The bronchi and lungs are part of the life-supporting respiratory system of the body. They are located in the chest cavity. The bronchi make up the so-called bronchial tree, through which air enters the lungs.
From the main wide bronchus, narrower ones extend to the right and left lungs, which, branching, end in small-caliber bronchi called bronchioles.
The lungs are a paired organ. On the outside, each lung is covered with a special serous membrane (pleura). The pleura also lines the walls of the chest cavity. Between these two layers of pleura is the pleural cavity. Each lung is divided into lobes: in the right lung there are 3 (upper, middle and lower), in the left there are two. Each share is divided into segments.
Lung tissue is not dense; it contains a large amount of air. It is in the alveoli of the lung that gas exchange occurs between the air entering from the outside during inhalation and the blood in the capillaries.
What can an MRI show?
Popular modern diagnostics can reflect various suspicious phenomena on an image, which gives doctors the opportunity for timely medical intervention, which often saves the patient’s life.
The tomograph clearly shows:
- vasculitis (inflammation of various vessels located in close proximity to the lung);
- pleurisy (inflammatory process in the area of the serous membrane);
- tuberculosis;
- pulmonary aneurysm;
- pleural neoplasms;
- pneumonia;
- pulmonary failure in acute and chronic form;
- cancer at all stages of development;
- atelectasis (pulmonary collapse);
- sequestration (separation of dead areas of lung tissue);
- pneumofibrosis (uncontrolled proliferation of connective tissue);
- condition of the structures, tissues and fluids of the lungs;
- suspicious changes in lymphoid tissues, etc.
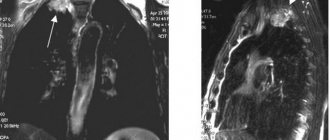
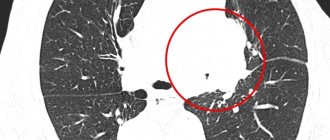
In the image, all pathological areas of the chest organs appear as darkened spots of varying sizes. However, clusters of hydrogen atoms also look similar. A doctor who has just received his medical school diploma may, due to his own inexperience, confuse the two phenomena with each other.
To avoid misinterpretation of the diagnosis, you need to trust your health only to professionals who have extensive experience and a worthy reputation.
Decoding the results of the procedure
During the procedure, the radiologist examines the resulting images, studying each image in detail. After completing the diagnosis, the doctor describes the changes present, but does not make a final diagnosis. It takes about 1 hour to decipher the results; in some cases, a specialist may need a day.
After receiving the finished results, the patient should contact their doctor. The main pathologies, as shown by magnetic resonance imaging of the lungs:
- various diseases of the respiratory system, in particular pulmonary failure;
- congenital anomalies;
- oncological diseases (benign and malignant neoplasms).
In the images after an MRI, dark and light spots are clearly visible, which may be a sign of cancer or inflammatory processes, or an infectious disease. When diagnosing oncology, the doctor describes not only the boundaries of the tumor, its size, but also the growth of atypical cells into nearby organs.
Main advantages of the procedure
MRI of the lungs and bronchi has a large number of “advantages”, which people especially who are under the strong influence of rumors and speculation regarding any medical procedures should be aware of.
The study is different:
Bronchoscopy of the lungs
- ultra-precision of the resulting image;
- increased information content;
- non-invasiveness (superficial conduct of the session without penetration into the body);
- lack of a special preparatory stage;
- the possibility of automatic reconstruction and reliable modeling in three planes (3D);
- increased level of contrast of the resulting sections;
- automatic adjustment of good quality images transmitted to monitors;
- absence of radiation characteristic of X-rays;
- visualization of data in any projection at the required angle;
- the possibility of parallel use of a contrast agent that stains the necessary parts of the organs;
- painlessness, etc.
At the moment, it is impossible to accurately indicate the absolute safety of the method, since there is no official data on the effects of scanning waves on the human body, or on proven cases of harm to health caused by magnetic radiation. However, the diagnostics in question are several times more harmless than X-rays and computed tomography (CT).
Contrary to popular belief, MRI can be performed on people who have become disabled due to a spinal fracture.
Innovative techniques
An innovative technique, tomosynthesis, can surpass CT in terms of safety. We are talking about the development of linear tomography. The diagnostic process uses a digital image detector, which is capable of taking a series of images over a period of 11 seconds as the radiation source moves. The result is a large number of slices of a three-dimensional anatomical structure in one session.
In the case of tomosynthesis, the patient receives a radiation dose similar to that of x-rays - 40-70 µSV. Modern CT equipment gives a dose of 4000 µSV - this is acceptable in the case of a single diagnosis, but too much if a repeated session is necessary.
Tomosynthesis will soon be in Russia...
