The phenomenon of bone separation and nagging pain in the pelvic area during pregnancy is familiar to almost every woman who has carried a child. For some, the pain is milder and can be tolerated, while others find it difficult to maintain minimal physical activity. However, you need to understand that these are temporary changes in the musculoskeletal system, the purpose of which is to create conditions for the birth of a child.
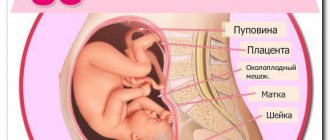
The pelvic bones, in particular the pubic, iliac and ischial bones, as well as ligaments and cartilage, “soften” under the influence of hormones. The hormone relaxin is involved in this. Thanks to this, the bones adapt to the size of the baby’s head even before birth. All painful sensations are concentrated in the pubic symphysis, popularly called the pubis. Outside of pregnancy, the pelvic bones support the internal organs.
When is it prescribed?
In the female body, the pelvic cavity performs many important functions: it is a container for internal organs and the fetus during pregnancy, a shock absorber for shocks and falls, and also, due to its pliability, facilitates the passage of the child during the process of delivery.
The pelvis itself is a closed ring, which consists of several bones:
- two ischial;
- coccyx;
- iliac pairs;
- sacrum;
- paired pubic bone forming the articulation.
At the same time, the cartilaginous structures of the symphysis pubis soften somewhat during pregnancy to ensure sufficient mobility and divergence of the pelvic bones at the time of birth. However, there are a number of signs and complaints indicating the development of a pathological process in the area of the pubic bones.
It is worth noting that pregnancy is not the only reason for the development of symphysitis or symphysiopathy (bone separation). The disease can occur as a result of connective tissue dysplasia, trauma to this area, kidney pathology, as well as a deficiency of vitamin D and ionized calcium in the blood.
Indications for prescribing ultrasound of the symphysis pubis:
- Painful sensations of a pulling or aching nature in the pubic area, occurring at rest and during dosed physical activity such as walking, climbing stairs.
- Pain on palpation of the pubic symphysis area.
- Edema, deformed or swollen pubic joint, as well as pathological changes in the soft tissues above it.
- Impaired duck-like gait, stiffness in movements, especially when abducting the hip anteriorly and to the side.
- Possible pain during sexual intercourse, urination and defecation disorders.
- The presence of symphysitis and a large number of births in the anamnesis.
- Large fetus, post-term pregnancy.
- The presence of congenital or acquired pelvic pathology (flat pelvis, simple flat pelvis, etc.).
If the above complaints and signs appear, it is recommended to do an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis, which will show the presence and extent of the lesion.
Syphmisitis - risk factors and signs of pathology
In the central lower part of a woman's abdomen are the pubic bones, connected by a fibrocartilaginous disc called the symphysis. Normally, the distance between the pubic bones in non-pregnant women does not exceed 2 mm. This joint is called the pubic joint, it is motionless. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the woman’s body begins to gradually prepare for the main event - childbirth, and therefore the production of the hormone relaxin increases. It is thanks to him that the pelvic bones can adapt to the baby’s head and “release” the baby into the outside world. This hormone also affects the frontal cartilage. Often, discomfort occurs when too much relaxin is produced and the cartilage becomes excessively mobile. Mobility of the bones of the symphysis pubis, caused by stretching and inflammation of the cartilage, is defined by doctors as symphysitis. The diagnosis of symphysitis is also made when the symphysis pubis is ruptured.
The development of symphysitis is provoked by:
- Hormonal disorders resulting in excessive production of relaxin.
- Lack of calcium - the main structural element of bone tissue.
- A lack of collagen causes ligaments and cartilage to lose their elasticity and become more vulnerable to stress.
- The hereditary factor that determines many pathologies of the musculoskeletal system also plays a significant role.
Among the main factors that increase the likelihood of symphysitis occurring are:
- Severe course of previous births.
- A large number of births.
- A woman carrying a large baby (child weight 4 kg or more), multiple pregnancy.
