The pituitary gland secretes several chemical compounds that regulate the activity of the endocrine glands, metabolism and development of the body. One of these hormones is somatotropin (somatropin). Its concentration is of particular importance for children, adolescents, women and athletes.
What is growth hormone?
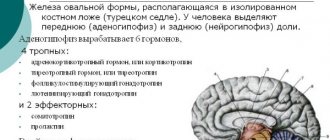
Growth hormone or somatotropic hormone, also known as somatotropin, is secreted in the human body in spurts and is produced by the anterior frontal part of the pituitary gland.
The pituitary gland is a cerebral appendage up to 2 cm in size, consisting of three lobes - anterior, intermediate and posterior. It is one of the main elements of the endocrine system, which synthesizes the most important hormones for the body - growth, regulatory and reproductive.
The growth hormone molecule is a chain of many amino acids with 2 sulfide bridges inside. In its structure, this hormone is similar to monkey growth hormone. In the blood, half of the somatotropin binds to the transport protein. The half-life of the remaining GH is from 20 to 50 minutes.
There are 2 types of somatotropic hormone: “big”-GH and “little”-GH. The second type has increased activity, and it is this that is the main one in all the effects of growth hormone.
Skin changes
When the body's normal production of growth hormone is disrupted and excessive production of this substance occurs, the skin becomes rough and thick. Visually this is noticeable by the abundance of wrinkles and folds. Most of them appear on the head, in the area covered with hair.
Quite often they notice the appearance of acne, hair grows faster, it is darker and thicker, almost the entire body is overgrown. Patients with acromegaly complain of sweating and greasy skin. This occurs due to an increase in the number of glands that produce sweat and sebum.
Functions of growth hormone
The fundamental effect of growth hormone is shown in children, from birth to the end of puberty, because responsible for growth and harmonious development. But this hormone is also very important for adults, because enhances anabolic processes, as a result of which the structural parts of cells, tissues and muscle structures are renewed.
In addition, somatotropin is involved in the following processes:
- has a fat burning effect;
- activates protein synthesis in the liver and muscle tissue;
- strengthens tendons;
- promotes wound healing and tissue regeneration;
- slows down the process of protein breakdown;
- enhances glycogenesis in the liver;
- rejuvenates the body by participating in the synthesis of collagen and elastin;
- protects blood vessels, vascular tissues;
- keeps cholesterol in balance;
- strengthens the immune system;
- reduces cell sensitivity to insulin;
- maintains the balance of potassium and sodium;
- optimizes the process of calcium absorption by bone tissue;
- ensures good lactation;
- improves DNA production;
- stimulates the excretion of fluid through the sweat glands.
Article on the topic:
Basic drugs for lowering blood cholesterol. Which to choose?
The main functions of somatotropin in the human body
Somatotropic hormone (GH) is synthesized throughout life and has a powerful effect on all systems of our body. Let's look at the most important functions of such a substance:
- The cardiovascular system. STH is a hormone that is involved in the regulation of cholesterol levels. A deficiency of this substance can provoke vascular atherosclerosis, heart attack, stroke and other diseases.
- Leather. Growth hormone is an essential component in the production of collagen, which is responsible for the condition of the skin. If the hormone (GH) is reduced, collagen is synthesized in insufficient quantities and, as a result, the aging process of the skin accelerates.
- Weight. At night (during sleep), somatotropin is directly involved in the process of lipid breakdown. Violation of this mechanism causes gradual obesity.
- Bone. Somatotropic hormone in children and adolescents ensures the elongation of bones, and in an adult - their strength. This is due to the fact that somatotropin is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D3 in the body, which is responsible for the stability and strength of bones. This factor helps to cope with various diseases and severe bruises.
- Muscle. STH (hormone) is responsible for the strength and elasticity of muscle fibers.
- Body tone. Somatotropic hormone has a positive effect on the entire body. Helps maintain energy, good mood, and sound sleep.
Growth hormone is very important for maintaining a slim and beautiful body shape. One of the functions of somatotropic hormone is the transformation of adipose tissue into muscle tissue, this is what athletes and everyone who watches their figure achieve. STH is a hormone that improves joint mobility and flexibility, making muscles more elastic.
In older age, normal levels of somatotropin in the blood prolong longevity. Initially, somatotropic hormone was used to treat various senile ailments. In the world of sports, this substance was used for some time by athletes to build muscle mass, but growth hormone was soon banned for official use, although today it is actively used by bodybuilders.
