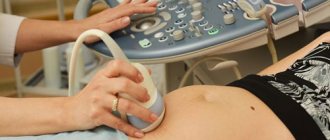
From the moment of conceiving a child, every expectant mother begins to tune in to many tests, analyzes and medical consultations. No matter how frightening all this may be for pregnant women, without such research it is impossible to identify likely serious risks associated with the health of the fetus. Throughout the entire period, it is necessary to adhere to the entire prevention program, which is prescribed by the treating gynecologist. It is important not to neglect the recommended tests. Biochemical screening is considered one of the most mandatory tests. Despite the unattractive name, this analysis is very useful for building a picture of the health of the unborn child.
What it is
Biochemical blood screening is a rather narrow-profile analysis. Applies to primary and secondary test categories. Detects signs of diseases such as hepatitis B and rubella. In the extended version, the analysis allows you to determine the presence of syphilis and HIV infection in the blood. Nevertheless, the main function of screening is considered to be to identify the fetus’s predisposition to pathologies. Also, the results of the analysis clearly demonstrate how certain diseases will develop in the embryo in the future. In this regard, the attending physician builds a step-by-step program for the treatment or prevention of pathologies.
Biochemical screening allows you to determine the Rh factor and blood type. These characteristics will be extremely useful in the future if the mother needs proper treatment. To prescribe serious hormonal drugs, it is important to know the Rh factor of the pregnant woman and her child. Screening at a later date can reveal the likelihood of so-called gestational diabetes.
What is chorionic presentation and why does it occur?
Until the placenta is formed, the embryo is surrounded by a villous membrane, which grows into the lining of the uterus. Until the 16th week of gestation, this is the chorion (from the 17th week - the placenta), which performs the following main functions:
- Nutrition of the embryo;
- Respiration – delivery of oxygen and removal of carbon dioxide;
- Isolation of metabolic products;
- Embryo protection.
During the normal course of pregnancy, the chorion attaches to the fundus of the uterus and grows along the anterior, posterior and lateral walls, but this does not always happen.
Chorion presentation is its incorrect location, in which there is complete or partial overlap of the internal os of the cervical canal.
Why this condition occurs is not completely clear. But a connection has been established with some factors:
- chronic inflammation of the uterus;
- previous operations;
- fibroids;
- abnormal development of the uterus;
- a large number of pregnancies and births;
- low attachment of the placenta in the previous pregnancy.
Who is the procedure indicated for?
Every pregnant woman should undergo biochemical screening. Some experts question the urgent need for the analysis. However, it is unlikely that anyone will guarantee that none of the expectant mothers have serious genetic disorders. The fact is that many women are not even aware of a pathological malfunction in their body, as well as infections. Some mothers have a hereditary predisposition to genetic diseases that can be passed on through generations. In Russia, such a biochemical test is one of the mandatory tests during the second trimester. However, it is performed on a voluntary basis. Doctors recommend the test as an additional insurance to obtain information about the condition of the mother and her child.
Treatment
With placenta previa, only symptomatic treatment is possible; at the moment, doctors cannot change the abnormal position of the fetal membranes.
Low and marginal presentation of the chorion at week 13 does not require any measures; in most cases, the organ will independently take the correct position. If after a few weeks the position of the placenta does not change, but the woman does not have bleeding, she is advised to avoid physical and emotional stress, refuse intimacy, sleep more than 8 hours a day, and get plenty of rest. Also, the expectant mother should follow a diet rich in vitamins and microelements, especially iron. It is recommended to include more fresh vegetables and fruits, lean meat, fish, and cereals in your diet.
In case of central placenta previa, as well as in the presence of bleeding, hospital treatment is recommended for the woman. In addition to bed rest and a balanced diet, the expectant mother is prescribed medications to support pregnancy.
