in their functionality. A rapidly developing child puts pressure on the kidneys and ureters, increasing the likelihood of developing congestive and inflammatory processes. The consequence of natural exposure is increased protein in urine.
In medical practice, many reasons are recorded that can cause deviations. However, not many factors are harmless. The following pathologies can provoke deviations:
pyelonephritis is an inflammatory process affecting the kidneys. Accompanied by elevated body temperature, often reaching 40 degrees. The patient experiences severe pain when urinating. A urine test for daily protein indicates an elevated level, and the presence of leukocytes,
glomerulonephritis is a pathological process accompanied by kidney damage, with further disruption of their functional purpose. As a result of the development of the disease, the urinary system is not able to remove excess fluid and toxins from the body. The consequence of this process is intoxication, increased body temperature and intense pain in the area where the kidneys are located,
gestosis - late toxicosis occurs from the 30th week of pregnancy. This is a complicated course of the natural process of bearing a child. Accompanied by swelling of the limbs and high blood pressure. In an advanced stage, it leads to cerebral edema, which is dangerously fatal,
cystitis is an inflammatory process affecting the bladder. It is characterized by acute pain during urination, burning and stinging. The appearance of pain in the lower abdomen is possible.
If signs of abnormalities appear, it is advisable to visit a gynecologist for an unscheduled examination. This action will prevent serious consequences and save the life of both the woman and her baby.
Possible complications
The development of proteinuria in the later stages is fraught with the appearance of severe complications. If there are deviations, the woman should be constantly under the supervision of doctors. It is dangerous to refuse hospitalization. An increase in protein can lead to the following complications:
- renal and heart failure in both mother and child,
- swelling of the lung tissue,
- placental abruption,
- intrauterine fetal death,
- high level of pressure,
- development of intrauterine infection,
- fatal damage to the abdominal organs,
- fetal developmental delay,
- hypoxia.
If the condition rapidly deteriorates, the doctor decides to artificially induce labor. What does this mean and why is it done? Artificial induction of labor is accompanied by the use of special drugs; in later stages, specialists use cesarean section. In this case, a greater emphasis is placed on the health of the mother and her child.
How to normalize protein levels
What to do if the indicator is too high? Treatment is aimed at eliminating the root cause of the development of the pathological process. The appointment of the optimal treatment regimen and its correction is carried out in a hospital setting. The decision to hospitalize a pregnant woman is made by the doctor, based on laboratory tests. It is impossible to lower protein levels on your own.
- proper nutrition. Diet can reduce the level of protein in urine. Perhaps a deviation from the norm is caused by excessive consumption of fatty, spicy, smoked and salty foods. Experts recommend giving preference to fruits, vegetables, cereals and dairy products,
- refusal of medications. Many women prescribe certain medications for themselves without consulting this issue with their doctor. Uncontrolled use of medications can lead to abnormalities in kidney function,
- gymnastics. To reduce the load on the urinary system, it is necessary to take a knee-elbow position several times a day.
The presented methods will help remove excess protein, but only if its appearance is due to physiological reasons. Deviations caused by pathological processes must be treated with medications. Complex therapy depends on the type of disease, the stage of its development and the general condition of the woman in labor. These factors also influence how long treatment will last.
Preventive actions
It is easier to prevent any disease than to get rid of it. To avoid the development of abnormalities in late pregnancy, experts recommend following preventive measures:
- do not miss scheduled visits to the gynecologist,
- take a urine test in a timely manner,
- Healthy food,
- spend more time outdoors
- remove trigger foods from your diet,
- monitor blood pressure and sugar levels,
- exclude uncontrolled medication use,
- control body weight (if it is rapidly gaining).
All these actions will help the expectant mother enjoy a pleasant position, and not spend all her time in hospital treatment. Prevention is the best way to look good and not worry about possible pathologies.
A healthy person cannot have protein in their urine. Therefore, a positive laboratory test result on a urine sample indicates the presence of a disease, often associated with kidney dysfunction.
It is especially important to identify the cause of pathology during pregnancy, since the disease can threaten not only the health of the mother, but also negatively affect the development of the baby.
