Analysis for salmonellosis. Salmonellosis is a dangerous food infection that can be contracted when a pathogenic bacterium, salmonella, enters the body.
The causative agent of the disease is a bacteria in the form of a stick with a curved end - Salmonella. The manifestation of the disease involves a rapid incubation period - from several hours to 5 days, after which the disease can be suspected based on characteristic symptoms. Ease of recognition also lies in the fact that these symptoms are not typical for other intestinal infectious diseases of the child.
Infection, as a rule, occurs through consumption of animal products: meat, eggs, milk, as well as through contact with infected people. Outbreaks of salmonellosis are most often widespread, with the peak incidence occurring in the summer.
Description of the disease salmonellosis
The causative agents of salmonellosis are bacteria of the genus Salmonella. These are small gram-negative rods that can persist in the environment. So, in water they last for about 5 months, in meat for about 6 months, and in a bird carcass for more than a year.
Salmonella survives on eggshells for 17 to 24 days, but it is known that when eggs are stored for a long time, bacteria can penetrate the shell and multiply in the yolk. In some products, for example, in milk, butter, cheeses, salmonella can multiply without changing the taste of the product.
Salmonella is ubiquitous. The reservoir and source of infection are cattle, pigs, domestic and wild birds. When examining domestic animals and birds, as well as their meat, salmonella was found in 1-5% of cattle, 4-30% of all examined sheep, 5-15% of pigs.
At a temperature of 70°C, salmonella die within 5-10 minutes. Salmonella enters the human body with food, most often with poorly cooked poultry, eggs, and meat. In hospitals, contact transmission of infection is possible through towels, toys, playpens, and hands. People become infected with salmonellosis very easily.
Salmonella was also found in 50% of ducks and geese. In healthy animals, these bacteria do not cause illness; animals and birds are simply carriers of bacteria. However, in weakened animals they penetrate from the intestines into organs and tissues and cause inflammatory diseases. A person with low immunity can also become infected from someone suffering from salmonellosis.
So, through the mouth, salmonella enter the gastrointestinal tract, reach the small intestine, attach to intestinal epithelial cells and release toxins. After some time, the bacteria penetrate into the epithelial cells.
This is prevented as best they can by phagocytes (white blood cells that protect the body by absorbing foreign particles and microorganisms). During the absorption process, inflammation develops. And when salmonella are destroyed, endotoxin is released, which stimulates the outflow of fluid into the intestinal lumen, increasing its peristalsis (contractions).
This leads to the development of diarrhea and dehydration. Due to intoxication of the body and its dehydration, the functioning of the cardiovascular system is disrupted - tachycardia develops, and blood pressure decreases. Dehydration also contributes to impaired blood microcirculation in the kidneys, which leads to the development of acute renal failure.
Salmonellosis is dangerous not only due to dehydration, it also has other serious complications - infectious-toxic shock, peritonitis, toxic dilatation of the intestine.
In the majority (95-99%) of cases, salmonella does not penetrate beyond the submucosal layer of the intestine. However, sometimes bacteria enter the blood, and then a generalized form of salmonellosis develops. This usually occurs in patients with reduced immunity.
Diet
You must follow the correct diet for a month. Exclude spices and smoked foods, fatty meats, canned food, sweets and full-fat milk from the menu. Mushrooms, raw fruits and vegetables should be taken with caution and, if possible, excluded.
Vegetables and fruits are consumed only after heat treatment: you can boil them, stew them, or bake them. It is better to include easily digestible products in the menu. These include:
- dairy products,
- mashed banana,
- baked apple,
- boiled potatoes and carrots,
- steamed fish cutlets made from lean meats.
Diversify the menu with cranberries and blueberries. Among drinks, preference should be given to compotes and jelly. You can eat white bread crackers, low-fat broths, water-based porridges made from rice and buckwheat.