To prevent placental abruption, progestin drugs are used - Duphaston, Utrozhestan. Their therapeutic effect is based on reducing the tone of the uterus. The woman is prescribed iron supplements that reduce the loss of hemoglobin - Ferrum-Lek. If bleeding develops, the expectant mother is given hemostatic agents - sodium etamsylate.
Also, the expectant mother is prescribed multivitamin complexes aimed at improving metabolism. If there are mental disorders, doctors recommend taking sedatives - Valerian, Motherwort. In case of persistent bleeding that is not amenable to drug treatment, the question of emergency delivery is raised.
During fetal development, a woman's body experiences many changes. First of all, the amount of hormones released changes. At the same time, some changes occur in the pregnant woman’s uterus. Most women don't even know about them. During development, the fetus receives all the elements necessary for development through the mother’s blood. This happens due to the activity of temporary internal organs that appear during pregnancy. One of these organs is the chorion, which appears almost immediately after conception. The chorion is a set of outgrowths located around the fetus. These growths constantly increase in size and begin to penetrate the lining of the uterus. And after a while it turns into a child's placenta. It is the chorion that allows blood to circulate through the placenta and can penetrate the walls of the uterus. The chorion is an organ that allows the embryo to develop normally. After all, only with its help can the fetus exist and not die. The chorion is formed approximately seven days after the conception process. The presence of this membrane is detected only through an ultrasound examination, since this is simply impossible to do during a routine examination. Several types of Chorion can be distinguished, changing during different periods of pregnancy. If the period is short (up to forty-five days), then this shell will have a circular shape. In this case, it is still impossible to see the embryo itself, but only its shell. In later stages of pregnancy, it may have a circular or villous form.
Particularly important for the normal development of the fetus is the place of attachment of the chorion to the uterus, or its localization. In medicine, the term chorionic presentation is used. In this case, the chorion is located in the lower part of the uterus, near the transition of the uterus to the cervix. This attachment of the chorion is very dangerous, as it can lead to severe bleeding during childbirth. And during pregnancy it can even lead to miscarriage. Most doctors perform a caesarean section in this situation. Because natural degeneration may be completely impossible. Chorionic presentation is a pathology, but there are no ways to eliminate it yet. But it can disappear on its own. After all, the chorion, like the placenta itself, migrates very often. This is what happens in most pregnant women. However, in some women the chorion remains in one place all the time, which leads to difficulties during childbirth. If it completely covers the cervix, then a caesarean section is mandatory. But if it is located more than five centimeters above the cervical canal, then perhaps the doctor will allow the woman to give birth independently. Bleeding can often occur in this position. But to prevent this from happening, you should completely abandon physical exercise, sudden movements and lifting heavy objects. You should also completely avoid sexual intercourse. Anterior localization of the chorion One of the types of chorion presentation is its localization on the anterior wall of the uterus. In this case, it passes from the anterior wall into the cervix. This localization is not dangerous, because in this case the uterus remains almost completely open. There is no need to worry too much when making this diagnosis. But it is very important that the chorion is localized several centimeters above the internal pharynx. Also, in this position of the chorion, its growth occurs much faster. But even with this arrangement of the chorion, some complications can occur. Indeed, in this case, the placenta grows and develops on the wall of the uterus that is located closer to the mother’s abdomen. Then the fetus can be located behind the placenta, through which the baby’s heartbeat and movements can be heard very faintly. Also, a caesarean section with this diagnosis is much more difficult. Well, besides, after preliminary birth, the placenta can adhere to the muscular layer of the uterus. Posterior localization of the chorion Very often, when undergoing an ultrasound scan, pregnant women learn that their chorion is located on the posterior wall of the uterus. This situation can be called classic. After all, the attachment of the chorion to the posterior wall of the uterus with simultaneous capture of the side walls is natural. This position, unlike the anterior localization of the chorion, is not pathological. Posterior localization of the chorion is normal and is not