The surgical method of treatment is characterized by the fact that its use is always accompanied by damage to the tissues of the human body. Sometimes the surgical trauma received during access to the affected organ is more significant than the cuts made during the main stage of the intervention.
The desire to minimize the size of incisions and preserve tissue has led to the emergence of such a direction as laparoscopic surgery. This expression was first used by medical researchers more than a hundred years ago. Laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed through small punctures in the anterior wall of the abdominal cavity. In the medical literature, which contains all the information about laparoscopy, other names for such an operation are sometimes used: “peritoneoscopy” or “abdominoscopy”.
Laparoscopy: what is it, essence and types
Using a modern minimally invasive method of intervention, surgeons gain access to organs located in the abdominal cavity and pelvic area. This technique is used for diagnosis, treatment of various diseases, and provision of emergency care.
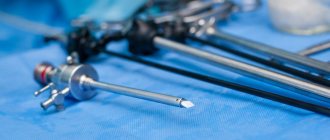
Laparoscopic surgery is performed using sophisticated medical devices. The main one, the laparoscope, consists of the following components:
- Telescopic special tube, which is a metal tube with two channels;
- A set of lenses that transmit an image from the organ under study to a video camera;
- A video camera that displays the resulting image on an enlarged scale on the screen;
- Illuminator – a source of cold light supplied to the area being examined.
During the operation, the surgeon inserts a laparoscope into the abdominal cavity. Another necessary device is an insufflator. It performs the following functions:
- Filling of the abdominal cavity with gas;
- Maintaining a certain level of pressure;
- Periodic gas renewal.
Carbon dioxide is supplied from a cylinder or through a mains network. Modern insufflators can create different gas flow rates.
Therapeutic laparoscopy is performed using special devices - trocars, which are inserted through additional holes. They are a hollow tube with a stylet inside for puncturing the skin and soft tissues. After the trocar penetrates the abdominal cavity, the stylet is removed, and the tube is used as a working channel through which instruments are inserted and the severed organs or tissues are removed. In order to prevent gas leakage, the device is equipped with a valve mechanism.
There are trocars that remain in the patient’s abdominal wall for a certain time and allow for repeated intervention. They are made from inert titanium alloys. Dynamic laparoscopy is used in cases where continuous monitoring of the condition of the affected organ is required.
Scientific and technical achievements in the field of electronics, optics, and materials science contribute to the constant improvement of equipment. This makes it possible to expand the scope of the method, for example, to use laparoscopy in pediatric surgery. In order to raise the abdominal wall and facilitate the insertion of instruments, carbon dioxide is pumped into adult patients using an insufflator.
Laparoscopy in children should be performed without this procedure, since increased pressure in the abdominal cavity negatively affects the child's heart, brain and respiratory system. The use of ultra-precise instruments, as well as special devices that protect organs from accidental damage, allows surgeons to perform minimally invasive operations on children.
Currently, complex, expensive equipment is available not only to large medical centers, but also to regional hospitals. This is especially important for emergency laparoscopy, when the patient's condition requires urgent intervention.
Carrying out the operation
When prescribing planned laparoscopy in gynecology, the woman’s menstrual cycle must be taken into account. If there is no need for urgency, then surgical intervention is prescribed for a “dry” period. The result of diagnostics in gynecology, as well as the effectiveness of treatment, directly depends on the phase of the cycle.
Immediately before the procedure, you are prohibited from drinking or eating. Usually the procedure is carried out in the morning. Its duration depends on the goal. Diagnostics and collection of biomaterial takes no more than 30 minutes, and therapeutic procedures can last 1–2 hours.
The essence of laparoscopic surgery
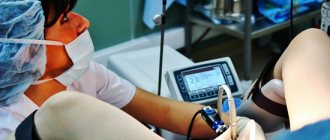
The number of punctures depends on the location of the operation. Usually 3 or 4 small holes are made, up to 1.5 cm in size. In most cases, general anesthesia or medicated sleep is used.