Express analysis of bacteria of the genus Salmonella
Analysis for salmonellosis. Salmonellosis is one of the ubiquitous zooanthroponoses. Economic damage from salmonellosis consists of the death of part of the sick young animals, retardation in growth and development of the ill livestock.
Today, the problem of prevention and treatment of gastrointestinal diseases of animals, including poultry, has not only economic, but also social significance. The cause of the disease is associated with the contamination of food of animal origin by pathogenic microorganisms.
The adaptation of the Salmonella enteritidis strain to the poultry body and the increase in its resistance created the prerequisites for the transmission of the pathogen from poultry to humans and back. According to WHO, the incidence of salmonellosis in people over the past decade has increased sixfold, and in the CIS countries - sevenfold.
At the same time, the etiological significance of S. enteritidis in the disease of humans increased by 30%, animals - 75%, and the number of cases of detection of the pathogen in food products increased by 50%. It is possible to carry out express diagnostics of droppings, washes from surfaces on the territory of the agricultural complex, as well as control quality of finished products.
Products containing salmonella
Salmonella is a resident of the intestinal tract of chicken, ducks, geese and other poultry. Moreover, the animals themselves do not suffer from this disease.
When a hen lays an egg and it passes through the birth canal, salmonella gets onto the shell. Since the shell is porous, the microbe gets inside and multiplies. Accordingly, if the egg is poorly cooked, then we can become infected.
You can also become infected through poorly cooked chicken. This is especially common in smoked chicken. If you cut it, you can still see red meat on the joints. It may contain salmonella.
It should be noted that Salmonella is quite heat-resistant. In order to kill it at a temperature of 70 degrees, you need to process it for at least 20 minutes. And if you process at a temperature of 100 degrees, then 3 minutes is enough. Conclusion - both the chicken and the egg should be cooked for more than 3 minutes. Accordingly, a soft-boiled egg is a very dangerous product.
Quails have a higher body temperature, so salmonella practically does not live there. Accordingly, their eggs are safe. And chicken eggs are completely infected with salmonella, since the microbe is a resident of the chicken’s body.
And the last product is milk. For residents of Russia, fresh milk is “manna from heaven.” But it can also be contaminated with salmonella and it should also be boiled for at least 3 minutes.
What tests are taken for salmonellosis?
Analysis for salmonellosis. If salmonellosis is suspected, the patient undergoes tests to confirm the diagnosis. The patient's stool and food samples are taken for analysis. Among the mandatory laboratory tests, a biochemical blood test is prescribed - kidney and liver tests, amylase levels, glucose, electrolytes, coagulogram.
Specific studies: identification of the pathogen by bacteriological inoculation on Ploskirev’s nutrient medium. Also used for diagnostic purposes are the ring-precipitation reaction, serological reactions - RA and indirect hemagglutination reaction (IRHA), immunofluorescence reaction (RIF).
To assess the severity of the patient's condition, it is necessary to:
- electrocardiography;
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs;
- X-ray of the lungs.
Symptoms of the disease
The incubation period for this disease lasts from 6 hours to 3 days, but most often the first symptoms make themselves felt after 12-24 hours. If the method of infection was contact, for example, inside a hospital, then the first symptoms of the disease may appear after 3-8 days. There are several types of salmonellosis. The most common of them is the gastrointestinal form, which occurs in 96% of patients. The disease begins acutely and is indicated by the following symptoms:
- A rapid increase in temperature, sometimes reaching 39 degrees.
- A person complains of weakness.
- He suffers from chills.
- The patient has a headache.
- Abdominal pain appears.
- After some time, the stool becomes liquid.
The severity of certain symptoms depends on the severity of the disease. If this is a mild form, then the temperature is slightly elevated, watery stools occur no more than 5 times a day, vomiting is not constant, and diarrhea lasts no longer than 3 days. With moderate severity of the disease, the temperature is high, stool occurs up to 10 times a day, and so on for a week, vomiting is repeated. In severe cases, the temperature reaches 39 degrees, sometimes even higher, the fever lasts 5 days, the person constantly vomits, diarrhea occurs more than 10 times a day, lasting 7 days. All these symptoms will help make a diagnosis, but to confirm it, you need to get tested for salmonellosis.
