What does the abbreviation TVP, known to many pregnant women, mean? This abbreviation stands for “thickness of the collar space.” It will be useful for expectant mothers to know what these mysterious words mean, as well as why TVP is assessed using ultrasound. In addition, knowledge of the standards for this parameter will also not harm any responsible parent.
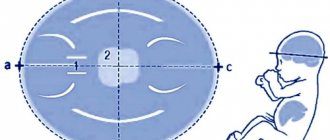
So, each fetus has a gap-like area between the skin and muscles and ligaments that covers the spine of the human fetus. This slit-like area is located at the back of the embryo's neck. The nuchal translucency is checked in the first trimester of pregnancy during an ultrasound.
It is this echographic marker of the fetus that has become the “gold standard” for a period of 11-14 weeks. Using this marker, the individual risk of having a fetus with chromosomal diseases is calculated.
After the 14th week of pregnancy, this space begins to decrease and soon disappears completely. In very rare cases, the fluid is not absorbed by the fetal lymphatic system, but turns into swelling of the neck or hygroma.
An ultrasound of the TVP area is performed so that doctors managing the pregnancy can accurately assess the risks of anomalies in the unborn baby.
How is a TVP examination performed?
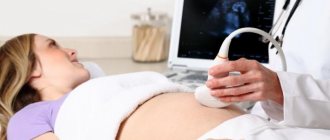
The TVP area is measured during a routine ultrasound, when the woman lies on a couch and the doctor places a sensor on her abdomen and displays images of the fetus on the screen. In some cases, if at 11,12,13,14 weeks the baby is not yet very clearly visible with a transabdominal ultrasound, the doctor takes measurements using a vaginal sensor. This ultrasound examination is carried out, as a rule, using expert-class equipment.
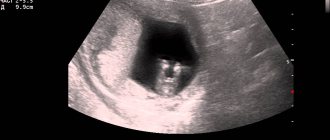
Before measuring TVP, the doctor measures the length of the fetus, that is, its CTE. This is extremely necessary because the thickness of the nuchal region changes depending on the stage of pregnancy. Then the echographer displays the upper part of the body and the head of the fetus on the screen strictly in the lateral projection, while in one section there should be simultaneously the bones and skin of the dorsum of the nose, the cavities of the 4th ventricle and the bone of the upper jaw. Using scaling increases the neck area. Then it measures the greatest thickness of the fluid accumulation along the back of the neck under the skin. The liquid is depicted on the screen in black, and the skin and soft tissue are white. After the measurements are taken, the doctor compares the result with the standard table.
It is worth noting that during the measurement the baby's head must be in a neutral position. If it is thrown back too much, then you can get overestimated measurements, or vice versa, if the chin is tucked too much towards the chest, then the measurements will be lower than the actual value. In order for the measurement to be taken correctly, it may be necessary to wait until the fetus is positioned correctly with spontaneous movement, or to encourage its movement by applying gentle pressure to the mother's abdomen or asking the patient to cough.
The nuchal space, the thickness of which is an important parameter, is highlighted in blue in the ultrasound photograph.
What is TVP?
TVP stands for “thickness of the collar space.” The collar space, or cervical fold, is an accumulation of fluid under the skin of the fetus in the occipital (back) part of the neck. The collar space at 11 weeks is not the most important, but not the least important indicator of the normal development of the child. After 13-14 weeks, the subcutaneous fluid is gradually absorbed by the child’s lymphatic system, and the measurement of this parameter ceases to be significant, such as the measurement of TVP at 11 weeks.
Monitoring of TVP at 11-12 weeks occurs through ultrasound examination - in other words, using a conventional ultrasound (sometimes, however, a vaginal ultrasound is required). The specialist measures the length of the fetal body and the thickness of the collar space, and based on the data obtained makes preliminary conclusions about the progress of the child’s development. The results of conventional and vaginal ultrasound may give different indicators of TVP. This is due to the fact that different devices “see” the child differently.
What is the significance of measuring the nuchal region at 11 weeks, and is it possible to make a final diagnosis based on it? Strictly speaking, deviations from the norm (see below) in the thickness of the nuchal translucency at 11 weeks do not indicate the presence of developmental pathology. TVP measurements are carried out to determine the risk group who will need additional research for the presence of Down syndrome in the baby. In itself, the thickened collar space does not mean anything.
