Diseases that can be detected using ultrasound
Having figured out how an ultrasound of the scrotum is done, you should find out what this diagnostic method shows.
First you need to understand the capabilities of each examination method. Conventional ultrasound of the scrotum is an ultrasound diagnostic method; the diagnosis is made based on the degree of absorption of ultrasound waves by the tissues of the organs. The device's sensor transmits ultrasonic waves, which are absorbed by some tissues of the scrotal organs and bounced off from others. Thus, the standard ultrasound procedure allows us to determine the following changes in organs:
- decrease or increase in testicular size;
- the presence of cysts, other benign and malignant tumors;
- inflammatory diseases;
- scars and adhesions;
- abscesses;
- prolapse and abnormal development of the testicle.
Ultrasound with Dopplerography allows you to assess the condition of the veins and vessels of the scrotum in men. Doppler ultrasound is indispensable in identifying such a common pathology as varicocele.
Modern ultrasound examination detects a wide range of diseases
Thus, using Doppler ultrasound of the scrotum, it is possible to identify a number of pathologies of the male genital organs.
- Ultrasound examination or ultrasound of the scrotum allows you to determine changes in the size of the testicles, characteristic of various pathological processes. This phenomenon may indicate testicular hydrocele or hydrocele, inguinal hernia, or congenital anomalies.
- Ultrasound of the scrotum in children is used for the early diagnosis of hydrocele, hypogonadism and testicular growth disorders, and therefore can be prescribed in childhood when alarming symptoms appear that indicate a pathological process or a disorder of organ development.
- Ultrasound of the scrotum with Doppler mapping or CD is used to diagnose varicocele. This pathology is varicose veins of the testicle with changes in blood flow speed, and is the most common cause of male infertility.
- Ultrasound can also reveal hypoplasia or complete absence of testicles.
- In the first months of life, a boy may undergo an ultrasound of the scrotum if there is a suspicion of impaired organ formation. An examination can reveal if one testicle is undescended. Normally, the testicles descend into the scrotum during the prenatal period. This pathology does not always require urgent surgical intervention; the likely risks can be assessed using Doppler ultrasound.
- The examination allows you to visualize the spermatic cord. It can be used to diagnose testicular torsion around the spermatic cord, inflammatory diseases of the testes and their appendages.
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotal organs allows us to determine the presence of calcifications in the testes, which is often the cause of pain and ejaculation disorders in men.
In addition, ultrasound is one of the most informative methods for diagnosing cancer and benign tumors. Routine ultrasound can detect cancer at a pre-symptomatic stage.
Indications for the study
Examination of male organs is done if there are indications for this:
- Inflammation of the testicular appendages.
- Inflammation of the testicle.
- Inflammation of the testicles and appendages.
- Tumor of the scrotum.
- Dilation of the veins of the inguinal canal.
- Dropsy.
- Injuries to the genitals, testicles.
- Infertility.
- The cyst is not inflammatory in nature.
- Accumulation of pus in the scrotum.
Very often, a man may additionally be prescribed a Doppler examination of the scrotum.
In what cases is testicular ultrasound prescribed?
This procedure is prescribed to men for the prevention of diseases, to monitor treatment or recovery in the postoperative period. In addition, ultrasound of the testicles is prescribed in the presence of certain symptoms. These include:
- swelling and pain in the scrotum area,
- changes in the size or shape of the testicles,
- the presence of lumps or tumors,
- erection problems,
- irregularities in spermogram readings,
- infertility.
Another reason for a testicular ultrasound is trauma. Strong blows to the groin area can lead to hematomas, hemorrhages and necrosis of testicular tissue. To assess damage to the genital organs, it is necessary to undergo ultrasound diagnostics. Ultrasound is also used during testicular biopsy to carry out the procedure accurately and safely for men’s health.
The most powerful means for penis enlargement
The guy went a little overboard with the product...
Gain weight
Find out details
dominator.ru
Ultrasound of the testicles may be prescribed to children and adolescents due to dwarfism or gigantism, obesity or excessive thinness, in which the child cannot gain the desired weight. In this case, the entire endocrine system is studied, including the gonads. Disturbances in the production of hormones can lead to early puberty or its delay, which is also a reason to visit the ultrasound room.
