In this article we will look at what protein and leukocytes in urine mean.
A general urine test, along with a blood test, is perhaps the most common type of study. Due to this, various diseases are determined, and not only of the genitourinary system. Urine testing takes into account parameters such as quantity, transparency, color, smell, pH. Each of these properties has its own norm. Leukocytes and protein in the urine are symptoms of the presence of various pathologies. But it is necessary to understand that when they say that these components are absent in urine, this does not always mean that there are no diseases. Even a completely healthy person can have traces of them.
Why does the content of red blood cells in urine increase?
An increase in the concentration of red blood components in the secretions is called a special term - hematuria.
If during the examination a minor is detected, such a condition indicates microhematuria. In this situation, there are no visible changes in the secreted liquid - it remains straw-yellow, as it should be. But if the urine acquires a burgundy or reddish tint, then this phenomenon is called gross hematuria (indicates serious kidney damage). When studying such biomaterial under a microscope, red blood cells are found in the urine, which completely cover the entire field of view of the magnifying device. Their shape often changes under the influence of various substances present in the discharge - which is also a sign of pathology.
What causes increased red blood cells in urine? The cause of this condition is often the following violations:
- Cystitis - with this disease, the presence of red blood components in urine is sometimes noted. If the bladder lesion has an infectious etiology, then during the examination proteins and bacteria in the urine are determined. The disease is more common in the female half of the population.
- Pathologies of the genitourinary organs - inflammatory processes always affect the permeability of the vascular walls. An increase in red blood cells in the urine is observed with urolithiasis, pyelonephritis, functional renal failure, and especially glomerulonephritis.
- Hemophilia is a disease that occurs with severe disorders affecting the circulatory system. In such a situation, the blood clotting function suffers, and hematuria also appears.
- Hydronephrosis - and the calyces of the filtering organs, which occurs due to improper outflow and retention of urine. Prolonged residence of fluid in the upper parts of the urethral canal leads to the fact that the discharge stagnates. Pathogenic microorganisms begin to actively multiply in them, so the level of red blood cells and bacteria in the urine increases significantly.
- Erosion of the uterine cervix occurs with damage to the vascular walls. With this disease, bloody impurities are almost always found in the urine.
- Traumatization of the urinary canal - severe mechanical damage to these organs is characterized by severe hematuria.
- Infectious diseases - a small amount of red blood cells often ends up in the secretions of malaria, febrile conditions, and chickenpox.
- Bleeding from the reproductive organs - red blood components are carried into the urine from the vagina, uterus or genitals during urination (for example, with uterine bleeding).
- Other pathologies - an increase in red blood cells in the secreted fluid often occurs with various disorders of the blood coagulation system, mononucleosis, heart failure, and tumor processes.
But the very presence of these components in urine does not always indicate a possible infection or pathological changes occurring in the patient’s body. The permeability of the walls of blood vessels is also affected by the use of certain medications - Ascorbic acid, Hexamine, drugs of the sulfonamide group and anticoagulants.
Hemoglobinuria
The presence of protein in the urine such as hemoglobin requires special attention. This liquid does not normally contain it. Its presence in urine indicates a serious disorder in the kidney tissues. There are two ways for it to enter the urine. The first is based on the processes of destruction occurring in red blood cells, and hemolytic anemia develops.
So, increased leukocytes and protein in the urine are due to:
- allergies;
- spleen diseases;
- intoxication of the body with toxic substances.
In this case, a large amount of hemoglobin is released from the red blood cells, some of it passes through the glomerular membrane.
The second mechanism occurs when there is a disorder with bleeding or defects in the urinary organs. This situation is possible when:
- oncology;
- kidney stones;
- glomerulonephritis.
In this case, the urine takes on a bright red hue. With this value in the analysis, one should remember about false hemoglobinuria, which occurs when the timing of the study is violated.
Protein and leukocytes in the urine should definitely alert you.
The number of leukocytes in the general analysis
A small number of leukocyte cells in the sample is acceptable. This is explained by the following phenomena:
- White blood cells enter the urine from the blood. Their number does not affect health if the permeability of the vascular walls is normal.