How to get your tests back to normal
If you have cystitis, you should not try to remove protein from urine with decoctions of diuretic herbs or herbal preparations (Phytolysin, Canephron and the like). During pregnancy, cystitis should be treated as quickly as possible before it causes complications. Only antibiotics can quickly eliminate a bacterial infection in the bladder. Among the many drugs, there are those that are allowed during pregnancy and do not interfere with the development of the baby.
As additional measures, cranberry juice, warm sitz baths with chamomile, calendula or sage will be useful. During the period of treatment, the woman is recommended to drink plenty of fluids and eat a diet that includes plenty of dairy products, vegetables, and cereals. Spicy, overly salty, spicy foods and soda are excluded.
If a pregnant woman develops pyelonephritis, she is always offered hospital treatment. You shouldn't give it up. Under the constant supervision of a doctor, it is easier to identify and eliminate complications at the initial stage, and select the most effective and safe antibiotic or combination of antibiotics. As a rule, vitamins and drugs that protect the kidneys are additionally prescribed.
For pyelonephritis, it is recommended to reduce salt intake and increase fluid volume. If pregnancy has led to edema, mild diuretics may be used. In later stages, it is advisable for a woman to be in a knee-elbow position more often. It allows you to relieve the kidneys from the pressure of the uterus and reduce protein in the urine.
Gestosis requires hospitalization. Daily monitoring of the fetal condition is mandatory. The woman is prescribed rest, bed rest, and a strict protein-vegetable low-salt diet. To improve organ functions, diuretics, antihypertensives, and drugs to increase blood flow are used. To normalize the functions of the nervous system, sedatives are prescribed. If the mother’s condition can be stabilized, a natural course of pregnancy becomes possible without interfering with the further development of the child.
What does the appearance of protein in urine mean?
The formation of urine in the kidneys occurs from the incoming blood. The liquid is filtered and some protein is absorbed.
When filtered again, the protein returns to the blood. This explains why it is impossible to trace protein in the urine of a completely healthy person.
Protein levels in urine during pregnancy in quantities not exceeding 0.030 g/l are simply not detected by modern laboratory diagnostic methods.
Normally, there is no protein in the urine of a pregnant woman, like any healthy person.
However, during pregnancy, the female body experiences a double load. Kidneys are no exception.
If the body is having a hard time providing the necessary metabolic processes, a urine test in a pregnant woman may show residual traces of protein, which should not exceed 0.14 g/l.
If the indicator is too high, we are talking about a pathology that needs to be identified.
That is why a woman during pregnancy should submit a urine sample for analysis at least 2 times a month.
How to reduce daily protein loss on your own
Protein in the urine of pregnant women can be reduced using folk remedies. Of course, you must first consult with your doctor and get his permission. The most proven traditional medicines are:
- cranberry juice;
- parsley decoction;
- infusion of birch buds;
- decoction of pumpkin seeds.
In case of severe proteinuria, none of the listed remedies will replace drug therapy. Treat them as aids.
CURRENT VIDEO
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of protein in the urine are quite varied and require careful diagnosis. Most often, factors that can lead to a positive test result are:
- Pyelonephritis.
Protein in the urine during pregnancy may also be increased due to pyelonephritis.
The disease is attributed to inflammatory processes occurring in the tissues of the kidneys. During pregnancy, the growing uterus puts pressure on organs, which leads to stagnation of urine.
The disease is accompanied by pain in the lumbar region, cephalalgia, chills, general weakness, painful and frequent urination. In chronic cases, symptoms are mild.
Most often, pyelonephritis is diagnosed at 22-24 weeks of pregnancy. There is a significant excess of protein loss - up to 1.5-2 g/l.
Along with a high protein concentration, a large number of leukocytes appear in a general urine test.
Protein in the urine is dangerous because when the level increases to 4-5 g, the risk of intrauterine fetal death increases significantly.
- Glomerulonephritis.
Most often, the glomeruli of the kidneys are affected, but it is possible that interstitial tissue and tubules are involved in the infectious process.
