Using laboratory diagnostic methods, doctors evaluate the functioning of internal organs; the GGT indicator in a biochemical blood test is a marker of damage to the biliary tract and liver. Studies aimed at studying GGT are prescribed if diseases of the hepatobiliary system are suspected. They are used to monitor treatment and detect the transition of the disease to a chronic form. A change in the activity of this enzyme in the blood plasma may indicate alcoholism, malignant tumors, taking narcotic substances, medications that have become a direct or indirect cause of liver damage.
To identify the problem at an early stage, and not to let the pathological process lead to irreparable consequences, you should regularly visit a doctor, conduct blood tests, know what GGT is, what its normal values are.
GGT - what is it?
Not all medical terms are understandable to people not involved in this field of activity. Meanwhile, explaining in simple terms what GGT is is not so difficult. GGT, GGT, GGTP, gamma-GT, γ-GTP are abbreviations for gamma-glutamyltransferase. This is the name of the microsomal enzyme found in cells. It ensures the occurrence of biochemical processes (acting as a catalyst), amino acid reactions, and is important for the metabolism of glutathione, the main antioxidant in the human body.
This enzyme has other names - gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. This word is synonymous with the term gamma glutamyl transferase. You should be aware that any of the above abbreviations may be indicated in the prescription for biochemical analysis (GGT - short for English Gamma-glutamyltransferase, γ-GTP - for γ-Glutamyltranspeptidase).
How to detect an increase in gamma GT?
The fact that gamma-GT is elevated can be suspected by a number of signs, since only a slight increase does not give clinical manifestations. Since usually in pathologies that are accompanied by an increase in gamma-GT, there is stagnation of bile, the patient experiences:
- yellowness of the skin and yellowing of the sclera;
- heaviness and pain in the liver area;
- sharp pain after eating;
- weakness and significant decrease in performance.
Quite often you can observe dyspeptic disorders - diarrhea, nausea and vomiting. In some cases, instead of diarrhea, the patient complains of constipation.
Since the causes of an increase in gamma HT can be various diseases, including heart pathologies, chest pain, fainting, shortness of breath, and pallor are possible.
Where is gamma glutamyl transferase located?
Accumulates in parenchymal organs, mainly in the kidneys, in significant quantities in the liver, bile ducts, and pancreas. A small number is found in the intestines and brain. In the heart, lungs, and skeletal muscles, its concentration tends to zero. In blood plasma, enzyme activity is normally insignificant - 4-6 times less than in urine. Its presence here is explained by the excretion of gamma-glutamyltransferase formed in the liver and the natural death of old cells in which the enzyme is localized.
Due to such normal processes, GGT in the blood is not zero. If the analysis showed that GGT is elevated, then this indicates massive cell death or problems with bile secretion, which led to an increase in the levels of compounds in the blood that are normally excreted along with bile.
What is glutamine transferase?
Glutamyltransferase (ggt) takes part in complex biochemical processes, being a catalyst in the transport and exchange processes of amino acids with the cells of the body.
The localization of this protein enzyme is located directly in the cell, in the membrane, lysosome and cytoplasm.
When the cell deforms, it enters the bloodstream. Slight increases in the indicator are normal, since the body is constantly undergoing processes of dying off old cells and replacing them with new ones. Pathological is a condition in which a large number of cells die, but much less are restored.
The final test result may include Y glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and gamma glutamine transferase (GGTP). They have a slight difference:
| This membrane-binding enzyme takes part in the metabolism of amino acids. Its highest concentration is in the spleen, pancreas, liver tissues, and kidneys. In all these organs it is found in the outer membrane. | It is an active participant in the formation of new protein molecules, catalyzes biochemical reactions and is a more significant test in diagnosing liver diseases. GGT indicates the presence of cholestasis and consists of a blood chemistry test called a liver function test, along with enzymes such as ALT, AST and alkaline phosphatase, as well as bilirubin. |
In the presence of pathological conditions, the process of cell deformation is significantly accelerated, which leads to a sudden increase in GGT in the blood plasma. It is he who reacts faster to damage to liver cells and is a more sensitive indicator. It helps to diagnose hepatitis very effectively, even before changes in other blood parameters and external symptoms.
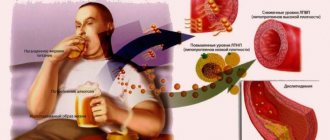
An indicator such as glutamyl transpeptidase is also very sensitive to the effects of alcohol, and is used to adjust treatment for alcoholism.
What affects GGT levels?
When deciphering the results of blood biochemistry for GGT, the age component should be taken into account - in infancy and childhood, enzyme levels exceed normal values for adults. Thus, the GGT value of 90 is within the normal range for newborns and infants aged 1-7 months. If such a concentration of the enzyme is detected in adults or older children, then increased activity of gamma-glutamyltransferase is diagnosed.
The gender of the subject is also taken into account: the rate of GGT activity in men is significantly higher than in women (the difference is up to 50% and is ensured by the influence of male sex hormones and the secretion of the enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase by the prostate gland). A similar pattern begins to be observed after reaching puberty.
The results of the GGT enzyme test are also affected by:
- diet – excess salty, sweet foods;
- deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- body mass;
- presence of bad habits – smoking, drinking alcohol, substance abuse;
- pregnancy (first weeks);
- drug therapy;
- use of hormonal contraception.
Analysis for gamma GTP
Diagnostics is performed using the enzymatic-colometric method.
The material for analysis is venous blood. The duration of the study is one day. The test must be taken on an empty stomach. It is important to remember that the enzyme reacts very sensitively to alcohol consumption.
Attention! Increased levels of gamma GTP after drinking alcoholic beverages can persist for up to three weeks.
Indicators of gamma glutamyl transferase
It must be remembered that in children under six months of age, normal enzyme levels are 2 to 4 times higher than in adults. It's connected
with metabolic features. The rates also differ between men and women.
Considering the content of GGT in prostate cells, levels in men exceed levels in women by 25 percent.