- According to some studies, some cells in white blood cells serve as “scouts” - they penetrate the urine and, in the presence of viruses, signal a problem by releasing substances of a special composition.
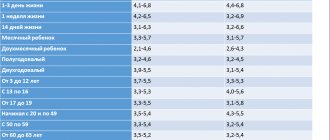
Acceptable leukocyte norms for women are up to 6 cells, normal levels for men are 2-3. In children, these numbers also depend on gender - up to 10 for girls and up to 7 for boys. The difference in norms is explained by the peculiarities of the anatomical structure: in women, the urinary and genital organs are located nearby and bacteria migrate freely, distorting the parameters of urine tests.
Urine analysis in adults is considered doubtful if the drug contains from 3 to 10 units. In such cases, a repeat study is carried out. If the indicators are too high the second time, the patient is sick. In case of increased leukocytes, further examination is carried out - ultrasound of the kidneys, urine culture in various media, scraping of the epithelium. Preparing for a urine test includes certain rules. If hygiene measures were not observed when collecting material, the result may be distorted. In any case, antibacterial therapy can only be prescribed by a urologist if comprehensive results are available.
What do you mean by the increase in the rate of leukocytes in the urine?
An increased content of leukocytes and erythrocytes signals an infection in the urogenital tract. There is a risk of the following diseases:
- pyelonephritis, urolithiasis;
- infection at the level of the ureter;
- cystitis or cancer;
- inflammation of the urethra;
- gynecological infections.
There are cases when the leukocyte content greatly exceeds the norm - 30-40 units. If there is no bacteriuria, then the result is caused by a recent course of antibiotics, renal tuberculosis, nephritis, or the banal collection of a sample in a non-sterile container. Do not neglect the rules for taking the test. By spending 2-2.5 minutes performing simple manipulations, you can ensure an accurate result on the first try.
What analysis determines?
In order to make an accurate diagnosis, when in doubt about a variety of pathologies and diseases, the doctor first of all orders a general urine test. A few days before the test, you need to lead a healthy lifestyle and avoid heavy physical activity. If the general analysis showed the presence of protein, leukocytes and red blood cells, then the following studies are prescribed:
- urine culture;
- daily analysis;
- examination according to Kakovsky-Addis;
- oxalate test;
- urine test according to Nechiporenko.
Therapeutic measures for proteinuria and leukocyteria
Any treatment prescribed independently when elevated levels are detected can lead to a worsening of the condition. Also, you should not be treated with traditional medicine without appropriate diagnosis and consultation with a doctor. To prevent an increase in indicators, it is necessary to identify the reason that served as a stimulator for the increase in values.
In most cases, a number of medications prescribed by a doctor are used, as well as physical procedures and a specific diet. In some cases, it is necessary to resort to surgical intervention.
Treatment
To accurately identify the type of pathological process or the growth of bacteria in the urine, the doctor will refer you for tests. Based on the data obtained, the following drugs are most often prescribed:
- Diuretics and disinfectants on a natural basis: Phytolysin, a decoction of calamus rhizomes, Canephron, a decoction of horsetail, cranberry or yarrow.
- For bacteria in the urine, which causes a burning sensation when urinating, antibiotics are prescribed on an individual basis.
- If an oncological disease is detected, treatment in a hospital setting, surgical removal of the tumor.
Detection of increased levels in urine indicates problems in the body. Therefore, if even a slight deviation is detected, it is necessary to undergo a full diagnosis and begin treatment as quickly as possible.
Prevention
To prevent an increase in the levels of red blood cells, protein or leukocytes in the urine, it is necessary to establish a healthy lifestyle: eat only high-quality food, balanced and nutritious. It is recommended to eat food according to the regimen. Live according to a clearly planned daily routine. You should not drink an increased amount of liquid, give up bad habits, especially alcohol.
For children, it is required to adhere to the vaccination schedule, carry out vaccinations on time and increase immunity.
Do not use antimicrobial soaps or gels. They stimulate the neutralization of beneficial microflora of the genital organs, which leads to the development of a number of gynecological and urological diseases. You should not change sexual partners often: refrain from casual relationships. To prevent congestion in men that provoke inflammation, it is necessary to periodically massage the prostate.