The procedure for performing an ultrasound of the pelvic organs
Transabdominal examination. The examination is carried out through the abdominal wall, and the bladder must be completely filled with fluid.
Transabdominal ultrasound determines the size, shape, structure and position of the bladder. All additional formations present in the walls or cavity of the bladder are recorded. A similar study is carried out on the size, shape, structure, contents of the prostate gland and seminal vesicles, as well as surrounding tissues adjacent to them.
The second stage involves emptying the bladder with repeated examination. This allows you to estimate the residual urine volume in the bladder.
TRUSY . With TRUS, the sensor is inserted into the previously prepared and cleaned rectum. The prostate gland is tightly adjacent to the anterior wall of the rectum, which allows the miniature sensor to accurately visualize its size, shape, and especially its structure with formations.
In addition to TRUS, color Doppler mapping is possible. This method allows you to assess blood flow in the pelvic organs and identify vascular pathology, which is important for establishing the correct diagnosis.
Possible results
Normally, the size, location and all anatomical features of the testicles fully correspond to the parameters appropriate for a particular age
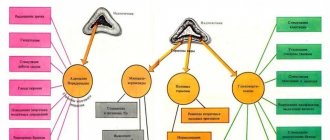
During an ultrasound, the doctor pays attention to the following characteristics of the gonads:
- Dimensions. In adult men, the testicles are usually 40–50 mm long and 20–30 mm wide. There is some liquid around them.
- Form. The gonads should have an oval shape, a uniform structure and clear, clearly visible contours. They may be uneven if the testicle is damaged, in which case fluid accumulates at the site of injury.
- Echogenicity. Normally, the testicles have average echogenicity (tissue density). In boys who have not reached puberty, the density should be low. A heterogeneous echostructure may indicate the presence of injury.
- Presence of neoplasms. They can be present both in the testicle itself and outside its cavity. Neoplasms have a reduced echogenic structure and can be of different sizes and shapes.
Anatomy of the testicles
The testicle is a paired organ of the male reproductive system, which is located in the scrotum, where it descends from the retroperitoneum during prenatal development. This is an oval-shaped glandular organ in which sperm matures. To make this process as effective as possible, the temperature in the testicles is 2-4 degrees lower than in the rest of the body. In the scrotum, the testicles are attached to the spermatic cords, which fix their position.
Their anatomical structure is complex. On the outside they are covered with serous, tunica albuginea and tunica vaginalis. Through their thickness pass the vessels that supply the organ with blood. The glandular tissue itself is divided into segments by connecting septa. In their thickness are the seminiferous tubules, which are the main component of the testicles. Their walls contain special cells from which sperm are produced.
Near the organ there is also an appendage in which all the main tubules converge. It is here that the vas deferens is formed, through which sperm are sent to the prostate gland, where the remaining components of sperm are produced.
How to prepare for an ultrasound of the scrotum
The advantage of the ultrasound method over other types of examination, including TRUS, is that there are few preparation requirements. There is no need for special nutrition or any restrictions, so you can do an ultrasound of the scrotum directly on the day of visiting the doctor.
There are several recommendations regarding preparation for an ultrasound:
- Be sure to wash yourself with soap before visiting a doctor;
- wear clean underwear;
- Warn the ultrasound specialist if you are taking any medications.
Some boys are afraid to go for an ultrasound for fear that it will hurt
In this case, psychological preparation is important; the doctor must explain to the child that the procedure is painless, if necessary, show the office and scanner, tell how the examination will be carried out
If it is necessary to do Dopplerography of the blood vessels of the scrotal organs, there are increased requirements for preparation. They are due to the fact that a number of foods and medications can affect blood flow and distort the results of the examination. For the man being examined, the doctor will recommend:
- stop drinking alcohol, coffee and tea within three days;
- stop taking medications that affect blood pressure one day before;
- 3 hours before the appointed time, do not drink;
- visit the toilet 30 minutes before;
- wash with soap.
If these recommendations are not followed, there is a risk of obtaining an erroneous result. In this case, the examination will have to be repeated, and this is undesirable: the sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of recovery.