Laboratory diagnosis of salmonellosis
Analysis for salmonellosis. As methods of serological diagnostics, RNGA is used with complex and group salmonellosis erythrocyte diagnosticums when staging a reaction in paired sera with an interval of 5-7 days.
With the septicopyemic variant of the disease, cultures of pus or exudate from inflammatory foci are possible. For epidemiological control of outbreaks of salmonellosis, bacteriological analysis of food residues suspected of contamination, as well as washings from dishes, is carried out.
It is mandatory to use enrichment media (magnesium medium, selenite medium), several differential diagnostic media (Endo, Ploskireva, bismuth sulfite agar), a fairly wide range of biochemical tests and a set of monovalent adsorbed O- and H-sera.
The basis of diagnosis is the isolation of the pathogen by culture of vomit and feces, and in the generalized form, blood. Stomach and intestinal lavage waters, urine, and bile can also serve as materials for bacteriological research.
The minimum diagnostic antibody titer in RNGA is 1:200. Unfortunately, serological methods in most cases are of value only for retrospective confirmation of the diagnosis.
More promising is the rapid detection of Salmonella antigens in RCA, RLA, ELISA and RIA. To establish the degree of dehydration and assess the severity of the patient’s condition, as well as to correct the ongoing rehydration therapy, hematocrit, blood viscosity, indicators of acid-base status and electrolyte composition are determined.
Treatment of salmonellosis with drugs
Salmonellosis (symptoms in an adult, as well as the diagnosis, allow the doctor to prescribe medication therapy) is not always treated with antibiotics. Depending on the patient’s condition and the type of disease, therapy will be prescribed (mild forms of the disease can be treated at home):
1. At the first symptoms, gastric lavage is done. At the same time, it is cleansed of possibly contaminated food, toxins and bacteria. The procedure requires a 2% soda solution, at least 3 liters, at room temperature. For mild salmonellosis, this procedure is sufficient.
2. When salmonellosis is severe, but there is no stool, a cleansing enema is necessary.
3. If loose stools are observed for more than 5 days, then fixative medications are prescribed (at the beginning of the disease this is not possible, toxins and bacteria are excreted in the feces):
- enterofuril;
- calcium gluconate;
- indomethacin
4. Preparations for cleansing the body of toxins and salmonella residues. They also normalize stool and reduce the amount of vomiting.
Prescribed funds:
- smecta;
- polysorb;
- enterodesis.
5. With frequent vomiting and loose stools, be sure to replenish the water-salt balance.
For this we use:
- rehydron;
- yells;
- saline solution (per 1000 ml of water requires 25 g of sugar, the same amount of salt and 15 g of soda). The temperature should not be higher than 20 degrees.
If the patient cannot take solutions due to a serious condition or constant vomiting, then the following drugs are administered using a dropper:
- trisol;
- salt;
- hemodesis.
The procedure is performed in a hospital setting.
6. In severe forms of the disease, antibiotics are required. But salmonella is not susceptible to many types of drugs.
Antibiotics that help fight bacteria:
- ampicillin;
- chloramphenicol;
- Salmonella bacteriophage.
- Means to reduce fever and relieve pain symptoms:
- paracetamol;
- analgin;
- no-shpa.
8. Means for normalizing the functioning of the digestive organs. They normalize stool and relieve residual pain in the abdominal area. The food consumed will be completely absorbed without overloading the digestive tract.
Preparations:
- festal;
- mezim;
- panzinorm.
9. It is advisable to maintain bed rest and not make sudden movements.
10. Gentle nutrition is prescribed. The diet is followed until complete recovery.
In joint treatment with medications, you can use decoctions and infusions of herbs. They will strengthen the body and shorten the recovery period. Their use is discussed with the infectious disease specialist.