Thus, if elevated levels of leukocytes and protein are detected in the urine being tested, it is necessary to consult a doctor and identify the causes of the inflammatory process. Only on the basis of the data obtained, effective and efficient treatment is prescribed, allowing you to quickly get rid of the pathology.
What to do?
Normalization of protein, leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine requires following a diet, taking pills, but less often, surgery.
Medicine recommends the following treatment methods:
- diet;
- physiotherapy;
- drug therapy;
- surgical intervention.
Before prescribing treatment, the doctor determines whether there is a disease or bacteria in the urine that led to an increase in indicators. He also recommends adhering to a special diet, excluding fried, fatty, salty foods and adding vegetables, fruits, and dairy products to the diet. Folk remedies can help achieve an anti-inflammatory effect (taking cranberry tea, birch sap, bearberry, flax), using herbal teas of chamomile, horsetail.
Features of treatment of pyelonephritis
The most important component of any treatment for kidney infections, as with any other bacterial infections, is the use of antibiotics under the supervision of your doctor. If the diagnosis of pyelonephritis is confirmed, a broad-spectrum antibiotic is prescribed that fights all possible bacteria that could be its cause.
In a clinical setting, treatment is prescribed with intravenous antibiotics, intravenous hydration, and other types of aggressive therapy aimed at eliminating symptoms. In cases of complicated pyelonephritis, hospitalization is also required.
To reduce the risk of developing infections, it is necessary to take plenty of fluids daily and maintain good hygiene. For chronic illness, or for people at increased risk of kidney infections, your doctor may prescribe small doses of antibiotics for prophylactic purposes. If pyelonephritis is treated early and correctly, therapy has a high chance of success.
When there is a high concentration of leukocytes in the urine, it is necessary to determine the cause of this phenomenon and prescribe treatment. Such symptoms themselves are only signs of certain diseases. It happens that there are deviations from the norm in urine due to non-compliance with recommendations for its collection.
In such a situation, it is worth retaking the analysis. The doctor, as a rule, prescribes another test for the patient. If the indicators deviate from the norm for the second time, then an ultrasound examination of the bladder and kidneys is used.
To determine what exactly is the cause of changes in urine, its analysis according to Nechiporenko, as well as the Reberg and Zimnitsky test, will help.
Urinary tract infections
Many factors can cause a UTI. Urinary tract infections are a common condition in pregnant women because the enlarged uterus, which puts pressure on the ureters, slows the flow of urine through the urethra. This gives the bacteria time to multiply and rise to the kidneys. The problem cannot be ignored even in the absence of symptoms, since the pathology can cause serious harm to the child.
Another factor contributing to the development of infection is menopause. In women after menopause, physiological factors (dry vaginal membranes, urinary incontinence, stagnation of urine, prolapse of internal organs) significantly increase the risk of UTI.
Other risk factors include family history, which suggests a possible genetic influence. Kidney stones and structural abnormalities of the urinary tract can also cause UTIs. Impaired drainage and blocked/delayed urine flow helps bacteria enter the kidneys without being washed away by urine. Thus, any urinary retention can be used by bacteria to spread infection to other organs of the genitourinary system.
Diabetes, in which the test shows sugar in the urine, may increase the risk of UTIs, due to which bacteria and white blood cells are found in the urine. Some medications that suppress the immune system are also a negative factor.
Urinary stents, inserted into the urethra to facilitate the flow of urine in the presence of stones or tumors, may also play a role in causing infection. Almost any operation or manipulation on the urinary tract (stenting, cystoscopy, biopsy) is a factor of infection.
Urinary catheters (Foley catheters) also increase the risk of UTIs. These catheters are often used in patients who are unable to empty their bladder on their own due to bladder paralysis (neurogenic bladder), enlarged prostate, or prostate cancer. Urinary catheters are a direct route for bacteria from the outside world to enter the bladder and genitourinary system.
Biochemical properties of urine
To evaluate these parameters, they resort to special reagents and analyzers.
- Protein. Its normal content in urine is close to zero - 0.033 grams per liter (no more).