Normal levels in U/L are levels up to:
- 185 for babies in the first five days of life;
- 204 from 5 days to 6 months;
- 34 from six months to a year;
- 18 from one to three years;
- 23 from three to six years;
- 17 from 6 to 12 years old;
- 33 (for women) from 12 to 17 years old;
- 45 (for men) from 12 to 17 years.
For reference. For adult men, the GGT norm ranges from ten to 71. The gamma glutamyl transferase norm for women over 17 years of age ranges from six to 42.
Please note that reference values (i.e. average values) may vary between laboratories. This does not mean that the difference will be drastic. But, depending on the equipment used, there may be differences. In any case, if there are problems, the result that does not fall within the norm will be highlighted in red.
Enzyme content standards
Normal values vary greatly by age. Laboratory test results should be interpreted based on the standards indicated on the GGT analysis form. Each laboratory, in accordance with internal regulatory standards, establishes and officially approves its reference ranges for a specific gender and age. The reason that the limits of norms may vary is due to differences in the equipment used and the blood analysis technique used. The content level is indicated in international units, designated IU or ED, per 1 liter of blood plasma. For reference, the table shows approximate data on the level of the GGT enzyme.
| Age | Reference limits (upper limit of normal) Female / Male |
| up to 6 months | 204 |
| 7-12 months | 34 |
| 2-6 years | 23 |
| 7-12 years | 19 |
| 13-17 years old | 38 / 52 |
| adults | 39 / 66 |
Decoding the results
Only a doctor can decipher the test result. Based on them, he can determine or deny the presence of pathology. As a rule, an increase in the level of this enzyme is observed in chronic and acute hepatitis, cholestasis, pancreatitis, alcohol dependence, and oncology. The norm for women over 17 years of age is 6-42 units/l. If the sample is more than 50 times higher than normal, and all other enzymes are normal, then the patient has chronic alcoholism.
Article on the topic:
Causes of increased alkaline phosphatase in the blood. Symptoms and treatment
In heavy smokers and overweight people, the level of gamma HT can be exceeded by 50%.
Reasons for increased enzyme levels
If there are elevated GGT values in a blood test, what could this mean? A doctor of appropriate specialization must determine the cause of changes in enzyme concentration, establish a diagnosis, and choose treatment tactics. When interpreting the results, the following are taken into account:
- influence of related factors;
- the magnitude of deviation from the norm;
- the content in the blood of other enzymes used to assess liver function - AST, AlAt, SDH, alkaline phosphatase, etc.;
- results of a complete examination of the body.
So, if blood biochemistry shows that GGT is increased significantly (5 times or more), then they suspect:
- cholestatic syndrome, cholangitis;
- the appearance of stones in the intrahepatic ducts;
- neoplastic changes in the liver;
- obstruction of the bile ducts, obstructive jaundice, intrahepatic or extrahepatic obstruction;
- inflammation of the gallbladder - cholecystitis;
- pancreatitis;
- alcoholism (even a single dose in high doses for several hours or days increases the concentration of GGT);
- alcoholic or primary biliary cirrhosis;
- poisoning with hepatotoxic substances - drugs, poisons;
- pancreatic tumors, liver damage by metastases.
The GGT test is the most sensitive marker because a change in values is observed even at an early stage of the disease. A moderate increase in GGT may indicate the presence of:
- infectious hepatitis;
- acute hepatitis of non-infectious nature;
- hepatocyte cytolysis;
- fatty hepatosis;
- diabetic ketoacidosis – a complication of diabetes mellitus;
- obesity.
High GGT is often caused by diseases of other organs containing this enzyme. Increased values are found in renal amyloidosis, infectious mononucleosis, chronic glomerulonephritis in the acute phase, renal pyelonephritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer of the prostate, breast, lungs or abdominal organs, after kidney transplantation.
It was found that serum GGT activity also increases during acute myocardial infarction and CHF. Due to the variety of possible diagnoses, it is difficult to independently decipher a blood test - a comprehensive examination and medical education are required.
Causes
As already mentioned, increased gamma-GT levels may be associated with cholestasis. The disease is characterized by congestion in the gallbladder. In this case, the enzyme concentration can increase very significantly - 5 times or more. If bile stagnation is associated with liver disease, doctors talk about intrahepatic cholestasis, in which case the following pathologies may be the causes:
- viral hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- sclerosing cholangitis;
- toxic damage from chemical compounds.
Extrahepatic cholestasis is called if a failure of bile excretion is observed in the extrahepatic ducts. This may be due to the following diseases:
- formation of stones in the bile ducts;
- tumor processes in the ducts;
- Oncology of the stomach or head of the pancreas, the tumor presses on the common bile duct.
The death of liver cells leads to the fact that the enzyme ends up in the general blood stream. Cytolysis is the name of this pathology. It is observed with toxic or viral liver damage. The influence of autoimmune or systemic diseases, for example, lupus erythematosus, is also possible.
Article on the topic:
Symptoms and signs of liver cirrhosis in men
Hepatotoxic poisons can also cause liver damage:
- cyanides;
- arsenic;
- phenol;
- bacterial toxins;
- pesticides;
- toxins from the fungus toadstool.
But, of course, the hepatitis B and C viruses play the main role in liver destruction.
Alcohol dependence is also a common cause of increased gamma TG. Alcohol enhances the production of gamma GT.
Important! If you stop drinking alcohol-containing products, the gamma-GT level decreases by 50% within 10 days.
In the absence of adequate treatment, alcohol dependence can develop into alcoholic liver disease, resulting in fatty hepatosis - fatty infiltration of the organ, which will lead to atrophy of liver cells. These phenomena are already irreversible, and the patient cannot be saved.
With oncology in the liver, as well as the presence of metastases, the activity of the enzymes discussed also increases. In this case, the cause is several factors - stagnation inside the ducts, death of cellular structures, toxic effects of cancer intoxication. During the period of remission, a decrease in concentration is observed.
