In the practice of every otorhinolaryngologist, situations arise when a conventional visual examination is not enough to make an accurate diagnosis. In these cases, as part of an additional examination, the doctor may suggest an ultrasound of the throat and larynx area. This is a safe and painless research method that helps exclude a number of diseases and conditions. Purpose of ultrasound
The examination is prescribed and used to clarify the presence and location of damage in the trachea, larynx, neck or thyroid gland. It allows you to identify benign and malignant neoplasms, track their growth and changes in size. Makes it possible to carry out differential diagnosis for some inflammatory diseases of the neck.
The absence of contraindications, the safety of the method, and the acquisition of real-time data allows it to be carried out in patients with various pathologies of all ages. The examination is not associated with unpleasant sensations and takes relatively little time.
Instrumental examinations
After listening to the patient’s complaints, the ENT doctor begins to perform indirect laryngoscopy. It is carried out directly in the office. No special preparation is required for this. To prevent the development of a gag reflex, it is advisable not to consume food or water immediately before the procedure.
The procedure consists of pressing the tongue with a spatula and using a mirror to examine the oral cavity and pharynx. The disadvantage of this method is its low information content. It is possible to diagnose a tumor only in 30% of cases. Due to the fact that it is not possible to fully examine everything, the otolaryngologist is forced to prescribe more labor-intensive studies.
Direct laryngoscopy is characterized by great diagnostic capabilities. A significant part of medical institutions are equipped with appropriate equipment to conduct such research. It consists of inserting a laryngoscope into the larynx using a flexible tube in order to study all its parts.
The study is carried out under local anesthesia by spraying the drug into the throat cavity. In addition, since the examination device is inserted through the nose, the patient is first instilled with vasoconstrictor drops, which reduce swelling and mucus production. A significant advantage of this technique is its information content, safety, the possibility of simultaneous removal of papilloma, as well as taking material for a biopsy.
The identified changes may vary significantly in nature. Warning should be caused by formations in the form of a tubercle or tuberous surface, localized in various places of the larynx, thickening of the vocal cord, and its bleeding. An altered mucous membrane in the form of an erosive area is also a cause for concern and further research.
After an instrumental examination through indirect laryngoscopy, the ENT doctor begins an objective examination of the patient. He is interested in the condition of regional lymph nodes. By palpating the cervical, mandibular, jugular lymph nodes, the doctor receives information about possible metastases.
Enlarged dense formations, fused with nearby tissues, indicate the spread of the process and the transition of the disease to the third stage.
At the same time, soft, painful lymphoid formations characterize the presence of an inflammatory process in the throat and oral cavity.
An ultrasound scan of the neck is used to clarify the nature of lymph node damage. Such a study makes it possible to assess their density, size and location. Considering the informativeness and safety of this technique, it has become widespread to clarify the extent of damage in throat cancer. Many lymph nodes are inaccessible to palpation. At the same time, they are well visualized when examined using ultrasound. Such echo-negative areas identified are subject to further biopsy to clarify the presence of metastatic lesions in them.
The organs of the digestive tract, kidneys, and brain are also subjected to ultrasound examination. Such studies are carried out to identify metastases in various organs. In addition, laryngeal cancer can develop secondaryly, through metastasis from the brain, mammary gland, bone and cartilage tissue. Having identified malignant neoplasms, the specialist must decide on the localization of the primary focus.
What does ultrasound diagnostics show?
Using an ultrasound, a doctor can detect the following diseases and problems:
- benign and malignant tumors, their boundaries and location;
- foreign object in the throat, its location;
- laryngeal injuries received after road traffic and other tragic accidents;
- purulent abscesses;
- thyroid diseases;
- advanced purulent and inflammatory processes in the throat area, their consequences.
The most dangerous thing a doctor can detect is throat cancer. Malignant diseases are common. They are difficult to detect, because at the initial stage their tumor size is very small, and they do not expand beyond the mucous membrane, which is the reason for the patient’s ignorance of his disease.
Watch a video about the first symptoms of laryngeal cancer below:
Attention! Throat cancer develops mainly in people who smoke, abuse alcohol or work in hazardous industries.
If detected at the initial stage, life can be extended for almost all patients. At the fourth stage, the situation worsens, but about a quarter of people who apply still have a chance.
In cases where it is the thyroid gland that is of concern, special attention is paid to its acoustic density and echogenicity. They are expressed on the screen in a dark color against the general background. Echogenicity can be absent, normal, decreased or increased.
In the absence of any changes in the thyroid gland, the doctor makes a reassuring verdict, and there is no longer any reason to worry. Identification of hypoechoic areas indicates the likelihood of developing malignant tumors. Hypoechoic zones are areas with increased density; they characterize the proliferation of connective tissue.
If the doctor finds nodes with hypoechoic areas, he prescribes other procedures for the patient - biopsy, computed tomography or radiography, fibrolaryngoscopy. A treatment plan is discussed, referrals for blood tests are made, recommendations are given, and medications are prescribed. It is possible to prescribe a puncture under ultrasound guidance.
Preparing for the study
No special preparation is required to conduct the study. It is carried out at any convenient time. To do this, you need to free the area under study from clothing, you need to remove jewelry in this area, they can create an obstacle to the manipulation.
Carrying out the procedure:
- The method is carried out only in a medical institution, in a specialized office. The patient's position is initially horizontal, sometimes the doctor asks to change it to clarify points of interest.
- A special gel is applied to the area under study; its composition improves contact between the skin and the sensor. It is absolutely neutral, colorless and odorless; modern medicine uses a hypoallergenic composition.
- The method is non-invasive; to obtain the result, a special sensor is touched to the skin. Sometimes specialists may ask the patient to talk, cough, or swallow saliva.
Since no preliminary preparation is required, it can be carried out urgently or planned. Often the method is used as an auxiliary method in case of unsuccessful attempts at insertion or intubation. Ultrasound scanning of the larynx is a safe method and does not burden other organs with ultrasound.
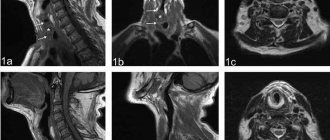
Preparation for MRI of the throat (contraindications)
MRI of the throat does not require any preliminary manipulations. Before performing an MRI of the larynx, the doctor must ensure that there are no contraindications. They are:
- The patient's age is less than 7 years. It is believed that children do not have proper perseverance and will not be able to behave calmly during the procedure.
- Early pregnancy (first trimester). At this time, there is a small chance of harm to the fetus. To completely eliminate the risk, other methods are used.
- Allergies and kidney failure. They become contraindications when a contrast agent is used during MRI.
- Presence of pacemakers or metal prostheses.
Before the study, you need to get rid of metal objects and things that could be damaged by the magnetic field. They are:
- Watches, piercings, coins.
- Bank plastic cards.
- Electronic devices, such as a mobile phone.
Diagnostic rules
There are several types of endoscopy of ENT organs: laryngoscopy, pharyngoscopy, rhinoscopy and otoscopy. Flexible direct laryngoscopy is performed by inserting a flexible pharyngoscope into the laryngeal cavity through the nasal passage. The instrument is equipped with a backlight and a video camera that transmits the image to the monitor screen. The study is performed under local anesthesia on an outpatient basis.