How to interpret ultrasound results?
Usually, a doctor can report the presence of pathologies in this part of the body during an ultrasound scan, but only the attending urologist can give a more detailed interpretation of the results. What should a healthy scrotum look like on screen? It represents echogenic tissue, which has several layers of different density and thickness. During scanning, both its anterior and posterior surfaces are examined. What matters to the doctor is the size and shape of the testicles, as well as how uniform their structure is. It is worth noting that in children the tissue density here is much lower; it will return to normal only in adolescence. Each testicle has its own appendage, which can be divided into a body, a head and a tail. The spermatic cord normally includes: arteries and veins, the vas deferens, lymphatic vessels and nerve endings.
What diseases can this ultrasound detect?
Already during the procedure, an experienced diagnostician can make a preliminary diagnosis, which will be clarified by the urologist after additional studies. Children are often diagnosed with the following pathologies:
- Congenital dropsy of one or two testicles. Also, hydrocele, as this disease is also called, can be acquired during inflammatory processes.
- In young children, a disease such as hypogonadism can be detected; it is characterized by a small amount of androgens and a lack of gametogenesis. In a healthy person, the body produces the necessary norm of these components on its own.
- Often, in newborn boys, one testicle may not descend into the scrotum; this is not a pathology, but a developmental feature that does not require drug treatment until a certain age.
- Calcifications may be detected.
- During the examination, various tumors and foci of inflammation are identified.
- Rarely, testicular cysts can also be diagnosed in children.
Hydrocele
Ultrasound results of the scrotum may indicate the presence of various diseases in adults:
- epididymitis;
- hydrocele, as well as lymphocele and hematocele;
- epididymal abscess;
- closed and open injuries;
- adnexal cysts;
- testicular tumor;
- infertility.
How harmful is it to do an ultrasound of the scrotum?
Despite the fact that many confidently declare the dangers of ultrasonic waves, not a single clinical study has confirmed that ultrasound has a negative effect on the male body. Compared to a similar method of examining the organs of the scrotum - x-ray, ultrasound is definitely a more gentle diagnostic method, since it does not produce harmful radiation on the tissues and organs of the body. That is why we can conclude that ultrasound scanning of the scrotum can be considered one of the most informative, accurate and fast methods for diagnosing diseases of the male reproductive system. With its help, you can not only identify a variety of pathologies, diseases and injuries, but also find out the causes of pain in this part of the body and problems with potency. Also, this study is mandatory for all males who have problems conceiving.
Decoding the results
The diagnosis is made by the attending physician based on the results of an ultrasound scan of the male scrotum. The doctor at the diagnostic office usually does not even make preliminary diagnoses. While waiting to see the treating urologist, a man can independently assume possible violations, based on the nature of deviations of the results from the norm.
Normal indicators
Ultrasound of the scrotum allows you to visualize the testicles, epididymis, spermatic cords, and also assess the condition of the blood vessels. The normal values are as follows:
- The size of testicles in men is on average 4-6 cm in length and 2-4 cm in width. Minor deviations from the norm are not pathology. In addition, for most men, one testicle is slightly larger in size than the other - this is also completely normal.
- Normally, the testes have a homogeneous echostructure, that is, the waves are absorbed equally throughout the entire volume of the organ. A healthy man does not have any neoplasms, scar tissue changes or adhesions.
- The walls of the scrotum are normally less than 7 mm thick. Skin thickening, changes in its structure, inflammatory fluid between the walls of the testicle are signs of pathology.
- Normally, the epididymis is not enlarged and is not completely visualized.
- If a Doppler examination is carried out, the blood flow and blood vessels are assessed in conclusion. In a healthy man they are not dilated, blood flow is normal.
Based on the nature of changes in the organ, one can assume diseases that caused the changes detected on ultrasound.
Pathology
There are no age restrictions; ultrasound can be performed at any age
The main pathological signs are a large amount of fluid between the membranes of the testes, enlargement or reduction of the testicles, changes in structure and visible foci of heterogeneity.
- If one testicle is not visualized on ultrasound, a congenital anomaly of the genital organs or an undescended testicle is diagnosed if the examination is performed on a newborn.