- Sahara. The maximum permissible value for their content in the urine of an adult patient is 0.8 mmol per liter. When this indicator increases, there may be physiological reasons such as excessive consumption of sweets, pregnancy, and the release of adrenaline as a result of stress. However, most likely we are talking about one of the following disorders: kidney dysfunction, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's syndrome, acute pancreatitis, adrenal damage.
- Ketone bodies. The presence of ketone bodies in urine may indicate endocrine diseases: acute inflammatory process of the pancreas, diabetes mellitus, Cushing's syndrome, thyrotoxicosis. You also need to keep in mind the likelihood of ketone bodies appearing in urine during alcohol intoxication, fasting, traumatic brain injury, and low-carbohydrate diets.
- Bile pigments (urobilinogen, bilirubin) are products of hemoglobin breakdown; they appear in the urine due to lesions of the biliary tract and liver, as well as as a result of the destruction of red blood cells in the blood during malaria, sickle cell anemia, toxic hemolysis, hemolytic disease.
- Indican. The presence of such a substance in urine indicates the processes of rotting and fermentation in the intestines. It should not be normal in a urine test.
Microscopic characteristics. Examination of urine under a microscope is additionally required if abnormalities are detected.
- Epithelium. Urine from a healthy person may include individual epithelial cells (under a microscope, up to ten per field of view), but this is most likely rare. An increased content of epithelium in the urine indicates, for example, diseases such as cystitis and certain types of nephropathy.
- Slime. Occurs in urine during genital infections and inflammation of the genitourinary system.
- Hyaline casts are formations that consist primarily of renal tubular cells and proteins. If there are more than twenty of them in one milliliter of urine, this may indicate pyelonephritis, hypertension, glomerulonephritis. This also occurs as a result of using diuretics.
- Blood cells (leukocytes, erythrocytes). May be present in urine in small concentrations. Normal values of red blood cells: for women - from 0 to 3, for men - from 0 to 1; by leukocytes: in women - from 0 to 6, in men - from 0 to 3. If red blood cells are elevated, this may be a sign of urolithiasis, kidney infarction, nephrotic syndrome, cancer of the genitourinary system, acute glomerulonephritis.
If protein in the urine and leukocytes are elevated, what this means should be determined by the doctor. Most likely, this is the result of pathologies of the urinary tract.
- Bacteria. The urine of a healthy person is sterile. Bacteria are detected due to insufficient hygiene before obtaining biomaterial or during an infection of the genitourinary system.
- Fungi are not detected normally. Their presence indicates the occurrence of an infection.
- Parasites. The presence of any quantities of parasites in urine is unacceptable; urgent additional diagnosis and treatment are required.
- Grainy cylinders. They are a mixture of kidney tubule cells and red blood cells, which appears in the urine during lead poisoning, inflammation of the urinary system, and viral infections.
- Salt. They are not normally found in urine; their presence may indicate urolithiasis.
- Wax casts form when a granular or hyaline cast becomes lodged in the lumen of the renal tubule. This happens with chronic kidney failure, nephrotic syndrome, and renal amyloidosis.
We found out what protein and leukocytes in urine mean.
Views: 5
The mechanism of protein appearance in urine
The majority of proteins do not normally penetrate the glomerular basement membrane. This occurs due to the large size of the protein units, as well as their shape and charge. If even a small defect appears in the membrane, then first of all albumin without leukocytes enters the urine, and in case of more significant violations, larger molecules appear. Even in a healthy person, the epithelial tissue of the tubules forms some of the proteins, and another part enters the urine from the urethra and ureters.
Acute inflammatory processes
Usually, pathological processes in the kidneys are not detected; inflammation occurs latently. The disease can be noticed already in its advanced form or by accident during a medical examination. It is recommended to constantly monitor your own body and if you identify the following symptoms, immediately contact a trusted doctor for diagnosis:
- Weakness throughout the body.
- Constant fatigue.
- Changes in the composition of urine (color, aroma).
- Pain during urination.
- Detection of pain in the lumbar region.
- Increase in temperature and blood pressure.
- Changes in skin color, pallor and dryness.
- The appearance of swelling of the face and limbs.
The sooner the disease is detected and therapy is prescribed, the greater the chance that it is possible to recover faster.