Rigid endoscopy is a more complex procedure that requires general anesthesia. During the examination, the doctor assesses the condition of the larynx, takes material for analysis, removes polyps, papillomas, removes foreign bodies, performs laser treatment or acts on the source of inflammation with ultrasonic waves. This diagnostic method is used when the formation of a cancerous tumor is suspected, for the treatment of pathological growths.
Preparation
Before endoscopy, the patient must inform the doctor about what medications he is taking, whether he is allergic to medications, and about concomitant systemic diseases. The procedure is carried out on an empty stomach, the patient must first abstain from eating food for 8 hours, and in the morning you cannot eat or drink. Before inserting the pharyngoscope, the patient rinses his mouth with a 25% alcohol solution and removes dentures.
Technology
How does the procedure work?
The neck examination follows a specific algorithm. There is nothing scary or painful about this. The patient should free his neck from scarves, collars and jewelry. Then lie comfortably on the couch, after which the doctor will apply a conductive gel to the skin. The sonologist begins to move the sensor along the neck, observing the image on the screen. Based on the results of the examination, a special protocol is issued in which all indicators are described and deciphered. The procedure does not take much time, on average its duration does not exceed 20 minutes.
Laryngoscopy
An endoscopic examination of the larynx is carried out with the patient sitting or lying down. The doctor carefully inserts a pharyngoscope into the patient’s throat through the nasal passages, examines the surface of the mucous membranes, the initial part of the trachea, and the vocal cords. The patient is asked to use phonation in order to better view some hard-to-reach areas.
Direct laryngoscopy can be performed using an Undritz directoscope. The instrument is inserted into the larynx of a person in a supine position. If necessary, a thin tube is inserted into the cavity of the instrument, with which bronchoscopy is immediately performed.
Rigid endoscopy is performed in the operating room after general anesthesia has been administered. A rigid pharyngoscope is inserted through the mouth into the lower parts of the larynx. After the procedure is completed, the patient remains under the supervision of doctors for several more hours. To avoid the formation of tissue edema, cold is applied to the neck.
Decoding the results
During the procedure, the doctor carefully examines the condition of the mucous membrane of the trachea and bronchi, identifies neoplasms, identifies inflammatory changes, and, if necessary, takes measures to stop bleeding.
While performing an examination, the otolaryngologist may detect a foreign body; to remove it, it will be necessary to carry out therapeutic manipulations.
The data that was obtained using an optical bronchoscope goes to the computer. Using it, all information can be recorded on a disk or other digital media. In addition to the video or photo, it will contain the conclusion of the study.
After the procedure, the doctor must explain to the patient in detail all the identified abnormalities of the trachea and bronchi, and, if necessary, refer him for consultation to another specialist or show the pictures to his colleagues. Only after this will an official doctor’s report with a signature and seal be issued.
Discomfort in the throat after the procedure
After the procedure, the patient should not drink or eat food, cough or gargle for 2 hours. If treatment of the vocal cords was carried out, the patient must comply with the vocal regime. After direct endoscopy, a person may feel nausea, discomfort when swallowing food, and due to the treatment of mucous membranes with anesthetics, slight swelling sometimes occurs.
Patients who have undergone rigid laryngoscopy often complain of sore throat and nausea. After taking a biopsy with mucus, a small amount of blood is released. Unpleasant sensations persist for up to 2 days; if your health does not improve, you should consult a doctor.
MRI of the larynx and throat with contrast
MRI of the larynx and throat can be performed using a special contrast agent. During such a study, the drug is administered intravenously. Thanks to the contrast agent, it is possible to assess the extent of the pathological process and establish its nature.
Our clinic uses the contrast agents Magnevist and Gadovist. Both of these drugs are based on gadolinium salts, a silver-colored rare earth metal. Gadolinium salts are non-toxic and are quickly eliminated from the body. However, there is a risk of an allergic reaction to the contrast agent (it is necessary to consult a specialist before the examination).
As a rule, MRI of the throat with contrast is used to diagnose cancer. Due to increased blood circulation in the tumor, gadolinium salts accumulate in it, which allows you to clearly see the localization of the tumor and its boundaries in the image. In the structure of oncological diseases, malignant neoplasms localized in the neck and head make up 6%. The first place is occupied by tumors of the larynx. Most often, specialists diagnose squamous cell carcinoma. The first symptoms of the disease are hoarseness and sore throat.
Stages of laryngeal cancer
Determining the stage of cancer is necessary for the correct choice of treatment.
The stage is determined by the size of the tumor, mobility of the vocal cords, and the presence of metastases. In the early stages, the formations are small, there are no metastases, then the oncology spreads to the lymph nodes. In the final stages, a large area of cancer cells spreads.
- Zero stage. Tumor formations are small in size and do not extend beyond the mucous membrane. There are no symptoms, so it is almost impossible to diagnose the disease.
- First stage. The tumor extends beyond the mucous membrane of the larynx, but is still within the organ. Voice changes are observed, but there is no hoarseness yet.
- Second stage. The tumor spreads throughout the larynx. The voice becomes hoarse and breathing becomes noisy.
- Third stage. There is a violation of the mobility of the vocal cords. The voice becomes quiet and hoarse, and in some cases disappears altogether.
- Fourth stage. The tumor spreads to nearby organs and tissues - lymph nodes, esophagus, oral cavity and tongue, neck and trachea, thyroid cartilage. Damage to the spinal canal, carotid artery and chest tissue is also possible.
Carrying out the procedure
An ultrasound of the throat shows the exact outline, density and size of the organs in the neck cavity. The signals reach the internal tissues of the part of the body being examined. Then they return, and the physician and patient see them on the display. The resulting image is compared with accepted standards. The specialist draws conclusions about the patient’s condition.
The procedure is as follows. The patient lies down on the couch. A special transparent gel is applied to the device and the neck area. It conducts ultrasound waves. The doctor smoothly moves the device around the examination site. A return echo signal appears, which is converted into an image using the program. The manipulation lasts from 15 minutes to half an hour.
Then the doctor records the results in a protocol, which must be shown to the otolaryngologist, therapist or endocrinologist who issued the referral. After this, the treatment tactics for the detected diseases are determined.
If no violations are identified, but the patient continues to be bothered by signs of malaise, you need to make an appointment with other professionals. You may need the help of a neurologist or psychotherapist.
Ultrasound of the throat and larynx: indications, what pathologies can be identified, technique
There are diseases the presence of which can only be determined by ultrasound. These options include tumors. An ultrasound of the throat and larynx can show various problems.
Ultrasound of the throat and larynx
Ultrasound of the throat and larynx is performed on both newborns and pregnant women. Depending on the device, the examination can be simple or advanced. The latter allows Doppler scanning.
The doctor moves an ultrasound sensor over the neck area. The impulses arrive to the tissues and glands, from which they are reflected back. The information is transmitted to the processor, where it is processed and displayed on the screen. The advantages include:
- Great diagnostic capabilities.