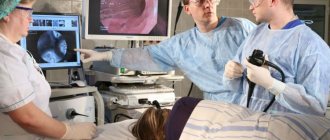
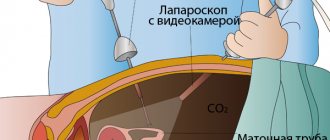
A puncture is made with a special device (trocar), and the necessary instruments are inserted into the operating area through it. The main instrument is a laparoscope; it is a hollow tube with a microscopic camera, with which doctors control their manipulations. Information from the camera is displayed on a monitor in the operating room. An optical cable is also used, which is equipped with a lighting installation.
To prevent tissue adjacent to the intervention area from interfering with the operation, they are lifted by injecting a gas mixture into the cavity. This allows you to create space for medical manipulations. This is followed by a thorough visual inspection. If necessary, a piece of pathological tissue is taken for laboratory testing.
After the surgical work is completed, the instruments are removed. Cosmetic stitches are applied to the punctures. A person spends 2 to 7 days in the hospital after surgery. This depends on the scope of the intervention performed. After 7–10 days, the sutures are removed. If self-absorbable threads have been applied, they do not require removal. Scars lighten over time and become practically invisible in appearance.
The role of diagnostic laparoscopy
The first developers of the laparoscopy method used it primarily in diagnosing diseases.
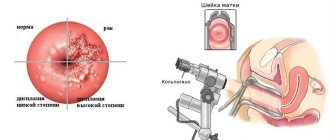
The term itself, translated from Greek, means examination of the abdominal cavity. Currently, there are many modern ways to study the human body that do not injure tissue: MRI, radiography, ultrasound, endoscopy and others. However, laparoscopy is often used for diagnostic purposes. The latest optical devices are capable of greatly magnifying the surface under study and detecting very minor pathologies. The diagnostic accuracy of such studies approaches 100%. A unique method makes it possible to examine not only the abdominal and pelvic organs, but also the retroperitoneal region. The peculiarities of the procedure make it possible to urgently carry out the necessary surgical procedures in emergency situations by introducing additional trocars for instruments. Of all medical specialties, laparoscopy is most often used by gynecological surgeons to determine an accurate diagnosis and as the main method of treatment. It makes it possible to visually assess the condition of the internal female genital organs. According to experts, up to 95% of gynecological operations can be performed laparoscopically.
In oncology, minimally invasive methods make it possible to painlessly analyze pathological material for research, determine the type of tumor, stage of the disease, and choose treatment tactics. If surgery is indicated, laparoscopy is used if indicated. Its use reduces the risk of unwanted complications and promotes rapid recovery of the patient.
Types of laparoscopy
Laparoscopy can be planned, with gradual preparation, or emergency, when treatment is required urgently. The method is divided into three main types. They differ in purpose of application:
- During diagnostic laparoscopy, the peritoneum and its internal organs are examined from the inside. This is done with the help of a manipulator. Diagnosis is required when the exact cause of the disease has not been identified by other methods.
- Operative laparoscopy is a low-traumatic surgical operation. In the process, the pathology is removed or a correction is made (pelvic adhesions are eliminated). Laparoscopy in gynecology is used most often.
- Control diagnostics are aimed at monitoring the patient’s condition after previous operations. During the procedure, the effectiveness of the surgical intervention is assessed, and a prognosis for future conception can be made.
Indications
The laparoscopic method is used for diagnosis in the presence of the following signs:
- Internal injuries, damage and bleeding;
- Acute forms of diseases of the stomach, intestines, pancreas, as well as the liver and bile ducts;
- Formation of various tumors;
- Suspicion of postoperative or acute peritonitis;
- Penetrating wounds in the abdominal area;
- Accumulation of fluid in the peritoneum.