Normal somatotropic hormone
In the male and female body, the quantitative norm is different, and age criteria also affect its content:
| Age and gender group | Hormone levels are normal |
| Newborn babies up to 24 hours | 5-53 µg/l |
| Infants up to 7 days | 5-27 µg/l |
| Children from 7 days to one year | 2-10 µg/l |
| Children from one year to adulthood | 1-20 µg/l |
| Middle-aged men (18-60 years old) | 0-4 µg/l |
| Middle-aged women (18-60 years old) | 0-18 µg/l |
| Men over 60 years old | 1-9 µg/l |
| Women over 60 years old | 1-16 µg/l |
For the harmonious functioning of the body, all indicators should be normal. HGH hormone is no exception.
With its excess, gigantism is observed in children, and acromegaly develops in adults, which can manifest itself with the following symptoms:
- the skin becomes thicker and facial features become rougher;
- increased hair growth and sweating;
- the fat content of epithelial tissue increases;
- diabetes mellitus develops;
- Cholesterol levels increase significantly and vascular atherosclerosis develops;
- calcium levels decrease;
- vision and smell deteriorate;
- dysfunctions in the nervous and reproductive systems are observed;
- constant headaches appear;
- epilepsy and gynecomastia develop;
- there is general weakness;
- Appetite and sleep deteriorate.
Acromegaly is a severe endocrine disease in which the functions of the cardiovascular system are disrupted and disproportionate growth of bones, cartilage, soft tissues, and internal organs occurs.
In addition, an increase in somatropin is observed in the presence of the following diseases:
- chronic renal failure;
- Laron's syndrome;
- dysfunctions of the adenohypophysis;
- benign formations of the pituitary gland;
- anorexia due to nervousness;
- hypoglycemia;
- hyperinsulinemia;
- in the post-traumatic and post-operative period.
If there is a deficiency of the GH hormone, then growth and sexual development slow down in children, and in adults, metabolic processes are disrupted, thyroid function deteriorates, and hypoinsulinemia .
Also, the following symptoms may appear in all age groups:
- weight loss or obesity;
- muscle tissue atrophy;
- development of osteoporosis;
- tendency to damage joints and ligaments;
- dryness and thinning of the skin;
- hair loss;
- rapid aging;
- increased sweating, especially at night;
- violation of thermoregulation;
- constant fatigue, depression, anxiety;
- forgetfulness, absent-mindedness, lack of concentration;
- development of hypoglycemia;
- deterioration of the heart and the entire cardiovascular system;
- decreased erection in men and libido in women.
Article on the topic:
What does elevated blood triglyceride levels indicate in adults? Causes and symptoms.
Normal indicators and deviations
The amount in which growth hormone is produced in the body depends on the patient's gender and age. So reference values for growth hormone (in honey/l):
- in boys up to 3 years of age, they normally produce from 1.3 to 9.1, in girls of the same age the figures are slightly lower - from 1.1 to 6.2;
- in boys under 9 years of age, the somatotropin level should be in the range of 0.4-14.0, in their peers - 0.4-8.3;
- at the age of 9-12 years, the level of growth hormone increases significantly. Boys of this age normally have from 0.4 to 29.1, and girls of the same age - from 0.3 to 23.1;
- The hormone should be produced in maximum quantities at the age of 13-17 years. For boys of this age, the normal growth hormone level is 0.6 - 30.4, for girls - 0.2-29.6;
- in adults, the norm of somatotropin content does not depend on gender and ranges from 0.2 to 13.0.
Low hormone levels
If a low level of GTS is detected in children, this is a serious violation. A deficiency of the substance in the blood can cause growth retardation, including the development of dwarfism, as well as symptoms such as:
- delayed sexual development;
- delay in general physical development.
The causes of these disorders may be pathology during pregnancy or a hereditary predisposition.
In most cases, if a lack of growth hormone in a child’s body is detected in a timely manner, this condition can be corrected. Patients are prescribed synthetic hormones and their development is not affected.
Advice! Short stature in humans is not always associated with disturbances in the production of somatotropin. Most often, short stature is due to heredity, various diseases suffered in childhood and other reasons.
If a low level of growth hormone is detected in the blood of adults, this usually affects the deterioration of metabolic processes. Low levels of the hormone may be one of the causes of osteoporosis.