- No harm.
- Get results quickly.
Indications for the study
- with complaints of a foreign body;
- suspected presence of tumors or neoplasms of the tonsils;
- changes in voice timbre that persist for a long time.
During the study, several problems are solved:
- Diseases of the larynx and throat are detected.
- The previously made diagnosis is confirmed.
- Selection of the appropriate treatment option.
- Monitoring the effectiveness of the impact.
What pathologies and diseases can be identified
Methodology and preparation
The examination cannot be carried out if there is an open wound on the surface of the neck. This is due to the need to apply a special gel aimed at conducting ultrasonic waves.
Ultrasound does not require preparation, so it can be performed both urgently and routinely. In some cases, your doctor may suggest you stop using antibiotics for a while.
This occurs in the presence of an abscess or other acute disease. Do not drink before an ultrasound of the throat and larynx and other drugs that can blur the picture of the disease. Therefore, you should listen to the doctor’s opinion.
If the doctor studies the shape and structure of the tumor, it is recommended not to take drugs with a pronounced antitumor effect. Such drugs distort the picture or temporarily affect the parameters of the tumor, which leads to incorrect assessment.
Technique
The information is entered into a special report, which is stored in two copies. One of them is issued to patients.
Technique and indications for ultrasound of the throat and thyroid gland:
What you need to know
Ultrasound of the throat and larynx is performed in both commercial and government institutions. The doctor must have certain qualifications that enable him to conduct such an examination.
If the examination reveals a pathology of the thyroid gland, the patient is referred to an endocrinologist. If there are nodes or polyps with hypoechoic signs, additional examination with biopsy, radiography, and computed tomography is required.
In children, ultrasound of the throat and larynx is performed in the same way as in adults. The procedure does not cause any discomfort, so the children agree to it. Babies can be swaddled during the examination so that their arms and legs do not interfere with working with the sensor.
Diagnostic value of the procedure
When using diagnostics, no radiation is released, so the study does not affect the general level of health of the patient. Thanks to the development of new equipment, this method is not inferior to the latest diagnostic methods.
What's next?
With the examination result in hand, the patient returns to the attending physician. He studies the examination protocol and prescribes therapy. If hypoechoic nodes are detected, then the diagnosis should be continued.
Patients should not panic when they read the phrase “hypoechoic formation” in the protocol. This is not a diagnosis, but a description of the density of the structure. In this place, the tissue structure is less dense than around it, and the ultrasound pulse moves more slowly. This means that the doctor will have to determine whether this is a pathology or the norm for this area. Sometimes the results obtained are simply incorrect when performing an ultrasound of the throat and larynx, which does not indicate the presence of serious health problems, but the low qualifications of the sonologist (the specialist who performed the ultrasound).
And one more clarification. Structures with low density may turn out to be cysts. This is a cavity with thin walls, the tissue of which resembles a mucous membrane. There is liquid inside the cavity. However, the term “cyst” is never written in the ultrasound report. Since to establish such a diagnosis it is necessary to perform a biopsy. The procedure can be performed with a special needle or other medical devices.
External examination of the larynx
The area of the larynx, which occupies the central part of the anterior surface of the neck, the submandibular and suprasternal areas, the lateral surfaces of the neck, as well as the supraclavicular fossa, is subjected to external examination. During the examination, the condition of the skin, the presence of an enhanced venous pattern, the shape and position of the larynx, the presence of edema of the tissue, unusual solitary swellings, fistulas and other signs indicating inflammatory, tumor and other lesions of the larynx are assessed.
Inflammatory processes revealed during examination may include perichondritis, phlegmon or adenophlegmon, tumor processes may include neoplasms of the larynx and thyroid gland, conglomerates of adhesive lymph nodes, etc. Skin changes (hyperemia, edema, infiltration, fistulas, ulcers) may occur with tuberculosis and syphilitic infections, with suppurating cysts of the neck, etc. With mechanical trauma to the larynx (bruise, fracture, wound), signs of this injury may appear on the anterior surface of the neck (hematomas, abrasions, wounds, traces of compression in the form of bruises during strangulation, strangulation grooves etc.).
With wounds and fractures of the cartilage of the larynx, bleeding from the wound canal with characteristic bloody foam bubbling on exhalation (penetrating wound of the larynx) or internal bleeding with expectoration of blood and signs of subcutaneous emphysema, often spreading to the chest, neck, and face, can be observed.
Palpation of the larynx and the anterior surface of the neck is carried out both in the normal position of the head and when it is tilted back, when individual elements of the palpated formations become more accessible.
Guided by this scheme, you can obtain additional information about the state of the elements of the larynx, their mobility and the sensations that arise in the patient during superficial and deep palpation of this organ.
With superficial palpation, the consistency of the skin and subcutaneous tissue covering the larynx and adjacent areas, their mobility is assessed by gathering the skin into folds and pulling it away from the underlying tissues; Using light pressure, the degree of swelling of the subcutaneous tissue is determined and the skin turgor is assessed.
With deeper palpation, the area of the hyoid bone, the space near the corners of the lower jaw are examined, then they go down the anterior and posterior edges of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, identifying enlarged lymph nodes. The supraclavicular fossa and the area of attachment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, the lateral and occipital surfaces of the neck are palpated and then proceed to palpation of the larynx. It is covered on both sides with the fingers of both hands and lightly pressed, as if sorting out its elements, guided by knowledge of their location, assessing the shape, consistency, mobility, and establishing the possible presence of pain and other sensations. Then the larynx is shifted en masse to the right and left, assessing its overall mobility, as well as the possible presence of sound phenomena - crunching in fractures, crepitus in emphysema. When palpating the area of the cricoid cartilage and conical ligament, the isthmus of the thyroid gland covering them is often revealed. Feeling the jugular fossa, ask the patient to take a sip: if there is a lobe of the thyroid gland ectopic by the manubrium of the sternum, its push may be felt.
Lymph nodes, infiltrates can be palpated on the surface of the thyrohyoid membrane, symptoms of fluctuation (abscess of the floor of the oral cavity), volumetric processes on the ventral surface of the root of the tongue and in the pre-epiglottic region can be detected. Pain on palpation of the area of the thyrohyoid membrane can be caused by lymphadenitis (and then these lymph nodes are determined by touch) or neuralgia of the superior laryngeal nerve, which penetrates this membrane.
The first experience of using ultrasound of the larynx in the diagnosis and treatment of dysphonia
Ultrasound machine HM70A
Expert class at an affordable price.
Monocrystal sensors, full-screen display mode, elastography, 3D/4D in a laptop case. Flexible transformation into a stationary scanner with a cart.
Introduction
Correction of voice disorders is a socially and economically significant problem, since voice-speech professions are becoming increasingly widespread in modern society; for many, the voice is not only a means of communication, but also a “means of production” that provides income and self-realization. If earlier “voice professionals” included singers, actors, teachers, now this group includes managers of various ranks, business and tourism workers, managers, insurance company employees and many others, whose professional activities in our communicative age are associated with a large voice. load [1].