The disease is characterized by swelling, arterial hypertension, fever, shortness of breath, pain in the lower back, cephalgia, and decreased urination.
In the acute course of the pathology, there is a high risk of spontaneous abortion and the development of gestosis in the 2-3 trimester, especially in the presence of hypertension. Protein levels are often recorded within 30 g/l.
In this case, the number of red blood cells in the urine is ten times higher than normal, which is why the color of the liquid acquires a reddish tint.
- Nephropathy.
Typically, nephropathy develops towards the end of the term in women with multiple or first pregnancies and accompanies gestosis. Pronounced signs of pathology are swelling throughout the body, high blood pressure.
There is increased protein in the urine, a decrease in the amount of fluid excreted per day, dizziness, and insomnia.
Depending on the severity of the process, the protein level in the urine ranges from 1-3 g/l.
- Increased load on the kidneys.
With the growth of the uterus, an overestimation of protein content in the blood also appears, associated with compression of organs and the mother’s body working “for two”. Protein in the urine is especially often detected during multiple pregnancies or large fetuses.
- Incorrect collection of urine for analysis.
Proteinuria, an increase in protein in the urine, may have a trivial cause - failure to comply with the rules for collecting a fluid sample. In this case, along with the urine, other biological materials containing protein initially enter the jar.
Collect the liquid on an empty stomach, early in the morning, after washing.
To avoid getting secretions from the genital tract into the jar, you can use a sterile cotton swab. The jar must also be thoroughly washed and sterilized.
To ensure a good urine test, it is not recommended to eat salty, spicy or sweet foods the day before.
Since in most cases proteinuria poses a danger to the mother and the unborn baby, it is necessary to carry out appropriate treatment of the pathology.
In order not to miss time, a woman should carefully monitor herself and pay attention to symptoms indicating an excess of protein in the urine.
What are the reasons for the increased concentration of protein in urine?
During pregnancy, this often happens as a result of the physiological characteristics of the body or due to the development of pathology. Increased protein is observed in the case of :
- improper collection of urine for analysis or genital hygiene
- overeating foods containing protein - cottage cheese, milk, eggs give a similar effect;
- too active physical activity;
- stress, anxiety;
- disorders of the kidneys and genitourinary organs - then the temperature rises, begins to shiver, and lower back pain appears;
- the development of dropsy, nephropathy or eclampsia, which pose a danger to the baby’s health.
If there are a lot of protein compounds in the urine, the doctor will prescribe appropriate treatment after finding out the cause of the pathology.
How can you self-diagnose proteinuria?
Even without special biochemical studies, one can suspect the presence of proteinuria by the turbidity of the urine, the appearance of white or grayish flakes in it.
This picture is observed if there is too much protein in the analysis.
As a rule, in addition to protein, such urine contains leukocytes, epithelium, and salts. Liquid collected in a container and left alone for several hours may become covered with “foam,” and sediment can be clearly seen at the bottom of the container.
If the urine looks normal and has a transparent color, it does not mean that there is no protein in it. A small amount of protein cannot be seen without special studies.
You can verify the presence of protein in the urine by heating the liquid to a boil. In this case, the protein will gather into characteristic flakes.
Of course, with kidney disease, specific symptoms of pathology are added to cloudy urine. However, often there are no signs of the disease, and urine testing for protein gives a positive result.
In this case, we are talking about an increased load that the woman’s body copes with to the limit of its capabilities. It is advisable to ease the work of the kidneys using simple methods available to any pregnant woman
Protein analysis
How to take a daily protein test
The need to take a daily urine test is caused by the detection of protein in the general analysis. There are situations where protein accidentally enters urine. To obtain a complete picture, a decision is made to collect daily urine. On the eve of the collection, it is recommended to exclude the consumption of multivitamins, excessive physical exertion, physiotherapy, contrast showers, and hypothermia.
To obtain a reliable result, a number of requirements must be met before collecting urine:
- A sterile container or glass jar, thoroughly sterilized, is required. Sterilization will ensure the destruction of bacteria. Part of the urine that is collected during the day is placed in this container.