- Narrow pelvis.
- Little physical activity both before pregnancy and during pregnancy.
- Post-term pregnancy.
- Congenital pathologies of the pelvis.
How is diagnostics carried out?
To perform the study, the patient does not require any special preparation. It’s enough just to perform morning intimate hygiene.
The subject needs to lie on the couch in a supine position and not make sudden movements. The doctor applies a special water-based gel to the sensor (to avoid creating an air gap), and then installs the transducer in the pubic area. Ultrasonic waves are reflected from the soft tissues of a person and “produce” an echo pattern on the monitor of the device.
As a rule, the examination does not take much time and is completely painless and safe.
Pathology will be determined by diagnostics
How can you determine whether your groin pain is normal or whether these are the first signs of pathology? First of all, you should tell your gynecologist about your concerns. He will definitely do the necessary research.
For example, if the distance between the bones is large enough, then the specialist will detect this by palpation. But most often it will be necessary to conduct hardware research. Usually we are talking about ultrasound in relation to the symphysis pubis, on which a conclusion is given. On its basis, pathology treatment is carried out.
Here's what the study determines:
- degree of discrepancy between bones;
- the presence of an inflammatory process.
Occasionally, arthrosis of the symphysis pubis may occur. This is a fairly serious disease. By the way, it can also occur outside of pregnancy, although one of the reasons for its occurrence is hormonal imbalance.
And, as you know, it is typical when carrying a child. How to find out about the disease? To do this, the doctor prescribes an x-ray of the symphysis pubis. In the image, the specialist will determine both the pathology itself and its location.
But during pregnancy, this type of examination is prescribed only as a last resort, since X-rays are dangerous for the baby. X-ray determines the size of the woman’s pelvis and fetal head. This information will help answer the question of how to give birth - naturally or by caesarean section.
After childbirth, if a woman had signs of pathology, an MRI and CT scan must be prescribed. With their help, two problems are solved: the patient’s condition is assessed and new pathologies are identified, if any.
Results standards and deviations
During an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis, the doctor takes measurements of the divergence of the symphysis, and also assesses the condition of the ligamentous apparatus and adjacent soft tissues (tears of muscles, ligaments, hematomas, etc. are excluded).
The width of the pubic symphysis, which does not exceed 6 mm, is considered normal. At the same time, a number of studies indicate that for late-term pregnant women it is permissible to increase these figures to 8-9 mm.
Degrees of symphysitis according to international standards:
- The first degree is an expansion of 6-8 mm.
- Second degree - the discrepancy between the upper branches of the pubic bones is 8-10 mm.
- The third degree is characterized by the fact that the area of the pubic articulation has a discrepancy of 10 mm or more.
Interpretation of ultrasound examination
The norm according to ultrasound for expansion of the symphysis pubis during pregnancy is within 6 millimeters.
If the discrepancy of the bones is more than 6 and up to 8 millimeters, then the first degree of pathology is registered. When diagnosing a gap of up to ten millimeters, the 2nd degree is recorded, the last is diagnosed with deviations of more than 10 mm. Phases I and II of symphysis dehiscence are characterized by taking medications with a high content of calcium and vitamins. Long walks in the sun, a source of vitamin D, are recommended; doctors prescribe the use of a bandage to prevent premature labor. Childbirth with this pathology usually takes place naturally without complications.
III degree of deviation, when the expansion reaches dimensions of more than 1 cm, causes severe lameness and pain when walking. There is a high risk of complete rupture; the pregnant woman is also prescribed calcium-containing medications, multivitamins, and the use of a support bandage. Childbirth is often planned and by caesarean section. After the birth of the baby, doctors do not stop the medications for some time; it is recommended to constantly use a bandage and regularly undergo ultrasound of the symphysis. It is extremely rare that surgery can be used to restore the functionality of the bone structure.