Diagnosis of salmonellosis in humans
Analysis for salmonellosis. If a person develops signs of an infectious disease that is similar to salmonellosis, he should immediately seek advice from a physician.
If there is painful discomfort in the abdominal area, diarrhea, then most likely you will need to visit a surgeon and an infectious disease specialist. If the clinical picture of the disease is acute and develops rapidly, it is best to call an ambulance.
Taking an anamnesis for salmonellosis
At the first appointment, the doctor will try to establish a preliminary diagnosis. A conversation is held with the patient, during which the specialist must learn about all complaints. The doctor will ask about the date when the first symptoms appeared, and will also find out what the patient ate.
It is very important to determine if people are still sick. If salmonellosis is suspected, diagnosis will include a medical examination. This method involves assessing the condition of the patient's skin. The abdomen is palpated, the heart is listened to, and blood pressure is measured.
Questions a doctor can ask a patient:
- what complaints are there;
- how long ago the disease began;
- are there any other sick people?
- with what symptoms, how quickly did the disease begin;
- what foods the patient consumed before, and whether other people consumed them.
Medical examination for salmonellosis
Analysis for salmonellosis. An examination by a doctor along with questioning helps to establish a preliminary diagnosis and prescribe the correct examination.
During the examination, the doctor assesses the color and condition of the patient’s skin and feels the abdomen. If necessary, listen to the lungs and heart using a phonendoscope and measure blood pressure.
Coprogram - general analysis of stool for salmonellosis
The coprogram does not allow an accurate diagnosis to be made, but this analysis helps to identify the inflammatory process in the intestine.
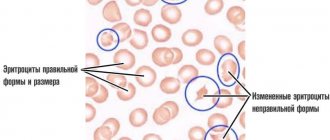
With salmonellosis, leukocytes - white blood cells - are detected in a general stool analysis.
The patient collects a small amount of stool in a special bottle and submits it to the laboratory, where the material is examined under a microscope.
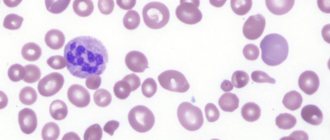
Bacteriological examination for salmonellosis
Analysis for salmonellosis. The main method for diagnosing salmonellosis and other intestinal infections. The patient submits the material to the laboratory, where it is inoculated on a nutrient medium and the resulting colonies are examined under a microscope.
In the laboratory, the material obtained from the patient is applied to a nutrient medium in a special Petri dish. If salmonella are present in the material, then after a few days colonies grow on the nutrient medium. They are stained using a special method and examined under a microscope. The causative agents of salmonellosis have a characteristic appearance.
Materials that can be used for bacteriological research:
- feces; vomit;
- water obtained during gastric lavage;
- blood; urine; bile;
- food products from which infection could occur.
Antibioticogram for salmonellosis
Study of the sensitivity of Salmonella to antibacterial drugs. An antibioticogram helps prescribe the correct treatment.
Usually an antibiogram is carried out together with a bacteriological examination. Colonies of microorganisms in a Petri dish are treated with antibacterial drugs, and they note which ones most effectively slow down the growth of bacteria.
Serological studies for salmonellosis
Serological studies for salmonellosis are aimed at identifying pathogen antigens in the patient's body. Usually, the patient's blood is taken for testing. In the laboratory, special immunological reactions are carried out to help identify the antigen.
Diagnosing salmonellosis during pregnancy
The test is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist and a laboratory assistant.
First, the specialist gets acquainted with the patient’s outpatient card. In the event that a citizen has suffered a viral or infectious disease, the doctor determines the potential risk group. We are talking about viral herpes, rubella and toxoplasmosis. The duration of the study does not exceed 24 hours.
Before pregnancy begins, it would be a good idea to undergo a number of other tests:
- Rubella - the doctor must make sure that the immune system of the expectant mother produces sufficient antibodies. If this does not happen, a decision is made on additional vaccination.
