Homocysteine is a substance formed in the human body from methionine, which is extremely important for bearing a healthy child. Blood circulation in the placenta and the proper development of the baby directly depend on this amino acid.
In the female body, the level of homocysteine constantly increases throughout life, and during pregnancy, on the contrary, it decreases. The maximum decrease in blood concentration is observed in the first and third trimester. To bear a healthy baby, it is necessary to control homocysteine when planning pregnancy.
The concept of norm.
This substance is produced in the human body from various foods rich in methionine. For example, milk, eggs, meat. To get pregnant safely, the amino acid level should not exceed 11 micromol per milliliter of blood.
It is better to find out whether the indicators correspond to the norm at the planning stage. This will allow:
- If the level is insufficient, adjust the diet according to the doctor’s recommendation (introduce foods rich in B vitamins into the menu). Special medications may also be prescribed that will allow the expectant mother’s body to return to normal very quickly.
- Prevent miscarriage or abnormal development of the baby in the womb. After all, it is always easier to provide conditions under which the placenta will function normally than to subsequently fight for proper placental blood circulation.
- Determine whether the norm corresponds to the indicators characteristic of a completely healthy person. During pregnancy, the analysis may show unreliable numbers.
Elevated homocysteine - causes and consequences
If homocysteine is elevated during pregnancy, then the main cause is a deficiency of folic acid and B vitamins - the body turns on protective mechanisms and releases this amino acid into the blood in large quantities. In such cases, hyperhomocysteinemia is diagnosed.
Symptoms of high homocysteine are upset stools, frequent bouts of dizziness, weakness, decreased appetite, shortness of breath, pain in the mouth of unknown origin.
One of the main signs is numbness, tingling and burning sensation in the upper and lower extremities.
Why are the indicators increasing:
- Homocystinuria is a hereditary disease that causes metabolic disorders;
- consumption of large quantities of animal products, especially cottage cheese;
- atrophic gastritis, some other diseases of the digestive tract that interfere with the normal absorption of nutrients;
- psoriasis, diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal pathologies, malfunctions of the thyroid gland and kidneys;
- sedentary lifestyle, excessive exercise, malnutrition;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol, drinking large quantities of coffee, narcotic drugs;
- long-term use of drugs for the treatment of psoriasis, autoimmune diseases, anticonvulsants.
How the analysis is carried out.
For the analysis to be reliable, a woman needs to properly prepare for it. The doctor explains all the details of preparation. He must prescribe an immunochemiluminescent blood test taken from a vein and give all the necessary recommendations.
You need to take this test three months before you plan to conceive. If there has already been a history of problems with amino acid levels, the analysis is carried out six months before conception.
Preparation for blood collection requires:
- do not smoke for half an hour before visiting the medical office;
- do not eat for eight hours (you are allowed to drink only clean water without gas);
- do not overload yourself with physical work and sports training for a day;
- Do not eat fatty foods for a day.
The laboratory will prepare the results in about two days. Based on the answer, it will be possible to clearly and reliably determine whether the amino acid is produced in sufficient quantities or whether drug support and nutritional adjustments are required.
Risks of elevated homocysteine
With a constantly elevated level of homocysteine, it is not the inner lining of veins and arteries that has a negative effect; particles of bad cholesterol easily settle on the walls. All this increases the risk of developing thrombophlebitis, thrombosis, atherosclerosis, and other serious vascular pathologies.
During pregnancy, thrombosis is especially dangerous - against the background of impaired blood flow, the fetus begins to suffer from a lack of oxygen and nutrients, which can cause the development of severe congenital diseases in the child, miscarriage, or intrauterine death of the baby.
With thrombosis, a blood clot can break off at any time and travel through the vessels to the heart, brain, lungs, causing a stroke or heart attack.
With high homocysteine, other unpleasant consequences can occur - chronic placental insufficiency, eclampsia and preeclampsia, placental abruption, nephropathy and retinopathy.
In vegetarian women, increases in homocysteine levels rarely occur, but doctors strongly recommend giving up vegetarianism during pregnancy, since with this type of diet the baby does not receive enough protein and iron, and these substances are essential for normal growth and development.
High level.
If homocysteine levels are elevated during pregnancy, do not panic ahead of time. Perhaps the test results were distorted or there are reasons that need to be eliminated.
For example, overestimation of the norm provokes:
- Lack of adequate physical activity. Sedentary work and a sedentary lifestyle do not have the best effect on the female body! To get rid of the problem, it is necessary to ensure moderate exercise. Excellent for swimming, skiing and cycling.
- Alcohol abuse. Women should not drink them for at least three months before pregnancy!