As for other reasons, they may be as follows:
- inflammatory process in the pancreas;
- diabetes mellitus, since it is directly related to pancreatic diseases;
- renal pathologies;
- injuries;
- neurological diseases;
- heart failure in severe form - congestion may develop, and as a result, cardiac cirrhosis of the liver;
- brain pathologies;
- extensive burns - in this case, the maximum concentration of the enzyme is observed after 10 days;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- taking hormonal drugs.
Reasons for reducing GGT
Deviation of the indicator from the norm to a lesser extent is less common; in most cases, this condition does not need correction. The doctor’s task is to cure the underlying disease that caused the decrease in the concentration of gamma-glutamyltransferase in the blood. If the result does not fall within the lower limits of the norm, this may be a consequence of:
- acquired or hereditary hypothyroidism – lack of thyroid hormone;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- lack of iodine in food;
- consuming large doses of ascorbic acid.
What is the reason for the decrease in GGT norm?
The concentration of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase can be not only increased, but also decreased.
Such a change in the biochemical composition of the blood is possible in the following cases:
- hypothyroidism is a disease in which the activity of thyroid tissue is reduced, which entails hormonal imbalance;
- extreme obesity;
- long-term use of phenobarbital or ascorbic acid;
- oncological diseases of bone tissue;
- pregnancy status;
- chronic renal failure.
A special increase in the level of GGT in the biochemical composition of the blood is not required. The patient and the attending physician are faced with the task of treating the underlying disease, getting rid of which will restore the normal function of the liver and other internal organs involved in the digestive process.
Article design: Mila Friedan
What are the dangers of deviations from the norm?
A high level of the GGT enzyme in the blood is not dangerous in itself. A pathological process that provokes an increase in the concentration of gamma-glutamyltransferase poses a threat to human health and even life. This protein is the first to respond to the destruction of liver cells and blockage of the bile ducts. Moreover, to determine the level of danger, the following statement is true: the greater the deviation of the value from the upper limit of the norm, the more severe the disease.
If the analysis reveals a low concentration of GGT in the blood plasma, then there is no health risk in this case. But this result of blood biochemistry serves as a reason for diagnosing the functions of the thyroid gland, determining the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland and the main thyroid hormones - T3 and T4. They coordinate the work of the digestive, reproductive, cardiovascular and other systems of the body.
What is GGTP?
Gamma-GT (synonyms: gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase, GGTP, gamma-glutamyltransferase) refers to an enzyme that is produced during a number of biochemical processes. This substance takes part in the metabolism of amino acids and is regularly found in and inside cell membranes. It is most present in the following organs:
If gamma-GT is elevated, the causes in women may lie in diseases of the listed organs. Since women do not have a prostate, the gamma-GT level will normally be lower than in men. Gamma-glutamyltransferase is present in small quantities in other organs, but its importance is not decisive.
An increase in the indicator never passes without leaving a trace; it always signals a problem in the body. GGTP is most abundant in the liver tissues, so damage to them should first be ruled out.
For women, the normal value is 6-32 IU/liter, or 10-66 units/liter (depending on the measurement in a specific laboratory).
For comparison, in men the figure is 18-100 units/liter, in children it varies by age. It is worth citing the most common reasons for the increase in indicators in women:
The blood test is taken on an empty stomach and is prepared within 24 hours. Afterwards, the doctor draws conclusions about the possible preconditions for an increase in the enzyme.
When is the test ordered?
A referral for analysis to the laboratory can be given by a general practitioner or local therapist, as well as a highly specialized doctor - hepatologist, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, gastroenterologist, narcologist. A biochemical blood test to determine the level of Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is carried out for preventive purposes; it is included in routine medical examinations, a list of measures prescribed in preparation for surgery. An indication for the test is also the appearance in patients of alarming symptoms indicating liver pathology or a disorder of the biliary system.
These characteristic features are:
- icteric discoloration of the skin, whites of the eyes, mucous membranes;
- general weakness, fatigue;
- skin itching;
- discolored stool;
- the appearance of dark urine;
- frequent attacks of nausea;
- lack of appetite;
- profuse vomiting;
- pain in the right hypochondrium, abdominal area.
Indications for the study are also:
- liver health assessment;
- suspicion of neoplasms;
- identification of dysfunction of the gallbladder, ducts, detection of bile stagnation;
- screening for alcohol abuse;
- monitoring the course of cancer;
- determining the prognosis in terms of recovery after myocardial infarction;
- the need to establish the exact cause of the increased activity of the protein enzyme ALP (alkaline phosphatase);
- assessment of the hepatotoxic effect of medications taken;
- monitoring the effectiveness of therapy.
How is GGT tested?
The GGT study is included in the biochemical blood test and is included in the group of liver tests. For the determination, human biological material (blood) is used, which is donated on an empty stomach, since with the consumption of food there is an increase in enzyme activity, which will lead to false results.
Blood is drawn from a vein.
It is very important to follow all the preparation steps before having a blood test so that you do not have to do it again.
The GGT level is recorded at different temperatures of the incubation sample and using different methods. The choice of method and temperature used depends directly on the laboratory in which the patient is tested and the equipment installed in them.
As a result of the analysis, next to the GGT indicator the temperature at which the study was carried out is noted. So, deciphering the analysis can only be done by an experienced doctor, since in addition to the temperature and method of examination, it is necessary to take into account the gender, age, and race of the patient.
What precautions should you take when preparing?
To avoid false indicators in the final results table, it is recommended to follow preparation measures. By following the rules listed below, the results will be the most reliable, which will help to correctly diagnose or refute the disease.