Indications for laparoscopy are situations where the clinical picture indicates an acute pathology: pain, fever, irritation of the peritoneum, and less traumatic research methods did not allow establishing a diagnosis. With the help of laparoscopy, it is possible, having determined the cause of the ailment, to immediately stop the bleeding, perform tissue excision, and remove the neoplasm. Laparoscopy is also used in the treatment of many diseases:
- Acute or chronic appendicitis;
- Cholelithiasis;
- Abdominal hernia;
- Malignant neoplasms in the pancreas, rectum, stomach area;
- Ulcers, adhesions, intestinal obstruction;
- Other diseases of the abdominal organs.
In the field of gynecology, laparoscopy is performed for the following indications:
- Infertility of unknown origin;
- Sclerocystosis, cysts and ovarian tumors;
- Endometriosis of the uterine appendages, ovaries;
- Adhesive disease;
- Ectopic pregnancy;
- Myomatous lesions of the uterus;
- Ovarian apoplexy, accompanied by internal bleeding;
- Other gynecological diseases.
Laparoscopic surgeries can be emergency or planned. Despite the fact that they are tolerated by patients better than interventions accompanied by a cavity incision, the likelihood of complications exists. Such an operation must be prescribed taking into account all available data on the patient’s condition.
What is uterine laparoscopy and its benefits?
A large number of patients in gynecological clinics undergo in-depth examination. Using a laparoscopic device, you can not only perform a full-fledged surgical intervention, but also make high-quality diagnostics. This method is often resorted to if a woman suffers from infertility.
If a doctor prescribes laparoscopy for a woman of reproductive or menopausal age, this indicates a serious illness and the impossibility of conservative treatment.
Laparoscopy to remove the uterus, despite its radical nature, gives the maximum sparing effect. The risk of bleeding during treatment is minimal, and the recovery period is significantly reduced due to minor incisions.
After laparoscopy, the patient’s condition quickly improves, and after 2 weeks she returns to normal.
After removal of an organ, it is impossible to carry a child to term. But maintaining health at the same time gives a chance for a full life. According to numerous reviews, after the operation for laparoscopic removal of the uterus, the patient’s condition quickly improves, and after 2 weeks she returns to normal. If the doctor decides to keep the ovaries, they will continue to produce hormones. Therefore, sudden early menopause is practically excluded.
Types of operations
- Laparoscopy in the cervix. Required for surgical interventions performed through vaginal access. Due to the small incision in this area, visibility is impaired, so an additional instrument with a camera is inserted through the abdominal cavity.
Surgery in the cervix.
- Laparoscopy of the fallopian tubes. It can be used for ligating organs during sterilization, as well as for expanding the lumen of the appendages during infertility treatment. Thanks to laparoscopic intervention, it is possible to eliminate the adhesions in the tubes.
It is used for organ ligation, as well as during the treatment of infertility.
Abdominal surgery to remove the uterus or other elements. The course of the operation may change if complications arise during laparoscopy or health-threatening conditions are discovered - peritonitis, cancer, abscess, heavy bleeding. In such cases, there is a transition from laparoscopy to laparotomy.
Contraindications
Like any surgical intervention, surgery performed laparoscopically has certain limitations. Doctors divide contraindications to laparoscopy into absolute and relative. The first category includes very serious manifestations: coma, clinical death, blood poisoning, purulent peritonitis, intestinal obstruction, uncorrectable blood clotting disorders, severe diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
The second category includes certain characteristics of the patient or his condition that can cause negative manifestations during and after surgery. Relative contraindications include:
- Advanced age. During this period of life, patients usually have a number of chronic diseases and disorders of the cardiovascular system. The disadvantages of laparoscopy, like any surgical intervention, are the use of general anesthesia. It can cause myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, and arrhythmia in very elderly people.
- Extreme obesity. Excess excess weight and accompanying health problems are contraindications for surgery by any method. During laparoscopy in obese patients, insertion of the laparoscope and trocars is difficult; puncturing the skin and soft tissues often causes bleeding. Due to the fact that the abdominal cavity contains a lot of fat deposits, the surgeon does not have enough free space for manipulation. If the operation is planned, such patients are usually given time to start losing weight.