Additional diagnostic measures
To accurately determine the pathological process and possible diseases of the urinary system, the doctor conducts a mandatory examination, collects an anamnesis and prescribes additional diagnostic methods:
- Examination by a therapist.
- Consultation with a gynecologist for women, and a urologist for men.
- For women - cytology, colposcopy.
- Taking analysis according to Nechiporenko.
- Bacteriological culture.
- Coagulogram, Ultrasound examination, radiography if necessary.
In some situations, the doctor resorts to using the Zimnitsky analysis. This type of test allows you to check the functioning of your kidneys.
The more tests and examinations are carried out, the more accurate the analyzes will be. Thanks to the results obtained, an accurate diagnosis of a person’s problem is determined and effective treatment is prescribed.
Urological diseases
If an increase in protein and leukocytes is detected in urine, then this pathology is diagnosed as leukocyturia. This suggests that diagnosis of urological diseases is necessary.
The following diseases affect an increase in the level of leukocytes and proteins:
- Pyelonephritis.
- Cystitis.
- Dysuria.
- Prostatitis.
- Vesiculitis.
- Narrowing of the urinary ducts.
- Hematuria.
In most cases, when the problem is identified, antibacterial drugs are prescribed.
Other reasons for increased levels of white blood cells and protein in the patient’s urine
If the level of protein or leukocytes is increased after a urine test, it is necessary to identify the causes of the problem. The following factors are identified that can affect the increase in the presence of leukocytes and traces of protein:
- Stressful situations.
- Physical stress.
- A woman is pregnant.
- Cottage cheese and any dairy products eaten in large quantities the day before.
- Incorrectly fulfilled hygienic requirements when collecting analysis.
- Hypothermia of both the entire body and the kidneys separately.
- Patient work in which he is constantly in an upright position.
- Exposure to excessive amounts of sunlight, which not only gives beautiful skin tone, but can also increase protein levels.
- Physiotherapy procedures - they not only have a therapeutic purpose, but in some cases they can cause side effects in the form of an increase in protein levels.
- Tumors of a malignant type.
- Autoimmune pathological processes.
- Diseases caused by infection (pneumonia, influenza).
- Reaction to irritants and allergens.
- High blood pressure.
Each reason tends to negatively affect the human body, and their combination leads to the appearance of various indicators in the urine and blood with an increased norm. Therefore, before taking tests, you need to eat only proper and healthy food, not worry and prepare yourself for a favorable outcome of the examination.
Possible symptoms of diseases
Major kidney problems often do not make themselves felt for a long time. Therefore, if there is at least one of the signs, you need to contact a medical facility. The earlier the correct drug treatment is prescribed, the greater the chance of recovery. Symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- changes in urine;
- swelling of the legs and face;
- pale and dry skin;
- pain in the lumbar region;
- increased blood pressure and temperature;
- fatigue;
- weakness.
Proteinuria classification
Physiological proteinuria is a diagnosis that is made when the daily protein concentration in urine collected in the morning increases. The norm should not exceed 0.033 g/l.
The reason for the increase is the presence of:
- Heavy physical activity;
- Excessive insolation;
- Hypothermia;
- Increased levels of norepinephrine and adrenaline in the blood;
- Excessive consumption of protein foods;
- Stressful state;
- Long-term palpation examination of the kidneys and abdomen.
If the reason for the increase in protein in the urine is physiological, then it is not dangerous in nature and the appearance does not look so scary and drastic. To be more precise, neither a child nor an adult needs to be afraid if such a diagnosis is made.
A pathology such as proteinuria (the appearance of protein in the urine in quantities that can be detected by tests) has two classifications. Let's look at them.
According to the place of occurrence, proteinuria is divided into:
- renal (due to kidney disorders);
- prerenal (due to increased tissue breakdown);
- postrenal (the pathology process is located in the urinary tract).
Renal proteinuria has two types:
- glomerular (if the filtration system of the renal glomerulus is damaged);
- tubular (based on a change in the normal mechanism of reuptake of low molecular weight protein units).
If there is increased protein and leukocytes in the urine, it is important to find out the reasons
Does this always indicate pathology?
When are leukocytes and protein in the urine considered normal?