- Cryptorchidism is a pathology in which the testicle is present, but located in an atypical location. This disease is congenital; surgery is performed to correct the location of the testes.
- A significant increase or decrease in only one testicle is an alarming symptom. If the length of the testis exceeds 6-7 cm, hydrocele can be diagnosed. Typically, a hydrocele (the second name for dropsy) is indicated by a large amount of fluid between the membranes of the organ. Too small sizes (less than 2-3 cm) indicate testicular atrophy or underdevelopment of the organ.
- Neoplasms with liquid contents localized on the testicle or epididymis are cysts. In general, this pathology is not dangerous, but timely removal surgery is required.
- A testicular abscess is determined by a noticeable enlargement of the organ, signs of a heterogeneous testicular structure and an accumulation of purulent contents. This pathology is accompanied by acute pain and high body temperature.
- Impaired blood flow in the vessels of the spermatic cord, detected by Doppler ultrasound, is a typical sign of testicular torsion.
- Vasodilation, decreased blood flow speed - all these are symptoms of varicocele, determined using Doppler ultrasound.
Only a doctor can decipher the examination results in more detail, make a diagnosis and select a treatment regimen.
Possible results and interpretation
The result of an ultrasound in a healthy man looks like this:
- normal testicle length is from 3 to 5 cm;
- width – from 2 to 3 cm;
- thickness – no more than 2 cm;
- the body and tail of the appendage are not visualized;
- the parenchyma does not contain inclusions and looks homogeneous;
- the diameter of the head of the appendage is 1-1.5 cm;
- the contours of the organs are smooth;
- additional education is not determined;
- there is liquid between the inner and outer shell of the testicle (but not more than 2 ml);
- organs have average echogenicity, but before puberty in a boy it will be slightly lower than in an adult man;
- The normal thickness of the scrotal wall is no more than 8 mm.
Normal testicular volume is 30 ml or more.
If the patient has epididymitis (inflammation of the appendage), then ultrasound shows an increase in the diameter of the head of the appendage and an increase in the volume of fluid between the membranes. The amount of free fluid also increases with hydrocele. Injuries are accompanied by bleeding, ruptures and disruption of tissue integrity, excess fluid often appears, and the shape and contours of the male gonads change.
With varicocele, ultrasound shows enlarged veins, which at the first stage change only in a vertical position. At a later stage, there is a thickening of the lumen of the vessels to 3 mm or more, and the testicle on the affected side decreases in size.
When an appendage becomes infected and an abscess forms, a low-echoic formation is visualized (its density is lower than that of normal tissue), which has unclear outlines. Its structure is heterogeneous.
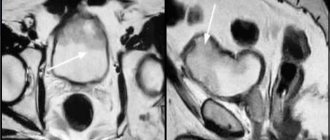
Using ultrasound, you can diagnose a cyst. It looks like a voluminous round formation with clear, even contours and liquid inside the cavity. Congenital cysts are usually small and contain clear fluid.
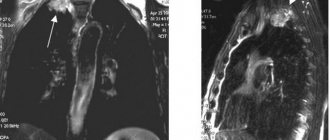
A malignant tumor is confirmed by changes in the shape and size of the testicles, an increase in the volume of fluid and the identification of a formation whose echogenicity is higher or lower than that of the surrounding unchanged tissue. Ultrasound of the scrotum makes it possible to detect leukemia in the early stages, in which the sex glands are involved in the process. Multiple small inclusions with reduced echogenicity (leukemic infiltration) allow one to suspect blood cancer.
If the doctor suspects cancer, an additional biopsy with histological analysis is performed. An additional Doppler study will help to accurately assess blood flow disturbances.
Ultrasound and other methods are only stages in the diagnosis of pathologies. The conclusions made by a specialist after an ultrasound scan are not yet a diagnosis. Only a urologist or andrologist, based on examination, questioning and examinations, can confirm or deny the disease, as well as recommend competent treatment. If suspicious symptoms appear, do not be afraid of an ultrasound. This is an accessible, informative and painless method.