- For a daily intake, you will need a glass container with a lid with a volume of two liters. It is also taken clean and sterilized.
- In the morning, urine collection begins. The collection period is a full day. Before each filling of the prepared container, you need to thoroughly carry out the intimate hygiene procedure. Only urine without impurities should enter the jar. The vagina must be separated with a tampon.
- Before going to bed, the jar is thoroughly closed and placed in the cold. Nighttime visits to the toilet also involve collecting urine.
- In the morning, the contents of the jar should be mixed and a certain amount should be poured into the prepared container. The remaining urine can be thrown away.
Why get retested?
If protein is detected, a decision is made to re-submit urine for testing. This is necessary to confirm or refute the diagnosis. The appearance of protein may not be associated with malfunctions of the body, but may be physiological in nature or caused by a violation of hygiene requirements.
A factor in detecting protein in urine can be:
- consumption shortly before the test of a large amount of protein food;
- excessive physical activity;
- temperature changes;
- stress, excessive fatigue, etc.
The day before taking a repeat test, it is necessary to exclude all of the above factors that influence the appearance of protein in the urine.
How to get rid of protein in urine
To reduce the amount of protein in the urine or completely eliminate its presence, you must:
- maintain a balanced diet.
A diet for proteinuria should completely exclude the consumption of spicy, fatty, salty and smoked foods. You should reduce your consumption of spices and adhere to a proper daily routine, devoting enough time to rest.
During pregnancy, it is advisable to take vitamin and mineral complexes, the composition of which should be discussed with a gynecologist.
- Eliminate salt.
Since salt significantly affects the metabolic processes occurring in organisms, it is necessary to reduce its consumption. If there are no contraindications, you can replace salt with citric acid or soy sauce.
In this case, the load on the kidneys will decrease and after some time the tissue swelling characteristic of diseases such as glomerulonephritis, nephropathy or pyelonephritis will become much less.
If a disease is detected, you must undergo treatment recommended by a gynecologist.
For example, for glomerulonephritis, a course of antibiotic drugs is indicated, the prescription of which occurs according to an individual scheme. Self-treatment can lead to serious consequences.
- Control weight and blood pressure.
If there is protein in the urine, a woman should monitor her weight and blood pressure. These indicators are mutually related.
Increased blood pressure is observed more often in overweight women. High blood pressure levels may indicate impaired renal function, and simple obesity can lead to increased load on the paired organs.
Fees and herbal remedies
Since the use of pharmacological drugs during pregnancy carries a certain threat, you can use folk advice to eliminate protein from urine.
You can remove protein in the urine during pregnancy using herbal remedies.
Decoctions prepared from lingonberry leaves, kidney collection, and “Brusniver” are very popular.
Before using decoctions, you should consult a gynecologist and make sure that the herbs will not cause an allergic reaction.
- "Brusniver".
This collection consists of 50% lingonberry leaves, which provides a slight diuretic effect. The herbal tea also contains rose hips, tripartite and St. John's wort. The drug is approved for the treatment of genitourinary infections at any stage of pregnancy.
- Kidney tea.
Orthosiphon staminate leaves perfectly relieve swelling of tissues. If Brusniver is allowed to be brewed like a regular tea drink, 1 packet per glass of boiling water, you should be careful when taking kidney tea.
As a rule, it is recommended to divide a brewed glass of herbal decoction into 3-4 doses.
- Lingonberry leaf.
During pregnancy, lingonberry leaves are brewed in accordance with the instructions on the package. The healing plant increases the flow of urine and helps fight inflammatory and infectious processes.
But before using the decoction, you should consult a gynecologist.
- Cranberry juice.
The drink has anti-inflammatory, diuretic and bactericidal effects, therefore it can replace pharmacological drugs necessary for the treatment of proteinuria.
Since cranberries contain a high content of vitamin C, which helps increase the tone of the uterus, it is advisable to follow the gynecologist’s recommendations regarding the volume of drink consumed.
If proteinuria is severe with high levels of protein in the urine, hospital treatment is recommended.