a deviation from the norm. But it has its effect on a woman’s body. After all, the growth rate of a pregnant woman’s belly depends on this. In the case of a posterior attachment, the abdomen is usually small. Whereas with anterior localization, the abdomen becomes quite enlarged, already in the first stages of pregnancy. In the future, the chorion can move upward. And this is a common occurrence, because this is how it should happen. So, a pregnant woman does not have to worry about anything. You just have to stick to the regime and constantly be under the supervision of a doctor, following all his instructions. And the chorion itself will rise up, and thus the problem of complicating pregnancy will disappear by itself. And the pregnancy itself in this case will end with a successful birth. But there is still a danger that with posterior localization of the chorion, the placenta can completely block the entrance to the uterus. In this case, constant monitoring of the pregnant woman is needed. And it is best for her to be in the hospital, even if she has no complaints and feels quite normal. If the uterus is blocked by the placenta, there is always a risk of bleeding, and this can be very severe and repeated frequently. In addition, it can begin without any preliminary symptoms. During pregnancy, women are subject to many tests. One of them is ultrasound. During such an examination, the doctor must examine both the chorion itself and its location. In this case, the presence of detachments in the membrane and its size are always taken into account, and all possible problems are diagnosed. Therefore, any problems associated with this organ are detected in the very early stages of pregnancy and can be treated immediately. So you should always follow all the doctor’s instructions, and your pregnancy will end successfully.
During pregnancy, many things frighten the expectant mother. The words about the attachment and presentation of the chorion at the first ultrasound sound especially scary. In most cases there is nothing to fear. But some situations require careful follow-up and treatment.
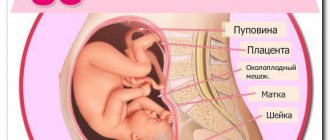
The fertilized egg with the embryo developing in it consists of two membranes. The chorion is the external one, which at 12-14 weeks turns into the placenta.
A feature of the structure of this structure is the abundant amount of villi on the surface. With their help, the fetus is attached to the wall of the uterus. This is an important stage affecting a normal pregnancy.
Possible risks
Any procedure for interfering with the current functioning of the body carries certain dangers. In reality, the risks of medical tests are minimized.
The first screening slightly increases the likelihood of fetal loss. This is the biggest risk associated with this type of analysis. Standard screening will not harm the fetus in any way. However, its perinatal varieties, such as chorionic villus biopsy and amniocentesis, can significantly aggravate the course of pregnancy. In the first case, tissue from the placenta is taken for testing. She will be tested for chromosomes. The risk of fetal loss with this procedure is about 0.9%. As for amniocentesis, during it a thin needle is inserted into the abdomen to obtain amniotic fluid. This procedure can harm the embryo only due to a doctor's error. The risk varies within 0.5%. It would not be amiss to identify categories of women who need primary and repeat screening. These groups may have a high risk of having a child with gene pathology. These categories of factors include: - age above 30 years, if pregnancy is the first; — the presence of serious genetic abnormalities; - with two or more terminations of pregnancy; — chronic infectious diseases; - hereditary pathologies in parents; - marriage with blood relatives; - any radioactive exposure of one of the parents before or after conception.
Pregnant placenta in normal condition: structure and functions
The placenta is also called the baby's place, since it is a temporary organ and appears for the purpose of successfully bearing a child and feeding it with all the necessary substances. Through it, gas exchange is carried out, waste products are removed and the fetus is supplied with oxygen, vitamins and microelements.
The placenta produces estrogen, progesterone, hCG and placental lactogen - hormones without which it is impossible to safely carry a baby. Thickening of the placenta begins already from 8-9 days after ovulation ends, subject to fertilization.
This process ensures normal fixation of the fertilized egg in the uterine cavity. Now it becomes clear what the thickness of the placenta means for a successful pregnancy. By the 14th week, the organ begins to perform its main functions.
The growth of the child's seat area continues until the middle of the 2nd trimester, after which the process stops. The organ matures or ages. Until the 30th week, the degree of maturity in the placenta is absolutely zero. A little later, it acquires a more dense consistency due to deposits of calcium salts.