However, there are cases in which increased levels of these elements in urine are not a symptom of the disease. This happens when consuming excess amounts of protein-containing food, severe physical activity, changing body position, or under the influence of low and high temperatures. It is very interesting that proteinuria can be a consequence of a stress factor.
What other possible causes of protein and leukocytes in urine?
Treatment
After diagnosis, depending on the cause of the development of leukocyturia and proteinuria, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
For urolithiasis, medications are prescribed that dissolve stones (Blemaren, Asparkam, Cyston, Canephron, Urolesan, Gortex). If there are indications, surgical crushing of stones is prescribed. In case of inflammatory pathologies of infectious etiology, a course of antibacterial therapy is prescribed, which is active against the identified pathogen (Ceftriaxone, Bisiptol, Flemoxin Solutab, Levofloxacin). For fungal diseases, antifungal drugs are used (Fluconazole, Flucytosine, Amphotericin). To increase the body's resistance, immunomodulators (Interferon, Kagocel, Ergoferon, Arbidol, Viferon) are used. To reduce pain and facilitate the passage of stones through the urinary tract, antispasmodic and painkillers are prescribed (No-shpa, Papaverine, Baralgin, Spazmalgon, Analgin). If leukocyturia and proteinuria are accompanied by hyperthermia, antipyretic medications (Paracetamol) are used, as well as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Nurofen, Ibuprofen), which not only reduce body temperature, but also have a pronounced analgesic and antiphlogistic effect
An important place during treatment is occupied by diet, which can reduce the load on the urinary system and speed up the healing process. For renal pathologies, treatment table No. 7 and its modifications a and b are prescribed, according to which you should avoid eating fatty, fried, spicy, smoked, salty, canned, sweet foods
According to the diet, you should strictly limit your salt intake - no more than 3-5 g per day. You should also give up fatty meats (pork, lamb) in favor of lean varieties (chicken, turkey, veal). The basis of the diet should be fresh or steamed vegetables and fruits, dairy products. It is important to drink a lot of water daily - more than 2 liters, unless there are contraindications. Diuretics (Lasix, Furosemide, Oksodolin, Veroshpiron) and traditional medicine, among which cranberry, currant, lingonberry, bearberry, chamomile, horsetail, flax seeds, birch leaves and buds are considered the most effective, help restore the impaired outflow of urine. To prepare decoctions and teas, you should purchase ready-to-use herbs at the pharmacy and prepare them according to the instructions on the package.
It is also important to give up drinking alcohol and other bad habits that negatively affect the functioning of the kidneys and vascular system. Increased levels of protein and leukocytes in the urine of a child and an adult often indicate improper collection of biological material for research or are a symptom of a disease of the urinary system, vascular pathologies
To identify the cause of proteinuria and leukocyturia, additional diagnostics should be performed using instrumental methods. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the cause of deviation from the norm
An increased level of protein and leukocytes in the urine of a child and an adult often indicates improper collection of biological material for research or is a symptom of a disease of the urinary system or vascular pathologies. To identify the cause of proteinuria and leukocyturia, additional diagnostics should be performed using instrumental methods. Treatment is prescribed in accordance with the cause of deviation from the norm.
How the urinary system works
The kidneys are a paired organ located on the sides of the spine, under the diaphragm, in the lumbar region. Each kidney is connected to the bladder in the pelvis by ureters (long, narrow tubes) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Urine accumulates in the bladder and leaves the body through the urethra. Together, this system forms the urinary tract, and the kidneys play an important role here.
The kidneys perform many important functions for the human body. The main thing is the filtration of the blood and the removal of waste from it, which is eliminated from the plasma as the blood circulates through the capillaries of the kidneys. In addition, the kidneys regulate blood pressure, maintain a constant balance of electrolytes (calcium, phosphorus, potassium, sodium and chlorine ions), and participate in the production of red blood cells. Therefore, if malfunctions occur in the urinary system, this will affect health in the most detrimental way.
Urine analysis allows you to find out whether pathologies are developing in the urinary system, for which its composition is studied in detail. In this case, leukocytes and red blood cells, protein and bacteria are measured.