The main recommendations for preparation are:
- Blood is donated on an empty stomach. To avoid deviations in blood counts caused by activation of enzymes due to food intake. The consumption of foods is limited at least eight hours (preferably more than ten) before the time of blood sampling. That is why the test is taken in the morning, since a person will not feel hungry at night. It is also prohibited to drink any drinks, including ordinary drinking water,
- Refuse to eat fatty, highly salted, spicy, overcooked foods that are difficult for the body for at least twenty-four hours (preferably forty-eight hours). Such products have too strong an effect on enzymes, significantly increasing the indicators
- to stop playing sports and avoid strenuous physical activity as much as possible , two days in advance, since physical effects on the body also affect the final results,
- A visit to a sauna, steam bath, or hot bath the day before can lead to fluctuations in normal values. You should avoid visiting places where the body is exposed to thermal effects,
- Limit alcohol intake and cigarette consumption at least 24 hours before the upcoming test.
- Stop using medications at least two days before the test. Drugs of certain groups can affect the parameters of a biochemical blood test. If it is not possible to stop using medications, you must inform your doctor about the use of medications. The doctor will make adjustments to the results, taking into account the effect of a particular drug on human blood,
- Come to donate blood 10-15 minutes in advance . This is necessary so that the body calms down, shortness of breath goes away, and the body acclimatizes to the temperature conditions of the room (especially after a cold street).
Fact! If you are very hungry, it is better to take food with you and satisfy your hunger immediately after blood collection.
What could affect the results?
In addition to liver disorders, the following factors may affect a normal result, leading to a false reading. These include:
- Long-term use of ascorbic acid can significantly reduce the GGT result,
- Elevated GGT levels are provoked by antibiotics, antidepressants, oral contraceptives, aspirin, paracetamol, testosterone and certain types of medications,
- Excessive excess weight.
Fact! When deciphering the analysis, it is also important to take into account other indicators in the biochemical blood test (lipase, LDH, bilirubin, ALT, AST, etc.), since almost all GGT deviations are accompanied by disturbances in the levels of other enzymes. ALT and AST are elevated, then the pathology is confirmed.
Preparing to take the Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase test
The patient should be instructed about the preparatory measures by the attending physician. He tells you what factors (medicines, oral contraceptives) can distort the result of a biochemical analysis and what should be done to ensure that the data obtained during the study are reliable. Standard training includes:
- Ensuring blood donation on an empty stomach - it is advisable not to eat food for 8-12 hours, do not overeat at the last meal, avoid fatty, pickled, spicy foods, and smoked foods. Fasting for more than 14 hours is not recommended. You are allowed to drink water (still).
- Avoid physical activity, emotional stress, and stressful situations on the eve of blood collection.
- Abstain from drinking alcoholic beverages. The restriction period must be at least 3-5 days.
- Stop smoking – at least 30 minutes in advance. before the procedure.
What does a GGT blood test show?
Gamma glutamyl transferase, GGT, in a biochemical blood test is an indicator used to identify possible abnormalities. Using GGT it is impossible to determine the type of disease or the nature of the disorder. The discrepancy in the concentration of this enzyme is regarded by doctors as an indicator for a comprehensive examination of the body, and especially the liver.
Such a study helps to identify:
- blockage of the bile ducts;
- the presence of stones in the gallbladder;
- pancreatic tumors;
- primary cirrhosis;
- sclerosing cholangitis.
How is biochemical analysis for GGT/GGTP performed?
The biomaterial for research is blood serum (from 1 ml.). Venous and capillary blood is used. The sampling is performed from the vein of the elbow or another vein accessible for fixation. A tourniquet is applied above the puncture site, and the skin area is treated with an antiseptic. The collected whole blood is transfused into a test tube and then, subject to a certain temperature, delivered to a biochemical laboratory (within 2 hours).
During transportation and storage, care must be taken not to cause hemolysis of the blood sample. There are several methods for determining GGT activity; each laboratory uses its own method. The period for completing the study and issuing the result presented in numerical form is from 3-5 hours to 1 day. The form issued to the patient or doctor who wrote out the referral for biochemical analysis indicates the value obtained during the study, the unit of measurement and the variant of the norm.
Other possible reasons
Regular examinations and blood tests are recommended for anyone undergoing long-term treatment. Many tablets cause cytolysis (cell death) of the liver. This provokes the release of large amounts of liver enzymes into the blood. In women, this often happens when taking a course of estrogens and corticosteroids.
Liver dysfunction is accompanied by a number of functional changes, each of which has its own symptoms. Laboratory tests, which are often called liver tests, can clarify the disease and make a diagnosis. In parallel, GGT is also studied in a biochemical blood test.
Enzyme level correction
Increased GGT activity indicates the development of the disease. The way to reduce the level of the enzyme in the blood plasma is to prescribe competent treatment to eliminate the provoking factor. Medicines and therapeutic procedures are prescribed by a doctor after a comprehensive examination of the patient (to eliminate the possibility of error) and an accurate diagnosis. If endocrine system dysfunction is not detected with low GGT, it is recommended to include iodine-rich foods in the diet as a treatment.
How you can lower GGT yourself
Doctors do not recommend trying to reduce the concentration of Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by taking any medications or traditional medicine. Diseases that provoke an increase in this indicator in the blood are quite serious; they require timely and adequate therapy. This will help avoid worsening the disease. Only an experienced doctor can choose the right treatment tactics.
To speed up the process of normalizing the biochemical composition of the blood and improving treatment results, the patient can:
- exclude alcohol, smoking;
- reduce weight;
- eat enough, give up unhealthy foods (fried, smoked, flour, spices and pickles, soda);
- include more vegetables (pumpkin, carrots, spinach are healthy) and fruits (citrus fruits, apricots) in your diet;
- normalize the drinking regime, replace coffee and tea with clean water;
- take vitamins, mineral complexes (with the approval of a doctor);
- strengthen the immune system;
- to walk outside.
If you start treatment at an early stage of the disease, the prognosis is quite favorable.
GGT is increased: the reasons for this phenomenon
Gamma glutamate transferase may vary throughout the day. This means that in the morning the concentration of this enzyme in the blood is lowest. By lunchtime there is more protein. In the evening, the concentration of GGT is highest. That is why a biochemical blood test is performed in the morning
and strictly on an empty stomach. Some foods also tend to increase GGT levels in a person's blood.