- Excessive coffee consumption. This drink, alas, also does not add health.
- Smoking is another bad habit that directly affects your ability to get pregnant. The doctor will recommend giving up cigarettes completely.
- Unbalanced diet. Most often, expectant mothers do not get enough B vitamins (thiamine, folic acid, pyridoxine and cobalamin - that is, B1, B6, B9 and B12). To eliminate vitamin starvation, the menu must include: cod liver, eggs, caviar, cottage cheese, cheeses, lean meat, beef liver, walnuts, herbs, citrus fruits.
It is necessary to eliminate all of the above factors and re-donate blood from a vein. If the analysis is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe treatment.
Therapy includes:
- subcutaneous administration of B vitamins;
- taking aspirin in small doses and heparin drugs (Cetroparin, Fragmin, Lovenox, and others).
Treatment is carried out under the constant supervision of the attending physician. Changing the dosage of medications on your own is strictly prohibited.
Course of pregnancy
The level of homocysteine in the physiological state of pregnancy is beyond what is generally accepted for women outside such a state.
To be more precise, the range of normal values simply narrows, and at different stages of pregnancy the values are characteristic:
- A decrease in homocysteine accompanies the onset of pregnancy, which requires activation of all reserves of the female body. Even a protein value at the lower limit of the recommended range is considered normal, since there is no supply of this substrate.
- Compensatory adaptation of the pregnant woman’s body leads to a gradual restoration of the proper concentration of the amino acid. A prerequisite for this is adequate nutrition for the pregnant woman, which should take into account the increasing substrate needs.
- The beginning of the second trimester is also accompanied by a drop in some proteins, which are used to build new structures of the developing body. Adequate nutrition requires additional intake of vitamin complexes, the need for which also increases during gestation.
- The homocysteine concentration returns to the absolute norm by the second day through natural delivery or cesarean section.
Qualified assistance from a gynecologist or therapist is required if the level of the indicated protein drops by more than 0.5 µmol/l. Sometimes normalizing the diet and taking additional vitamins cannot compensate for the growing deficiency; medication is required.
Low level.
A too critical deviation from the norm (about 4 units) in the direction of decrease leads to poor health of the woman. In such a situation, the doctor may advise reducing physical activity and even drinking coffee in the morning.
It should be noted that exceeding the norm poses a great danger. With an increase of 2 units, the level of homocysteine leads to disruption of blood flow to the placenta - the baby does not receive enough oxygen and nutrients. As a result, there is a sharp slowdown in development. Miscarriages or fetal death are possible.
But the reduced level does not in any way affect the pregnancy and intrauterine development of the baby. Only the woman will suffer. She may feel weak and fatigued during pregnancy. A correct daily routine with long breaks for rest, walks, a balanced menu and long sleep will help correct this unpleasant situation.
To exclude fetal death, you must consult a doctor six months before pregnancy, undergo an examination and pass all tests, including homocysteine. The doctor will definitely tell you how to bring the body back to normal. A woman can only strictly follow medical instructions and then the pregnancy will pass without any health problems.
Who needs to get tested for homocysteine?
According to statistics revealed in recent studies, 30% of the adult population of the planet has more than twice the level of homocysteine.
The following people should pay attention to the level of this substance in the blood and get tested for its content from time to time:
- elderly (over 60 years old);
- people after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract;
- people with thrombosis and vascular and heart diseases;
- people with diabetes;
- people suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland and endocrine system;
- patients with renal failure;
- persons with alcohol and drug addiction.
Separately, mention should be made of people who have a number of hereditary diseases associated with the production of enzymes.
It is also necessary to regularly get tested for homocysteine during pregnancy, especially if the previous birth was complicated. Women who have experienced gestosis during pregnancy need to monitor their homocysteine levels in everyday life.
Diagnostics and reduction of indicator
Diagnosis in the perinatal period should not be neglected. Delay is harmful both to the mother’s body and to the health of the unborn child.
In order to correctly donate blood for homocysteine, you need to follow simple rules.
- Follow a diet that excludes fatty foods on the eve of the test.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Stop taking medications.
They can significantly affect the reliability of the results. The test can be taken after finishing taking the medications in 3-5 days.
When planning which day of the cycle to take a homocysteine test, it does not matter.
Up to 2 ml of blood serum is used for diagnosis. It is taken from a vein.
This happens in a antenatal clinic in a doctor's office. After blood is taken, it should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than two hours until the test.
The examination does not begin with identifying diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
BabyMother
Contents [Show]
The real enemies of modern humanity are vascular diseases, in particular atherosclerosis. Elevated homocysteine is often one of its causes, so its control is important for everyone who cares about their health.