Diseases of the larynx are almost always accompanied by impaired vocal function, which persists even after the elimination of the pathological process. Accordingly, to restore working capacity it is necessary not only to remove the tumor or cure the inflammatory process, but also to restore the voice. Due to insufficient attention to this problem, the prevalence of dysphonia is steadily growing, reaching, for example, up to 65% among teachers according to the data on visits to phoniatric offices [2], among students of speech departments from 35% in the first year to 60% at the end of their studies [3 ].
At an outpatient appointment with an otorhinolaryngologist and phonopedist, the study of vocal function begins already during a conversation with the patient when assessing the timbre of the voice and sound paraphenomena. The condition of the vocal folds is judged on the basis of laryngoscopy and endoscopy of the larynx with stroboscopy, obtaining visual information about the structural features and closure of the glottis. The difficulty lies in the need to overcome the pharyngeal reflex and the limited quantitative criteria for assessing vocal function.
The widespread introduction of ultrasound diagnostics into clinical practice has essentially determined a revolution in non-invasive visualization of organs and systems. The larynx, an organ that until recently was considered inaccessible to ultrasound due to its small size and air in the lumen, was no exception [4]. The diagnostic role of Doppler ultrasound examination of the larynx has been studied to a greater extent in children [5]. In a few publications on this topic, the authors argue about what is stained during Doppler sonography: a column of air or soft tissue, and believe that the resulting picture is dominated by artifacts, because the staining extends far beyond the actual vibrating structures.
In order to understand the features and significance of the nature of staining of the vocal folds during phonation in Doppler mode, it is necessary to recall the anatomy of the laryngeal muscles [6], which are divided into three groups (Fig. 1).
- Muscle that expands the glottis: posterior cricoarytenoid muscle (m. cricoarytenoideus posterior).
- Muscles that narrow the glottis: lateral cricoarytenoid muscle (m. cricoarytenoideus lateralis), thyroarytenoid muscle (m. thyroarytenoideus), transverse arytenoid muscle (m. arytenoideus transversus), oblique arytenoid muscle (m. arytenoideus obliquus).
- Muscles that change the tension of the vocal cords: cricothyroid muscle (m. cricothyroideus), vocal muscle (m. vocalis), internal thyroarytenoid muscle (m. thyroarytenoideus internus).
Rice. 1.
Muscles of the larynx.
A)
Posterior cricoarytenoid muscles (Mm. cricoarytenoidei posteriores).
Function: dilatation of vocal folds. b)
Lateral cricoarytenoid muscles (Mm. cricoarytenoidei laterales).
Function: reduction of vocal folds. c)
Transverse arytenoid muscle (M. arytenoideus transversus).
Function: reduction of vocal folds. d)
Vocal, thyroarytenoid and cricothyroid muscles (Mm. vocales et mm. thyroarytenoidei) (thin arrows). Function: shortening and relaxation of vocal folds. Cricothyroid muscles (Mm. cricothyroidei) (thick arrows). Function: tension and lengthening of the vocal folds.
All muscles of the larynx are paired, except for the transverse arytenoid muscle, which narrows the glottis. The single cricothyroid muscle is innervated by the superior laryngeal nerve, all others by the inferior laryngeal nerve. The blood supply to the larynx is carried out by the superior laryngeal arteries, which are branches of the superior thyroid arteries, and the inferior laryngeal arteries, which are branches of the inferior thyroid arteries. Lymphatic drainage occurs in the deep lymph nodes of the neck - internal jugular and preglottic lymph nodes. As a result of the action of muscles on the cartilages and joints of the larynx, the position of the vocal folds changes, the glottis expands or narrows.
We have not found comprehensive information on the use of laryngeal ultrasound for voice disorders in adult patients in the available resources.
The purpose of this work was to evaluate the possibility of ultrasound in determining the functional state of the larynx to objectify the effect of therapeutic and phonopedic measures in patients who have suffered a disease of the larynx and received a full course of complex treatment.
Material and methods
We observed 52 patients who had a disease of the larynx and received a full course of complex treatment over the past 4 years, with the following diseases: paralysis, laryngeal paresis - 17 people, inflammatory diseases - 8, benign neoplasms of the larynx - 20, laryngeal cancer - 1, functional dysphonia - 6 The main complaint in all patients was changes in the voice of varying severity (weakness, hoarseness, fatigue, lack of voice).
In all cases, the standard examination by an otorhinolaryngologist was supplemented with endoscopy of the larynx with video recording and stroboscopy. Before the start of treatment and over time, the accommodation coefficient was determined in 42 patients using the VOCASTIM apparatus, which characterizes muscle function and the ability of the neuromuscular apparatus of the larynx to accommodate. All patients underwent ultrasound examination of the larynx before and at the end of treatment according to the method described by A.Yu. Vasiliev and E.B. Olkhova [7], using modern ultrasonic devices with linear sensors with a frequency from 7.5 to 18.0 MHz. The sensor was installed on the anterior surface of the neck in the area of the vocal folds in the transverse projection. A series of images were obtained in gray scale mode at rest and in Doppler mode during forced breathing and with phonation tests with mandatory viewing of the cine loop. The structure and echogenicity of the cartilage and soft tissues of the larynx were determined in gray scale mode, then the presence of vascularization, completeness, synchrony, symmetry and duration of staining of the vocal folds and surrounding structures when pronouncing the sounds “i” and “a” were assessed in Doppler mode. In addition, to more fully assess the effectiveness of treatment, a questionnaire was conducted: patients were asked to characterize the degree of their vocal load, the immediate and long-term results of treatment.
The main types of treatment were phonopedia and a complex of rehabilitation of external respiration (in all patients), electrical stimulation of the laryngeal muscles using the VOCASTIM device (in 42 people), 8 patients underwent surgery.
results
Normally, with ultrasound, the cartilage and soft tissues of the larynx are located symmetrically and avascular (Fig. 2, a). In gray scale mode, one can observe how the vocal folds diverge during inhalation and come together during exhalation; their internal contour is hypoechoic and unclear, so it is impossible to assess the degree of closure by analogy with endoscopy of the larynx (Fig. 2, b) using ultrasound. Visualization of small marginal formations on the vocal folds is also extremely difficult.
When Dopplerography with phonation tests (Fig. 2, c) is normal, when all muscle groups work in concert, with adequate scanning mode settings, the coloring of the vocal folds and elastic cone is symmetrical and synchronous.
Rice. 2.
Ultrasound and endoscopy of the larynx are normal.
A)
Ultrasound of the larynx in gray scale mode. Transverse section at the level of the vocal folds.
b)
Endoscopy of the larynx.
V)
Ultrasound of the larynx in Doppler mode with phonation test. Transverse section at the level of the vocal folds.
Variants of pathology diagnosed by ultrasound of the larynx are presented in Figures 3–5. The papilloma, located on the surface of the anterior segment of the right vocal fold (Fig. 3, a–c), contrary to expectations, looks like a hypoechoic round structural defect; it is inactive during phonation tests; a clot of mucus on the right vocal fold (Fig. 4, a–c), on the contrary, looks like an echo-positive formation, excessively mobile during phonation; the tumor is visualized as a hypoechoic structural defect of irregular shape (Fig. 5, a–c); during phonation tests, there is no staining in the area of the tumor lesion.
