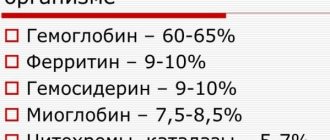
A low level of hemoglobin in the blood is dangerous for the development of iron deficiency anemia. Anemia is a dangerous condition for humans in which body tissues suffer from oxygen starvation.
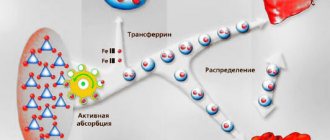
The lack of B vitamins and heme iron in the body makes the formation of hemoglobin in the blood impossible. Hemoglobin plays an irreplaceable role in human blood, binding free oxygen molecules coming from the lungs and delivering them through the bloodstream to the cells of the body's tissues.
High levels of iron in the blood can be achieved by prescribing special medications containing iron.
What type of iron does a person need?
Iron is a valuable element for the proper and stable functioning of the human body. Large amounts of iron are found in foods of animal and plant origin. But not all iron is absorbed equally by the body.
Scientists have proven that a person gets the bulk of iron from meat products. The iron contained in the meat of animals and birds is similar in composition to the iron needed by humans and is called heme. In plant tissues, the microelement is found in the unbound free form of divalent and trivalent iron. This type of iron is called non-heme iron and is less easily absorbed, while trivalent iron is not absorbed by the human body.
PREVENTIVE MEDICINES
In addition to medicinal ferrodrugs used to improve hemoglobin levels, there are a number of nutritional supplements on the pharmaceutical market. They cannot be used to treat anemia. However, such supplements are a good preventive measure for healthy children with normal hemoglobin levels. One of the most popular drugs in this group is traditionally hematogen. This tasty and healthy product has been used for decades as an additional source of iron in children's diets. The basis of hematogen is albumin - cattle blood processed in industrial conditions. This substance is rich in complex multicomponent proteins and is easily absorbed by the child’s body. The group of hematogens also includes such a biologically active food supplement as “FERROGEMATOGEN®-PHARMSTANDARD”.
Classification of iron-containing drugs, their advantages and disadvantages
Preparations containing iron can be divided into two large groups:
- oral – tablets and solutions for oral administration, drugs pass through the gastrointestinal tract and are absorbed naturally,
- parenteral - the active substances enter the tissues, bypassing the gastrointestinal tract; these include intravenous injections.
Oral iron supplements
Oral iron preparations may contain both organic and inorganic Fe II (ferrous iron) salts and Fe III (ferric iron) salts. The benefits of such drugs for the body are different, the digestibility of FeII drugs reaches 30-40%, the bioavailability of Fe III is much less - up to 10%. It is necessary to take medications in long courses from 30 to 90 days, after which there is a steady increase in hemoglobin content in the blood.
Such drugs have a number of side effects:
- The patient suffers from nausea and vomiting.
- Appetite disappears and the taste perception of food changes.
- When taken for a long time, a person suffers from constipation or diarrhea.
- Iron solutions taken orally have a strong coloring effect and can ruin the color of teeth.
Oral ferrodrugs also have a number of serious contraindications:
- diagnosing a patient with oncology, especially blood cancer,
- stomach ulcer,
- it is impossible to combine taking medications with iron with taking drugs of the tetracycline group,
- chronic diseases of the liver, kidneys,
- the patient has enteritis.
Iron supplements are prescribed with extreme caution during pregnancy; women are advised to increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood by consuming foods rich in iron and vitamins.
The selection and prescription of drugs containing iron is carried out by the attending physician, and in no case independently.
Nutrition to increase hemoglobin concentration
Prevention of anemia in a child must be carried out during the period of intrauterine development. A pregnant woman should eat foods that contain a lot of iron: meat, buckwheat, pomegranates.
Breastfeeding women should include iron-rich foods in their diet. If the newborn is bottle-fed, then you need to choose a formula with a high iron content.
From 6 months, vegetables, such as Brussels sprouts, can be introduced into a newborn’s diet. Buckwheat porridge and meat puree (chicken or turkey) will also have a beneficial effect on the baby’s condition.
The child can be given fruit compote or rosehip tea. Before drinking, pomegranate juice must be diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio to prevent dyspepsia (digestive disorders).
A specific diet for children over 2 years old should include foods with iron, which is easily absorbed by the body, for example, boiled beef. Prepare dishes with veal, pork, lamb, and rabbit meat. A lot of iron is found in the kidneys, lungs, liver, and tongue. Caviar, shellfish, and shrimp are preferable to fish, which contains less iron than the seafood described above.
Include soy, lentils, buckwheat, wheat and rye bread in your diet. Prepare dishes from soybeans, beans, peas and other legumes. To increase hemoglobin, you need to regularly consume the side dish.
You can’t do without vegetables and fruits: beets, bananas, apples, spinach, carrots. Pomegranate is very useful for the body of a child with low hemoglobin. Include berries in your diet: rose hips, currants, raspberries, strawberries.
At the time of treatment, it is necessary to reduce the amount of fermented milk products in the child’s diet . Remove foods that contain a lot of calcium from the children's menu: yogurt, sour cream, cottage cheese, cheese, etc.