Before taking the test, the doctor prohibits the patient from eating junk food for 12 hours before the actual collection of biological material. This is a guarantee that the analysis result will be the most accurate.
Reasons for increasing GGT
may be different:
Dangerous is the fact that most of the above pathologies first occur in a latent form.
.
They may not manifest themselves in any way, but at the same time, the transcript of the biochemical blood test will indicate an increased level of GGT. The data will enable the doctor to suspect the presence of problems in the patient’s body and their severity. For example, if GGT exceeds the norm by only 2-3 times, then, most likely, the disorder is not serious and can be easily cured. But in the case when the GGT level is tens of times higher, it is necessary to conduct serious examinations
and, based on the results obtained, prescribe a therapeutic course.
Is it possible to normalize GGTP using folk remedies?
Many medicinal herbs have hepatotoxic effects. Therefore, folk remedies to reduce GGTP must be used extremely carefully, with the consent of the attending physician.
Herbal remedies that increase the production and flow of bile
| Plant raw materials/extracts | Industrial name / dietary supplement |
| Rose hip | Holosas, Holemaks, Holos |
| Artichoke | Hofitol, Holebil |
| Immortelle flowers | Flamin |
| Corn silk | Peridol, Insadol |
| Tansy | Tanacehol, Tanaflon, Sibektan, Solaren |
| Barberry leaves and roots | Berberis-Gomaccord Berberis – plus |
| Milk thistle | Silibor, Silibin, Karsil, Legalon, Zdravushka |
In the complex therapy of cholestatic diseases, infusions of medicinal herbs are used to reduce GGTP.
How to prepare the infusion: Mix the raw materials. Pour 1 tablespoon of herbal mixture into 1 glass of boiling water and heat in a water bath for 15 minutes. Cool at room temperature. Strain, squeeze. Bring the resulting volume of infusion to 200 ml with boiled water.
Herbal collection for hepatitis, cholecystitis: Immortelle flowers – 1 tablespoon Yarrow herb – 1 tablespoon. Wormwood herb – 1 tbsp. Fennel seeds – 1 tbsp. Peppermint leaves – 1 tbsp.
Take half a glass of infusion 4 times a day 15 minutes before meals.
Herbal collection for cholangitis and cholecystitis Peppermint leaves – 1 tbsp. Common wormwood herb – 1 tbsp. Valerian root – 1 tbsp. St. John's wort herb - 1.5 tbsp. Hop cones – 0.5 tbsp.
Take the infusion 0.5 - 1 glass 30 minutes before meals 2-3 times a day.
Choleretic phyto-collection for jaundice Flowers of sandy immortelle – 2 tbsp. Three-leaf leaves - 1.5 tbsp. Peppermint leaves – 1 tbsp. Coriander fruits – 0.5 tbsp.
Take half a glass of infusion 30 minutes before meals 3 times a day.
Herbal collection for cholelithiasis Flowers of sandy immortelle – 3 tbsp. Tunguska rhubarb roots – 2 tbsp. Yarrow herb – 5 tbsp.
Take the infusion once a day at night, half a glass.
The course of treatment with folk remedies is 2 weeks. If well tolerated, after a week's break, preventive therapy can be repeated.
Milk thistle to reduce GGTP
Milk thistle enhances the formation and excretion of bile, increases the resistance of liver cells to infection and toxins.
Dry milk thistle seed powder Take half a teaspoon before each meal, 20 minutes before meals.
A decoction of milk thistle roots, pour 1 tablespoon of crushed raw material into 1 cup of boiling water. Heat in a water bath for 30 minutes. Immediately strain, squeeze, bring the volume of the decoction to 1 cup of boiled water. Take 1 tablespoon before meals 3 times a day.
The course of treatment with milk thistle is 1-2 months.
We recommend reading: Liver tests: interpretation, normal indicators
Diagnosis and treatment of diseases with elevated GGTP is carried out by a doctor
Save the article for yourself!
Source: aptekins.ru
Analysis transcript
Testing may show a slight increase or decrease in the enzyme in the blood serum, but the indicator must fit within the reference values. The permissible norm depends on the gender of the patient:
- for women – 0-38 units/l;
- for men – 0-55 units/l.
In rare cases, the GGTP level in the blood may be 0, but this is an extremely rare result.
Exceeding reference values
Five pathological processes can cause an increase in GGTP. This:
- alcohol poisoning;
- neoplasm growth;
- drug poisoning;
- cytolysis;
- cholestasis.
But the following pathologies can become specific reasons that can provoke an increase in GGTP:
- cirrhosis of the liver. Chronic pathology accompanied by replacement of liver tissue with fibrous tissue;
- liver cancer. A malignant tumor characterized by damage to the lobes or bile ducts;
- stagnation of bile – cholestasis. This pathology is typically characterized by a decrease in the volume of bile secreted or a complete cessation;
- hemolytic jaundice. A condition characterized by active destruction of red blood cells and an increase in free bilirubin in the blood;
- acute hepatitis;
- pathologies of the renal system;
- mononucleosis of infectious origin. Acute viral pathology, accompanied by damage to the liver, spleen and lymph nodes;
- diabetes. Endocrine pathology, accompanied by disturbances in the processing and absorption of glucose;
- pancreatitis. Inflammation of the pancreas;
- pancreas cancer;
- oncopathology of the prostate gland;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland. A condition characterized by the active production of triiodothyronine and thyroxine by the gland;
- alcoholism.
Exceeding the permissible norm is recorded in the following cases:
- after kidney transplantation;
- with hyperthyroidism;
- while taking certain groups of medications.
Myocardial infarction and bone tissue pathologies do not cause an increase in the level of GGTP in the blood serum. When deciphering the analysis, it is important to understand that protein levels increase with any liver disease. GGTP can reach its maximum when there is blockage of the hepatic ducts. In this case, the permissible norm is exceeded by five to thirty times.