Urine, like other fluids of the human body, in a healthy state does not contain bacteria, proteins, leukocytes, or red blood cells. True, doctors take into account that a person will collect material for analysis incorrectly, eat a certain type of food before collecting urine, or attend a training session. Therefore, the presence of these elements in urine is allowed in small quantities. For example, the norm of leukocytes and erythrocytes should not exceed 3-5 units. in the field of view, protein – 0.033 g/l.
Urinalysis interpretation, norms, indicators
Urine testing takes place according to several parameters.
Organoleptic properties of urine.
- Color. Normally varies from light straw to deep yellow. If other shades are mixed, the patient should be wary.
- Smell. The urine of a healthy person has a specific, mild odor, which can become stronger with cystitis and have an ammonia tint.
- Transparency. Precipitation or cloudiness of the urine indicates the possible presence of salts, fats, pus, mucus, bacteria, red blood cells and other substances that should not be present normally. Urine should be clear.
- Foaminess. When shaken, urine normally foams little and the foam settles quickly. If it is stable, then this indicates the presence of protein.
Physical and chemical indicators. This category includes only two parameters that are currently determined using special test strips.
- Acidity. This indicator normally allows values from 4 to 7 pH in the general urine analysis form for adults, that is, from a moderately acidic to moderately alkaline environment. This is not a deviation. If the acidity is slightly reduced, this is typical for chronic renal failure, high potassium levels in the blood, increased activity of the parathyroid gland, bladder or kidney cancer, and ureaplasmosis. This indicator can be high during fasting or dehydration, frequent consumption of meat, taking a number of medications, and elevated body temperature. This may also be a sign of diabetes.
- Urine density. Normally, this figure for children over twelve years of age and adults ranges from 1.010 to 1.022 grams per liter. If, due to impaired metabolism or infection, it contains large quantities of foreign cells or substances, the density increases. This also occurs when the body is dehydrated. Low density can be observed as a result of the use of diuretics, diabetes insipidus, and kidney failure.
Requirements for collecting urine for analysis
Urine tests are divided into planned and special. Planned ones are carried out at the initial visit to the doctor and during treatment, special ones - exclusively for medical indications.
To properly collect liquid you should not:
- drink diuretics of any origin;
- drink plenty of fluids;
- eating foods that change the color of discharge;
- take medications that change its composition;
- drinking alcohol;
- give it to women during menstruation;
- Collect fluid sample after cystoscopy for up to 7 days.
Necessary:
- donate morning urine collected after the night or part of the daily urine;
- separate the first part and send the remaining liquid for analysis;
- collect the liquid in a standard sterile container;
- Before collecting fluid, wash the genitals thoroughly;
- transfer the liquid to the laboratory within two hours after collection (urine stored in the evening becomes unusable due to the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and salt precipitation)
Increased levels of leukocytes in urine causes
Any inflammatory reaction that affects the urinary tract occurs with an increased content of white blood cells in the urine. In adult females and males, the norm of leukocytes in the secretions is no more than 3 units. For pregnant patients and children, this value is considered normal when the content of white components is from 0 to 4-6 in the field of view.
An increase in concentration of more than 8-10 units, visible in the lens of the device, indicates an infectious or inflammatory lesion of the genitourinary area. If the level of these cells increases, the patient is urgently referred to the appropriate doctor - urologist, nephrologist. Often, with leukocyturia, a large number of bacteria are found in the urine during the study.
The following pathologies can cause an increased content of white blood components in urine:
Pyelonephritis - this disease is a purulent inflammation of the pyelocaliceal apparatus of the kidney. It occurs due to infection, so the disease is characterized not only by leukocyturia, but also by the presence of bacteria in the urine. Malignant neoplasms of the kidneys - oncological processes also occur with an increase in the level of leukocytes and red blood cells in the secretions
At the beginning of the development of a tumor, its appearance is often indicated only by some changes in the urine test, which is why it is so important to monitor this indicator. Timely detected pathology is cured in 8 cases out of 10. Urolithiasis - the formation of stones in the urethral canal is also accompanied by leukocyturia
When a stone with sharp edges moves through the lumen of the ureters, it can scratch the mucous membrane and cause minor blood loss. In this case, a person experiences an increase in leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine. Tuberculosis of the urinary tract - manifests itself as a result of human infection with the tuberculosis bacillus. In the absence of timely treatment, urethral damage develops 2.5-3 years after the mycobacterium enters the body. Harmful microflora is carried by blood throughout the body and causes a corresponding immune response. Leukocyte cells try to fight infection in the urinary tract, which is why they are found in the secreted fluid. Cystitis - if the pathological process occurs due to bacterial or viral infection, then an increase in leukocytes is necessarily detected in the urine. Other factors in such a situation include chronic, sluggish inflammation of the genital area and sexually transmitted diseases, hypothermia, allergies, helminthiasis, decreased efficiency of the immune system, physical inactivity, use of medications (Ampicillin, Kanamycin, Aspirin) and the use of iron salts.