Controlling homocysteine during pregnancy is also important. Deviation of its indicators from the norm can not only negatively affect the health of the expectant mother, but also have an impact on the fetus. Information about the level of homocysteine allows you to prevent one of the most dangerous companions of pregnant women - preeclampsia.
Methionine, one of the essential amino acids, enters the human body with protein foods. As a result of protein processing from methionine, homocysteine is synthesized - its by-product.
It is also an amino acid, but, unlike methionine, it cannot be obtained from foods. Methionine is an important component of metabolism and is found in large quantities in meat, dairy products and eggs. There is especially a lot of it in cottage cheese.
Normally, homocysteine is found in the body in very small quantities. B vitamins and folic acid play an important role in the metabolism of homocysteine.
If there are not enough of these substances for processing, then the level of homocysteine increases. In this case, the body triggers defense mechanisms and releases it into the blood in large doses.
An increase in the level of this amino acid leads to weakening of the walls of blood vessels and, as a result, the development of atherosclerosis and the formation of blood clots. Older people have an increased risk of developing Alzheimer's disease and age-related encephalopathy.
Elevated homocysteine during pregnancy can lead to fetal death, and in people with diabetes, the risk of vascular complications increases.
When studying the level of homocysteine in the blood, the following is considered normal:
- in men: 5.9–16.0 µmol/l;
- in women: 3.4–20.4 µmol/l.
However, the listed norms are not so clear. In women, the homocysteine level during pregnancy is slightly different from the standard. For expectant mothers, the optimal range is 4.6–12.4 µmol/L.
In children, homocysteine is at a level of about 5 µmol/l, regardless of gender. With the onset of puberty, the indicators increase first to 6–7, and then to 10–11 µmol/l, and in boys the increase in homocysteine is more pronounced than in girls.
It remains at approximately the same level in adults, but gradually increases with age.
As noted, homocysteine levels during pregnancy may differ slightly from normal, and even go beyond generally accepted limits.
In the first weeks of pregnancy, the level of this amino acid may be at the lower limit of the specified range and, in this case, this is considered the absolute norm.
Also, low homocysteine during pregnancy can be observed at the beginning of the 2nd trimester, which also should not cause concern. Its level will finally return to its previous level within a few days after birth.
However, it is important that the permissible deviation from the norm should not exceed 0.5 µmol/l, otherwise an urgent consultation with the supervising gynecologist and therapist is necessary.
It is important to eat rationally and properly while carrying a baby. This is not only a guarantee of the health and full development of the unborn child, but also a guarantee of maintaining the balance of important substances in the body, such as homocysteine. Read more: pregnant woman's diet→
Women who are seen by a gynecologist for pregnancy are prescribed B vitamins and folic acid in prophylactic doses. These substances have a beneficial effect on the breakdown of homocysteine and its normal level.
Since the body expends a lot of resources during pregnancy, such prevention is an additional protection against increased amino acid levels.
Before getting pregnant, the best decision would be to undergo an examination, including a blood test. In case of deviations from the norm, before conceiving a child, it is best to take a course of vitamins, which should be prescribed by a doctor.
Additionally, to normalize the level of this substance, you need to stop smoking and drinking coffee in large quantities. When planning pregnancy, homocysteine is an important indicator that affects both the possibility of conception and pregnancy.
According to statistics revealed in recent studies, 30% of the adult population of the planet has more than twice the level of homocysteine.
The following people should pay attention to the level of this substance in the blood and get tested for its content from time to time:
- elderly (over 60 years old);
- people after surgery on the gastrointestinal tract;
- people with thrombosis and vascular and heart diseases;
- people with diabetes;
- people suffering from diseases of the thyroid gland and endocrine system;
- patients with renal failure;
- persons with alcohol and drug addiction.
Separately, mention should be made of people who have a number of hereditary diseases associated with the production of enzymes.
It is also necessary to regularly get tested for homocysteine during pregnancy, especially if the previous birth was complicated. Women who have experienced gestosis during pregnancy need to monitor their homocysteine levels in everyday life.
Hyperhomocysteinemia - increased levels of homocysteine in the blood can be caused by a number of reasons. This is a hereditary factor, and some diseases, and an incorrect lifestyle.
The most common causes of hyperhomocysteinemia are:
- heredity;
- avitaminosis;
- hormonal diseases, kidney and thyroid dysfunction;
- lack of physical activity;
- smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- taking certain medications.
A hereditary disease that causes an increase in homocysteine is homocystinuria. This is a metabolic defect caused by genetic predisposition.
During the disease, the absorption of certain amino acids, in particular methionine, is impaired, which leads not only to jumps in the level of homocysteine and other substances in the blood, but also to dysfunction of the central nervous system, heart and joints.