- Cytomegolovirus - the danger of the pathogen lies in its ability to provoke a miscarriage. Even if it does not happen, the baby risks being born prematurely.
Immediately after registering at the antenatal clinic, the doctor will inform the woman about the need to undergo a series of tests. It is highly recommended to do this before conceiving the baby. In this case, gentle medications are used to reduce the likelihood of pathological complications.
Examination of stool for salmonellosis using the polymerase chain reaction method
Salmonella (salmonella) is a genus of gram-negative bacteria with over 2000 serotypes. Salmonella enters the body by drinking contaminated water, eggs or meat and can cause salmonellosis, an acute intestinal infection.
Analysis for salmonellosis. When the intestines and abdominal lymph nodes are affected, salmonella gastroenteritis develops, which is accompanied by nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping abdominal pain and fever. If the infection is generalized, in 5-10% of cases thromboembolic complications, Salmonella sepsis and meningitis, pneumonia, endarteritis, endocarditis, and pyelonephritis are possible.
To diagnose salmonellosis, along with serological and bacteriological studies, the polymerase chain reaction method is used to detect the DNA of bacteria of the genus Salmonella.
When cells of the reticuloendothelial system are damaged, a systemic infection develops - typhoid fever with fever, stool disturbances, rash in the abdomen and chest and symptoms of damage to the central nervous system (lethargy, impaired consciousness and delirium).
Bacterial carriage is possible - acute (isolation of the pathogen within 3 months after recovery), chronic (isolation of the pathogen for more than 3 months from the moment of recovery) and transient (one-time positive result of a bacteriological or serological study in the absence of clinical manifestations of the disease).
How to properly prepare for research:
- the study is recommended to be carried out before starting antibiotics and other antibacterial chemotherapeutic drugs;
- do not use laxatives, rectal suppositories, limit the intake of medications that affect intestinal motility (belladonna, pilocarpine, etc.) and the color of stool (iron, bismuth, barium sulfate) 72 hours before donating stool.
Analysis for the expectant mother
It is advisable to undergo screening for salmonellosis at the planning stage. Salmonellosis is very dangerous for mother and child. Early diagnosis of bacterial carriage will help get rid of the infection before pregnancy.
Examination plan:
- Blood for antibodies to salmonella;
- Feces for PCR;
- Bacterial inoculation from the anus.
Symptoms of intestinal infection are similar to signs of toxicosis, so the initial period of the disease often goes unnoticed. Often a woman is admitted to the hospital in serious condition. Decreased immunity during pregnancy can lead to generalization of infection and the development of Salmonella sepsis.
Modern diagnostic methods will help to detect the infection in time and prevent its spread.
Diagnostics and tests for salmonellosis in animals
Bacteriological method for diagnosing salmonellosis
Analysis for salmonellosis. Material for research: during life – feces, blood serum; posthumously - corpses of small animals and birds, parenchymal organs, mesenteric lymph nodes, aborted fetuses.
Microscopy: staining methods: simple method, Gram; micropicture: rods with rounded ends up to 4 microns, arranged singly or in pairs; gram negative; do not form a dispute; do not form a capsule; mobile (with the exception of S.pullorum).
Cultural properties: all Salmonella have similar cultural characteristics, close to Escherichia; on MPB – intense turbidity, formation of easily breaking sediment; on MPA - juicy, round, gray-white colonies with smooth edges; on Endo medium - colorless or pinkish colonies, on Levin medium - light purple colonies.
Cultivation: sowing on nutrient media: MPA, MPB, differential diagnostic - Endo, Levina, etc., cumulative; Features of pathogen isolation: facultative anaerobes; optimal temperature 37oC; cultivation period is 18-20 hours.
After isolating a pure culture of lactose-negative bacteria, their genus is determined, then differentiated to species and serovariant. For this purpose, their biochemical properties and antigenic structure are studied by performing a plate agglutination reaction (serological differentiation).