According to statistics, only 7% of children whose nuchal translucency thickness differed from normal at 11 weeks were born with Down syndrome. Do not panic if additional examination is required - this is not a death sentence for the child!
Why may the fetus have deviations in TVP from the norm?
Reasons that lead to an increase in the amount of fluid in the cervical region and an expansion of the collar space in the fetus. This can lead to:
- anemia,
- cardiac dysfunction,
- pathologies of connective tissue development,
- accumulation of blood and stagnation of blood in the upper parts of the body,
- disturbances in the outflow of lymphatic fluid,
- morphological (concerning structure) anomalies of the lymphatic system,
- hypoproteinemia,
- infections
- skeletal structure disorders.
These pathological mechanisms occur in various genetic anomalies, but most of all, the expansion of TVP is associated with Down syndrome (trisomy 21 chromosome), Edwards syndrome (trisomy 18 chromosome), Patau syndrome (trisomy 13 chromosome), Turner syndrome (absence of one of the X chromosomes) . Trisomy is the presence of an extra chromosome in a person’s karyotype, which leads to various developmental abnormalities.
In addition, expansion of the TVL occurs in more than 50 different fetal malformations and in intrauterine fetal death. However, a large number of cases with increased thickness of the collar zone result in the birth of healthy babies.
If during the study an increase in TVP is detected, then the woman is prescribed an additional ultrasound after 1-2 weeks, and is also recommended to take a blood test to determine the risks of chromosomal abnormalities. To do this, an analysis is carried out of two substances produced by the placenta (PAPP-A and free beta-hCG), which in fetuses affected by chromosomal abnormalities have indicators that differ from those found in fetuses with a normal chromosomal complement.
It is this kind of comprehensive examination that makes it possible to most accurately determine the individual risk of chromosomal pathology in the fetus. At the same time, the age of the pregnant woman must also be taken into account.
The main reasons for deviations from the norm
Various factors can lead to an increase in TVP in the fetus. They can be divided into those associated with the mother and those directly associated with the growth and intrauterine development of the fetus. The first include:
- Decreased blood protein levels (hypoproteinemia).
- Anemia.
- Infections (herpes, toxoplasmosis, sexually transmitted diseases).
The second group of reasons causing the expansion of the fetal TVS include:
- Chromosomal abnormalities.
- Anomalies in the structure of the heart, most often incompatible with life.
- Anomalies in the structure and development of connective and bone tissue.
- Improper functioning of the lymphatic system, leading to stagnation of lymph and the formation of edema.
Watch a video review from a gynecologist on deviations in indicators:
Normal values for the thickness of the collar space
The norm of TVP developed for each stage of pregnancy is presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
| Gestational age | Normal value of TVP, mm |
| 10 weeks 0 days – 10 weeks 6 days | 0,8 – 2,2 |
| 11 weeks 0 days – 11 weeks 6 days | 0,8 – 2,4 |
| 12 weeks 0 days – 12 weeks 6 days | 0,7 – 2,5 |
| 13 weeks 0 days – 13 weeks 6 days | 0,7 – 2,7 |
If during an ultrasound your unborn child’s TVP is revealed to be higher than normal, you should not immediately panic, since we have already described above that there may be many reasons for this, including his completely healthy condition.
But still, fetuses with TVP of more than 3.0 mm at 11-14 weeks have a high risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
TVP is also measured to predict possible risks of pregnancy. In fetuses with a normal karyotype and an increase in TVP, the risk of preterm birth, heart defects and other fetal abnormalities increases.
Increased fetal TVP. My story has a good ending.
UPD: Added information about the child's development.
Having encountered this phenomenon at one time, I, like many, began to look for information on the Internet. And there was a lot of it there, but, let’s say, it wasn’t quite what I wanted. I wanted to read real stories of people who dealt with this problem. Stories with a good ending. I hope my post will at least provide some encouragement to those in a similar situation.
My second pregnancy came 2 years after the previous one, and compared to the last one, this one was just some kind of holiday :) . There was toxicosis, yes, but not for long and quite tolerable. Otherwise, everything is fine. No tones, threats, bad tests, blood flow disorders, etc. In general, an ideal pregnancy with one exception: increased fetal TVL on a screening ultrasound.