The information content of tomosynthesis in relation to CT is 95-97%. Even without taking into account the privilege of lower cost of the study, tomosynthesis is a privileged option for diagnosing the lungs when periodic monitoring of the state of the organ system is necessary, for example, when treating patients suffering from tuberculosis.
MRI, CT, X-ray, fluoroscopy are diagnostic techniques that are used to assess the condition of the respiratory system, however, they differ in information content, basic principle and a number of other characteristics. X-ray is the primary diagnostic measure.
CT and magnetic tomography will help clarify the clinical picture when there is a lack of radiographic information, while MRI is inferior to CT in diagnosing pathologies of the lungs, bronchi, trachea and other elements of the respiratory system.
An excellent alternative to computed tomography is tomosynthesis - a safe, informative, and simple way to monitor the condition of a patient’s lungs.
Indications for use
There is a relatively large list of suspicious human health conditions that require an immediate thoracic scan. Among the alarming factors are: accumulation of fluid in the pleura, apnea syndrome (short-term or long-term cessation of breathing during sleep), any changes in the composition of the lung tissue, bronchial asthma, accompanied by acute and frequent attacks.
The list continues with bronchiectasis (chronic suppuration processes), the suspected presence of foreign elements in the lungs, suspicion of the formation of a benign or malignant form, long-term cough of unknown origin (a special reason to see a doctor), suspicion of tuberculosis.
If specialists suspect a patient has pulmonary tuberculosis, they should not put off the check, on which the reliability of the diagnosis depends, since a dangerous progressive disease can lead to the painful death of a person in a short period of time.
Why is MRI preferred?
MRI is an extremely valuable examination also because it very accurately detects a variety of neoplasms. But it is timely detection that serves as the best guarantee in cancer treatment. With the introduction of MRI, detecting lung cancer has become much easier and more effective. When examining a patient, the doctor examines three-dimensional photographs of the lungs, sees the size of the tumors, their shape, and exact location. This is very important for choosing the most effective treatment, as well as prognosis of a person’s condition. The more accurate the diagnosis at an early stage, the greater the patient’s chances of healing.
Equally important is the earliest possible detection of pulmonary tuberculosis, especially since this disease has become one of the most common problems of the respiratory system, which leads to death. The sooner the study is carried out and the disease is identified, the more successful the treatment will be. Detection of tuberculosis in the later stages leaves the patient with virtually no hope for recovery and a normal life.
Contraindications
Unfortunately, not every person can undergo examination using a tomograph. MRI is contraindicated if the prospective patient has:
- implanted metal implants of any type;
- excess weight beyond 120–130 kg;
- extremely serious condition;
- acute heart failure;
- epileptic seizures;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- inappropriate behavior;
- uncontrollable seizures;
- thyroid diseases.
Before the procedure, the specialist is obliged to find out the characteristics of his patient, which, one way or another, affect his safety during the session. If there are contraindications, tomography is replaced by alternative research methods.
If a person experiences claustrophobia, you should immediately warn your doctor about this, since this phenomenon is also a contraindication for MRI.
How does the procedure work?
Like any other study, MRI of the respiratory organs takes place in three stages: preparation, conducting the study, and issuing the results.
Preparation and organization of MRI diagnostics:
- To conclude an agreement for the provision of paid medical services or check referrals and other medical documentation, you must come to the clinic or diagnostic department in advance.
- Patients are given a questionnaire to fill out. This measure serves to timely identify possible contraindications.
- Next comes weighing.
- Body weight and concomitant chronic diseases serve as the basis for choosing a drug that creates a contrast environment in the body at the time of the study and calculating the correct dosage.
- In the changing room, the patient must remove metal objects, jewelry, and leave the phone. You can throw on comfortable clothes without studs or a disposable uniform issued by the nurse.
- A brief briefing is necessary for the patient to become familiar with the sequence of the procedure and the rules of conduct during the study.
- After this, you can proceed to the tomograph.
Conducting research:
- The nurse assists the patient on the extendable table and into a comfortable position for an extended scan.
- To maintain complete immobility, the patient’s body is fixed with soft fixations.
- The table is directed into the scanning capsule, and the installation starts.
- If the study is performed with contrast, then a basic scan is also necessary. A contrast solution is then injected and an MRI is performed again.
- After applying a contrast solution or anesthesia, the patient can remain under the supervision of staff for some time.
Output of results:
- Each medical institution has its own level of workload, so the time to obtain results varies from an hour to one day.
- The patient receives a printed study protocol, photographs and/or recording of images on a CD.
- Some clinics practice sending results by email to the patient and/or his doctor.
An MRI report is not a diagnosis; it serves to make an accurate diagnosis. This will be done by the attending physician or specialist of the required profile, if the MRI was performed on a self-referral basis. Until the results are no longer relevant, you should consult a doctor. This must be done within the next week.