Biochemical properties:
- have high saccharolytic activity;
- to establish the generic affiliation, cultures are carried out on a short “color row” (Hiss medium), while salmonella ferment glucose and mannitol with the formation of acid and gas, and do not break down lactose and sucrose;
- further study to establish the species is carried out by sowing on a long “color row”, which includes carbohydrates, and other tests;
- salmonella do not liquefy gelatin, form hydrogen sulfide, and do not form indole; give a positive reaction with methyl red: the medium turns pink-red, a negative Voges-Proskauer reaction - the medium turns yellow.
Serological method for diagnosing salmonellosis
Analysis for salmonellosis. If the result is positive with the group serum, test the same culture grown on a slant of MPA with individual monoreceptor sera included in the mixture of polyvalent serum.
Then the same cultures are tested with monoreceptor sera, phases 1 and 2, indicated by numbers and small letters - RIF.
Serological method for diagnosing salmonellosis:
- RA is used with blood serum: (blood) in the diagnosis of paratyphoid abortion in mares, hay fever in chickens;
- RA is used to differentiate: isolated Salmonella cultures in order to determine their type and serovariant;
- in Salmonella there is a somatic thermostable antigen and a flagellar thermolabile antigen;
- the Salmonella culture is preliminarily tested with group (polyvalent) Salmonella agglutinating sera in RA on glass. Based on the antigen common to several species of Salmonella, they are divided into serological groups, designated by capital letters of the Latin alphabet.
Consequences and complications
Complications can develop at any period of the disease. In severe cases, the following complications of salmonellosis are likely:
- collapse;
- acute heart failure , kidney failure;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- hemorrhagic syndrome;
- pneumonia;
- pulmonary edema;
- cerebral edema;
- toxic encephalopathy .
An unpleasant consequence of the disease is dysbiosis . To eliminate it, a course of probiotics is required.
With the wrong approach to treatment, chronic salmonellosis can develop. A person who has developed a chronic type of disease can be a carrier of the bacteria for a long time and infect others.
Where can I get tested?
For addresses of medical centers where you can order a study, please call 8-800-100-363-0 All CITILAB medical centers in Moscow >>
| Code | Name | Term | Price | Order |
| 45-20-114 | Anti-Yersinia enterocolitica IgG | from 5 w.d. | 700.00 rub. | |
| 45-20-115 | Anti-Yersinia enterocolitica IgA | from 5 w.d. | 700.00 rub. | |
| 45-20-404 | Anti to Shigella sonnei (Shigella Sonne, RPGA, total) | from 3 w.d. | 530.00 rub. | |
| 45-20-405 | Anti to Shigella flexneri (Shigella Flexner, RPGA, total) | from 3 w.d. | 530.00 rub. | |
| 45-20-407 | Anti-Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (RPHA, total - pseudotuberculosis) | from 3 w.d. | 600.00 rub. |
* The website indicates the maximum possible period for completing the study. It reflects the time it takes to complete the study in the laboratory and does not include the time for delivery of the biomaterial to the laboratory. The information provided is for reference only and is not a public offer. For up-to-date information, contact the Contractor's medical center or call center.
Combined infections
Doctors will want to take blood (from a vein) or stool. For Shigella, urine is taken; the pathogen often appears in the bile. Laboratory diagnosis of salmonellosis takes up to a week. The first results are sometimes obtained the next day. If the population density is high, Salmonella will appear quickly.
The bacterium often exists in the form of nosoparasitism. They become a “flower” from a “bouquet”. The laboratory will not rest until they test the nutrient (differential) media and reagents available. This is the reason for the dependence of the price on the place of testing for the seed tank.
Patient culture tank
Prevention
In most cases, the source of infection is animals or products obtained from animals. The rules of prevention in this case are quite simple.
These include:
- In order to protect yourself as much as possible from the disease, you need to stop eating raw meat, fish and eggs. The risk of infection is quite high, since even after several hours of cooking, salmonella may not die. When meat is thicker than 15 centimeters, the likelihood that the bacterium will survive increases significantly. Before cooking, the meat must be cut into thin slices.