A course of diuretics and sedatives is prescribed, as well as drugs whose action is aimed at eliminating the cause of the pathology.
How to remove protein from urine - treatment
Proteinuria and its treatment are of particular interest to people who care about their health. A urine test is performed less frequently than a blood test, but it is still quite informative. Not all characteristics and their meanings are known to ordinary people. What does the presence of protein in urine and how to treat this condition?
What does protein in urine mean?
There is normally no protein in urine, since it must be completely processed by the kidneys. Acceptable values are 0.033 g/l (this concentration does not indicate pathology). Moreover, this indicator differs depending on gender and age.
Protein in the urine does not always mean pathological processes occurring in the body. During the study, healthy people receive protein in their urine provided:
- increased physical activity;
- during pregnancy (protein is not significantly increased due to the fact that the kidneys are compressed by the growing uterus);
- eating protein-rich foods too often;
- after stressful situations.
Read all about protein in a child’s urine in our article.
What to do if the level is exceeded?
An increased level of protein in the urine indicates damage to the kidney tissue. Normally, the kidneys should filter out almost all the protein. If there is an increase in protein in the urine, you should under no circumstances wait or hesitate.
It is necessary to promptly identify the exact cause of proteinuria and begin treatment.
The doctor will prescribe clarifying tests to determine a more accurate level of protein concentration. Very often urine is examined according to Nechiporenko , as well as daily urine. Research will help the doctor when choosing a further treatment plan.
Treatment
If changes in your health occur, visiting a doctor will not be difficult. In the future, the results of the prescribed tests will help the doctor in choosing a treatment method. They do not treat proteinuria, but the cause that caused it. The following treatment methods are distinguished:
- Medication.
- Folk remedies.
Medication
The main task is not only to identify, but also to eliminate the cause of the appearance of protein in the urine. When quantitative indications of proteinuria are more than 3 grams, drug therapy is mandatory. The following drugs are used for treatment:
- Antihypertensive - if the cause of proteinuria is arterial hypertension, then it is necessary to bring the pressure to the most optimal levels for the person.
- Antibiotics – to eliminate the infection.
- Anti-inflammatory – effective in inflammatory processes: pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, etc.
- Diuretics - will reduce swelling and remove excess fluid from the body, thereby facilitating the functioning of the kidneys.
- Antitumor – prevent the proliferation of malignant cells.
Treatment with tablets is not required in all cases. Only a therapist or nephrologist should decide this.
There should be no uncontrolled use of drugs!
Traditional medicine
Folk remedies have an excellent ability to restore the functional ability of the kidneys.
The use of traditional recipes is advisable only in conjunction with medications, if required.
Preparing decoctions and tinctures and preparing ingredients requires time, but the results are worth it. Treatment options for proteinuria:
- Cranberries in the form of fruit drink or juice are consumed throughout the day, without forgetting to drink pure water. On an empty stomach, you can drink a glass of pumpkin juice - a good remedy.
- 20 grams of parsley seeds are ground and poured with 200 ml of boiling water. Within two hours, the infusion will be ready for oral administration in small sips.
- 20 grams of parsley root are crushed, and then pour 200 ml of boiling water and leave for an hour and a half. It is allowed to use 30 ml of infusion at one time, drink it 4 times a day.
Folk recipes are very diverse and number more than a dozen types. It is best to decide which type of herbs or plant fruits to use for treatment only by a qualified specialist.
Uncontrolled use of traditional medicine can have unpredictable consequences for the body.
Diet
For proteinuria, a special diet is usually prescribed . Products must meet the following requirements:
- There should be as little protein in food as possible. This is especially true for meat and fish.
- Eating pumpkin, raisins, and beets will promote a speedy recovery.
- Remove salt completely.
- Milk and dairy products are recommended to be consumed daily.
How to get rid of protein in urine before analysis?
If a person suffers from an illness, the concentration of protein in the urine may decrease by only a small level. In a healthy person, the protein content is so low that if certain conditions are met, this indicator be reduced Before analysis, it is possible to reduce protein by observing the following rules:
- Hygiene - it is very important to carefully clean the external genitalia before taking a urine test.