Until 33-34 weeks, doctors should record the 1st degree, and from 35 weeks - the second. And the last degree - the third - is observed before childbirth and indicates the depletion of the organ, as well as all its resources. This is what the “life” of the placenta looks like during a normal pregnancy process.
Factors influencing the test
Biochemical screening may depend on a number of things. This applies to analysis in both the first and second trimester. Such factors must be taken into account in the final risk assessment. The most common cause of analysis error is maternal overweight. If she is obese, her blood counts will certainly be elevated. If a woman is significantly underweight, then the results will be underestimated.
Multiple pregnancy is also a factor in screening rejection. It is even theoretically impossible to calculate any risk here. The indicators will be elevated, but this is not always considered a genetic disorder. The fact is that in this case the test results are distributed over two or more embryos. Therefore, even repeated indicators will not lead to a clear picture of what is happening. Bad habits can affect the analysis. This is especially true for smoking. Also, a failure can be recorded if a pregnant woman has a cold during the screening. It is worth noting that this type of analysis is prohibited for diabetes mellitus, as it always gives false results.
Preparing for screening
Diagnosis of the body during pregnancy should always be approached seriously and thoroughly. However, preparation for testing is considered an equally important step, especially if this is the first blood screening. This analysis identifies special markers that indicate the presence of chromosomal diseases. That is why it is important to do everything to eliminate even the slightest possibility of a false rejection. Firstly, the day before testing, it is prohibited to consume foods such as smoked meats, citrus fruits, chocolate, fried foods, fatty and spicy foods. Otherwise, instead of blood serum, fatty elements are formed in the body. During the centrifugation procedure, it will be almost impossible to separate important cells. In any case, this will significantly complicate the test, and there will be a need to repeat it, which can negatively affect the fetus.
The analysis should always be done on an empty stomach. You are allowed to drink some still water 4-5 hours before the test.
Screening during the 1st trimester
The most suitable period for conducting a primary biochemical test is considered to be 10-13 weeks. It is not recommended to do screening at earlier stages. The price of such an analysis varies from 1800 to 2000 rubles. Based on the results of the initial test, specialists evaluate the health and development of the fetus, as well as the condition of the mother. Screening during the 1st trimester allows you to identify pathologies such as Down and Edwards syndromes, neural tube defects, heart defects, etc. Before assessing the results, the doctor should always rely on personal examination data, such as blood pressure, temperature, maternal weight, etc. auxiliary factors. In parallel with screening, urine and blood tests are taken for infections. Confirmation of risks is done on the basis of ultrasound.
Factors that increase protein levels
The amount of protein is influenced by cholesterol and lipid levels. In healthy people, the average blood CRP concentration is 0.8 mg/l. In people with cardiovascular diseases, the concentration increases, although it remains within normal limits. Based on the level of CRP, one can assume the risk of developing atherosclerosis, angina, and heart attack. The higher the score, the higher the risk of heart disease.
CRP increases when consuming fatty foods and taking hormonal contraceptives. Its amount is reduced by drugs from the NSAID group, steroids, and statins.
Positive CRP is observed in the following conditions:
- insomnia;
- apnea;
- smoking;
- addiction;
- lack of vitamins A and D;
- chronic stress;
- accommodation in mountainous areas;
- obesity;
- menopause
At the same time, the indicator remains within the normal range, but reaches the upper limit.
CRP is increased in conditions accompanied by tissue damage - burns, trauma, surgery.
Screening during the 2nd trimester
Biochemical testing is carried out from 15 to 20 weeks of pregnancy. Doctors do not recommend screening at the end of the trimester. The price of this procedure is about 3,000 rubles. It includes several tests at once. First, chromosomal abnormalities are detected. Secondly, damage to the embryo’s body is detected, in particular in the abdominal cavity and spine. The analysis also allows us to predict the development of Down syndrome in the fetus.