Reasons for decreased somatropin levels
In addition to genetic prerequisites, such as diseases at the chromosomal level, problems with metabolism from birth, the presence of Down, Turner, Noonan syndromes, dwarfism, somatotropic insufficiency can be affected by:
- tumors inside the skull;
- presence of a pituitary cyst;
- poor development of the pituitary gland;
- development of hypopituitarism syndrome;
- damage to the central nervous system by infectious or toxic agents;
- overexertion of the adrenal cortex (Itsenko-Cushing syndrome);
- inflammatory diseases of the colon;
- radiotherapy and chemotherapy;
- some drugs, for example, glucocorticoids, progesterone, somatostatin, glucose, etc.
Also, a decrease in the concentration of GH in the blood may be associated with the so-called. pseudohormone deficiency, which is caused by:
- obesity;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- hypercortisolism;
- heart failure;
- Addison's disease;
- physical activity at negative temperatures;
- postpartum condition.
What happens next?
Over time, growth hormone has a significant effect on all tissues of the body. There is a growth of various organs: internal, external. In particular, the tongue will be larger. But inside the body they grow more than normal:
- heart;
- respiratory system;
- intestinal system;
- kidneys;
- liver;
- glands responsible for the production of saliva.
At first, people notice greater strength and the ability to withstand physical activity increases sharply. However, this then passes and sclerotic processes become more active. Because of this, the muscles weaken and atrophy.
Sclerotic destruction is characteristic of all organs of a person suffering from acromegaly. The lungs and heart are the first to suffer.
As the cartilage increases in volume, the joints become deformed, hurt and lose the ability to move normally. Patients whose body produces excess growth hormone complain of arterial hypertension. The frequency of this disease relative to its occurrence in healthy people is five times higher.
Analysis for growth hormone
If the above symptoms are present and there is a suspicion that they were caused by an excess or deficiency of the hormone somatropin, a test for growth hormone is prescribed. The analysis is also prescribed to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy for acromegaly or gigantism.
To obtain an accurate result, the following recommendations should be followed before the study:
- do not eat food for at least half a day;
- forget about smoking at least 180 minutes before donating blood;
- Do not eat fatty foods or drink alcohol for 24 hours; also during this period, try to maintain emotional calm and not overexert yourself physically;
- if possible and in agreement with your doctor, stop taking all medications for a day;
- Do not do X-ray examinations for a week.
Also, for a more accurate diagnosis, studies are carried out with stimulation or suppression of growth hormone.
If hormone deficiency is suspected, a stimulation study is performed. To do this, venous blood is first taken from the patient as a starting point for understanding the situation, then insulin, clonidine or arginine is injected into the vein, and then at certain intervals (depending on the selected substance), blood is drawn again. If after stimulation the hormone level does not increase, then somatropin is reduced.
If it is assumed that there is an excess of the hormone in the body, a suppression test is performed. To do this, a control blood test is first taken, then the patient drinks a glucose solution , and then blood is taken again at a certain frequency. If the level of growth hormone does not decrease, it means that there is really a lot of it in the body.
The level of growth hormone in the body constantly varies, so deciphering the results must be approached with great care so as not to mistake physiological daily fluctuations of the hormone for an anomaly. If a pathology is nevertheless identified, then therapy should be prescribed as soon as possible.
Article on the topic:
Calcium levels in blood tests for women depending on age
What rules should be followed before conducting an analysis?
A week before the analysis for growth hormone (growth hormone), it is necessary to refuse an X-ray examination, as this may affect the reliability of the data. During the day before blood sampling, you should adhere to a strict diet, excluding any fatty foods. Twelve hours before the test, avoid eating any foods. It is also recommended to stop smoking, and within three hours it should be completely eliminated. A day before the test, any physical or emotional stress is unacceptable. Blood sampling is carried out in the morning, at this time the concentration of somatotropic hormone in the blood is maximum.
Treatment
To reduce STH
When problems are detected early, drug therapy is usually started. Drugs that inhibit the functioning of the pituitary gland are used; most often they are based on the hormone somatostatin, and, as a result, the hormone somatropin is released in a smaller volume.
If the cause of increased growth hormone is a tumor in the brain, then more radical measures are taken:
- surgical intervention, which results in the removal of the tumor;
- irradiation is used extremely rarely and only when surgical treatment is impossible.
To increase growth hormone
To increase growth hormone, surgery is used if the problem is caused by a tumor; in other cases, conservative treatment is used.
If therapy is prescribed to a child, then hormones are used that adjust the thyroid gland to function properly.