How to prepare for the examination?
Before undergoing the procedure, you do not need to adhere to a special type of diet or take any medications, since this procedure does not involve scrupulous preparation. It is very important to remember that before visiting the relevant institution, it is strongly recommended to wear clothing that does not contain metal fasteners, inserts, locks or decorative elements.
You should also remove all jewelry in advance, including hair clips, clips, belts with metal buckles, crosses and piercings. If the patient’s body contains special bone wires, a defibrillator, a pacemaker, plates, fragments, dental pins, crowns and other metal inclusions and implants, it is necessary to immediately notify the treating doctor.
People who have previously made tattoos using inks with metal particles should also warn doctors about this in order to avoid an accident.
We must not forget that the tomograph is a giant, super-powerful magnet, capable of attracting any ferromagnetic metals with incredible force during the examination. This phenomenon can cause death if the patient neglects the safety rules that include the above points.
If a person experiences severe psychological discomfort when located in a semi-enclosed space or when listening to the intermittent sounds of a tomograph for a long time, he should take a sedative immediately before the procedure, for example:
- Pulsatilla;
- Persen;
- Novopassit;
- Corvalol;
- Veloferin;
- Nobrassite;
- Valerian, etc.
If a child is to be examined, his parents should take responsibility for explaining the essence of the upcoming test. It is imperative to make it clear that the device will not cause pain. In some cases, it is permissible to use earplugs (earplugs) to stop unpleasant sounds.
Is magnetic resonance imaging allowed for everyone?
Despite its safety, the procedure still has some contraindications. This:
- Early pregnancy, since the effect of magnetic rays on the formation of fetal organs has not been studied;
- Severe claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces) in the patient;
- The patient’s condition is critically serious, for example, he is on artificial ventilation;
- The patient's body has a metal-containing implant, for example: a pacemaker, dental pins, metal plates, fixed dentures, a non-ferromagnetic hearing aid in the middle ear, an insulin pump, hemostatic clips, and others.
- Liver failure;
- Epilepsy.
Patients with tattoos on their bodies are not recommended to undergo the procedure, as the tattoo ink may contain metal particles. In patients with heart failure, MRI is prescribed only in cases of urgent need, when other studies have not provided information.
Pregnant women over 13 weeks of pregnancy are prescribed MRI with caution, after consultation with therapists and a gynecologist managing the pregnancy.
MRI with contrast is contraindicated in patients who have individual intolerance to the components of the contrast material.
For children, MRI of the lungs is harmless; they only need psychological preparation for a long stay inside the tomograph.
MRI or CT?
CT and MRI are the best types of examination of the lungs and bronchi, which are rather complementary rather than competing procedures. Magnetic resonance imaging allows for better visualization of the condition of organs, specializing, first of all, in the chemical composition of tissues, fluids and blood vessels. The main operating unit is magnetic radiation.
A contrast agent is used only when recognizing the stage of the tumor process. A CT scan is performed using x-rays. Although the procedure is relatively safe for people, patients still receive a small amount of radiation.
The presence of tattoos painted with paints containing metal particles is not a contraindication for undergoing a CT scan of the lungs
Computed tomography, unlike MRI, involves studying not the chemical, but the physical composition of the elements of the chest. Therefore, this technique gives the best results in a detailed study of fibrosis, aneurysms and the condition of lung tissues susceptible to the pathological process. The administration of contrast during CT scanning is mandatory. This type of diagnosis is possible for people with artificial joints and other types of implants.
When is a CT scan prescribed?
A computed tomograph better displays the alveolar parenchyma, so the appointment is relevant when the tissue of the lung itself is damaged. The images visualize blood and lymphatic vessels.
We list the conditions when CT scanning is relevant:
- pneumonia;
- emphysema;
- exudative pleurisy;
- compactions in the lung tissue;
- internal bleeding;
- stratification or thickening of the walls of blood vessels;
- chest injuries;
- oncology.
CT is faster than MRI, so the method is prescribed for injuries or hidden bleeding, when minutes count. For the remaining listed conditions, the images will be informative and will allow you to make an accurate diagnosis.
Trachea and bronchi
MRI of the trachea and bronchi is usually done together with either the thoracic region or the cervical region, depending on the location of the area being examined.
To improve the quality of the result, contrast can be used (introduction of an appropriate substance into the body). In this case, the study shows more accurate data in narrow areas (the tops of the lungs, the gap between the lungs and the diaphragm) in a volumetric image (in three coordinate axes).
MRI makes it possible to assess the condition of the trachea and bronchi, detect fluid accumulation and the appearance of new formations in the lungs and surrounding organs.