With vitamin deficiency, namely a lack of B vitamins and folic acid, hyperhomocysteinemia also often occurs. In this case, it is treated by simply taking vitamins prescribed by your doctor.
Poor nutrition, a sedentary lifestyle and bad habits disrupt the metabolic process, resulting in untimely breakdown of homocysteine and, accordingly, its increase.
To normalize the condition, you need to give up alcohol and smoking, play sports and review your diet.
A common cause of the disorder may be medication use. Medicines to treat psoriasis neutralize the effect of folic acid, and anticonvulsants and immunosuppressive (to treat autoimmune diseases) drugs break down vitamin B in the body.
It is their lack that leads to disruption. Some antidepressants also affect homocysteine.
The consequences of increasing levels of this amino acid can be serious. This primarily concerns blood vessels, since homocysteine weakens their walls.
The consequences of hyperhomocysteinemia include:
- thrombosis and atherosclerosis;
- dementia and Alzheimer's disease in older people;
- heart failure and myocardial infarction.
If homocysteine is elevated during pregnancy, then this is a reason to start urgent treatment under the strict supervision of a gynecologist.
An excess of the substance has an extremely negative effect on the fetus and can lead to serious developmental disorders or its death. In the second half of pregnancy, preeclampsia (preeclampsia) or eclampsia may develop - a dangerous pathology that threatens the life of the mother and child.
Low levels of homocysteine in the blood may indicate pregnancy. In this case, not too much of a decrease is normal.
Another reason is multiple sclerosis. Often this indicator in a blood test becomes the first “bell” about the onset of the disease. The diagnosis is made based on the results of additional studies.
If homocysteine is too low during pregnancy, you still shouldn’t worry. Bringing its indicator back to normal is not so difficult; for this you need to eat right and do not forget about moderate physical activity.
Walking in the fresh air or swimming are perfect for expectant mothers. Another “cure” for low homocysteine is a cup of quality coffee in the morning.
Disturbances in homocysteine levels are easily corrected and are most often treated in simple ways.
Taking multivitamins, moderate exercise and proper nutrition are three pillars for normalizing its level. But it is important to understand that any correction of blood test parameters should be carried out exclusively by the attending physician.
Author: Irina Maslova, especially for Mama66.ru
We recommend reading: Drotaverine in case of threat of miscarriage
Homocysteine is an important and essential amino acid for the human body, especially during pregnancy and its planning. An increase in homocysteine levels can lead to unpleasant consequences, so it is very important to take a blood test for homocysteine at the stage of planning pregnancy or during it if you have a history of miscarriages.
As already mentioned, homocysteine is an amino acid variety and is an active substance. Unlike other amino acids, this enzyme does not enter the body with food, but is synthesized by methionine and is considered a product of its processing. Methionine enters the body through food products of animal origin.
Homocysteine levels vary depending on age, but in general the amount should be minimal. Without folic acid and B vitamins, homocysteine metabolism is impossible. When there is a shortage of them, the level increases greatly, as a result of which the processed product is released into the blood. After this, the walls of blood vessels begin to collapse, against which atherosclerotic plaques and blood clots form. During pregnancy, this can even lead to fetal developmental failure.
So, in order for homocysteine levels to be normal, it is necessary to ensure that the body receives folic acid and vitamins B6, B12 in sufficient quantities. If a person is deficient in these vitamins and your diet contains too much protein, then homocysteine levels increase.
We present to your attention a video that talks about foods that can lead to miscarriage. The program touches on the topic of increased homocysteine as a result of an unbalanced diet, which can lead to miscarriage.
A blood test for homocysteine is needed for:
- preventing miscarriage caused by increased homocysteine;
- timely detection of deficiency of B vitamins and folic acid;
- determining the risk of heart and vascular disease;
- detection of a hereditary predisposition to a disease called homocystinuria.
Homocystinuria refers to a genetic disease that entails consequences such as mental retardation, thinness, atherosclerosis and other diseases of the blood vessels, heart, visual apparatus, and skeletal system.
Most often, during pregnancy, homocysteine is reduced, which helps improve blood circulation in the placenta. This is a physiologically normal phenomenon.
Every woman planning a pregnancy and having a history of more than 2 miscarriages must undergo a blood test for homocysteine. If a deviation is detected, drug therapy aimed at balancing the level of folic acid and B vitamins is necessary.
In a healthy adult, the normal homocysteine level should be:
- absence or planning of pregnancy – 4.44-13.56 µmol/l;
- during pregnancy - 4.6-12.4 µmol/l, deviations in each direction of 0.5 µmol/l are possible.