What to do if you find symphysitis
Due to the fact that symphysitis mainly occurs in pregnant women, management tactics are decided based on the results of ultrasound of the symphysis pubis, objective examination data (in particular, the size of the pelvis) and indicators of ultrasound examination of the fetus (amount of amniotic fluid, multiple pregnancy or not, estimated weight of the unborn child). pregnancy and upcoming birth.
Doctors strongly recommend that women limit physical activity (exclude heavy lifting and, if possible, climbing stairs) and spend as much time as possible in a lying position. Multivitamin complexes, calcium supplements, and extensive bandaging of the pelvic area are also prescribed.
Until the birth itself, pregnant women should:
- attend special exercise therapy courses;
- wear a pelvic band;
- eat foods that are rich in vitamins and microelements;
- try to avoid prolonged sitting.
In more severe cases, women are hospitalized in the department of pathology of pregnant women and are constantly under the supervision of a gynecologist and traumatologist, and also receive specialized medication and physiotherapeutic treatment.
The choice between natural birth or cesarean section depends on the degree of divergence of the symphysis, the general condition of the pregnant woman (whether there is gestosis or other pathology), as well as on the size of the fetus. In the case of the first degree of symphysitis, normal fetal weight, absence of early and late gestosis, as well as exacerbation of any underlying diseases in the mother, childbirth is possible physiologically. In other cases, doctors tend to favor a caesarean section.
Symptoms of symphysitis
The insidiousness of symphysitis is that pain is often felt subjectively. For example, a woman may have a serious discrepancy in the bones of the symphysis pubis, but she experiences mild pain. But more often, on the contrary, even the slightest discrepancy makes itself felt with severe pain. Therefore, with symphysitis during pregnancy, dynamic observation is very important.
What are the signs of inflammation in the symphysis pubis?
- Pulling or periodically shooting pain in the pubic area;
- It is difficult for a woman to move her hip to the side, turn around, or get out of bed;
- Pain when palpated in the iliosacral region;
- The characteristic “duckling” gait of pregnant women, especially after childbirth;
- Painful sensations when moving and their absence at rest.
Similar sensations in a weak form accompany all pregnant women; they are diagnosed as normal. But if a pregnant woman experiences exceptionally strong pain, it is difficult to move and it is impossible to touch the pelvic bones, then in this case they are already talking about an inflammatory process of the symphysis pubis.
These symptoms usually appear in the last weeks before giving birth.
However, in some pregnant women, dysfunction of the symphysis pubis can make itself felt in the early stages, in the second and even in the first trimester.
Moderate and severe sprains and ruptures can make themselves felt both during and after childbirth. A woman can experience pain from absolutely any movement. More often they say that it is difficult to stand up on your own, go up and down the stairs, or sit on a chair.
During routine routine ultrasound screenings, the doctor does not look at the problem of symphysis pubis discrepancy. However, if the pain is severe, the attending physician may prescribe an additional ultrasound. During this ultrasound session, the condition of the pelvic bones and symphysis pubis will be assessed from all sides.
Features of the event
Ultrasound scanning of the hip joint is performed at a time when newborn babies do not have colic in the abdomen, an allergic reaction or painful sensations in the gums. The baby should be well-fed, however, the manipulations of medical specialists can contribute to his excitement - in order to avoid regurgitation (regurgitation), diagnostics are performed half an hour after feeding.
The baby's anxiety and excessive physical activity lead to the fact that the results of the study will be incorrect. To perform an ultrasound, the child is placed on a hard surface, the limb being examined is rotated 30º. During the procedure, the angles are measured, which will allow one to evaluate dysplastic changes in the hip joint using the Graph table:
- The α-angle denotes the level of the iliac crest;
- β-angle – the size of the cartilage covering of the acetabulum.
Before performing an ultrasound scan, an adult patient does not need to specially prepare for the procedure - it is enough to have a direction and a towel with him, which is used to remove the remains of the gel, which facilitates the sliding of the ultrasound sensor and improves the visualization of tissues.