Preparing for the study
Preparing the patient for this diagnostic examination depends on the ultrasound diagnostic method. The doctor should be informed if the patient has had an x-ray with contrast material (eg barium) within the last 2 days. Barium that still remains in the intestines may subsequently interfere with ultrasound examinations.
The patient may need to remove clothing from the waist down and put on a dress before the test.
Preparation for the transabdominal method:
- avoiding foods that contain high amounts of fiber and legumes 2-3 days before the test to minimize gas production;
- it is advisable to refrain from eating for 5-6 hours before the start of the study;
- drink half a liter of still water 2 hours before the start of the study;
- 2 hours before the ultrasound you should refrain from urinating;
- if you have a strong desire, you can urinate a little, but not completely, and after that you need to drink an additional glass of water;
- if the patient is unable to drink the required amount of water, the bladder can be filled with water through a thin flexible tube (catheter) inserted into the bladder;
- When the examination is done, the gel is cleared from the skin. The patient can then urinate once the test is completed.
To prepare for the transrectal method, all the above preparation steps are used, but added to them:
- the use of drugs that cleanse the intestines, for this the patient drinks 3-4 packs on the eve of the test;
- if the study is planned for the second half of the day, then in the morning, immediately on the day of the study, drink two packets;
- a cleansing enema is an alternative method and is performed in the morning, just before the examination; the volume of liquid that is injected into the rectum must be at least 200 ml;
- It is important to inform your doctor if you have a latex allergy so that the sensor cannot be covered with a latex cap before using it;
- If a person is having a prostate biopsy, they may be prescribed antibiotics the day before the test.
How to prepare for the examination and procedure
Ultrasound of the testicles in men is performed after normal hygiene procedures; for convenience, you can shave the pubis. When going for an examination, you should take the results of previous tests with you. Preparing for an ultrasound for a child is similar, but it is better that clothes are comfortable and easy to remove.
Examination of the testicles is carried out in a horizontal position. A special ultrasound gel is first applied to the scrotum area, which is preheated. This is necessary so that the testicles do not retract inward from exposure to cold.
This technique helps make comparisons, since each man has individual characteristics in the structure of his organs. The ultrasound sensor is moved in different planes to obtain the most reliable picture of the disease. The total research time is 10-20 minutes.
An image of the testicles is displayed on the monitor screen; it allows you to measure their size and evaluate their structural features. After the ultrasound, the doctor offers the patient a napkin to remove the gel. In some clinics, a man must take his own diaper and napkin.
Preparation and progress of the examination
Preparatory measures before an ultrasound examination include toileting the genitals and shaving the groin area. The last point is not mandatory; this is done for the convenience of removing the gel from the scrotum after an ultrasound. No other preparation for the study is needed.
Before attending your scheduled procedure, it is better to find out in advance how a testicular ultrasound is usually done. Diagnostics follows a standard procedure. The patient lies on his back on a covered couch. The area being examined is lubricated with a neutral gel, which improves visualization and facilitates the movement of the scanner. The sensor is first installed at right angles to the scrotal organs, then they are examined from different angles. The procedure usually lasts no more than 20 minutes. During the examination, the doctor records the results in the protocol. At the end of all manipulations, the gel is removed from the genitals using a napkin.
Ultrasound diagnostics in children does not have significant differences. One of the parents is usually present during the procedure. If we are talking about young children and infants, then parents help hold the baby so that he moves less during the study.
Interpretation of ultrasound testicles
Cryptorchidism
With this pathology, the purpose of ultrasound diagnostics is to clarify the location of the “disappeared” testicle.
Cryptorchidism is an anomaly of location in which the male reproductive gland is present, but due to some reason it is retained in the abdominal cavity. In 90% of cases, the “lost” testicle is found in the inguinal canal.
As a rule, an atypically located testicle has an unclear contour, is reduced in size, has a heterogeneous structure, and its appendage is not visualized.
Varicocele
On ultrasound with varicocele, dilated, modified veins are clearly visualized, the diameter of which is more than 3 mm. As you know, there are 3 stages of varicose veins.
In the first, visualization of the veins occurs when intra-abdominal pressure increases or during diagnosis in a vertical position; in the second, the modified veins do not disappear even in the horizontal position of the patient; in stage 3, the veins are visible below the pole of the reduced testicle.