In some laboratories, the norm for pregnant women is up to 10 µmol/l, and for non-pregnant women - up to 15 µmol/l, so it is still recommended to focus on the norms of the laboratory where the test was taken!
When homocysteine levels exceed the norm, doctors make a diagnosis of hyperhomocysteinemia. Increasing the level of this amino acid may not always lead to unpleasant consequences. This only increases the risk of miscarriage or other adverse consequences, but if the situation is changed in time, then this risk is minimized.
Causes and consequences
Causes of hyperhomocysteinemia:
- Since methionine comes with some products of animal origin, the risk of pathology occurs when a woman consumes large quantities of meat, dairy products (especially cottage cheese) and eggs.
- Lack of B vitamins and folic acid in the body, which in turn occurs with an unbalanced diet.
- Some diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (atrophic gastritis, etc.), which impair the absorption of nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Presence of renal failure and/or hypothyroidism.
- Drinking large quantities of coffee, alcoholic beverages, smoking.
- A sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, excessive physical activity.
- Strict diets, malnutrition.
Note that homocysteine levels are rarely elevated in vegetarians. However, this does not speak in favor of vegetarianism, since with this type of nutrition for a pregnant woman, the fetus does not receive enough other useful substances (in particular, protein and iron, which are so necessary for the normal development of the fetus).
Unpleasant consequences:
- spontaneous miscarriage;
- preeclampsia and eclampsia;
- fetal developmental delay;
- fetal hypoxia;
- placental insufficiency in chronic form;
- placental abruption;
- venous thromboembolism;
- nephropathy and retinopathy, as a complication if a pregnant woman has diabetes.
The most effective treatment for high homocysteine levels is vitamin therapy. In general, treatment can be like this:
- Prescription of folic acid (5 mg per day) and B vitamins in large quantities . This allows you to replenish the deficiency of these substances in the body and balance the synthesis of homocysteine. In addition, hematopoiesis is stimulated, the functionality of internal organs is improved, metabolic processes are accelerated, and many amino acids are synthesized. Plus, blood clotting is normalized, nucleic acids are formed in sufficient quantities, and cell growth and division are accelerated. But the main thing is that the embryo develops correctly.
- Following a diet aimed at reducing protein consumption and increasing the proportion of vegetables and fruits in the diet.
- Antiplatelet treatment involves taking aspirin in small doses (up to 100 mg per day) or heparin drugs - fraxiparin, clexane, fragmin, etc. This reduces the risk of developing atherosclerosis (formation of cholesterol plaques) and thrombophlebitis.
If elevated homocysteine levels are detected, it is also recommended to donate blood for sugar, creatinine and TSH.
Prevention:
- get rid of bad habits;
- eat more foods rich in vitamins B 6, B 9, B 12;
- do not drink a lot and often of coffee;
- lead an active lifestyle, but without fanaticism (strength training in the gym is already too much for those planning a pregnancy and for pregnant women, only light weight in the form of dumbbells is allowed);
- walk more in the fresh air;
- strictly monitor your diet (protein is very important for the developing fetus, but there should also be enough vegetables).
Taking aminophylline may temporarily increase homocysteine levels. Therefore, during treatment with aminophylline, blood is not tested for homocysteine.
Reduced levels of homocysteine during pregnancy are not dangerous, but, on the contrary, are beneficial. The fact is that this significantly improves blood supply to the placenta, as a result of which the embryo receives a sufficient amount of nutrients. Therefore, a pregnant woman should not worry if the level of homocysteine in her blood is below normal.
The only negative side is a feeling of weakness, fatigue and deterioration in general well-being, but it happens that such symptoms are not observed. It all depends on the characteristics of the pregnant woman’s body.
Causes, consequences
The main reasons for decreased homocysteine levels:
- Onset of pregnancy . A decrease in homocysteine levels in the first trimester of pregnancy is not a deviation. Next, the level must reach the established norm.
- Multiple sclerosis , which affects the spinal cord and brain.
In order for a woman to feel good and for weakness to not cause discomfort, the following rules must be followed:
- It is strictly forbidden to lead a sedentary lifestyle, this will only worsen the situation. If a person has a sedentary job, he needs to do light exercise every hour to tone the body.
- Take walks in the fresh air. If possible, visit the botanical garden and other places with a large number of living plants where fresh air abounds.
- Be careful about your diet. Eat more fresh vegetables, berries and fruits. Avoid foods high in cholesterol (smoked, canned, etc.).
- Don't drink coffee or strong tea; it's better to take vitamin premixes. If you really can’t do without caffeine, then drink 1-2 cups of coffee a day, but not strong coffee.
- Visit your doctor promptly.