To perform all diagnostic procedures, the patient must remove or lower his underwear
The study of the anatomical structures of the hip joint is carried out in the following planes:
- Anterior – the sensor is installed parallel to the vertical axis of the body. This allows you to visualize the anterior surface of the femoral head, wings of the ilium, inguinal lymph nodes and elements of the ligamentous-muscular apparatus.
- Posterior - to examine the condition of the ischial tuberosity, the surfaces of the cartilages and gluteal muscles, the patient is asked to lie on his side and pull his legs towards his stomach.
- Medial - to study the condition of the flexor muscles and articular ligaments, the patient needs to bend the knee and move the lower limb outward.
- Lateral - to assess the protruding surfaces of the tibia and the greater trochanteric bursa, the patient needs to rotate the femur inward.
The choice of examination option is chosen by the sonologist based on the preliminary diagnosis and localization of the affected areas. The duration of the procedure is 15–20 minutes.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
Softening of the symphysis pubis is a physiological change in a woman’s body during pregnancy. Sometimes physiology develops into a pathological process, and excessive divergence of the pelvic bones occurs, while the patient is bothered by unpleasant symptoms.
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis in the following cases:
- Pain in the affected area, which radiates to the lower abdomen, perineum, leg and lower back.
- Pain while moving. Unpleasant symptoms occur when rising from a chair or stairs, while walking and standing, and while bending down. Painful sensations disappear during rest.
- Weakness, general fatigue, muscle cramps and deterioration in general health during pregnancy.
- Change in gait pattern. Clicking and grinding noises may occur during movement.
- Complete loss of mobility, characteristic of a rupture of the symphysis pubis.
- If the woman suffered from symphysis pathology during previous pregnancies.
There are no contraindications to the procedure. The exception is the situation when the skin over the affected area is severely injured. The rash or wound should be treated first and then an ultrasound scan will be performed.
Diagnostic and treatment methods
For citation: Logutova L.S., Chechneva M.A., Lysenko S.N., Cherkasova N.Yu. Ultrasound diagnostics of the condition of the symphysis pubis in women // Breast Cancer. Mother and child. 2020. No. 1. P. 42
Relevance
Bone pelvic pathology occupies a certain place in the structure of abnormal births. Pathological expansion or the appearance of pain in the symphysis is classified as dysfunction of the symphysis pubis (PA) (symphysiopathy, symphysitis).
This complication, which occurs during gestation, is considered in the structure of the syndrome of pelvic girdle pain during pregnancy (Pregnancy-related pelvic girdle pain (PPGP)).
When examining a large population of women, it was proven that up to 50% of pregnant women experience pelvic pain, which may be a consequence of changes in the joints of the pelvis, most often the pubic joint, and require additional examination.
Despite the low incidence, rupture of the pelvic joint remains a serious complication of labor during symphysiopathy; restoration of the function of the pelvic joints takes up to 5 months. after childbirth.
Trauma to the left leg may be accompanied by rupture of one of the sacroiliac joints and damage to adjacent organs [3]. The incidence of this complication is low historically and currently.
In recent decades, discrepancies and ruptures of the LM occur, according to various authors, from 1:380 to 1:3400 births [4–6].
The LS is formed by the fibrocartilaginous interpubic plate (lamina fibrocartilaginca interpubica or Discus interpubicus) and fibrous ligaments: on top - lig. pubicum superius, below - lig. arcuatum pubis, front - lig. fibrosum ant. and behind - lig. fibrosum post [7].
One of the most detailed descriptions of the morphology and structure of the drug was given by M.F. Eisenberg in 1962. According to him, the drug “has sexual characteristics and has individual differences. All types of joints are observed - from synchondrosis to a real joint.
Features of the structure and condition of drugs... in women... of course... are in close connection with the endocrine and functional processes occurring in the body.” Morphologically, the cartilaginous interpubic plate is heterogeneous - most of it is represented by hyaline cartilage; along the periphery of the interpubic gap there is a zone of fibrous cartilage.