- Since poultry is also quite often a carrier of the pathogen, special attention should be paid to the preparation of eggs. The duration of their cooking should not be less than six minutes. On the very surface of the shell there may be particles of bird droppings containing the pathogen. Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap after contact with the shell. There is an exception to this rule. Quail eggs are practically not susceptible to bacterial infection, so they can be eaten even raw.
- To cut raw foods, you need to use a separate knife and a cutting board. All utensils used for raw meat, poultry and fish should be washed thoroughly after use and never used for other products.
- Do not consume raw milk. You can only drink boiled or pasteurized.
- Bacteria can also live in foods that may not be related to animals. In particular, these include confectionery and baked goods, for the preparation of which contaminated eggs can be used. You should avoid buying food from street vendors.
The remaining precautionary rules are identical to ordinary hygiene rules.
They are:
- regular hand washing after walking outside or contacting animals;
- refusal to drink unboiled water;
- strengthening the immune system;
- treatment of chronic diseases that make the body more vulnerable to infection.
Due to the fact that there are many types of bacteria that lead to salmonellosis, vaccination against this disease is not done. It is impossible to make a universal vaccine that could equally effectively fight all types of pathogens. Human immunity to salmonellosis wears off quite quickly, so the resulting vaccine would not be effective for long.
Treatment of salmonellosis with folk remedies
Traditional healers recommend folk remedies for salmonellosis for mild forms of the disease.
Doctors allow these methods only in combination with basic methods of drug treatment. Chamomile. Pour 1 tbsp. spoon of chamomile with a glass of boiling water, put the product on the fire and boil for about 5 minutes, then leave for 4 hours, strain and drink during the day in 4 doses, 10 minutes after meals.
Calendula. Pour 1 teaspoon of calendula flowers into a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave for 40 minutes, then strain and drink 2-3 times, 30 minutes before meals. Efficiency increases when taken simultaneously with infusions of yarrow and chamomile.
Snake mountaineer. Pour 15 g of snakeweed into a thermos and pour a glass of boiling water over it, set aside for 8 hours to infuse. You need to take the infusion 1 tbsp. spoon 3-4 times a day, 30 minutes before meals. The product has antiseptic, antidiarrheal, astringent and anti-inflammatory properties.
Burnet. It has antiseptic, disinfectant, analgesic and hemostatic properties. For cooking you need 1 tbsp. Pour a spoonful of crushed burnet roots into a glass of boiling water and place on the stove for 30 minutes to boil. Afterwards, the infusion is set aside for an hour to infuse and cool, filter and take 1 tbsp. spoon 5-6 times a day.
Plantain. Thoroughly washed, dried and crushed plantain leaves in the amount of 1 tbsp. spoons, pour a glass of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes, strain. You need to drink the infusion within 1 hour, in small sips.
Collection 1. Make a collection of 7 parts (hereinafter referred to as parts) of St. John's wort herb, 4 parts of fireweed herb, 3 parts of yarrow herb, 3 parts of cocklebur herb, 3 parts of blueberry leaves, 2 parts of shepherd's purse herb, 2 parts . birch buds and 2 teaspoons of fruits with juniper needles. Mix everything thoroughly, chop and 2 tbsp. spoons of the collection, pour 500 ml of boiling water, boil for 10 minutes, leave for 2 hours, strain and take ¼ cup 3-4 times a day, 30 minutes before meals.
Collection 2. Make a collection of 4 parts of thyme herb, 4 parts of alder cones, 4 parts of blueberry shoots, 3 parts of St. John's wort, 3 parts of nettle leaves, 2 parts of calamus root, 2 parts of raspberry leaves and 1 teaspoon elecampane root. Mix everything thoroughly, chop and 2 tbsp. Add 500 ml of boiling water to spoons of the mixture, boil over low heat for 10 minutes, leave for 2 hours, strain. You need to take 1/3 cup 3-4 times a day, 30 minutes before meals.