Rice. 3.
Papilloma of the right vocal fold.
A)
Ultrasound of the larynx in gray scale mode: the right vocal fold is thickened, an avascular hypoechoic oval-shaped area with a clear contour without additional acoustic effects measuring 2.0 x 2.5 mm is visualized in its anterior section.
b)
Endoscopy of the larynx: the right vocal fold is thickened, a papilloma measuring up to 2.0 mm is visualized in the anterior section.
V)
Ultrasound of the larynx in Doppler mode with a phonation test: there is less intense staining of the anterior part of the right vocal fold compared to the contralateral side.
Rice. 4.
A clot of mucus on the right vocal fold.
A)
Ultrasound of the larynx in gray scale mode: along the free edge of the right vocal fold in its anterior section, an avascular formation of medium echogenicity without additional acoustic effects measuring 1.5 mm is visualized.
b)
Endoscopy of the larynx: a clot of mucus is visualized on the surface of the right vocal fold in its anterior section.
V)
Ultrasound of the larynx in Doppler mode with a phonation test: the coloring of the vocal folds themselves is symmetrical; along the free edge of the right vocal fold in its anterior section, a local increase in vibration is visualized in the form of a brighter spot corresponding to a clot of mucus.
Rice. 5.
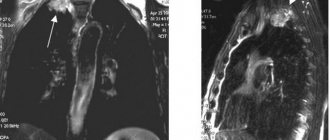
Laryngeal cancer.
A)
Ultrasound of the larynx in gray scale mode: a hypoechoic formation is visualized, located predominantly in the left vocal fold, spreading to the area of the anterior commissure and partially to the anterior part of the right vocal fold, irregular in shape, with an uneven, unclear contour without additional acoustic effects, measuring 6 x 4 mm.
b)
Endoscopy of the larynx: there is an uneven thickening of the left vocal fold with a transition to the area of the anterior commissure and the anterior part of the right vocal fold.
V)
Ultrasound of the larynx in Doppler mode with a phonation test: there is a staining defect in the anterior and middle sections of the left vocal fold and the anterior section of the right vocal fold, corresponding to the area of the tumor lesion.
With dysphonia (Fig. 6), loss or weakening of the function of a particular muscle or group of muscles is noted. As a result, the staining defect can be symmetrical or asymmetrical, synchronous or asynchronous.
Rice. 6.
Variants of vocal fold mobility impairment in functional dysphonia.
A)
Symmetrical impairment of mobility of the anterior sections of both vocal folds.
b)
Impaired mobility of the anterior and middle sections of the right vocal fold.
V)
Symmetrical impairment of the mobility of both vocal folds along the entire length.
G)
Complete immobility of the left vocal fold.
A sequential series of images obtained when viewing a cine loop (Fig. 7) shows that at the beginning of phonation the Dopplerographic pattern is synchronous with a slight shortening of the staining zone due to the immobility of the posterior parts of the left vocal fold. As phonation continues, the vibration of the left vocal fold weakens much faster, the vibrations die out, and only the right half of the larynx provides sound.
Rice. 7.
A sequential series of Doppler images with a phonation test for functional dysphonia (cine loop viewing).
A)
Beginning of phonation.
b)
Midpoint of phonation.
V)
End of phonation.
Phonopedic treatment, adjusted on the basis of topical ultrasound analysis and aimed at stimulating or relaxing a specific affected muscle or group of muscles, turned out to be more effective, which was consistent with the measurement data of the accommodation coefficient and was reflected in a reduction in treatment time compared to known standards, more durable restoration of voice and increasing patient satisfaction. During dynamic observation, according to repeated ultrasound and endoscopic examinations of the larynx, as well as based on the results of a questionnaire, complete restoration of voice function was noted in 34 patients, partial in 12, and no effect in 6 patients.
An important role in achieving results is played by the patient’s increased awareness of his problem at the initial stage of treatment and visual evidence of the improvements occurring under his influence, strengthening compliance, or adherence to treatment, that is, the degree of compliance between the patient’s behavior and the recommendations received from the doctor.
conclusions
Doppler ultrasound of the larynx with phonation tests allows for a deeper understanding of the pathophysiological processes occurring in the larynx during various diseases accompanied by dysphonia. Ultrasound monitoring of the dynamics of voice restoration can serve as the basis for optimizing the individual selection of functional exercises and current parameters during electrical stimulation of the laryngeal muscles.
Literature
- Taptapova S.L., Sergeeva T.A., Ryabova S.V. Experience in voice restoration in diseases of the larynx of various origins. M., 2003. P. 4.
- Orlova O.S., Vasilenko Yu.S., Zakharova A.F., Samokhvalova L.O., Kozlova P.A. Prevalence, causes and characteristics of voice disorders among teachers // Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology. 2000. N5. pp. 18–21.
- Rodionova O.I. Early diagnosis and prevention of voice disorders in people of voice-speech professions. Author's abstract. diss. ...cand. honey. Sci. M., 2013.
- Olkhova E.B., Soldatsky Yu.L., Onufrieva E.K., Shchepin N.V. Ultrasound examination of the larynx: possibilities, prospects, limitations // Bulletin of Otorhinolaryngology. 2009. N5. pp. 9–12.
- Olkhova E.B., Soldatsky Yu.L., Onufrieva E.K., Shchepin N.V. The diagnostic role of Doppler ultrasound examination of the larynx in children // Ultrasound and functional diagnostics. 2006. N3. pp. 42–51.
- Netter FH Interactive Atlas of Human Anatomy // University of Rochester, School of Medicine and Dentistry, Rochester, NY // www.netterart.com. // 2003 Icon Learning Systems LLC: Plate 75.
- Vasiliev A.Yu., Olkhova E.B. Ultrasound diagnostics in emergency pediatric practice // Guide for doctors. M., 2010. pp. 55–65.
Ultrasound machine HM70A
Expert class at an affordable price.
Monocrystal sensors, full-screen display mode, elastography, 3D/4D in a laptop case. Flexible transformation into a stationary scanner with a cart.
Possibility of complications
The use of modern medical technology in endoscopic diagnostics helps the doctor detect pathology and determine the degree of its development, which is especially important for drawing up a treatment program. In addition, this is an excellent opportunity for the patient and his relatives to visually familiarize themselves with the problem and understand the need for treatment.
If cancer is suspected, the results of autofluorescence endoscopy become the most reliable diagnosis of the problem. However, it is worth considering that any type of endoscopic diagnosis is associated with a possible risk for the patient’s condition.
- The consequence of treatment with an anesthetic may be difficulty swallowing, a feeling of swelling of the root of the tongue, as well as the posterior pharyngeal wall. A certain risk of swelling of the larynx cannot be excluded, which results in impaired respiratory function.