- Sterility of dishes - urine should be collected in a sterile container; it would be best to purchase a container for collecting urine in advance.
Complications caused by the appearance of protein in the urine during pregnancy
If treatment is not carried out if the protein test result is positive, you can face quite unpleasant consequences. The kidneys are a vital organ, the untreated inflammatory process in which affects the general condition of the mother’s body.
Kidney dysfunction leads to the accumulation of toxic substances and further intoxication of mother and baby.
Proteinuria also leads to a high risk of impaired fetal development and labor. For example, nephropathy or pyelonephritis significantly increases the risk of premature birth.
Prevention of proteinuria
To reduce the risk of protein appearing in the urine, a woman during pregnancy must:
- monitor your health;
- undergo inspections in a timely manner;
- follow the recommendations of the gynecologist;
- adhere to a balanced diet;
- reduce the consumption of hot spices and salt;
- if you have diabetes, monitor your cholesterol levels;
- control blood pressure and weight.
At the slightest suspicion of increased protein content in the urine, you should undergo examination and treatment, which will allow you to avoid common complications.
Proteinuria - protein in the urine during pregnancy - is a disease that can lead to the development of serious pathologies that interfere with the normal functioning of the body.
Content
If such a symptom is present, it is important to immediately identify the cause of the pathology and begin therapy. The inflammatory process, if left untreated, can provoke irreversible negative changes in the development of the child. The presence of protein in the urine may indicate displacement of internal organs, in which there is a risk of internal hemorrhage, leading to the death of the unborn child.
Treatment
Treatment of proteinuria is aimed at stopping the disease of which it is a symptom.
A low protein diet is recommended for the expectant mother. She should also reduce the amount of salt she consumes. If the expectant mother has late gestosis, antihypertensive drugs are indicated - Methyldopa, Nifedipine. Medicines can lower blood pressure numbers. She was also recommended drugs that improve blood supply to the placenta - B vitamins, Curantil.
Preeclampsia is an indication for emergency cesarean section. Before surgery, the expectant mother is advised to administer magnesium sulfate. The drug lowers blood pressure and prevents the development of seizures.
To reduce proteinuria in glomerulonephritis, low molecular weight heparins are used. They change the structure of the renal tubules, preventing the release of albumin. In order to get rid of edema, the expectant mother is prescribed diuretics - Lasix. If there is a severe deficiency of protein in the blood, a woman is recommended to receive intravenous infusion of solutions with albumin.
The basis of treatment for pyelonephritis is taking antibacterial drugs. During pregnancy, the use of Ampicillin or Ceftriaxone is indicated. Medicines do not affect the development of the unborn child.
Consequences
Why is protein in urine dangerous during pregnancy? It can lead to:
- disorders of the nervous system of a pregnant woman;
- hormonal imbalances, which leads to nervous breakdowns and increased aggression;
- the onset of premature birth;
- convulsions;
- intrauterine pathologies of development of the unborn child.
In some cases, the fetus is fatal, and the mother may experience the following symptoms:
- severe weakness;
- headaches and dizziness;
- tachycardia;
- dysfunction of the visual organs;
- spasms;
- itching and burning, urticaria, various rashes.
To avoid all the points described above, there is a table of the norm of protein in urine during pregnancy.
| Color | Yellow |
| Clearness | Clear liquid |
| Bacteria | Must not be |
| Density | 1010 — 1035 |
| Protein | Up to 0.14 g/l |
| Hemoglobin | Must not be |
| Glucose | Allowed 1.6 mmol/l |
| pH level (acidity) | Up to 8.0 |
If the indicators are within the specified limits, then there are no health problems.
It is very difficult to independently determine the concentration of protein in urine. Accurate results can be obtained from a medical laboratory.