Closer to week 20, the embryo is already quite large. Therefore, it is possible to take a sample of amniotic fluid with minimal risk. This type of screening is called amniocentesis. It is contraindicated to do it if the uterus is toned. During the 2nd trimester, the most important types of research are ultrasound and biochemical screening.
Timing of ultrasound during pregnancy
The first screening is carried out between 10-14 weeks. Usually this is double testing - in addition to ultrasound diagnostics, the blood of the expectant mother is also checked. Based on the results, possible pathologies and deviations in the development of the developing fetus are determined.
The second ultrasound is performed from 16 to 20 weeks. The best time for examination is 17-19 weeks. Perinatal screening is carried out later, after a blood test - in the period 20-24 weeks. The second examination also includes ultrasound and biochemistry. If desired, a woman can refuse the 2nd part of the examination, but this is not recommended to avoid negative consequences.
The third ultrasound scan is performed between 30 and 34 weeks. During this period, obvious pathologies of the child’s development can be detected. If deviations were noticed earlier, then the third time they are confirmed or refuted. Some changes are noticeable only in the third trimester.
Decoding and norms of indicators (1st trimester)
Perinatal diagnosis in the first weeks of pregnancy consists of determining several important blood and gene characteristics. The most significant of them are human chorionic gonadotropin (abbreviated as hCG) and PAPP protein. These are extremely important hormones on which the course of pregnancy directly depends. From 10 to 12 weeks, the normal hCG level is considered to be from 20 to 95 thousand mU/ml. Deviations of 1-2 thousand units are allowed. The normal hCG level at week 13 is 15-60 thousand honey/ml. PPAP protein in the last month of the 1st trimester should be in the range from 0.3 to 6 mU/ml. At weeks 10 and 11, normal values range from 0.32 to 3.73 units. By the end of the trimester, the protein level should increase to 0.71-6.01 mU/ml.
To exclude deviations due to the age and weight of the pregnant woman, the MoM coefficient is used. Using this medial indicator, it is easier to decipher the biochemical screening of the 1st trimester. Here, the acceptable range is 0.5-2.5 units.
When do placental thickness indicators begin to be monitored?
The formation of the baby's place begins from the very beginning of pregnancy, when the fertilized egg attaches to the wall of the uterus. In this case, the so-called chorion is first formed, which develops and subsequently becomes the placenta. It can be detected by ultrasound as early as 11–13 weeks, that is, during the first planned ultrasound examination, but it begins to perform its functions by the middle of the second trimester.
The thickness of the placenta is measured by ultrasound
Measuring the thickness of the placenta begins at 20 weeks of pregnancy. It makes no sense to do this earlier, because the obtained indicators do not carry any meaning. During an ultrasound, a specialist determines and records the width of the largest value of the child’s seat, and then this indicator is compared with previously developed and accepted standards.