- For a short time after endoscopy of the larynx, symptoms of nausea, signs of hoarseness and pain in the throat, and muscle soreness may be felt. To alleviate the condition, regularly rinse the throat walls with a soda solution (warm).
- If a biopsy sample was taken, a cough with bloody clots in the sputum may begin after it. The condition is not considered pathological; unpleasant symptoms will go away in a few days without additional treatment. However, the risk of bleeding, infection, and respiratory tract injury exists.
The risk of developing complications after endoscopy increases due to blockage of the airways by polyps, possible tumors, and inflammation of the cartilage of the larynx (epiglottis). If a diagnostic examination provokes the development of airway obstruction due to spasms in the throat, emergency assistance is required - a tracheotomy. To perform it, a longitudinal dissection of the tracheal area is required to ensure free breathing through a tube inserted into the incision.
When is an ultrasound scan of the throat and larynx performed?
Ultrasound scanning is considered one of the safest and most convenient diagnostic procedures. Ultrasound has no contraindications, is painless (even small children can easily tolerate the procedure), and most importantly, it is highly accurate and informative. All these advantages can rightfully be attributed to ultrasound scanning of the throat.
The throat is an organ of the upper respiratory tract, the larynx is the part of the throat that connects it to the trachea. Often in reference and medical literature they are considered as separate organs. Otolaryngologists prescribe ultrasound quite often – both for typical inflammations and for suspected more serious illnesses. One of the biggest advantages of ultrasound scanning is its high informativeness in detecting throat cancer, even in the earliest stages.
According to Russian statistics, men over 45 years of age are at risk; they account for 80-90% of all patients. And timely ultrasound helps prevent a terrible disease or begin treatment as early as possible.
Ultrasound examination of the larynx is necessary in the following cases:
- upon detection of any throat diseases;
- if you need to confirm or refute the diagnosis;
- when choosing treatment methods (after diagnosis);
- to track the effectiveness of treatment (including cancer therapy).
Contraindications
Doctors do not recommend performing the procedure for people with stage III pulmonary and cardiovascular insufficiency. An obstacle to performing this study is neuropsychic disorders and the extremely serious condition of the patient - conditions that do not allow the diagnostic procedure to be fully performed.
The study is not recommended for patients suffering from disorders of the blood coagulation system, asthma in the acute phase, recent serious illnesses (heart attack, stroke), severe cardiac arrhythmia.
Bronchoscopic manipulation, in the presence of concomitant diseases, is prescribed only when the diagnostic benefit significantly exceeds the expected harm and possible complications.
Diagnosis of the disease
There are a considerable number of methods that help detect a cancerous tumor and determine the extent of its development.
- Tumor marker for throat cancer. A tumor marker is a chemical substance that is released into the human blood during the activity of cancer cells. As a rule, tumor markers have their own specificity, relating to cancer of a particular organ or organ system. In case of throat cancer, a general blood test helps to identify the presence of these same tumor markers. Before donating blood for this purpose, it is not recommended to be nervous, and the last meal should be no later than eight hours before the test. Do not forget that such an analysis is not capable of accurately determining the presence of oncology; this is only possible in a group with other types of examination. But if a tumor marker in the blood is still found outside the norm, you should immediately consult a doctor.
- Inspection and palpation of painful areas. During the examination, the shape and contours of the neck, the mobility of the larynx, and the condition of the skin are assessed. Particular attention is paid to the patient's complaints, which will help determine the location of the tumor and the duration of its development. Palpation will help determine the size and shape, as well as the displacement of the tumor to neighboring tissues. Indirect laryngoscopy (examination) will help determine the condition of the mucous membrane and oncological lesions (if whitish spots and ulcers are identified). It is not advisable to take food or water before the examination, as the doctor’s actions may cause gag reflexes.
- Direct laryngoscopy. It is carried out by inserting a flexible laryngoscope into the throat. The device helps to thoroughly examine the inside of the throat and take a piece of the tumor for a biopsy.
- Biopsy. A tumor piece or lymph node is taken to be examined under a microscope. Allows you to confirm a malignant formation, determine its stage and type.
- Ultrasound examination of the neck. An ultrasound of the neck allows you to examine the lymph nodes for changes and the presence of metastases in them.
- Chest X-ray. Allows you to determine whether a tumor is parasitizing the lungs. X-rays are taken in “profile and full face”, which makes it possible to examine even small seals and spots.
- Computed and magnetic resonance imaging. CT and MRI are modern diagnostic methods and allow one to obtain high-quality images and layer-by-layer sections of the organs being studied. These scans help identify the location and size of the tumor, its spread and progression to other organs. These techniques allow you to obtain the most accurate clinical picture and picture of the disease. The studies are safe, since there is no radiation exposure to the body.
- Electrocardiography. Necessary for assessing the condition of the heart and its functioning. This type of examination is mandatory when diagnosing any disease.
- Bronchoscopy. Using an endoscope, the bronchial mucosa is examined. If necessary, they take a photo or take a piece for a biopsy. This type of examination is not mandatory and is prescribed only if deficiencies are identified during a chest x-ray.
None of these survey methods can be used as the only one. A doctor can make an accurate diagnosis only on the basis of several types of examination.
First of all, this is an examination and questioning, then a biopsy of pieces of the affected tissue. Other methods will be of an auxiliary nature to identify the full picture of the disease.
When is an ultrasound of the larynx and throat prescribed: indications, procedure, interpretation of results
› Head and throat
12.11.2018
The autumn season is characterized by frequent colds, and the ENT organs suffer first of all, because an advanced infection can lead to serious complications. An ultrasound (ultrasound examination) of the throat and larynx will come to the rescue.
What does an ultrasound show?
Ultrasound is a method of studying changes in organs by passing ultrasonic waves through them. When the waves are reflected from the tissues, they are read by a special sensor, displaying a picture on the screen from which the pathology is judged. Ultrasound of the throat, which includes the larynx and pharynx or only ultrasound of the larynx, is performed using the same technology.
This technique has gained popularity in medicine due to its wide range of diagnostic capabilities. It helps to identify:
- Diseases of the trachea and larynx, which are visible on ultrasound. Their narrowing, inflammation, foreign bodies.
- Malignant formations. Patients wonder if throat cancer is visible on ultrasound. Ultrasound diagnostics can answer it only indirectly. Malignancy has its own signs, such as tissue heterogeneity, increased blood flow inside the tumor, but the diagnosis is reliably confirmed by the results of a biopsy.
- Inflammatory diseases of the larynx, throat. It is especially important to refer for this study if you suspect a retropharyngeal abscess, which is dangerous for the development of pneumonia and the entry of pus into the respiratory tract.
- Age-related changes in the tissues of the larynx.
- Benign tumors (fibromas, lipomas, hemangiomas, cysts).
Advantages of the method
Ultrasound examination has become widespread due to:
- Credibility. The method is informative; the sonologist (ultrasound doctor) immediately sees the organ on the monitor.
- Painless procedure. The study does not require the insertion of needles or damage to the skin.
- No radiation exposure to organs and tissues. The technique does not involve the use of X-rays; ultrasound, which is safe for humans, is used.