If you adhere to all the requirements and rules during pregnancy and its planning, your homocysteine level will always be normal.
Modern standards for managing a pregnant woman in our country involve passing a huge number of laboratory tests over a period of 9 months. Including in some antenatal clinics and perinatal centers, a relatively new biochemical test for homocysteine is taken during pregnancy .
The level of homocysteine in the blood serum during pregnancy is not tested in everyone; it refers to analyzes of a detailed coagulogram. It is usually taken from expectant mothers with various pathologies (premature aging of the placenta, frozen pregnancy, etc.). Or in women with problems conceiving and carrying a pregnancy before.
A blood test for homocysteine is performed not only during pregnancy, as it is a fairly popular therapeutic test. Homocysteine is an amino acid formed from methionine, which in turn enters the body with food. Cysteine is formed from homocysteine under the influence of vitamins B2, B6, B12 and folic acid.
At high concentrations in the blood serum, it has a toxic effect on the endothelial wall of blood vessels (the delicate inner lining of arteries and veins), and this leads to the fact that “bad” cholesterol easily settles on them, causing the formation of blood clots. Thrombosis, in turn, disrupts blood flow, including placental, and can lead to thromboembolism - separation of a section of a blood clot and its transfer to the brain, heart, lungs or other organs, causing a stroke, heart attack or lungs.
Thus, this analysis is necessary to evaluate the coagulation system of the expectant mother or when examining a woman planning a pregnancy.
Its normal values in non-pregnant women are from 5-10 µmol/l; in the stronger half, this figure is higher due to greater muscle mass. The norm of homocysteine during pregnancy in the 1st trimester is almost the same - from 4 to 12 µmol/l. In the 2nd trimester, the amount of homocysteine should decrease by 50% and remain constant until the birth of the child. When the content of this amino acid increases above the indicated figures, a pathological condition called hyperhomocysteinemia occurs.
Elevated homocysteine during pregnancy will not always lead to any consequences. Increasing it increases the risks of various situations (they will be given below). It has been proven that the higher the homocysteine level and the older the woman, the higher the risk.
Why does HHC occur?
Homocysteine is formed from methionine. Methionine is an amino acid that comes from food.
Foods high in methionine:
- Animal origin: Eggs
- Liver
- Fish
- Milk
- Legumes
It should be noted that there is much more methionine in animal products. Legumes and nuts also contain sufficient amounts, but it is better for a pregnant woman to reduce them in her diet.
These are the so-called external factors. They do not mean that if you are a smoking vegetarian working as a loader, then you will 100% have elevated homocysteine levels during pregnancy, but the percentage, of course, will be high in such a situation. However, the main factor in increasing its level is genetic. Mutations were found in the corresponding genes responsible for the transformation of homocysteine.
During pregnancy, when homocysteine increases, it is necessary to use vitamin complexes containing B vitamins. Also, a certain diet during pregnancy when homocysteine increases is important.
In addition to following a diet, in some cases special anticoagulant therapy is carried out (prescription of low molecular weight heparins). Anticoagulants are prescribed when, along with an increase in homocysteine during pregnancy, there are other changes in the blood coagulation system, which are collectively called hypercoagulation (increased blood viscosity). Aspirin is sometimes prescribed, but less often than low molecular weight heparins.
If elevated homocysteine is detected once during pregnancy, you need to retake the test again.
Homocysteine is low during pregnancy
Very rarely, the opposite situation occurs when homocysteine is reduced during pregnancy (this is a level below 4 µmol/l). Starting from the second trimester, this is a normal phenomenon, since, as stated above, its level is normally twice the original level. If homocysteine is low when planning pregnancy, then you should think about your diet - perhaps there is not enough meat.
In any case, low homocysteine levels are not dangerous or even harmful! On the contrary, a decrease in homocysteine levels during pregnancy promotes normal blood flow to the uterus and fetus.
Homocysteine may be reduced during pregnancy, as well as many other laboratory and instrumental parameters characterizing the condition of the mother and fetus. It is important to control the level of this protein compound, as it can prevent a dangerous condition in pregnant women - gestosis. Homocysteine partly reflects the condition of the blood vessels, the length of which increases during pregnancy, which creates favorable conditions for the development of new diseases and complications of existing ones.
Homocysteine decreases during certain periods of pregnancy. Its deficiency is compensated for by vitamins and a balanced diet, unless it is a consequence of illness.
Protein compounds in food consist of a certain amount of amino acids, including methionine. When it is converted in the digestive tract, it leaves behind its by-product homocysteine, which no longer occurs naturally outside the human body.
The sources of methionine are:
- all dairy products and especially cottage cheese;
- eggs;
- meat products.