High levels of the enzyme are determined in liver cancer. This applies to both primary neoplasia and metastatic cancer. In addition, an increased rate will be observed with cholecystitis, cholangitis and obstructive jaundice. GGTP level readings are more informative than other tests if you suspect:
- hepatitis of infectious origin;
- fatty liver degeneration;
- drug poisoning;
- diabetic keatocidosis.
In this case, an excess of the norm by two to five times is recorded. With diagnosed pancreatitis, cirrhosis of alcoholic origin and pancreatic cancer, an increase in GGTP by five to fifteen times is recorded. It is especially important to perform blood testing for GGTP during long-term alcohol use.
Reduction of acceptable indicators
A reduced GGTP value is extremely rare, so there are only three reasons for its decrease:
- during the treatment of alcohol dependence. This condition is caused by the lack of ethanol, which is the main stimulator of the production of this enzyme in a drinker. A drop in protein levels is recorded approximately a month after the start of therapy;
- hypothyroidism A set of symptoms caused by a lack of hormones produced by the thyroid gland;
- treatment with certain medications. In particular, the drug Chlobifrate can have this effect.
The analysis should be deciphered by a specialist, since when interpreting the result obtained, it is necessary to take into account the results of accompanying laboratory tests. If the reference GGTP values are exceeded/lowered, a biochemical blood test should be repeated to confirm the values.
Correction approaches
Only a doctor can balance the level of gamma-glutamyltransferase, taking into account data from other tests. The essence of correction is treatment of the root cause. The enzyme level returns to normal on its own after the underlying pathology is eliminated or compensated for.
When alcohol is excluded from the diet, the level of the enzyme, which was elevated due to alcoholic beverages, returns to its place, while ensuring normal outflow of bile, the growth of the enzyme disappears against the background of obstruction of the bile ducts, the abolition of drugs leads to automatic normalization of the concentration of GGTP in the blood.
“GGTP Treatment” - How to lower GGTP in the blood
/consultation with a doctor is required, there are contraindications/
- To reduce GGTP, it is necessary to find out and eliminate the reason for its increase.
In other words: in order to lower GGTP, it is necessary to treat the disease being sought (hepatitis, cholelithiasis, cholangitis, tumor, etc.) and/or stop taking alcohol and GGTP inducing medications.
The first line of treatment for cholestasis is considered to be ursodeoxycholic acid drugs: Urdoxa, Ursofalk, Ursosan, Ursoliv, Urso, etc.
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C), veganism, and physical activity reduce GGTP levels.
To treat skin itching due to bile stagnation, Cholestyramine or Rifampicin are usually used.
Essential phospholipids improve liver function and liver function tests: Essentiale, Rezalut, Livolin, Essliver, etc.
When bile stagnation, choleretic drugs are traditionally prescribed: Allohol, Cholenzym, Vigeratin, Liobil, Hologon, Dekholin, Hofitol, Urolesan, etc.
In acute hepatitis and cholelithiasis, choleretic agents are used to a limited extent, strictly as prescribed by the attending physician.
To reduce viscosity and facilitate the excretion of bile, alkaline mineral waters are useful: Naftusya, Borjomi, Narzan, Essentuki 17, 4, Smirnovskaya, Slavyanovskaya, Arzni, Izhevskaya, Jermuk, etc.
To relieve pain in the right hypochondrium, antispasmodics are prescribed: Besalol, No-Shpa, Spasmolitin, Duspatalin, etc.
GGTP: general information
In the cells of the liver, as well as the biliary tract, there is an enzyme that is a kind of catalyst for certain biochemical reactions. It is called GGTP (gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase) and is found only in cells, when destroyed it enters the bloodstream. Since the renewal of some cells is a completely normal process, the presence of a small amount of GGTP in the blood is acceptable. However, if a significant number of cells are destroyed, large amounts of this enzyme can be released, which is an alarm signal. This situation indicates the presence of acute diseases of the liver or biliary tract.
GGTP: 9 reasons for the increase, norm, preparation for analysis, interpretation of results
GGTP stands for gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Sometimes this indicator is called GGT, which stands for gamma-glutamyl transferase. Both of these names refer to the same enzyme.
Where is it formed
This enzyme can be found in the nephron tubules of the kidneys, in the epithelium lining the bile ducts. Most of it is found in liver cells. Therefore, when these tissues are damaged, the enzyme enters the blood, which allows the doctor to diagnose a malfunction of these organs.
Main functions
Glutamyltransferase is an enzyme. And the main role of an enzyme is to catalyze any reaction. GGT catalyzes reactions that transfer glutamyl to amino acids or other compounds. This transfer is very important in the metabolism of amino acids: the enzyme promotes their transport, for example, through the intestinal wall from its lumen into the blood.
The determination of this type of transferase can be prescribed separately or in combination with other liver enzymes, for example, aspartate aminotransferase or alanine aminotransferase, to diagnose the condition of the hepatobiliary tract.
This enzyme has great diagnostic value in diagnosing diseases of the liver and biliary tract in such categories of people as children and pregnant women, since other liver enzymes increase at a physiological level.
Glutamyl transpeptidase activity also increases when the liver is exposed to toxic substances, such as certain medications or alcohol. This way you can understand whether the liver damage was caused by alcohol or not.
Glutamyltransferase is not found in bones. Accordingly, the level of GGT will not be affected by bone tissue pathology. This allows us to search for reasons for the increase in another enzyme - alkaline phosphatase.
Alkaline phosphatase is a diagnostic indicator of bone tissue pathology or damage to the hepato-biliary system.
GGT also makes it possible to assess the state of the kidneys, and if their functioning is disrupted, this enzyme will indicate this to the doctor.
Thus, gamma-glutamyltransferase makes it possible to carry out differential diagnosis of conditions that cause disruption of the liver, pathology of the kidneys and biliary tract.
How to prepare?
The determination of gamma-glutamyltransferase refers to a number of biochemical blood tests. In order to obtain accurate information about GGT in the body, the patient must properly prepare for blood donation.