Leukocyturia
Urine normally contains up to three leukocytes per field of view in men, and up to five in women. A large amount of these elements in urine indicates inflammation either in the urinary tract or in the kidney tissue. An increased content of leukocytes in chronic processes is more informative compared to bacteria. It is not always possible to detect the latter.
With an increased concentration of leukocytes in the urine, purulent clots become noticeable. This phenomenon is called pyuria. It is also often accompanied by discoloration and an unpleasant odor.
If leukocytes have an increased value, then there may be the following reasons:
- inflammation processes in the bladder, urethra, kidney tissue;
- inflammation of the prostate;
- urolithiasis disease;
- nephritis of tubulointerstitial origin;
- glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis of chronic and acute type.
We looked at the causes and symptoms of protein in urine and white blood cells in urine. How to treat this pathology?
Taking antibiotics and other medications
If the root cause is infectious inflammation, then antibacterial medications must be prescribed. In addition, it is advisable to drink plenty of fluids and eat a diet that excludes salty, fried and spicy foods.
If tuberculosis affects the urinary system, therapy with special drugs is required. In case of urolithiasis, a specialist prescribes medications that can remove sand; if the stones are large, surgical removal or crushing of the stones is indicated.
All the techniques listed above are also relevant for eliminating nitrites in urine, because they also act only as a symptom and not as an independent disease.
Protein and leukocytes are found in urine, which means
When examining general urine, the indicators and values that indicate inflammation in the body are clarified. Most often, pathology develops in the kidneys.
The kidneys are a paired organ. The kidneys are located under the diaphragm, on both sides of the spine, in the lumbar region. Each organ is connected by long narrow tubes (ureters) to a bladder in which urine is collected.
Thanks to the functioning of the kidneys, the blood flow in the capillaries is filtered and toxic substances and waste are removed from the lymph. In addition, this organ helps normalize electrolytes and stimulates the production of red blood cells in the urine. Through the work of the kidneys, urine is excreted, which reflects all the problems and malfunctions of the organ. Therefore, when protein and white blood cells in the urine are elevated, the doctor diagnoses kidney disease and prescribes appropriate treatment.
An increased content of proteins in urine is medically referred to as proteinuria. If the growth of white blood cells is noticeable, then leukocyturia is diagnosed. Increased values are detected if there is a pathology that begins to develop in the renal glomeruli. But at the same time, an increase in the indicator also occurs in those patients in whom no disease is subsequently detected.
The occurrence of indicators in urine can be observed due to poor nutrition, poor hygiene or simple hypothermia, as well as stress. Therefore, there is no need to panic ahead of time; it is recommended to undergo a full diagnosis or retake the tests, but following all the rules for collecting material for analysis.
The blood is normal, but there are leukocytes in the urine
White blood cells that are elevated only in the urine may indeed be a false indicator. It would be a good idea to give urine up to 3 times in a row. It is very important to take a shower before having a bowel movement. If the result is the same, then the cause may be an inflammatory process in the body, then the doctor will have to identify the cause. For this purpose, an ultrasound of the pelvic organs and consultations with specialist doctors may be prescribed.
Elevated white blood cells may be a consequence of nervous strain. Stress that occurred on the eve of the analysis can affect its results. Therefore, before any clinical study, it is necessary to remain calm. This is especially true for children; they may be nervous, worried and capricious before taking the test. The baby should be calmed and distracted for the result to be reliable.