Table: normal placental thickness by week
| Week of pregnancy | Lower and upper limits of normal, mm | Average value, mm |
| 20 | 16,7–28,6 | 21,96 |
| 21 | 17,4–29,7 | 22,81 |
| 22 | 18,1–30,7 | 23,66 |
| 23 | 18,8–31,8 | 24,52 |
| 24 | 19,6–32,9 | 25,37 |
| 25 | 20,3–34,0 | 26,22 |
| 26 | 21,0–35,1 | 27,07 |
| 27 | 21,7–36,2 | 27,92 |
| 28 | 22,4–37,3 | 28,78 |
| 29 | 23,2–38,4 | 29,63 |
| 30 | 23,9–39,5 | 30,48 |
| 31 | 24,6–40,6 | 31,33 |
| 32 | 25,3–41,6 | 32,18 |
| 33 | 26,0–42,7 | 33,04 |
| 34 | 26,8–43,8 | 33,89 |
| 35 | 27,5–44,9 | 34,74 |
| 36 | 28,2–46,0 | 35,59 |
| 37 | 27,8–45,8 | 34,35 |
| 38 | 27,5–45,5 | 34,07 |
| 39 | 27,1–45,3 | 33,78 |
| 40 | 26,7–45,0 | 33,50 |
Decoding and norms of indicators (2nd trimester)
Biochemical screening of the 2nd trimester consists of blood characteristics such as hCG, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and free estriol (E3). All these are the most important hormones that provide a detailed picture of fetal development. Biochemical screening standards for the 2nd trimester for AFP are from 15 to 95 U/ml. By the end of the period, the levels may increase to 125. The hCG level in the first half of the trimester should be from 8 to 58 thousand mU/ml. By the end of the period, the figures drop significantly - from 1.6 to 49 thousand units. Free estriol should be between 5.4 and 28 nmol/l. At the beginning of the period, the maximum threshold is 21 units. By the end of the trimester, the minimum acceptable levels are 7.5 nmol/l. If the final result of the analysis is presented as a ratio, then the norm is considered to be a risk of less than 1:380.
Treatment for deviations from the norm: therapeutic complex for hypoplasia and hyperplasia
Reviews from young mothers confirm the non-danger of hypoplasia, as well as the ease of treating the disease.
Therapy includes:
- taking vitamin complexes;
- adjustment of the daily routine;
- changes in diet;
- doctor's supervision.
The Women's Forum also contains stories about the treatment of hyperplasia, which depends on the specific causes of thickening of the fetal protective membrane.
In such cases, therapy consists of:
- antivirals and antibiotics if infection is suspected;
- medications that increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood for anemia;
- vitamin complexes for rapid delivery of nutrients to the child;
- medications to normalize blood glucose.
Treatment is selected according to the stage of pregnancy, since some drugs that can be used in the second trimester can be dangerous in the late or early stages. The most important thing during pregnancy and at the time of planning a child is to regularly attend an antenatal clinic in order to identify disorders in the body as quickly as possible and eliminate them.
It will be useful for every woman to listen to the webinar “Cervical Erosion. To Treat or Not to Treat?”, which provides 2 hours of practical information and answers to the most important questions regarding physical, mental and sexual health.
Reasons for hCG deviation
The results of biochemical screening do not always provide 100% confidence in the presence or absence of a genetic abnormality. Minor deviations from the norm can occur due to a number of reasons. However, you should not pay attention to them if all other tests are in order.
On the other hand, a significant increase in hCG levels indicates trophoblastic disease in the mother, as well as multiple pregnancy. Decreased rates may be a consequence of ectopic fetal development. If fears are confirmed by ultrasound, then the risk of a genetic disease becomes real.
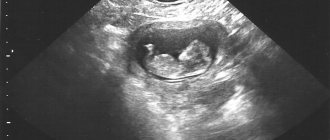
Fertilized egg on ultrasound: sizes by week of pregnancy
The fertilized sac is a round or ovoid (egg-shaped) formation that surrounds the embryo, usually located in the upper half of the uterine cavity.
In the early stages of pregnancy (in the first trimester), an ultrasound examination is performed to determine the localization (location) of the fetal egg. On an ultrasound, the fertilized egg looks like a small dark gray (almost black) spot with clear contours.
The presence of a fertilized egg in the uterine cavity eliminates the possibility of an ectopic pregnancy. In a multiple pregnancy, you can see two separately located fertilized eggs.
Deviations of other indicators
A highly elevated PPAP level indicates a possible imminent miscarriage or infection. Low protein means the development of Down or Edwards syndrome. Elevated AFP levels increase the risk of central nervous system defects, umbilical hernia, and liver necrosis. If the level of this hormone is greatly reduced, there is a possibility of premature death of the fetus. AFP can also signal Down syndrome. Deviation of free estriol from the norm indicates a threat of premature birth, fetal anencephaly, placental insufficiency, and liver disease in the mother.