Among them are:
- glucocorticosteroids;
- estrogens;
- progesterone;
- testosterone;
- thyroid regulators.
If treatment is intended for an adult, then drugs are prescribed that stabilize the hormone level in the short term and for a long time.
These include:
- Rastan;
- Humatrope;
- Biosome;
- Somatropin;
- Norditropin;
- Genotropin and analogues.
Genotropin Rastan Biosome Norditropin Somatotropin Humatrope
In general, all these drugs are designed to enhance protein production, have a positive effect on mineral metabolism, and increase body weight and height. Since medications have a serious effect on the body, you will definitely need a prescription to purchase them. It is also necessary to follow the treatment regimen prescribed by the doctor, even if the instructions for use say differently.
Non-drug treatments
How to increase growth hormone through nutrition?
To do this, you must not only adhere to a certain diet, but also follow a number of nutritional rules, such as:
- eat fractionally (5-6 times a day) and in small portions;
- have dinner at least 3 hours before bedtime;
- drink at least 2 liters of clean water without gas per day;
- Eat the maximum amount of slow carbohydrates in the first half of the day;
- give up fatty, fried, salty, flour and sweet foods, as well as alcohol;
- Try to boil, steam or bake foods;
- Vegetables and fruits are eaten raw.
The menu should be varied and balanced and include the following products:
- dairy and fermented milk;
- meat;
- fish and seafood;
- legumes;
- cereals;
- eggs;
- nuts;
- vegetables, fruits, berries, herbs;
- vegetable oils.
Physical exercise.
You can increase the level of growth hormone if you regularly (at least 3 times a week for 45 minutes) train your muscles. The exercises don’t have to be complicated; even regular walking at a rhythmic pace or running will do. Ideally, it will take place in the fresh air - this will increase the effectiveness of the training.
If possible, then in addition to running (walking), it would be good to include anaerobic exercises in the complex, and after them - strength exercises.
Night sleep.
It is one of the most important components of lifestyle, allowing you to increase the level of growth hormone. But in order for sleep to “work”, you need to go to bed no later than 22 hours, and the duration of sleep must be at least 8 hours.
By following these simple rules, you can prevent the development of growth hormone deficiency, and if it is present, you can increase it faster and more effectively.
Growth hormone: blood test for children
Testing of growth hormone levels in children may be prescribed in the following cases:
- If during pregnancy the mother had health problems due to hormonal imbalance.
- If the child has congenital genetic abnormalities.
- If the baby received a birth injury or has a severe head injury.
- During the development of tumor processes in children and after treatment with radiation therapy.
- If there is a suspicion of a child’s developmental delay, pathology of the adrenal glands, thyroid gland, etc.
When a child’s body experiences a hormonal imbalance, the negative impact of this process affects many organs and systems.
Taking blood from a vein
In some cases, analysis can only show a deficiency or excess of somatotropin in a hospital, where a comprehensive examination is carried out.
Important! GH deficiency can be determined by analyzing blood glucose levels. If it is lowered after birth, then this is one of the first signs of somatotropin deficiency.
Parents may suspect growth hormone deficiency if the child does not grow more than 5 cm per year. Sometimes such features go completely unnoticed in children under 3 and 5 years of age.
What is STG
Growth hormone (somatropin) is produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland. In turn, its production is regulated by the hypothalamus. In this part of the brain, 2 substances are formed:
- somatoliberin (increases the production of growth hormone);
- somatostatin (reduces the production of growth hormone).
The greatest production of the hormone occurs when a person is sleeping. Perhaps related to this is the idea that a child grows while he sleeps.
Typically, the amount of growth hormone decreases in the evening and rises sharply in the morning.
In the body, somatropin disintegrates within 1 hour. It acts on tissues through insulin-like somatomedins, which are formed in the liver. They are intermediaries between growth hormone and body systems. Therefore, in case of disturbances in the production of somatotropic hormone, an additional test for insulin-like growth factor is prescribed.
In the body, somatropin performs the following functions:
- Stimulates protein and fat metabolism.
- Promotes bone growth.
- Maintains normal glucose levels.
- Stimulates DNA formation.
- During lactation, it enhances milk production.
- Participates in the formation of glycogen in the liver.
In babies, in the first 3 months of life, the optimal level of hormone production is formed. In children, its content is higher than in adults; growth hormone is necessary for the growing body.
Particularly high levels of somatropin are observed in children during puberty.
Then the production of growth hormone begins to gradually decline and reaches a minimum by age 60.