Sexual and gender dimorphism of the structure of the drug, as well as age-related changes, confirm the latest literature data [9].
N. Lottering and MS Reynolds (2013) state age-related changes in the structure and zones of ossification of the LM during its three-dimensional CT reconstruction [10].
The pathogenesis of changes in drugs, in particular during pregnancy, cannot be called thoroughly studied.
Due to the loosening of the symphysis during pregnancy, the cavity in the interpubic cartilaginous plate can increase to a significant size, sometimes with a divergence of the symphysis bones by 1–2 cm.
Some authors believe that this phenomenon in pregnant women can also be considered from the point of view of metabolic disorders, and interpreted as the initial stages of osteomalacia.
Disturbances in the structure and function of drugs can occur under the influence of other etiological factors (syphilis, TBC, jaundice, hemorrhagic diathesis, arthritis) [8].
Sports medicine specialists believe that symphysis lesions are the result of injury to the ligamentous apparatus of the pelvic ring and the muscles of the hip and lower back [15].
There is a theory of muscle spasm in the genesis of symphysiopathy, which may be due to disturbances in calcium metabolism.
Diagnostic methods
Until recently, X-ray methods were considered the “gold standard” in diagnosing changes in LM.
During pregnancy, preference is given to ultrasound diagnosis of drugs (Fig. 1). Magnetic resonance imaging is used primarily in sports medicine. The advantages of the ultrasound method are accessibility, the ability to assess not only the degree of divergence of the ligaments, but also, in contrast to the x-ray method, to determine the condition of the soft tissues and ligaments.
The ultrasound method for studying the symphysis in pregnant women, proposed over the past 20 years by a number of authors for diagnosis and prognosis in symphysiopathies, mainly comes down to measuring the width of the symphysis.
By itself, this indicator does not reflect the degree of pathological changes in the symphysis, and also poorly or does not correlate at all with clinical manifestations and complaints and does not allow one to predict the most dangerous complication of symphysitis - discrepancy or rupture of the womb during childbirth.
As a result of the study, we can propose new ultrasound symptoms that reflect structural changes in the LM during symphysitis in pregnant women, promising in terms of their use for differential diagnosis.
Materials and methods
Group 1 - pregnant and postpartum women without clinical signs of drug dysfunction:
- 1A — at full-term pregnancy (n=30) — a single ultrasound of the LM was performed;
- 1B - primigravida women (n=27) - dynamic observation;
- 1C - multiparous pregnant women (n=30) - dynamic observation;
- 1D - after childbirth (n=18).
Group 2 - non-pregnant women of fertile age (n=30) without clinical manifestations of LS pathology.
Group 3 - 60 pregnant women with clinical manifestations of symphysitis.
On sagittal scanning, the LS appears as an oval formation of a heterogeneous structure with a clearly distinguishable “core”, which includes hyperechoic and hypoechoic areas.
Based on the outer surface of the cartilaginous girdle, in most cases it is possible to differentiate along the upper edge of the lig. pubicum superius, below - lig. arcuatum pubis, front - lig. fibrosum anterior and posterior - lig.
fibrosum posterior (Fig. 2).
In the structure of the cartilaginous girdle, hyperechoic inclusions of round or irregular shape, single or grouped, can be found - zones of ossification (Fig. 3).
The linear dimensions of the LM in women during ultrasound examination are presented in Table 1.
Like other researchers, we saw that during pregnancy there is an increase in the width of the LM, with a more significant increase in the upper parts of the cartilage. The width of the symphysis in the upper third of a pregnant woman was on average 1.45 times greater than in the lower third (1.23–1.70 times).