The preparation rules are very simple:
- For biochemical studies, blood should be donated on an empty stomach, that is, after an overnight fast for 10–12 hours. This way you can be sure that the blood will be suitable for research and will reflect the exact content of the test indicator in the blood;
- It is recommended not to smoke for several hours before blood collection;
- emotional experiences a day before the analysis can affect the accuracy of the research results;
- training and other physical overload of the body should be cancelled. They can also affect the final result;
- If the patient is prescribed medications, then you should consult a doctor - can they affect the level of the enzyme in the blood? The patient should not cancel or prescribe anything on his own!
Blood sampling to determine the level of glutamyl transferase takes place in a special room at a medical institution. Most often this is a local clinic. This simple analysis can also be carried out in private medical organizations.
Price
When visiting a clinic at your place of residence, the determination of gamma-glutamyl transferase is carried out free of charge for patients with a compulsory medical insurance policy. If the patient expressed a desire to donate blood to determine the level of this enzyme in a private medical center, then the price for this analysis will be about 150 - 300 rubles.
Please remember that there is an additional charge for the blood collection procedure itself. On average, this will be about 150 – 300 rubles, depending on the region.
Norm for men and women
The normal range of gamma-glutamyltransferase levels differs between men and women. The norm for women is no more than 30 units per liter (U/L), and for men – no more than 50.
The reference values are provided for informational purposes only. You should not try to decipher the analysis results yourself. Let a specialist handle this.
Also, only approximate norms of GGTP were given above. In each laboratory, standards may differ depending on which test systems are used to determine the activity of this enzyme in blood serum.
Taking this into account, it is better to study GGT levels over time in the same clinical diagnostic laboratory.
Norms for children
Normal GGT levels are higher in children than in adults and vary depending on the age of the child.
In the first week of a child's life, the GGTP level should not exceed 180 units per liter. Then the enzyme level can increase, but not more than 200 units during the first half of the year.
By the first year of a child’s life, the level of gamma-glutamyl transferase decreases to a level of no more than 35 units per liter. During the growth and life of a child, the level of glutamyl transferase does not change much. Around the age of twelve, normal levels of the enzyme become the same as for an adult.
Deviation from the norm
A change in the activity of the enzyme glutamyltransferase above the reference values indicates pathology. In addition to diseases, taking medications can cause the indicator to deviate from the norm, but more on that later.
The higher the enzyme activity in the blood, the more severe the patient’s condition.
There are a number of pathologies of the liver and biliary tract that are accompanied by increased activity of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. These include:
- disruption of the outflow of bile through the ducts due to blockage of the lumen by a stone or tumor, which causes the development of mechanical (obstructive or subhepatic) jaundice in the patient;
- liver damage caused by alcohol, such as hepatitis;
- replacement of liver tissue with connective tissue, which is called cirrhosis;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- autoimmune damage to the liver and bile ducts;
- diabetes;
- liver damage due to infectious mononucleosis;
- liver cancer;
- kidney pathology, for example, chronic renal failure.
Correction approaches
Only a doctor can adjust the level of gamma-glutamyltransferase. After analyzing the data from other test results, he will be able to find out the cause and carry out competent treatment of the primary disease. After treatment, the enzyme level will return to normal.
For example, if increased GGT activity is caused by high alcohol consumption, then when you stop drinking it, the enzyme level will return to normal.
What can lead to improved results, besides diseases?
Elevated gamma-glutamyltransferase levels can be caused by alcohol abuse on the eve of a blood test. It was also previously mentioned that some drugs can affect the results of the study, inflating the actual values.
Such medicines include:
- barbiturates;
- statins are a group of drugs used to lower blood cholesterol levels;
- antidepressants;
- some types of antibiotics;
- oral contraceptives and some other hormonal drugs;
- Aspirin, Paracetamol.
Also noted is the fact that in obese individuals the level of the enzyme will be higher than normal. The doctor should take this into account when interpreting the study results.
Conclusion
Gamma-glutamyltransferase is an important diagnostic indicator. This enzyme makes it possible to diagnose liver damage, bile ducts and kidney function. GGT is a sensitive indicator, so it is important to properly prepare for the study.
Article rating
We have put a lot of effort into making sure you can read this article and would welcome your feedback in the form of a rating. The author will be pleased to see that you were interested in this material. Thank you!
(16 4,75 of 5) Loading...
If you liked the article, share it with your friends!
You might be interested
Source: //UstamiVrachey.ru/analizy/ggtp
Increased GGTP and alkaline phosphatase
The highest concentration of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) in the blood is observed in liver pathologies, when acute massive necrosis of hepatocytes (liver cells) develops. In this case, the analysis results may exceed the normal value by 50-100 times.
Thus, acute viral hepatitis is accompanied by the destruction of liver cells, which leads to an increase in the concentration of alanine aminotransferase in the first few days after the onset of the first symptoms of the disease and the development of jaundice (see the article “Causes of increased levels of bilirubin in the blood. Jaundice”).
As the patient recovers, alanine aminotransferase levels gradually return to normal levels (within 6-8 weeks).
A similar process accompanies the destruction of liver cells under the influence of hepatotoxic substances (for example, in the case of an overdose of paracetamol, the concentration of alanine aminotransferase in the blood can exceed the normal value by 100 times) and in acute circulatory failure (cardiogenic shock).
The development of chronic liver pathology (chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis, primary or secondary cancer) is characterized by a persistent moderate increase in the level of alanine aminotransferase (10 times). Diseases associated with obstruction of the biliary tract (gallstones) are accompanied by a normal or slightly increased ALT level.
Isolated moderate increases in alanine aminotransferase levels (approximately 5 times higher than normal) are found quite often.
However, the results of other liver test parameters remain within normal limits.
The most common causes of such an increase in ALT are - alcoholic fatty liver disease (most often), drug-induced liver damage , or chronic hepatitis C.
With non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis, an abnormal amount of fat accumulates in the liver due to general obesity and the associated metabolic syndrome (see the article “Steatohepatosis. How to deal with it”).