- Possibility of formation of adhesions. This factor is relevant for those who, shortly before laparoscopy, underwent conventional abdominal surgery.
- Diseases of the cardiovascular or respiratory system. They may worsen during the administration of anesthesia.
All contraindications apply to planned surgical interventions. In emergency cases, when not only the health but also the life of the patient is at risk, the operation can be performed after appropriate preparation.
Possible complications after anesthesia
The likelihood of complications is minimal, but possible if the recommendations are ignored. After anesthesia, the following unpleasant consequences may occur:
- disturbance of heart contractions;
- headache and back pain;
- ingestion of stomach contents (food remains) into the esophagus;
- accumulation of air in the pleural cavity;
- thrombosis of the pulmonary artery or deep veins;
- blockage of blood vessels;
- allergic reactions;
- damage to the central nervous system;
- accumulation of pus due to improper injection;
- vomiting, nausea;
- breathing disorder.
In conclusion, we can say that laparoscopy is an absolutely safe, easy operation, because anesthetics intended to put a patient under anesthesia have been repeatedly tested by specialists and patients and almost never cause any unpleasant consequences.
Preparing for surgery
If the doctor has ordered a laparoscopic examination or surgery, serious preparation is required. The patient must undergo a number of examinations:
- ECG;
- Fluorography;
- X-ray and ultrasound of the affected organ;
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy (if the intervention is related to the digestive system).
Mandatory laboratory tests:
- General urine analysis;
- General and biochemical blood test;
- Blood clotting test;
- Determination or confirmation of blood group and Rh factor;
- Check for syphilis, hepatitis and HIV infection.
The patient’s task is to follow all recommendations for preparing for laparoscopy. In addition to directing blood and urine tests, as well as other examinations, the doctor usually prescribes a diet that should be followed 6-7 days before surgery. Foods that promote increased gas formation should be excluded from the diet. These are peas, beans, lentils, white cabbage, rye bread and others. The last meal is allowed no later than six o'clock in the evening on the eve of surgery. A little later, a cleansing enema is prescribed. This procedure must be repeated the next morning before surgery.
Rehabilitation: what happens after laparoscopy
Of course, the recovery period after laparoscopy is significantly shorter than after laparotomy, but it still takes about 1 month.
On the first day immediately after the operation, the woman is prohibited from getting up and moving. All physiological needs are fulfilled using a special vessel.
On the second day you are allowed to get out of bed, but only by wearing compression stockings or tights and a support bandage on your stomach. This “ammunition” will need to be put on every time before you start walking. Doctors insist that after the second day a woman needs to walk a lot to prevent the formation of adhesions, as well as the onset of congestion in the lungs.
The hospital stay lasts from 3 to 5 days. At this time, nurses treat the woman’s wounds and also inject painkillers as needed.
After discharge, once home, it is forbidden to take a bath or shower - you absolutely must not get the stitches wet until they are removed. Partial washing is allowed.
A component of rehabilitation after laparoscopy is dietary restrictions. Excluded from the diet:
- sweets;
- coffee;
- chocolate;
- White bread;
- fatty and spicy dishes.
The main task of the diet after the procedure is to prevent constipation. It is necessary to switch to a fractional nutrition plan - eat 5-7 times a day in small portions. Dairy and vegetable soups, cereals, and fermented milk products are allowed on a woman’s menu after surgery.
Physical activity, especially focusing on the abdominal area, is strictly prohibited, so you will need to hold off on lifting weights or doing abdominal exercises. It is also necessary to abstain from sexual intercourse. The doctor may recommend special therapeutic exercises. It also determines the duration of restrictions imposed on food, intimate life and physical activity.
Sutures are removed approximately 2 weeks after the intervention.
When is it better to do laparoscopy for women?
The date of minimally invasive surgery for women is directly related to the course of the menstrual cycle. Elective laparoscopy is not prescribed on menstruation days. During this period, the likelihood of bleeding and infection increases. Due to normal physiological changes occurring in the female body, these days it is more difficult for the patient to cope with the stress associated with surgical intervention.