Due to the long queue for ultrasound at the LCD, I had screening at almost 13 weeks. It was there that they measured me a 5.2 mm TVP. And no more abnormalities were found in either me or the child. I heard something about this TVP since last time, but just in passing. It seems like it’s bad when it’s not normal, but what’s bad, I don’t know. The ultrasound doctor told me that this could be a sign of both chromosomal abnormalities and other problems, in particular with internal organs, and that a fetal karyotype study should be done. And then her nurse signed me up for a consultation with geneticists at the 17th Maternity Hospital in Moscow the next day.
I went with my husband as a support group. There is a repeat ultrasound, it shows a total TVP of 5.9... Then a conversation with a geneticist, during which we were told that this is just one of the indicators. Yes, it’s serious, but it’s impossible to draw clear conclusions based on it alone; research is needed. And I was offered to undergo a chorionic villus biopsy, which I, of course, agreed to. Since it is done up to 14 weeks, and I was running out of time, I was booked in as soon as possible. I had to run around a lot to get tested. The procedure itself went well, even though the puncture had to be done twice. There were no negative consequences. I was warned that the result would be in 2 weeks, and they would call me when it was ready.
After a while they called and told me to come for the results (they don’t talk on the phone). When we arrived at the appointed time, a paper was waiting for us, which indicated the karyotype of our child - 46xx, the norm. And again a girl :)). The further plan of action, voiced by the geneticist, was as follows: at week 18 we do an expert ultrasound to see if there are any developmental defects. If yes, then welcome to contact them again for further consultation. If not, then we leave the child alone and happily continue the pregnancy.
I was advised to an intelligent ultrasound doctor, and, unable to stand the wait, I made an appointment with her first at the 16th week, then there was an ultrasound at the LCD, then I went to see my doctor again. Not a single ultrasound showed even the slightest deviation. Nothing. In general, no one understood what it was.
I gave birth to a good girl at 40 weeks, 8/9 Apgar. The birth itself went well, and most importantly, quickly :). We were discharged on the 3rd day, completed the required doctors for a month, no complaints against us. The only thing there is stridor, noisy breathing. But this often occurs even without any TVP. I took my daughter to the head of the ENT department at the Morozov hospital, he did an endoscopy for us and said that this was due to the characteristics of the larynx, but did not require any intervention, just need to take care of all kinds of acute respiratory viral infections, since the likelihood of stenosis with laryngitis is higher. With age, when the child grows up, everything should go away.
The only thing I could not find information about at all is how such children develop at an older age; I am mainly interested in mental development. As my daughter grows up, I will update the post, maybe someone will also be interested.
Health to you and your children!
As promised, I am sharing information about my daughter’s development. Now she is 7 months old. At 4 months she learned to roll over, at 5 months she learned to stand on all fours. Now she crawls on her bellies, stands on her knees near a support, knows how to sit, but she still can’t sit down on her own, although she’s almost done it. Yesterday I clearly said “mom” :)))
In general, in motor development, Zhenya is very ahead of her older sister, but lags behind in conversations: Nikusya at 7 months, in addition to mom, also knew how to call dad and grandma :) .
That's all for now :)
Health to everyone and less worries!
PS found a small foreign study of children with a normal karyotype, but a history of increased TVP, can be viewed at the link (in English): https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/store/10.1046/j.1469-0705.1998.11060407.x/asset /1122_ftp.pdf?v=1&t=jccdpupe&s=97295669158510c539100bd30e54ec1bfd8b2d6a
And now Zhenya is already one and a half years old. Of course, there were very emotional moments associated with being underweight, but now I’ve given up on that. Although we were even sent to a geneticist about this. And we got stuck (taking into account the medical history), and wasted the person’s time, IMHO. Because, according to the doctor, “we are absolutely not her type.”
In general, today Zhenya is 80 cm and 9500. She went to 1.3. There are no questions about physical development. All vaccinations were age-appropriate, I didn’t bother with imported vaccines, I did what was available at the clinic. The reaction was 1 time to the very first DPT with an increase in temperature.
From 1.3 she began to eat on her own, carefully, without having to feed her extra food. He tries to get dressed, but it doesn't work out very well. At the same time, he indignantly rejects help