Their physiological transformation results in the formation of rather small amounts of homocysteine, which are found in the blood. In order for homocysteine to continue to be used by the body, the pregnant woman must have a sufficient concentration of folic acid, as well as some representatives of vitamins belonging to group B.
For non-pregnant women, a homocysteine level of 3 to 20 µmol per liter is considered acceptable. If there is a problem of infertility in the family, it is recommended to bring the level of this compound into the required range.
When pregnancy occurs, the acceptable correlation of the indicator narrows from 4.5 to 12 µmol/l.
This concentration will correspond to the optimal functioning of blood vessels throughout the woman’s body and in a new organ for her - the placenta. The optimal level of homocysteine ensures the full development of the fetus, the absence of threats of hypoxia and nutritional deficiencies.
The level of homocysteine in the physiological state of pregnancy is beyond what is generally accepted for women outside such a state.
To be more precise, the range of normal values simply narrows, and at different stages of pregnancy the values are characteristic:
- A decrease in homocysteine accompanies the onset of pregnancy, which requires activation of all reserves of the female body. Even a protein value at the lower limit of the recommended range is considered normal, since there is no supply of this substrate.
- Compensatory adaptation of the pregnant woman’s body leads to a gradual restoration of the proper concentration of the amino acid. A prerequisite for this is adequate nutrition for the pregnant woman, which should take into account the increasing substrate needs.
- The beginning of the second trimester is also accompanied by a drop in some proteins, which are used to build new structures of the developing body. Adequate nutrition requires additional intake of vitamin complexes, the need for which also increases during gestation.
- The homocysteine concentration returns to the absolute norm by the second day through natural delivery or cesarean section.
Qualified assistance from a gynecologist or therapist is required if the level of the indicated protein drops by more than 0.5 µmol/l. Sometimes normalizing the diet and taking additional vitamins cannot compensate for the growing deficiency; medication is required.
Consequences of a fall
Low homocysteine levels can signal pregnancy. It is quite acceptable to expect its decrease in the early stages; this condition does not require additional therapeutic measures. Reduced homocysteine in other stages of gestation or in cases where compensatory therapy is not effective requires caution.
A pronounced decrease in the methionine follower is observed in multiple sclerosis. Often the onset of pregnancy is accompanied by overstrain of all organs and systems, so that some latent or sluggish diseases make themselves felt for the first time. Sclerosing lesion is one of these diseases that threatens both the child and the mother.
Yet this condition is rarely observed. Typically, sclerosis is a systemic disease that is hereditary. If pregnancy is planned, a predisposition to the disease can be identified before the child is conceived and appropriate treatment can be carried out for adequate preconception preparation.
To prevent a physiological decrease in amino acids, a pregnant woman should adhere to the following recommendations:
- A balanced diet should be accompanied by dosed physical training, which will also help normalize amino acid metabolism.
- No matter how many opinions deny the beneficial effects of coffee, during pregnancy this product can perfectly potentiate the body. Only coffee should be of high quality, freshly brewed, and should be consumed a little in the morning.
- The purchase of multivitamins should be strictly agreed with a doctor, who can assess physiological deficiency and the need for certain substances.
Thus, homocysteine is an important indicator in matters of the possibility of conception, gestation, and the diagnosis of certain diseases.
Homocysteine is a biologically active amino acid, a breakdown product of protein foods such as meat, dairy products and eggs. During protein digestion, the essential amino acid methionine is synthesized, and homocysteine is a byproduct of its formation. The content of homocysteine in the body is extremely low; its amount, as deterrent factors, is especially affected by folic acid, as well as B vitamins: with their deficiency, the amount of homocysteine increases sharply.
Negative consequences in the body of the mother and fetus are caused by a deviation in homocysteine levels towards a decrease or increase. Having received timely information about the complications and consequences of these abnormalities, the pregnant woman begins to monitor the level of homocysteine in the blood, take measures to reduce this indicator, thereby avoiding an extremely life-threatening condition for the fetus and mother - gestosis.
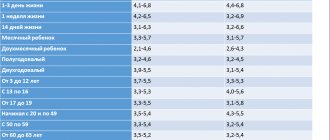
Homocysteine during pregnancy is normally in the range from 4.6 to 12.4 µmol/l. In childhood (up to 14 years), its level is 5 µmol/l, regardless of gender, in adolescence – 10-11 µmol/l. The normal levels of this amino acid in men are slightly higher - 3.5-20.5 µmol/l, while in non-pregnant women the norm is 5.9-16.0 µmol/l. During pregnancy, the norm of homocysteine levels is divided depending on the period:
- The first trimester is the norm 4.6-12 µmol/l.