Signs and symptoms of developing problems
The most common pathological causes of protein in the urine are infection of the urinary organs, kidneys, nephropathy as one of the manifestations of gestosis.
| Disease | Characteristic symptoms | Reflection of the disease in urine analysis |
| Preeclampsia | Rapid weight gain. Visible swelling of the legs, hands, face (may be absent). High blood pressure, thirst, nausea. | Severe proteinuria (>3 g/day), increased urine density. Other indicators are usually normal. Daily protein is considered more informative during pregnancy (all urine per day is sent for analysis). |
| Cystitis | Frequent urination with a small volume of urine, burning or pain when passing urine. | The urine is cloudy, sometimes with blood. The density is reduced, mucus and bacteria are detected. Protein and leukocytes in the urine during pregnancy complicated by cystitis are increased. |
| Pyelonephritis | Pain, heaviness in the lower back, nausea, fever, weakness, symptoms of cystitis. | Leukocytes are higher than normal, bacteria are detected (>100 thousand in 1 ml). Increased protein in the urine, but the level is lower than with gestosis: less than 1 g/l. In biochemical analysis, phosphates, oxalates, and urates are increased. |
If protein appears in the urine during pregnancy for physiological reasons, this process is not accompanied by any special symptoms. Such a protein can only be detected by chance by taking a test at this time. A single detection of protein in the urine cannot be a sign of a disorder. If the rest of the urine indicators do not fall outside the normal range, it is advisable to retake the test the next day.
You can independently evaluate the protein in your urine using test strips: Bioscan, Uribel and similar ones. The minimum detectable protein level in this way is 0.1 g/l. The price of the strips is low (from 120 rubles), one package is enough for the entire pregnancy. The tests are most sensitive to albumin and do not always reliably detect other proteins. Up to a quarter of these analyzes may not be true.
Home protein determination cannot completely replace regular testing in the laboratory. A urine test for protein during pregnancy is prescribed every month, and even more often during longer periods: from 28 weeks - every 2 weeks, with an increased risk of complications - weekly.
How to reduce protein in urine during pregnancy
First, it is necessary to determine the source of the disease and its cause, only in this case the treatment will be effective and the protein level will decrease significantly.
To do this, a comprehensive examination of internal organs is carried out.
Treatment
When an inflammatory process is detected in a particular organ, medications that are safe for mother and fetus are prescribed.
In such cases, therapy with anti-inflammatory devices and antibiotics is necessary.
To increase effectiveness, diuretics are prescribed. It is worth noting that if the cause of the increase in the concentration of the element is not cured, then the possibility of relapse of the pathology will arise, but with complications.
In particularly difficult situations (preeclampsia, vaginitis), specialists do everything to stabilize medical indicators and provide the woman with a normal, painless birth.
Prevention
To avoid an increase in protein levels in the urine during pregnancy, prevention is necessary, namely:
- reduce the number of stressful situations;
- strictly follow a diet;
- maintain careful personal hygiene.
How to properly collect urine for protein during pregnancy
There are rules for collecting urine for testing that people follow when taking the test so that they can collect their 24-hour urine during pregnancy and the test result is accurate. This will help the doctor monitor the condition of the pregnant woman’s body and avoid complications that will affect both the woman and the fetus.
- In 4-5 days, the woman cancels the medications. Exceptions are drugs that cannot be excluded as prescribed by the gynecologist together with the therapist.
- The pregnant woman's diet begins 2 days before testing. Fatty, fried, overly salty foods are excluded. The amount of meat and dairy products is decreasing.
- The patient must maintain a drinking regime (1.5-2 liters of fluid per day), provided there is no swelling.
- First buy a sterile container from the pharmacy. The use of other containers is unacceptable; inside them there are microbes and foreign substances that will distort the result.
- Before urinating, a pregnant woman washes her genitals and closes the vaginal opening. This prevents the entry of foreign microorganisms into the biomaterial. The urine of a healthy woman does not contain bacteria and is initially sterile.
- Protein is determined using a general clinical urine test (UCA), so the entire portion of biological fluid is collected.
- The sample will be delivered as soon as possible. If there is a reason why this cannot be done, the container is placed in the refrigerator. Freezing is prohibited. The storage time of refrigerated material is no more than 2 hours.
- A piece of paper is attached to the container on which the patient’s name is written.