Hydrocele
With this pathology, fluid accumulates between the two layers of the testicular membrane. Dropsy can be acquired, which is facilitated by a number of factors, and congenital, which is caused by congenital anatomical defects.
Acquired dropsy, as a rule, appears after inflammatory processes, scrotal injuries, and surgical interventions. During an ultrasound examination, diagnosing the accumulation of fluid between the membranes is not particularly difficult. On a sonogram, hydrocele appears as an anechoic zone around the testicle and its epididymis.
Some patients experience multilocular dropsy or figure eight dropsy (if fluid also accumulates in the inguinal canal).
Seminal cysts (spermatoceles) can be congenital or acquired. A congenital cyst is often small in size, the fluid inside is transparent. Acquired seminal cysts arise due to inflammation or trauma, due to which the duct is blocked with the appearance of a cyst. According to ultrasound of the scrotum, the cyst looks like a round-shaped formation, with an even, clear contour, and an anechoic structure.
Orchitis and epididymitis orchitis
As a rule, inflammation of the epididymis is extremely rare and occurs in isolation. More often, orchitis and orchiepididymitis develop when tissues are damaged by microbial flora against the background of reduced immunity.
On the sonogram, the appendage is enlarged, has reduced echogenicity, and has a heterogeneous structure.
Acute inflammation of testicular tissue (orchitis)
Chronic orchiepididymitis
The size of the testicle is any, it doesn’t really matter. The structure is heterogeneous, the contour is uneven. An enlarged appendage is visualized.
It is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis with tumor processes.
Seminoma
Pathological neoplasms are most often diagnosed in the right testicle. Bilateral tumors (on both sides) are detected in 1-3% of cases.
A tumor on ultrasound looks like an irregularly shaped formation, sometimes consisting of several neoplasms with a heterogeneous structure. The size of the diseased testicle is larger than normal, and reactive dropsy is present.
If there is a suspicion of testicular cancer, then the retroperitoneal space and regional lymph nodes must be examined to exclude or confirm metastatic processes.
A biopsy of the lesion is required.
In what cases is this procedure prescribed?
A urologist and, in rare cases, a surgeon can prescribe this test for a man. If you were sent to an ultrasound room, most likely the doctor suspected diseases of the male genital organs. If necessary, the doctor may additionally prescribe a scan of the blood vessels of this part of the body. If testicular torsion is suspected, Doppler ultrasound is additionally prescribed. So, for what indications is an ultrasound scan of the scrotum prescribed?
- If a man has already been diagnosed with “male infertility”, or has problems conceiving a child, but the diagnosis has not yet been made.
- Research is necessary when the epididymis and testicles are enlarged.
- In situations where a representative of the stronger sex is unable to achieve an erection.
- When the scrotum is swollen and painful.
- If the doctor suspects inflammation of the scrotal organs, which may include orchitis, as well as epididymitis and orchiepididymitis.
- An ultrasound of the scrotum should be done immediately if there has been injury to its organs, a hematoma or bruise.
- In the event that tumors or dubious formations appear on or near the testicles.
- Ultrasound examinations are often prescribed for adolescents who are experiencing early or late puberty.
- If the spermogram readings raise questions.
- Less often, but ultrasound is still prescribed for inflammation of the lymph nodes, which may indicate diseases of the male genital organs.
- The doctor suspects the appearance of varicocele.
- This type of diagnosis is often used to monitor the progress of chronic diseases of the male reproductive system, various tumors and infections.
- If a man is missing one or both testicles.
- There are diseases of the endocrine system.
- If there is concern that the inguinal hernia may have partially entered the scrotum.
- Ultrasound of this part of the body is performed after urological operations.
Varicocele
How to prepare for this scan?
Ultrasound of the scrotal organs does not require special preparatory procedures if we are talking about an adult. If the research is carried out on a child, he must be mentally prepared and explained that it will not be painful or unpleasant. Many children are suspicious of procedures and examinations in this part of the body. Before ultrasound scanning, both adults and children need to undergo a set of normal hygiene procedures.