- Second trimester – norm 5.5-12.2 µmol/l.
- Third trimester – norm 6-12.4 µmol/l.
With a nutritious diet, the mother guarantees her baby’s development and health, since the balance of the most important nutrients (amino acids, vitamins) is maintained. A slight downward deviation in homocysteine levels in the first weeks of pregnancy, as well as at the beginning of the second trimester, may be physiological (no more than 0.5 µmol/l). A situation where homocysteine is reduced to lower levels (by 3 µmol/l) often causes the mother to feel unwell, with virtually no effect on the vital functions of the fetus. Gynecologists claim that such a decrease protects the blood vessels of the placenta, as well as the blood vessels of the baby’s heart and brain, from ischemic processes, which has a good prognosis in the future.
Accumulating in the vascular walls and endothelium of the arteries, homocysteine during pregnancy can have a damaging effect on these vessels. High levels of homocysteine lead to the formation of blood clots, plaques, and the appearance of atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. For the mother and fetus in such a situation, there is a threat of miscarriage due to thrombosis and impaired placental circulation. In the last trimester and in the prenatal period, there is a threat of intrauterine fetal hypoxia.
Early signs of increased homocysteine in the blood of the expectant mother are:
- Increased thirst.
- Gain weight in a short time.
- Decreased diuresis.
- Swelling of the legs, sometimes arms and body.
Homocysteine when planning pregnancy is an extremely important factor in a woman’s health. To prevent complications during pregnancy, it is necessary to know the limits of normal homocysteine values, since it is this that has a very great influence on the fetus. It is highly advisable to be examined for the level of homocysteine in the blood before pregnancy, since an elevated level of this amino acid is often the reason for a woman’s childlessness or miscarriage.
It has been proven that by quitting smoking, as well as consuming large amounts of caffeine, the homocysteine level during pregnancy returned to normal. Additionally, the gynecologist observing the woman necessarily prescribes folic acid and vitamin B in preventive or therapeutic doses, depending on the level of the indicator. If a woman experiences preeclampsia during pregnancy, then in subsequent years of life she needs to regularly monitor homocysteine levels and identify elevated levels, especially if she is planning a subsequent pregnancy.
Reasons when low homocysteine is detected during pregnancy:
- Genetic predisposition. As a rule, a genetic defect in the absorption of amino acids (methionine) causes metabolic disorders and poor tolerance of protein foods. Not only the level of homocysteine (increased) and methionine suffers, but the functions of the joints, blood vessels, heart, and nervous system are also impaired.
- Vitamin deficiencies. Lack of B vitamins and folic acid in food leads to hyperhomocysteinemia. Most often, the administration of vitamins leads to an improvement in the condition.
- Low activity during the day and bad habits. Due to poor metabolism due to poor nutrition and lack of physical activity, the breakdown of homocysteine slows down and accumulates in the walls of blood vessels and blood, that is, it increases. Even moderate physical activity, walking, swimming, cycling, skiing, skating, giving up alcohol and smoking, significantly improves your general condition.
- Taking medications, especially for the treatment of autoimmune diseases, taking antidepressants. These drugs destroy B vitamins (thiamine, cobalamin, pyridoxine) in the body and lead to the phenomenon of vitamin deficiency. In the treatment of psoriasis, drugs are used that neutralize folic acid, which also leads to its vitamin deficiency.
- Hormonal problems with the thyroid gland, kidney disease, diabetes, stomach and intestinal diseases.
Homocysteine levels in the blood are monitored by regularly donating blood. The night before, a light meal is allowed 10 hours before the test; 3-5 days before the test, increased food loads of smoked and fried meat are excluded. Blood is taken from a vein on an empty stomach. To differentiate from other pathologies, doctors often perform a stress test with methionine: early in the morning (8-9 a.m.), the pregnant woman takes methionine, and then a blood sample is taken for homocysteine.
If high levels are detected, a DNA test is performed to clarify enzymopathies in the synthesis of folic acid, and the intracellular enzyme MTHFR is checked, which reveals the pathology of the vitamin B1, B6, B12 complex.
As additional studies, tests are often performed for thyroid antibodies, antiphospholipids, and lupus anticoagulant. When a pathology is detected, the doctor prescribes treatment and diet. To lower homocysteine, foods rich in protein are excluded: cottage cheese, hard cheeses, eggs, nuts, all types of fried meat (pork, beef, chicken, lamb), fried fish, as well as canned fish. It is undesirable to consume rice, semolina, and buckwheat from cereals. Vegetables and fruits are not limited. In any case, based on laboratory tests (test for homocysteine), the diagnosis is made by the doctor, who then treats and corrects the condition of pregnant women.