Most gynecological operations are performed on any non-critical days of the cycle. In the middle of it, just before ovulation, there are optimal conditions for operations for ovarian cysts and diagnosing infertility. In any case, choosing the date of surgery is the prerogative of the doctor.
Consequences and pregnancy
The risk of complications during laparoscopy is minimal, since the operation is performed under visual control. But, as with any surgical intervention, there is a possibility of postoperative bleeding and wound infection. If laparoscopy was performed for problems with conception, women are more interested in what the chances of getting pregnant after it are, and how quickly they can plan a pregnancy. It depends on the pathology that led to infertility.
After interventions such as removal of a tube, fibroid, or ovarian cyst, recovery time is required, and doctors recommend using contraception for 2–3 months, and only then planning a pregnancy.
If infertility was associated with adhesions, then after cutting the adhesions, you can get pregnant even in the current menstrual cycle. When preparing for IVF and laparoscopic tubectomy, the rehabilitation period is 3 months, only after this can you enter into the protocol.
With PCOS, additional drug therapy may be needed; it is prescribed individually, based on the woman’s hormonal background. Also, with polycystic disease, women are advised not to postpone pregnancy, since laparoscopy does not cure the disease and hormonal imbalances still remain. Dissection or wedge resection of the ovaries only creates favorable conditions for ovulation. Over time, the ovaries are again covered with a sclerotic membrane. Laparoscopic gynecological operations are performed in many clinics in Moscow.
How is laparoscopy done?
Minimally invasive operations without layer-by-layer dissection of the soft tissues of the abdominal cavity are performed by general surgeons, gynecologists and urologists. Currently, extensive experience in such interventions has been accumulated, and optimal methods for their implementation have been developed.
How is the preliminary stage of laparoscopy performed?
In the process of preoperative preparation, the anesthesiologist develops a premedication and anesthesia plan that matches the individual characteristics of the patient. The patient’s natural anxiety about surgical intervention can cause cardiac arrhythmia, hypertension, and increased acidity of the stomach contents. Reducing the level of anxiety and gland secretion is the main goal of the premedication.
In the operating room, the patient is connected to a machine that monitors cardiac activity. Anesthesia during the procedure can only be administered intravenously, but most often a combination of this method with endotracheal is used. In addition to anesthesia, relaxants are instilled to help relax the muscles. Then an endotracheal tube is inserted and connected to a ventilator.
How the operation itself is performed
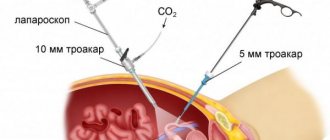
The small internal space of the abdominal cavity makes it difficult to examine organs and manipulate surgical instruments. Therefore, the technique of performing laparoscopic surgery involves preliminary injection of a large volume of gas. To do this, a small incision is made in the navel area through which a Veress needle is inserted. The abdominal cavity is filled using an insufflator; carbon dioxide is considered the optimal filler.
After the required pressure has been established in the patient’s abdomen, the needle is removed and a trocar is inserted into the existing incision. The tube from this device is intended for insertion of a laparoscope. The next step is to insert trocars for additional surgical instruments. If during the operation damaged tissues or organs are excised, neoplasms are removed, the extraction is carried out in special container bags through trocar tubes. To crush large organs directly in the cavity and then remove them, a special device is used - a morcellator. This is done during operations such as hysterectomy.
Vessels and aortas are clamped during laparoscopy using titanium clips. To apply them, a special device is inserted into the abdominal cavity - an endoscopic clip applicator. Surgical needles and absorbable suture material are used to place internal sutures.
The final stage of the operation is the final examination and sanitation of the cavity, removal of instruments. Then the tubes are removed and small skin punctures at the sites of their installation are sutured. A drainage must be placed to remove blood debris and pus to avoid peritonitis.
How is anesthesia administered during laparoscopy?