To quickly normalize hemoglobin levels, exclude tonic drinks (cocoa, tea, coffee, sweet soda) from your diet. Herbal teas and filtered water without carbon have a beneficial effect on the child’s body.
In addition to iron-containing foods, it is recommended to consume foods high in ascorbic acid. This vitamin facilitates the absorption of iron by the child's body. To do this, include oranges, lemons, kiwis and other citrus fruits, as well as paprika, in your diet. Other iron-containing foods: persimmon, quince, plum, tomatoes, etc.
You can find out more about products to increase hemoglobin here.
Parenteral ferropreparations
Parenteral ferrodrugs are prescribed in cases of extreme necessity, after a thorough examination of the patient. Here is a list of reasons why adults and children are prescribed injections that increase hemoglobin:
- Chronic diseases of the digestive system. In pathological diseases: pancreatitis, enteritis, celiac disease, the body’s ability to absorb iron naturally is impaired.
- Ulcerative colitis, gastric and duodenal ulcers.
- Allergic reaction to iron salts.
- Resection of the stomach or part of the small intestine.
Injections to raise hemoglobin are prescribed if it is necessary to saturate the patient’s body with iron in a short period of time before surgery, when there is a possibility of large blood losses.
Iron injections to raise hemoglobin in the blood do not involve the introduction of a microelement in an amount greater than the body's daily requirement of 100 mg at a time.
A patient who receives injections to increase hemoglobin may experience the following consequences:
- seals and abscesses may appear at the injection sites,
- an allergic reaction to the drug, up to anaphylactic shock, is possible,
- bleeding disorders may occur,
- An overdose of iron in the body can lead to nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation.
Injections for hemoglobin can be prescribed to both adults and children; the only differences are in the dosage of medications for injection.
Consequences of low hemoglobin in a child
Hemoglobin transports oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and removes carbon dioxide from them. When its concentration decreases, the functionality of the oxygen supply system is disrupted, which causes tissues and organs to wither. As a result, the functioning of the entire body is disrupted.
Due to hemoglobin deficiency, the immune system is weakened and pathogenic microorganisms enter the body . Serious interruptions in the functioning of the immune system occur, so even a common cold provokes dangerous complications. In addition, the child lags behind his peers in mental and intellectual development.
Injections to raise hemoglobin in the blood and the names of drugs
The list of injections to increase hemoglobin, the names of medications and their brief characteristics are given in the table below.
| Drug name | Active substance | Method of administration and dosage |
| Ferrum Lek | iron hydroxide, dextran | 2 ml ampoules for intramuscular injection |
| Venofer | iron hydroxide sucrose complexes | 5 ml ampoules for intravenous injection |
| Ferkoven | iron saccharate, cobalt gluconate, carbohydrate solution | 1 ml ampoules for intravenous injection |
| Zhektofer | iron-sorbitol-citric acid complex | 2 ml ampoules for intramuscular injection |
| Ferrlecite | sodium – iron gluconate complex | ampoules of 1 ml for IM and 5 ml for IV injection |
| Ferbitol | iron sorbitol complex | 1 ml ampoules for intramuscular injection |
The use of iron-containing medications by pregnant and lactating women
During pregnancy, many representatives of the fairer sex may be diagnosed with iron deficiency anemia. In particularly severe situations, the attending physician will prescribe iron injections, but in practice they try to avoid such measures.
In most cases, if the hemoglobin level deviates from the norm, pregnant women are prescribed a special diet and preventive use of ferrodrugs. The dose of iron intake per day is prescribed by the doctor for each case individually.
Recommendations for the correct use of drugs that increase iron levels in the blood:
- in the absence of pregnancy pathologies in the 3rd trimester, iron-containing medications are prescribed for preventive purposes,
- for anemia diagnosed before pregnancy, iron medications are used throughout pregnancy and during breastfeeding,
- If anemia develops during pregnancy, ferrodrugs can be prescribed in the early stages of pregnancy.
Recommendations for pregnant and lactating women with low hemoglobin levels:
Traditional methods of increasing hemoglobin in a child
There are many recipes that help normalize hemoglobin levels, but they can only be used for children over 2 years of age:
- Take 200 g of walnut kernels and raw buckwheat, grind in a meat grinder or blender. Pour the dry mixture with May honey (200 ml), stir and place in a cool place. Daily dosage – 1 teaspoon twice;
- Take 100 g of walnut kernels, dried apricots, raisins, prunes, grind all the ingredients in a blender and pour into a glass jar. Grind 1 lemon in a blender along with the skin and pour into a jar with the rest of the ingredients. Pour the mixture with honey (220 ml), mix everything, cover with a lid and refrigerate. Dosage – 1-2 teaspoons twice a day;
- Pour 30 g of rose hips with 200 ml of boiling water in a thermos, close and leave for 3 hours. Strain the broth, add 10 ml of honey and a slice of lemon. Give your child 100 ml twice a day;
- Mix natural juice of apple (90 ml), beets and carrots (50 ml each). Let the child eat 30 g of sour cream and drink it with juice. If the baby cannot drink all the juice at once, then the dose can be divided into 2 times;
- Take fresh beets, radishes and carrots and prepare juice. Mix vegetable juices in a ratio of 1:1:1, give your baby 30 ml of liquid before meals.
Before using traditional recipes, consult your doctor.