1) the minimum diastasis of the pubic bones in groups 1 °C and 1B did not differ significantly (5.4 ± 1.3 (3.7–8.0) mm versus 5.4 ± 1.0 (3.8–8.2 ) mm; p=0.83);
2) maximum diastasis in groups 1B and 1 °C also did not differ significantly (6.2±1.7 (3.5–10.0) mm versus 4.5±9.0 (3.4–9.0) mm; p=0.76);
4) visualization of the “apophysis” in 33.3% in group 1B (43.3% in group 1 °C);
5) single hyperechoic inclusions in the structure of the symphysis in 48% in group 1B (in 93% in group 1 °C);
6) grouped hyperechoic inclusions in 22% in group 1B (40% in group 1 °C);
7) the thickness of the superior ligament of the left limb in group 1B was 3.8±1.02 mm on the right, 3.8±0.98 mm on the left (p=0.98); in the 1 °C group - 4.2±1.0 mm on the right, 4.4±1.0 mm on the left (p=0.46).
When measuring the superior ligament in the middle above the symphysis, the latter was thickened in women in the 1 °C group (7.8 ± 1.7 mm versus 6.6 ± 1.5 mm) (p = 0.01).
As an additional research method, we studied the echo density of the cartilaginous interpubic plate in women.
The construction of histograms of tissue density of the left leg in all examined patients was carried out in the same scanning modes. The echo density of the interpubic cartilaginous disc was measured in various zones.
Thus, the relative echographic density of the fibrous “core” of the LM is higher than the density of the hyaline cartilage.
As a result of the study, we found that by the end of pregnancy the LM undergoes the following changes: moderate diastasis of the womb relative to the womb of non-pregnant women, an increase in the echo density of the cartilaginous disc - both the hyaline and cartilaginous parts.
Of greatest interest is the study of group 3 - patients with clinical manifestations of drug dysfunction during pregnancy.
signs of pubic discrepancy were identified in 2 (3.3%) cases (Fig. 4). The measurement results are presented in Table 3.
As can be seen from the presented material, the average values of the linear dimensions of the symphysis do not have significant differences in different clinical groups, with the exception of the width of the symphysis. In this regard, the results of the study do not contradict previously presented literature data.
When is an ultrasound of the symphysis pubis performed?
Diagnosis of the symphysis pubis is carried out based on the presence of even one of the above risk factors. The patient is included in the risk group. It is mandatory to perform a clinical and ultrasound examination during pregnancy over time. That is, ultrasound is performed:
- At the initial stage of pregnancy;
- In the middle of pregnancy;
- 7-10 days before the baby is born.
Depending on the results of the study, the specialist gives recommendations for childbirth. A caesarean section is prescribed when, during pregnancy in the middle of the term, as well as 7-10 days before the birth of the baby, pain sensations affecting the pelvic area increase. A significant indication for a cesarean section is a noticeable increase in the diastasis of the symphysis pubis. When the discrepancy of the pubic bones is more than 10 mm.
After any birth, an X-ray examination of the pubic bones is prescribed. It must be carried out during the period from the first to the third day.
Decoding the results obtained
The obtained ultrasound values of the hip joints in children are taken as the norm, and the development of the hip joint occurs in accordance with age if the echogenicity of the femur and acetabulum is increased. On the oscilloscope screen they are visualized as white spots, and the femoral head and hyaline cartilage tissue look like dark, slightly blurred areas. The older the child, the more pronounced the contrasting outlines of the hip joint are due to the formed foci of ossification. The deciphering of the obtained values is carried out by a diagnostician who measures the angles obtained after drawing linear segments on the photographs. When connecting the lower part of the small ischial muscle to the ilium, only straight lines should be obtained, and the hyaline cartilaginous structures with the acetabulum should be curved. When lines intersect in such projections, alpha and beta angles are formed, measured by a diagnostician using the Graph method. The norm is characterized by the following digital parameters:
- an alpha angle of more than 60°, formed by bends and horizontal straight lines, indicates the correct formation and hardening of the surfaces of the acetabulum;
- a beta angle of less than 55° indicates the degree of development of the cartilaginous zones in the acetabulum and is normal.