General anesthesia, which is widely used in general surgery, involves complete loss of consciousness and sensitivity of nerve endings. Throughout the laparoscopic procedure, the anesthesiologist monitors the patient’s reaction to anesthesia and also maintains his vital signs (heart rate, blood pressure).
Drugs are administered intravenously through a catheter or by inhalation of inhaled drugs through a breathing apparatus or a combination of both. The anesthetic is administered in different dosages at different stages of anesthesia and the course of the operation, and its concentration depends on the general condition of the patient. More painful stages during surgery require a greater depth of anesthesia.
In addition to general, regional or local anesthesia, the use of sedation is practiced in medical practice. This is the simplest type of anesthesia, which is performed during minimally invasive procedures (colonoscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging studies) to protect the patient from discomfort and allay his fears.
Is it worth doing laparoscopy - advantages and disadvantages
The use of laparoscopy allows the patient to recover as quickly as possible. The average length of hospitalization is 2-3 days. Due to the fact that the surgical intervention occurs with virtually no incisions, there is no pain during the healing process. For the same reason, bleeding during laparoscopy is rare.
An undeniable advantage is the absence of postoperative scars. The disadvantages of laparoscopy are due to the specifics of the operation:
- A small, limited working area creates difficulties in the surgeon's work;
- The doctor uses sharp special instruments, the handling of which requires certain training and experience;
- It is difficult to assess the force with which the instrument acts on the affected organ, because it is not possible to use the hands;
- When observing an internal cavity on a monitor, the perception of the third dimension - depth - may be distorted.
All these shortcomings are currently being eliminated. Firstly, thanks to the spread and popularity of laparoscopic operations, medical centers and hospitals employ surgeons who have performed many minimally invasive interventions, have extensive experience, and have developed skills.
Secondly, the devices, devices and instruments used in laparoscopy are constantly being improved. For this purpose, advances in various fields of knowledge are used. In the future, it is planned to use robots controlled by surgeons for laparoscopic operations.
Hesitation often occurs in a patient for whom laparoscopy is prescribed as a diagnostic procedure. When assessing the pros and cons of laparoscopic examination, you need to remember that today this method allows you to establish a diagnosis with maximum accuracy. In addition, having detected pathology, the surgeon can simultaneously carry out treatment.
What is laparoscopy in gynecology
A method that causes the least amount of trauma and damage during diagnosis or surgery, with the smallest number of invasive penetrations - this is what laparoscopy of the uterus and ovaries is in gynecology. To reach the female genital organs without a large incision, three or four punctures are made in the abdominal wall, after which special instruments called laparoscopes are inserted. These instruments are equipped with sensors and lighting, and the gynecologist “with his own eyes” evaluates the process occurring inside, coupled with the diagnosis of the female genital organs.
Possible complications
Laparoscopy is a serious surgical operation, so the possibility of various negative consequences cannot be ruled out. The main complications that arise as a result of the intervention:
- Swelling of subcutaneous tissue not only in the peritoneum, but also in other areas. This is called subcutaneous emphysema, occurs due to the action of carbon dioxide, does not require treatment, and goes away in a few days.
- Damage to an organ or vessel as a result of incorrect actions by a doctor. In this case, the damaged tissue is immediately sutured and measures are taken to stop internal bleeding.
- Suppuration of surgical wounds occurs when an infected excised organ is inaccurately removed through a wound or due to a decrease in the patient’s immunity.
- Failure of the cardiovascular or respiratory system occurs under the influence of anesthesia and increased pressure in the abdominal cavity due to the intake of carbon dioxide.
- Bleeding from a trocar wound may be the result of a medical error or poor blood clotting of the patient.
To date, complications, including minor ones, occur in 5% of the total number of operations performed. This is much less than with abdominal surgery.
Description of laparoscopy, its features
What is laparoscopy? This is an examination or surgery that eliminates large incisions in the peritoneum. The operation is performed using a modern medical device - a laparoscope. The devices are inserted into the abdominal cavity through small punctures. This eliminates stitches and the appearance of keloid scars, which are typical for the traditional method of surgical intervention.