- Speed. Depending on the scope of the examination, the time varies from 15 minutes to 40.
- Conducting research in real time.
Indications and contraindications
The indication for a study is the appearance of the following symptoms:
- pain in the throat;
- dysphagia (difficulty swallowing solid or liquid foods);
- swelling in the neck (enlarged thyroid gland, lymph nodes);
- decreased sonority of the voice, hoarseness, hoarseness;
- the presence of a benign or suspected malignant tumor of the throat;
- cough in the absence of visible problems with the lungs and bronchi;
- complaints of bad breath without dental problems.
Diagnosing problems of the throat and larynx in the early stages helps to increase the effectiveness of further therapy.
There are no contraindications to performing an ultrasound scan of the larynx area. The method is painless and does not contain radiation exposure. Avoiding diagnosis is possible if there are open wounds in the area where the sensor is installed.
How to prepare for the examination?
The ultrasound procedure of the internal structures of the throat and larynx does not require special preparation, special nutrition, or the exclusion of medications before it. You can bring a towel and diaper with you to your appointment.
How is the procedure done?
An ultrasound of the throat and larynx is quite simple. The technique itself is carried out in a lying position with the head slightly tilted back. You may be asked to place a small cushion under your neck. The sonologist applies a special gel to the skin in order to enhance contact with it. After the examination of the necessary organs is completed, the gel is removed, and the patient can await the conclusion.
The following parameters are assessed:
- the inner surface, the structure of the lower parts of the throat and larynx with a description of changes, compactions in the tissues;
- the size of the lumen of the larynx, pharynx, trachea, as well as its uniformity;
- the condition of the walls of the organs being studied along with the lymph nodes;
- fiber around the pharynx, larynx, where abscesses occur;
- formations in the throat and determination of their nature (benign or malignant);
- inflammatory changes.
Research results
You should know that ultrasound does not make a diagnosis. A person who has undergone diagnostics receives a conclusion describing the structure of the organs studied, the size of the lymph nodes, and additional formations, if any.
Based on the conclusion, the attending physician can exclude or confirm the preliminary diagnosis and prescribe additional techniques. For example, conducting a biopsy - sampling organ cells, CT or MRI.
Don't worry if you read "hypoechoic mass." This means that the ultrasound sensor has detected a structure with a lower density than the surrounding tissue. It occurs normally or in pathology, for example a cyst, tumor, abscess, thyroid follicles.
See what laryngeal cancer looks like on an ultrasound:
X-ray examination of the larynx
Due to the fact that the larynx is a hollow organ, there is no need for contrast during X-ray examination, but in some cases this method is used by spraying a radiopaque substance.
During the review
and
tomographic
radiography,
frontal
and
lateral
projections are used. With a direct projection, the overlap of the spine on the cartilages of the larynx almost completely obscures them, therefore, in this projection, X-ray tomography is used, which removes the shadow of the spine beyond the image plane, keeping only the radiopaque elements of the larynx in focus (Fig. 6).
Rice. 6.
X-ray tomographic image of the larynx in a direct projection (a) and a diagram of identifying elements (b): 1 - epiglottis; 2 - folds of the vestibule; 3 - vocal folds; 4 - pyriform sinuses
Using a tomographic examination, clear radiographs of frontal sections of the larynx are obtained, and it becomes possible to identify space-occupying formations in it. With functional radiography (during deep inspiration and phonation), the symmetry of her motor function is assessed.
When analyzing the results of an X-ray examination of the larynx, one should take into account the patient’s age and the degree of calcification of its cartilage, islands of which can appear from 18-2 years of age. The thyroid cartilage is most susceptible to this process.
Diagnostic progress
Diagnosis is carried out in a supine position. The doctor applies a small amount of acoustic gel to the outer part of the neck for better glide of the device. The device emits ultrasonic waves that are reflected from soft tissues and returned back.
The data is displayed on the monitor. The doctor examines the inner surfaces of the neck. Without certain knowledge, it will not be possible to decipher the picture on the screen. Only the attending physician can announce the result of a diagnostic examination.
Diagnostics lasts 15–30 minutes. Immediately after the examination, the patient needs to remove any remaining gel with a dry cloth and can return to their normal lifestyle. There is no need for a long stay in a medical facility.
If any pathological processes are detected, treatment should be started as soon as possible. Ignoring the selected therapy and doctor’s recommendations is strictly prohibited.
Preparation and performance of ultrasound
Special preparation in the form of diet or taking certain medications is not provided. The patient is required to come for examination in comfortable clothes, with the throat area exposed and without neck jewelry (chains, beads, etc.). If the study is carried out specifically to identify a malignant tumor, you need to stop taking antitumor medications a couple of days in order to obtain objective results.
The procedure itself is performed with the patient in a horizontal position. The area under study and the ultrasound sensor are treated with a medical gel that conducts ultrasound waves. The doctor moves the sensor quietly along the neck. Ultrasound waves are reflected by a return echo signal, which a computer program converts and displays an image of the organs on the monitor. The time interval of the procedure ranges from a quarter of an hour to 30 minutes.
The results are recorded by the ultrasound specialist in a protocol, which the patient presents to the otolaryngologist who referred for the ultrasound. He also determines the treatment tactics for identified pathologies.
Endoscopic examination techniques
The examination is carried out by a doctor who treats diseases of the ears, nose and throat. The possibility of instrumental research allows you to accurately determine the diagnosis in order to prescribe the correct treatment regimen for people of different ages. What types of larynx diagnostics are prescribed?
Indirect view of laryngeal endoscopy
For the study, which is carried out in a darkened room, the patient should sit with his mouth wide open and his tongue protruding as much as possible. The doctor examines the oropharynx using a laryngeal mirror inserted into the patient’s mouth, which reflects the light of the lamp refracted by the frontal reflector. It is attached to the doctor's head.
To prevent the viewing mirror in the throat cavity from fogging up, it must be heated. To avoid gagging, the examined surfaces of the larynx are treated with an anesthetic. However, the five-minute procedure has long been outdated and is rarely performed due to the low information content of the semi-reverse image of the larynx.
An important condition: before prescribing a modern method for diagnosing the condition of the larynx, the patient should be convinced of the need for endoscopy and familiarized with the features of preparation for it. It is also necessary to find out information about the health problems of the person being examined, it is useful to reassure the person that he will not be hurt, there is no danger of lack of air
It is advisable to explain how the manipulation is carried out.
Direct method of research
This type of laryngoscopy is flexible when a movable fiber laryngoscope is used. In the case of using a rigidly fixed device, the technique is called rigid, and is used mainly for surgical intervention. The introduction of modern equipment makes it easier to make a diagnosis and allows you to achieve the following goals:
- identify the causes of changes or loss of voice, pain in the throat, difficulty breathing;
- determine the degree of damage to the larynx, the causes of hemoptysis, as well as problems with the respiratory tract;
- remove a benign tumor, rid a person of a foreign body trapped in the larynx.