Some patients are diagnosed with both fatty hepatosis and type 2 diabetes mellitus (see article “Metabolic syndrome in obesity”).
In recent decades, there has been an increase in the number of people with overweight and obesity, which causes a significant increase in the incidence of diabetes mellitus and obesity-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (in some patients, this pathology progresses to cirrhosis, liver failure or cancer). In the early stages, non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis is asymptomatic and is diagnosed during liver function tests or liver biopsy (in most cases, this pathology remains undiagnosed).
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is by far the most common cause of increased concentrations of liver enzymes (ALT, GGTP and alkaline phosphatase). Statistics show that non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis is diagnosed in approximately 30% of the population living in economically developed countries.
Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase (Gamma-glutamyltransferase)
The level of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGTP) in the blood increases (as a rule, the level exceeds the norm by about 5 times) in all types of diseases of the hepatobiliary system (hepatitis (acute and chronic), obstructive jaundice, cirrhosis, etc.). Analysis of GGTP content makes it possible to identify patients with pathology of the hepatobiliary tract, however, this study is not informative enough to determine the true cause of the disease.
Determination of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity can be used in the management of patients with liver pathology caused by alcoholism , since, unlike other liver enzymes (ALT and ALP), the production of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase is triggered by alcohol - if the patient drinks alcohol, the concentration of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood increases , even if there is no liver damage. As alcohol consumption ceases, GGTP concentrations return to normal. That is, if a person suffering from alcoholism has a persistently high GGTP value, there is a high probability that he continues to drink alcohol or has liver damage (alcoholic hepatitis or cirrhosis). Note that the result of the GGTP analysis cannot be used as absolute proof, since in approximately 30% of alcohol abusers, the activity of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase remains within the reference values.
Alcohol abuse is not the only reason for increased gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activity. This indicator may increase with non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis , which, by definition, develops in people who do not abuse alcohol.
Some drugs can also induce an increase in the level of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood (for example, paracetamol, phenobarbital, phenytoin, tricyclic antidepressants, etc.).
If the patient takes such drugs, he may experience a slight increase in the level of tricyclic antidepressants in the blood (in this case there is no reason to assume the presence of any pathology of the hepatobiliary system).
Please note that an increase in the concentration of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in the blood is observed in pathology of the pancreas (pancreatitis). In some cases, an increase in GGTP activity is observed in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Alkaline phosphatase
The concentration of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in the blood increases both in pathologies of the hepatobiliary system and in pathologies of bone tissue (alkaline phosphatase is found in large quantities, in addition to liver cells, in osteoblasts - young bone tissue cells).
The highest concentration of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is observed with pathology of the biliary tract , as a result of which the process of outflow of bile into the lumen of the duodenum is disrupted (cholelithiasis, cancer of the head of the pancreas). Alkaline phosphatase activity increases in cirrhosis and liver cancer (primary and secondary). In acute hepatitis, the level of alkaline phosphatase increases slightly (may remain within normal limits).
Osteoblasts , which also contain large amounts of alkaline phosphatase, are responsible for the formation and constant renewal of inert tissue.
Elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase in the blood can be caused by any condition associated with high osteoblast activity, such as bone growth and formation (this causes high alkaline phosphatase levels in children).
However, abnormally high osteoblast activity can be caused by certain bone diseases (for example, Paget's disease , which is characterized by bone deformation (diagnosed mainly among middle-aged people), or osteomalacia due to rickets in children as a result of vitamin D deficiency). Note that in Paget's disease the concentration of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is very high. The formation of new bone tissue during healing of bone fractures is also accompanied by an increase in alkaline phosphatase levels.
Bone cancer (primary and secondary) is accompanied by an increase in alkaline phosphatase levels. Note that primary tumors quite often metastasize to bone tissue. An increase in the concentration of alkaline phosphatase in cancer means the spread of the malignant process beyond the primary focus, which is a negative prognostic sign.
Treatment, symptoms, drugs
- GGTP - gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase
Designation of GGTP in assays: GGT GGTP Gamma GT
GTP
Ggtp - what is it in simple terms
GGTP (or GGT) is a protein enzyme, a specific catalyst for intracellular biochemical reactions, and a participant in amino acid metabolism.
GGTP is found inside the cells of parenchymal organs: liver, kidneys, spleen, pancreas, prostate glands, etc.
GGTP enters the bloodstream mainly when the tissues of the biliary tract (gallbladder and bile duct system), liver and pancreas are damaged.
Unlike “liver” transaminases (ALT), GGTP “works” on the surface of cell membranes.
Therefore, inflammatory or mechanical damage to the epithelial cells of the intrahepatic and external bile ducts leads to a massive “washing out” of GGTP from the tissues into the blood and, accordingly, to a significant increase in its level.
Therefore, a high concentration of GGTP in the blood is mainly associated with impaired bile flow and pathology of the biliary system, and an increase in ALT is associated with the destruction of soft tissue cells of the liver - hepatocytes.
GGTP and alcohol
Alcohol stimulates the synthesis of this enzyme. Therefore, even in the absence of liver and biliary tract diseases, after drinking alcohol, GGTP significantly exceeds the norm. When you give up alcohol, its level returns to normal.
This property allows the use of GGTP analysis for the management of patients with alcoholism. If during the treatment period the concentration of the enzyme in the patient’s blood remains high, then either he continues to drink alcohol, or his liver is already irreversibly damaged (alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis).
GGTP is a highly sensitive diagnostic test for toxic-alcoholic liver damage
What is GGTP analysis - when is it prescribed?
A blood test for GGTP is one of five biochemical functional liver tests - an indicator of the functioning of the biliary system.
GGTP is a marker of cholestasis
- Cholestasis (simpler: bile stagnation) is a violation of the formation, secretion and outflow of bile.
Source: //PryshOff.ru/info/povyshenie-ggtp-i-shhelochnoj-fosfatazy/