The method reduces the risk of side effects and complications. Unlike traditional surgery, it has a short recovery period. Surgical instruments are equipped with illuminated micro-cameras, so the desired organ is clearly visible. To increase the information content, the peritoneum is inflated with pneumoperitonium air. Little preparation is required before the operation.
Postoperative period
After laparoscopy surgery, the patient awakens on the operating table. The doctor assesses his condition and the functioning of his reflexes. After five hours, a patient placed in a ward is allowed to get up with outside help. It is recommended to walk around, but slowly, carefully, avoiding sudden movements. On the first day, eating any food is not allowed. You are only allowed to drink still water.
Sutures should be treated with an antiseptic. They are removed one week after surgery. Pain in the abdomen and back is mild. If they bother the patient, the doctor will allow painkillers to be taken. Unpleasant heaviness in the lower abdomen is a consequence of carbon dioxide entering the abdominal cavity. The condition will improve as soon as all the gas leaves the body. Discharge from the hospital is made according to the doctor's decision.
Hospitalization can last 2–5 days depending on the complexity of the operation and the patient’s well-being. For 4 weeks, a gentle diet is prescribed with the exception of foods that are difficult to digest: fatty meat, milk, eggs. Fruits and vegetables are allowed, they stimulate metabolism and help remove residual gas.
Heavy physical work and intense sports activities are prohibited for a month. The majority of those who have undergone laparoscopic surgery note a rapid recovery and return to normal life.
Rehabilitation period
Wound healing after laparoscopic intervention occurs much faster than after classical surgery. Basic care is treatment with an antiseptic solution. If you follow the doctor's recommendations, there are practically no complications. In the first days, pain is possible, but it goes away on its own. Sometimes it is necessary to wear a post-operative bandage. After a week you can return to your normal rhythm of life.
The only limitation is avoidance of heavy physical activity for 1–2 months. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism.
Indications and contraindications for laparoscopy
Today, laparoscopy is the standard for diagnosing and treating the causes of female and male infertility. In comparison with abdominal operations, which severely injure the pelvic organs and negatively affect the general condition of the patient, laparoscopy has a number of important advantages. Not surprisingly, this is the best treatment for young patients.
Indications for laparoscopy:
- infertility of unknown etiology;
- lack of effect from hormonal therapy;
- acute and chronic pathologies of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes;
- adhesive process;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- diagnosis of disorders in the pelvis.
Contraindications:
- blood clotting disorder;
- pronounced changes in clinical tests;
- exhaustion of the body, weakened immunity;
- shock, coma;
- severe pathologies of the heart and blood vessels;
- severe lung diseases;
- hernia of the diaphragm, linea alba and abdominal wall.
Planned laparoscopy should be postponed for a month if an acute respiratory viral infection develops. For hypertension and bronchial asthma, surgery is prescribed in case of urgent need.
On what day of the cycle is it done?
Many women do not attach importance to what day of the menstrual cycle the operation will be scheduled for, and are surprised by the questions of the gynecologist asking when the last menstruation was. However, preparation for laparoscopy in gynecology begins with clarifying this issue, since the effectiveness of the procedure itself will directly depend on the day of the cycle at the time of the operation. If a woman has her period, there is a high probability of infection in the upper layers of the uterine tissue, in addition, there is a risk of causing internal bleeding.
Gynecologists recommend doing laparoscopy immediately after ovulation, in the middle of the monthly cycle. With a 30-day cycle, this will be the fifteenth day from the start of menstruation, with a shorter one - the tenth or twelfth. Such indications are due to the fact that after ovulation, the gynecologist can look at what reasons prevent the egg from leaving the ovary for fertilization; we are talking about diagnosing infertility.
- Diet for a diseased liver
- Symptoms of inflammation of appendicitis in women
- At what age are cats castrated?
Why is an enema done before surgery?