Alpha angles with values of 39-40° are considered deviations from the norm during ultrasound of the hip joints. Such parameters of a diagnostic study indicate the presence of a subluxated joint in a child. When the alpha angle is less than 43°, children are diagnosed with hip dysplasia. Beta angles in these diseases are almost always greater than 77°.
In adult patients, the increased echogenicity of the acetabular labrum, the fibrous arrangement of the ligaments of the synovial capsule, and the lack of visualization of the synovial membrane are taken as the norm for the structure of the hip joint. The normal distance from the femoral neck to the articular capsule is 0.6-0.9 cm. The main task of the doctor when examining adults is to carry out differential diagnosis, which makes it possible to separate intra-articular pathology from extra-articular one. This helps the doctor choose treatment tactics and the best medications. What intra-articular pathologies are detected by ultrasound:
- the presence of effusion in the joint cavity, or synovitis. A thickened joint capsule indicates accumulation of foreign fluid. The thickness of this structural element is compared with a similar one in a healthy joint. If the difference is more than 0.2 cm, then the synovial joint capsule is not functioning properly. The resulting images measure the length of the line connecting the joint capsule and the femoral neck. Values above 1 cm allow us to establish developed synovitis;
- the presence of foreign fragments in the synovial fluid. This pathological condition is usually preceded by fractures, avulsions of particles of cartilage or bone. The cause of the appearance of tiny foreign bodies is osteoarthritis, accompanied by an acute or chronic inflammatory process. Foreign particles penetrate the joint capsule and are visualized on the resulting images in the form of an intra-articular mobile hyperechoic structure;
- formation of a false joint. With delayed fusion of fragments, irregular extraneous joints are formed. Their formation is provoked by surgical reposition of bone fragments with the help of various fixing structures for closed fractures of the femur, the complication of which was suppuration and osteomyelitis. Ultrasound of the hip joint reveals false joints. Signs of their formation are intermittent outlines of bone structures with uneven calluses. Areas of inflammation and swelling of nearby soft tissues are also well visualized.
Ultrasonography is prescribed to detect necrotic changes in the femoral head, a pathology that most often affects men. The disease progresses quickly and severely, causing decreased ability to work and disability. An ultrasound scan of the hip joint allows you to identify pathology at the initial stage and begin treatment immediately. With necrosis, the symptoms are dominated by pain, atrophic muscle damage, limited range of motion and gait disturbance. When deciphering the results of an ultrasound, the disease is indicated by a violation of the symmetry of the contours of the joint, narrowing of the joint space, and uneven outlines of the head.
Anatomical features of the joint
The hip joint is formed by the head of the femur, which fits into the acetabulum - a depression in the ilium, which is part of the pelvic bones. Their surfaces are covered with thick cartilaginous tissue, which ensures the trouble-free functioning of the joint - keeping the body of the human body in an upright position, the motor activity of the torso and lower extremities.
The structure of the hip joint is made up of powerful bone and soft tissues - ligaments, muscles, vessels and tendons, which are involved in various movements of the human body.
Thanks to the function of the hip joints, a person has the ability to walk, perform household duties, engage in professional activities and sports. The development of pathological changes in the structure of the hip joint leads to the appearance of discomfort and pain - these sensations can occur in both elderly and young people. If it is impossible to determine their causes by palpation and visual examination, the doctor prescribes sonography.
Timely implementation of the diagnostic procedure will allow for a correct diagnosis and successful treatment.
The most important things about ultrasound
Ultrasound examination or sonography is prescribed if injury or disease of the joints is suspected. This diagnostic method helps detect changes in soft tissue, cartilage and bone using ultrasound waves. Ultrasound of the hip joint in adults is usually used for a comprehensive examination of the body.
Indications for use
Ultrasound of the hip joint determines the condition of the cartilage, tendons, muscles and soft tissues. Most often it is prescribed when the patient complains of pain, discomfort and impaired motor activity in the joint.