If the information content of indirect diagnostics is insufficient, examination by the direct method is relevant. Endoscopy is performed on an empty stomach, but under local anesthesia after taking medications to suppress mucus secretion, as well as sedatives. Before starting the procedure, the patient must warn the doctor about heart problems, blood clotting characteristics, a tendency to allergies, and possible pregnancy.
Contraindications for
An absolute contraindication to the study is pregnancy at any stage, since the dose of radiation received from an X-ray of the human trachea is significant. This type of diagnosis is not recommended for children under 15 years of age, as well as for patients in serious condition. X-ray of the trachea with contrast is contraindicated in those who have an allergic reaction to iodine or other contrast agent.
Advantages and disadvantages of the procedure
Fluoroscopy allows you to see the functioning of an organ in real time, but in this case you have to rely entirely on the qualifications of the doctor performing the procedure. The radiation dose during fluoroscopy is higher due to the fact that the patient has to remain under the sight of the x-ray machine for a long time. The main advantage of tracheal radiography is its low cost compared to other research methods, as well as its efficiency: in fact, the trachea is photographed, and it only takes a few seconds.
However, we should not forget that an X-ray of the trachea does not show so much that it should be done without a doctor’s recommendation. This is one of the diagnostic methods with a relatively high level of radiation exposure. For these reasons, it is not applicable to pregnant women and children. The low information content of the standard examination makes it less and less popular compared to CT. Therefore, if problems are detected, the doctor usually prescribes an additional examination of the trachea using a more modern diagnostic method.
#!RentgenVRA4!#
Direct and indirect laryngoscopy
The procedure is carried out using a special device - a laryngoscope, which shows in detail the condition of the larynx and vocal cords. Laryngoscopy can be of two types:
- straight;
- indirect.
Direct laryngoscopy is performed using a flexible fiber laryngoscope, which is inserted into the lumen of the larynx. Endoscopic equipment can be used less frequently; this instrument is rigid and, as a rule, is used only at the time of surgery. The examination is performed through the nose. A few days before the procedure, the patient is asked to take certain medications that suppress mucus secretion. Before the procedure itself, the throat is sprayed with an anesthetic, and the nose is dripped with vasoconstrictor drops to avoid injury.
Indirect laryngoscopy - this examination of the larynx is performed by placing a special mirror in the throat. The second reflective mirror is located on the otolaryngologist’s head, which allows the lumen of the larynx to be reflected and illuminated. This method is used extremely rarely in modern otolaryngology; preference is given to direct laryngoscopy. The examination itself is carried out within five minutes, the patient is in a sitting position, the pharyngeal cavity is sprayed with an anesthetic to remove the urge to gag, after which a mirror is placed in it. To examine the vocal cords, the patient is asked to pronounce the sound “a” in an extended manner.
There is another type of laryngoscopy - this is a rigid examination. This procedure is quite difficult to perform; it is done under general anesthesia and takes about half an hour. A fibrolaryngoscope is inserted into the pharyngeal cavity and the examination begins. Rigid laryngoscopy allows not only to examine the condition of the larynx and vocal cords, but also to take a sample of material for a biopsy or remove existing polyps. After the procedure, an ice bag is placed on the patient's neck to prevent swelling of the larynx. If a biopsy was performed, sputum mixed with blood may come out within a few days; this is normal.
Laryngoscopy or fiberoscopy allows you to identify the following pathological processes:
- neoplasms in the larynx, and a biopsy can already reveal a benign or malignant process;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx and larynx;
- Fibroscopy will also help to see the presence of foreign bodies in the pharynx;
- papillomas, nodes and other formations on the vocal cords.
Prices
| Name | Price | until September 2 | October 3 and 4 |
| Magnetic resonance imaging of the hypopharynx | 4 060 ₽ | 4 060 ₽ | 4 060 ₽ |
Prices Make an appointment
The diagnostic and treatment center offers MRI of the throat, pharynx and larynx in Moscow with or without contrast using modern equipment.
The larynx is the part of the respiratory system located between the pharyngeal cavity and the trachea. MRI of the throat and larynx is a research method that produces clear, high-quality, high-resolution images of the area under study. The information content of diagnostic results makes it possible to establish an accurate diagnosis and prevent the development of various diseases.
In the pictures you can see:
- individual characteristics of the throat structure;
- size, shape, structure and contours of lymph nodes;
- soft tissues and blood vessels;
- structural features of the nasopharynx and upper esophagus;
- presence of formations.
Indications for ultrasound of the throat
Most often, ultrasound diagnostics are prescribed during an examination of the thyroid gland, which is located under the larynx. As a rule, an ultrasound of the throat is prescribed by a surgeon, endocrinologist or otolaryngologist after a preliminary consultation (collecting anamnesis, patient complaints).
Indications for an ultrasound examination of the larynx are the presence of the following pathological symptoms in the patient:
- The appearance of acute pain in the throat, which is accompanied by an increase in temperature, fever;
- Difficulty swallowing, sensation of a lump in the larynx;
- Presence of purulent discharge;
- A sharp change in voice timbre (the appearance of hoarseness);
- Long-term persistent inflammatory pathologies of the larynx;
- Increased size of the thyroid gland and cervical lymph nodes;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the esophagus;
- Feeling of skin tension in the larynx area.
If cancer is suspected, an ultrasound procedure can detect a neoplasm and visualize the size and condition of the tumor.
Ultrasound scanning of the larynx is also performed to monitor the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy.
Indications for ultrasound
An ultrasound scan is necessary at the slightest sign of discomfort - soreness, cough, the notorious “lump in the throat”, etc. The most dangerous symptoms are if, when palpating the neck from the front, any tumors or lumps are detected.
The otolaryngologist is required to send the patient for an ultrasound scan of the larynx if there are the following signs:
- constant pain in the larynx, difficulty swallowing;
- pain when swallowing radiates to the ears;
- long cough (not associated with diseases of the bronchopulmonary system);
- purulent or bloody discharge (especially if there is no cold or inflammation);
- hoarseness and other changes in voice timbre;
- feeling as if something is stuck in the throat;
- Upon palpation, neoplasms were detected.
If, during the examination, the doctor discovers enlarged cervical lymph nodes or the thyroid gland, he will write a referral for an ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland. If necessary, your doctor will also check your throat and larynx during the scan.
Ultrasound
A study such as an ultrasound of the neck area may
identify a number of pathologies, such as:
- goiter;
- hyperthyroidism;
- neoplasms in the neck, but malignancy can only be confirmed by a biopsy;
- cysts and nodes.
An ultrasound will also show purulent inflammatory processes. But according to the ultrasound conclusion, the diagnosis is not established, and additional diagnostic procedures are required. For example, if an ultrasound revealed a formation in the esophagus, an endoscopic examination method with a biopsy will be prescribed. If the lymph nodes in the neck are affected or there is a suspicion of a tumor in the larynx, a CT or MRI will be prescribed, since these methods provide a more comprehensive picture of what is happening than ultrasound.
Methods for examining the larynx are varied; the use of one or another depends on the expected pathology and the affected organ. Any symptoms that do not go away should alert you and be a reason to visit an otolaryngologist. Only a specialist, having carried out the necessary examination, will be able to accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.