The intestines of an adult with a normal diet contain up to 8 kg of feces. They contain waste secretions, bacteria, and toxins. Normal digestion is accompanied by gas formation, swelling and collapse of intestinal loops, contraction of the muscle layer in the form of waves of peristalsis. Even at rest, the intestines form wave-like movements. A patient with constipation may experience fecal blockages, sudden dilatation, and swelling of the loops of the small and large intestines.
Let us imagine the position of the operating surgeon when opening the abdominal cavity. The doctor tries to minimize the incision and choose the best access to the intended intervention site. When the intestines are clogged, immediately after opening the peritoneum, a nearby swollen loop crawls out into the wound on its own. It is difficult to put it back, the rest of the intestine makes it difficult to find the pathology and assess the severity of the lesion.
- The risk of traumatic damage to the mesentery, blood vessels, disruption of the integrity of the intestinal wall, and nerve fibers increases sharply.
- With the laparoscopic approach, the view of the operating area is reduced.
- The constant threat of feces entering the abdominal cavity and severe peritonitis requires preliminary maximum cleaning of the intestines and removal of gases.
If the patient is to be operated on under general anesthesia, this means not only pain relief, but also complete muscle relaxation. To limit the entrance “gate” of infection through an open wound, complete atony is required. But the loss of contractility of the anal sphincters causes arbitrary leakage of urine and feces and violates the sterility of materials and linen. Due to the same relaxation of the esophagus, stomach contents can enter the airway, so anesthesiologists insert a suction tube.
Why an enema is needed in a trauma department becomes clear when considering the technical features. Surgical interventions on bones make it difficult to maintain high tone in muscle groups that hold a limb or joint in an incorrect position. The problem of relaxation is also fraught with the release of feces. An enema is necessary for emergency and planned operations.
Before birth, when contractions begin, the baby's path should be free of infection. But pushing is accompanied by defecation. Therefore, midwives first give a cleansing enema to women sent to the delivery room.
Important! During gynecological operations (including abortion), the doctor needs a palpable feeling of the density of the uterus. Intestinal fecal stones and spasmed muscles do not provide opportunities and interfere with forced diagnosis.
For 2-3 days after the operation (sometimes more), complete rest and artificial absence of bowel movements, provided by an enema, are required. Meals are reduced, only liquid meals are allowed. Pre-cleaning helps prevent post-operative complications. To combat constipation, stimulation is used on the fifth day if stool does not appear on its own. By this time, the wound begins to heal, and the danger of sutures coming apart from straining disappears.
Stages of laparoscopy
Planned operations are carried out in the morning. It is usually recommended to follow a light diet before the procedure. On the day before surgery, you should not eat or drink after ten in the evening. Keeping food and liquid out of the stomach prevents vomiting during surgery.
Before the patient is sent to the operating room, additional bowel cleansing is performed using an enema. If there is a risk of thrombosis, the legs are bandaged with elastic material, or anti-varicose compression stockings are worn. Before laparoscopy, you need to remove glasses, contact lenses and dentures.
Both inhalation and intravenous anesthesia are possible. During the operation, an endotracheal tube is placed in the trachea to support breathing, and a catheter is placed in the bladder to monitor kidney function.
The number of punctures during laparoscopy will depend on the location of the pathology and the scope of the intervention. Usually 3-4 punctures are made. The doctor inserts a trocar (a device for piercing tissue and inserting instruments) under the navel, and two more on the sides of the peritoneum. One of the trocars is equipped with a camera, the others with instruments, and the third illuminates the cavity.
Through a trocar, the abdominal cavity is filled with carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide to improve access to the pelvis. Typically, the technique and scope of the operation are determined after the introduction of instruments and examination of the pathology.
Laparoscopy without surgical complications can last from 15 minutes to several hours. It all depends on the severity of the disease. At the end of the manipulations, the doctor examines the cavity again, checks the results, and removes blood and fluids that have accumulated during the process. It is very important to check for bleeding.
After the control audit, the gas is eliminated and the trocars are removed. The punctures are sutured subcutaneously, and cosmetic sutures are applied to the skin.