The main indications for ultrasound examination of the hip joint (HJ):
- Presence of injuries, including old ones;
- Spasms in the gluteal and thigh muscles;
- Pain in the joint at rest or when walking;
- Limited range of motion;
- Pain syndrome;
- Swelling in the hip area;
- Characteristic crunch of the joint;
- Shortening of one limb;
- The presence of diseases that can provoke complications: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis.
Interesting!
This diagnostic method has no contraindications and can be used by pregnant and lactating women. Ultrasound of the hip joint is also performed in children of any age.
Indications for ultrasound of the hip joint
Advantages of the research method
Despite the variety of diagnostic techniques, ultrasound has a number of advantages that distinguish it from the rest. The main advantages of ultrasonography:
- Safety. Can be used by pregnant women, children and people with implants and dentures;
- Painless. This is especially important when conducting research in children;
- Non-invasive. The method does not require the introduction of any substances into the blood, so the skin is not damaged;
- Information content. Monitors the body's condition in real time;
- Availability. It has a relatively low cost; diagnostic equipment is available in most medical institutions.
Attention!
It is recommended to carry out ultrasound diagnostics once every two months.
Cost of ultrasound for an adult
In public clinics, hospitals, as well as in commercial clinics, you can undergo sonography. The cost of diagnostics depends on the equipment used and the status of the medical institution. On average, the price of an ultrasound of the hip joint is up to 1,500 rubles.
Why is a symphysis rupture dangerous?
Symphysiolysis makes itself felt before, during, or immediately after childbirth. A postpartum woman cannot raise her legs, get out of bed on her own (only sideways), climb stairs, and sometimes even move her limbs to the required extent. Any physical activity causes pain.
Symphysiopathy, although it causes a lot of inconvenience, does not threaten health or life. But a rupture of the symphysis pubis during childbirth is already an injury, a fracture of the pelvis.
- If the bones are separated by 2 cm, then such a fracture is stable and rarely causes complications.
- And if the distance between the edges of the ruptured symphysis is 5 cm or more, this is a direct danger to health.
The edges of the bones can damage the urethra, bladder, and clitoris. Hemorrhages may occur in the joint area, which will subsequently lead to arthritis. Therefore, such tears must be treated with surgery. Fortunately, such cases are very rare.
What does the diagnosis show?
An ultrasound of the joints shows what is happening to them at the moment. With the help of an examination, injuries, pathologies, cysts, degenerative and inflammatory processes can be identified. Let's look at each point in more detail.
Pathologies in the joints
Ultrasound of joints is also done to identify pathologies. These can be transformations after operations, inflammatory processes, dystrophic changes.
Based on the results of the examination, heterogeneity of the structure, hyperechoic formations, edema, displacement of ligaments and tissues can be revealed. These changes may indicate degenerative processes.
Detection of a cyst
A cyst is a hollow tumor, usually filled with fluid. Using ultrasound, you can identify a cyst in the joints and evaluate its development. Most often, cyst removal is only possible through surgery. If left untreated, it can grow and/or become malignant.
Injuries
Joint injuries can occur for various reasons: a fall, high load, awkward movement. During ultrasound diagnostics, it is possible to identify the consequences of these injuries: rupture of ligaments, tendons, hematomas.
Degenerative processes
Factors in the development of degenerative diseases are osteoporosis (decreased bone density) and wear and tear of the joint with subsequent destruction of cartilage. Mostly elderly people are susceptible to these processes. Subsequently, various types of arthrosis arise. Ultrasound clearly shows these processes and the condition of the joints (for example, narrowing of the gap between the joints, irregularities).
Joint inflammation
Inflammation is a normal reaction of the body to the ingress of pathogenic bacteria. For any manifestations of inflammatory processes in the joints (pain, swelling, redness, limited mobility, crunching, fever), you must immediately consult a doctor to undergo an examination and receive the necessary treatment. Neglected inflammatory processes lead to chronic diseases (gout, various arthritis) and even disability. During an ultrasound of joints and limbs, inflammation is indicated by free fluid in them.